Deck 14: Money and Banking
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/116
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 14: Money and Banking
1
Money is
A) an indicator of the scarcity of wants.
B) anything that the government classifies as a trade commodity.
C) anything that sellers accept in exchange for goods and services.
D) a form of credit.
E) a form of barter.
A) an indicator of the scarcity of wants.
B) anything that the government classifies as a trade commodity.
C) anything that sellers accept in exchange for goods and services.
D) a form of credit.
E) a form of barter.
anything that sellers accept in exchange for goods and services.
2
Liquidity refers to the
A) ability of an asset to be exchanged for goods and services.
B) difference between real and nominal money values.
C) ability of money to be a store of value.
D) availability of credit as a form of money.
E) ability of a precious metal to be converted into spendable bank notes.
A) ability of an asset to be exchanged for goods and services.
B) difference between real and nominal money values.
C) ability of money to be a store of value.
D) availability of credit as a form of money.
E) ability of a precious metal to be converted into spendable bank notes.
ability of an asset to be exchanged for goods and services.
3
Money that is not backed by any other good (like gold) is called
A) fake money.
B) financial money.
C) fidelity money.
D) trusted money.
E) fiduciary money.
A) fake money.
B) financial money.
C) fidelity money.
D) trusted money.
E) fiduciary money.
fiduciary money.
4
Which of the following assets would be considered least liquid?
A) A silver coin
B) An antique automobile
C) A U.S. savings bond
D) A money market account
E) A certificate of deposit
A) A silver coin
B) An antique automobile
C) A U.S. savings bond
D) A money market account
E) A certificate of deposit

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Many recent changes affecting the banking industry include all of the following except:
A) the emergence and growth of the internet
B) government deregulation
C) the financial crisis of 2007-2008
D) non-bank financial institutions offering checkable deposit accounts
E) none- all of these impact(ed) the current banking industry
A) the emergence and growth of the internet
B) government deregulation
C) the financial crisis of 2007-2008
D) non-bank financial institutions offering checkable deposit accounts
E) none- all of these impact(ed) the current banking industry

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following is the most liquid asset in the U.S. economy?
A) U.S. Treasury bonds
B) Credit cards
C) Demand deposits
D) U.S. currency
E) Travelers' checks
A) U.S. Treasury bonds
B) Credit cards
C) Demand deposits
D) U.S. currency
E) Travelers' checks

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Exchanging one good for another without the use of money constitutes
A) liquidity.
B) token exchange.
C) deferred payment.
D) barter.
E) illegal activity.
A) liquidity.
B) token exchange.
C) deferred payment.
D) barter.
E) illegal activity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
A commodity will not likely be classified as money if it is
A) portable.
B) divisible.
C) perishable.
D) homogeneous in nature.
E) predictable in value.
A) portable.
B) divisible.
C) perishable.
D) homogeneous in nature.
E) predictable in value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The $25 you deposit into your savings account when you receive a paycheck is an example of money being used as a
A) medium of exchange.
B) store of value.
C) unit of account.
D) standard of deferred payment.
E) currency substitution.
A) medium of exchange.
B) store of value.
C) unit of account.
D) standard of deferred payment.
E) currency substitution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The functions of money do not include a(n)
A) medium of exchange.
B) standard of deferred payment.
C) unit of account.
D) store of value.
E) exchange of purchasing power.
A) medium of exchange.
B) standard of deferred payment.
C) unit of account.
D) store of value.
E) exchange of purchasing power.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The narrowest definition of the money supply is
A) currency.
B) currency + checkable deposits.
C) M2.
D) M1.
E) M1 + M2.
A) currency.
B) currency + checkable deposits.
C) M2.
D) M1.
E) M1 + M2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The $5 price tag on a sandwich at the school cafeteria is an example of money being used as a
A) medium of exchange.
B) store of value.
C) unit of account.
D) standard of deferred payment.
E) barter transaction.
A) medium of exchange.
B) store of value.
C) unit of account.
D) standard of deferred payment.
E) barter transaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The concept of double coincidence of wants refers to the fact that
A) married couples like the same goods.
B) a financial asset needs to be priced correctly to be exchanged.
C) both parties have to want what the other party has for barter to take place.
D) people can never exactly agree on an equilibrium price.
E) different people value goods differently.
A) married couples like the same goods.
B) a financial asset needs to be priced correctly to be exchanged.
C) both parties have to want what the other party has for barter to take place.
D) people can never exactly agree on an equilibrium price.
E) different people value goods differently.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Barter is inefficient for all of the following reasons except it
A) requires a double coincidence of wants.
B) allows for direct exchanges of goods and services.
C) results in high transaction costs.
D) does not allow for specialization of labor.
E) results in high search and information costs.
A) requires a double coincidence of wants.
B) allows for direct exchanges of goods and services.
C) results in high transaction costs.
D) does not allow for specialization of labor.
E) results in high search and information costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
If you work for someone today but do not receive your paycheck until a month later, money is used as a
A) store of value.
B) unit of account.
C) medium of exchange.
D) wage liability.
E) standard of deferred payment.
A) store of value.
B) unit of account.
C) medium of exchange.
D) wage liability.
E) standard of deferred payment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
An asset that can easily be exchanged for goods and services is called a(n)
A) financial asset.
B) liquid asset.
C) illegitimate asset.
D) barterlike asset.
E) service.
A) financial asset.
B) liquid asset.
C) illegitimate asset.
D) barterlike asset.
E) service.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The introduction of money into the economic system
A) decreased the risk of inflation.
B) lowered transaction costs.
C) established the need for a double coincidence of wants.
D) increased information costs.
E) made exchanges of goods and services less efficient.
A) decreased the risk of inflation.
B) lowered transaction costs.
C) established the need for a double coincidence of wants.
D) increased information costs.
E) made exchanges of goods and services less efficient.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The use of money as a unit of account
A) discourages specialization and division of labor.
B) inhibits the exchange of goods and services.
C) makes it difficult to compare the relative values of goods and services.
D) lowers information costs relative to barter.
E) relies on the existence of a double coincidence of wants.
A) discourages specialization and division of labor.
B) inhibits the exchange of goods and services.
C) makes it difficult to compare the relative values of goods and services.
D) lowers information costs relative to barter.
E) relies on the existence of a double coincidence of wants.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
A $2 payment for a bus ticket is an example of money being used as a
A) medium of exchange.
B) store of value.
C) unit of account.
D) standard of deferred payment.
E) barter transaction.
A) medium of exchange.
B) store of value.
C) unit of account.
D) standard of deferred payment.
E) barter transaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
If Mexico experienced a period of rapid inflation, causing Mexicans to lose confidence in the peso as a store of value, which of the following would be most likely to occur?
A) The value of the peso would appreciate on the foreign exchange market.
B) Foreign currency would be used as a substitute for the peso.
C) The peso would be used as a store of value in other countries.
D) Mexicans would save more.
E) The purchasing power of the peso would increase.
A) The value of the peso would appreciate on the foreign exchange market.
B) Foreign currency would be used as a substitute for the peso.
C) The peso would be used as a store of value in other countries.
D) Mexicans would save more.
E) The purchasing power of the peso would increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
In 2010, the largest component of the M1 definition of money was
A) coins and currency in circulation.
B) savings account balances.
C) money market deposits.
D) checkable account balances.
E) travelers' checks.
A) coins and currency in circulation.
B) savings account balances.
C) money market deposits.
D) checkable account balances.
E) travelers' checks.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Trade between developing and developed nations typically is invoiced in the
A) currency of the developing nation.
B) currency of the developed country.
C) currency of the exporter.
D) currency of the importer.
E) international reserve currency.
A) currency of the developing nation.
B) currency of the developed country.
C) currency of the exporter.
D) currency of the importer.
E) international reserve currency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Other checkable deposits (OCDs)
A) are accounts at financial institutions that pay interest and give the depositor check-writing privileges.
B) do not include credit union share draft accounts.
C) refer to demand deposits at mutual savings banks only.
D) are not included in the M1 money supply.
E) refer to savings deposits that earn interest at savings and loan associations.
A) are accounts at financial institutions that pay interest and give the depositor check-writing privileges.
B) do not include credit union share draft accounts.
C) refer to demand deposits at mutual savings banks only.
D) are not included in the M1 money supply.
E) refer to savings deposits that earn interest at savings and loan associations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The main source of interest profits for banks is
A) government securities.
B) savings accounts.
C) reserves.
D) loans.
E) checking account fees.
A) government securities.
B) savings accounts.
C) reserves.
D) loans.
E) checking account fees.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The purpose of financial intermediaries is to
A) discourage consumption spending.
B) control economic growth.
C) allow more saving than investment.
D) collect income taxes for the government.
E) serve as agents between savers and borrowers.
A) discourage consumption spending.
B) control economic growth.
C) allow more saving than investment.
D) collect income taxes for the government.
E) serve as agents between savers and borrowers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
In the United States, the different categories of money supply measurement are based on the
A) elasticity of money.
B) liquidity of money.
C) amount of purchasing power provided.
D) reserve requirements in the banking system.
E) velocity of money.
A) elasticity of money.
B) liquidity of money.
C) amount of purchasing power provided.
D) reserve requirements in the banking system.
E) velocity of money.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Currencies which governments hold as a temporary store of value until they are needed to settle international debts are known as
A) composite currencies.
B) European currency units.
C) global monies.
D) special drawing rights.
E) international reserve currencies.
A) composite currencies.
B) European currency units.
C) global monies.
D) special drawing rights.
E) international reserve currencies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The international medium-of-exchange function of money is dominated by the
A) currency of the importing country.
B) currency of the exporting country.
C) currencies of developing countries.
D) currencies of industrial countries.
E) European currency unit.
A) currency of the importing country.
B) currency of the exporting country.
C) currencies of developing countries.
D) currencies of industrial countries.
E) European currency unit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Prior to the dominance of the U.S. dollar, the ____ was the world's most important reserve currency.
A) Japanese yen
B) Chinese yuan
C) Euro
D) British pound
E) None of these - the U.S. dollar has always been the world's most important reserve currency.
A) Japanese yen
B) Chinese yuan
C) Euro
D) British pound
E) None of these - the U.S. dollar has always been the world's most important reserve currency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following is not considered a financial intermediary?
A) Commercial banks
B) Savings and loan associations
C) Credit unions
D) Mutual savings banks
E) The Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation
A) Commercial banks
B) Savings and loan associations
C) Credit unions
D) Mutual savings banks
E) The Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
As a measure of money, M1 emphasizes the use of money as a(n)
A) medium of exchange.
B) store of value.
C) unit of account.
D) non-liquid asset.
E) standard of deferred payment.
A) medium of exchange.
B) store of value.
C) unit of account.
D) non-liquid asset.
E) standard of deferred payment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Sales contracts between developed countries usually are written (invoiced) in
A) the national currency of the exporter.
B) the national currency of the importer.
C) international reserve currency.
D) U.S. dollars
E) Euro.
A) the national currency of the exporter.
B) the national currency of the importer.
C) international reserve currency.
D) U.S. dollars
E) Euro.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The two major measures of the money supply used by the Federal Reserve are
A) currency and coins.
B) savings deposits and checkable deposits.
C) institution-only money market mutual fund balances combined with small-denomination time deposits.
D) M1 and M2.
E) Retail Money Market Mutual Fund Balances.
A) currency and coins.
B) savings deposits and checkable deposits.
C) institution-only money market mutual fund balances combined with small-denomination time deposits.
D) M1 and M2.
E) Retail Money Market Mutual Fund Balances.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which of the following is a transactions account?
A) Currency
B) Travelers' checks
C) A savings account
D) A credit card balance
E) A demand deposit
A) Currency
B) Travelers' checks
C) A savings account
D) A credit card balance
E) A demand deposit

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Commercial banks
A) are nonprofit banking institutions.
B) are owned by the Federal Reserve.
C) are overseen by the Federal Savings and Loan Insurance Corporation.
D) control U.S. monetary policy.
E) are financial institutions that offer deposits on which checks can be written.
A) are nonprofit banking institutions.
B) are owned by the Federal Reserve.
C) are overseen by the Federal Savings and Loan Insurance Corporation.
D) control U.S. monetary policy.
E) are financial institutions that offer deposits on which checks can be written.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
M2 includes all of the following except
A) demand deposits.
B) U.S. government securities.
C) savings deposits.
D) money market deposits.
E) certificates of deposit.
A) demand deposits.
B) U.S. government securities.
C) savings deposits.
D) money market deposits.
E) certificates of deposit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which of the following is not part of the other checkable deposits component of M1?
A) Credit union share draft accounts
B) Demand deposits at mutual savings banks
C) Negotiable orders of withdrawal accounts
D) Stock negotiating accounts
E) Automatic transfer system accounts
A) Credit union share draft accounts
B) Demand deposits at mutual savings banks
C) Negotiable orders of withdrawal accounts
D) Stock negotiating accounts
E) Automatic transfer system accounts

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The broadest measure of the U.S. money stock is
A) M1.
B) the total of all outstanding bank loans.
C) M2.
D) currency and coins in circulation.
E) commodity money.
A) M1.
B) the total of all outstanding bank loans.
C) M2.
D) currency and coins in circulation.
E) commodity money.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
In 2000, a new physical European currency began circulating among members of the European community; the name of this new currency is
A) ECU.
B) Ekhymosis.
C) European dollar.
D) the Euro.
E) Super Money.
A) ECU.
B) Ekhymosis.
C) European dollar.
D) the Euro.
E) Super Money.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The primary international reserve asset is
A) the Japanese yen.
B) the Euro.
C) the Chinese yuan.
D) gold.
E) the U.S. dollar.
A) the Japanese yen.
B) the Euro.
C) the Chinese yuan.
D) gold.
E) the U.S. dollar.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Which of the following is not true of International banking facilities (IBFs)? IBFs
A) allow domestic banks to take part in international banking on U.S. soil.
B) are not physical entities.
C) are a bookkeeping system set up in existing bank offices to record international banking transactions.
D) are not subject to the regulations and FDIC insurance premiums that apply to domestic U.S. banking.
E) None of these - all of these are true of IBFs.
A) allow domestic banks to take part in international banking on U.S. soil.
B) are not physical entities.
C) are a bookkeeping system set up in existing bank offices to record international banking transactions.
D) are not subject to the regulations and FDIC insurance premiums that apply to domestic U.S. banking.
E) None of these - all of these are true of IBFs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
For a bank to grow, it should focus on a(n) ____ scale.
A) local
B) state-wide
C) national
D) international
E) unit
A) local
B) state-wide
C) national
D) international
E) unit

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The Eurocurrency market consists of banking transactions
A) denominated in European currency.
B) involving exports from and imports to Europe.
C) generally denominated in currency other than the one of the country in which the bank is located.
D) involving European monies held by U.S. banks.
E) denominated in U.S. dollars that were printed in Europe.
A) denominated in European currency.
B) involving exports from and imports to Europe.
C) generally denominated in currency other than the one of the country in which the bank is located.
D) involving European monies held by U.S. banks.
E) denominated in U.S. dollars that were printed in Europe.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
A ROSCA is a(n)
A) Italian banking system allowing loans to small businesses.
B) financial intermediary among major European nations facilitating Euro transfers.
C) old Soviet-style central banking system.
D) communal system of lending in developing countries.
E) alternative to FDIC insurance.
A) Italian banking system allowing loans to small businesses.
B) financial intermediary among major European nations facilitating Euro transfers.
C) old Soviet-style central banking system.
D) communal system of lending in developing countries.
E) alternative to FDIC insurance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Banks that operate under Islamic law do all of the following except:
A) do not charge interest on loans
B) do not pay interest on deposits
C) take a predetermined percentage of the borrowing firm's profits until the loan is repaid.
D) finance mortgages on property in the United States.
E) None - Islamic banks do all of these.
A) do not charge interest on loans
B) do not pay interest on deposits
C) take a predetermined percentage of the borrowing firm's profits until the loan is repaid.
D) finance mortgages on property in the United States.
E) None - Islamic banks do all of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
A system in which banks keep less than 100 percent of the deposits available for withdrawal is known as a(n)
A) incomplete reserve banking system.
B) fractional reserve banking system.
C) trustable reserve banking system.
D) bankruptcy-free banking system.
E) charitable reserve banking system.
A) incomplete reserve banking system.
B) fractional reserve banking system.
C) trustable reserve banking system.
D) bankruptcy-free banking system.
E) charitable reserve banking system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The FDIC was established in 1933 to
A) force banks to be more cautious in their lending practices.
B) discourage bank runs by insuring deposits in commercial banks.
C) guarantee that a minimum rate of interest is paid on every deposit.
D) outlaw bank failures.
E) increase reserve requirements for commercial banks to 100 percent of deposits.
A) force banks to be more cautious in their lending practices.
B) discourage bank runs by insuring deposits in commercial banks.
C) guarantee that a minimum rate of interest is paid on every deposit.
D) outlaw bank failures.
E) increase reserve requirements for commercial banks to 100 percent of deposits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Today, about ____ of automated teller machine (ATM) transactions occur at banks that are not the customer's own bank.
A) 1%
B) 5%
C) 10%
D) 25%
E) 50%
A) 1%
B) 5%
C) 10%
D) 25%
E) 50%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
A hawala is a
A) system of financial intermediation used among farmer groups.
B) system of lending among small traders.
C) system for repatriation of funds by workers living abroad.
D) conspiracy among lenders to avoid financial regulation.
E) method of aggregating funds for investment.
A) system of financial intermediation used among farmer groups.
B) system of lending among small traders.
C) system for repatriation of funds by workers living abroad.
D) conspiracy among lenders to avoid financial regulation.
E) method of aggregating funds for investment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
In a fractional reserve banking system,
A) banks can never experience a banking panic.
B) bank reserves are always greater than bank loans.
C) banks keep less than 100 percent of deposits in cash.
D) total reserves always equal required reserves.
E) bank reserves need to be backed by gold.
A) banks can never experience a banking panic.
B) bank reserves are always greater than bank loans.
C) banks keep less than 100 percent of deposits in cash.
D) total reserves always equal required reserves.
E) bank reserves need to be backed by gold.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The balance sheet of a depository institution lists
A) loans to the institution as assets.
B) excess reserves as liabilities.
C) checkable deposits as liabilities.
D) required reserves as liabilities.
E) loans from the institution as liabilities.
A) loans to the institution as assets.
B) excess reserves as liabilities.
C) checkable deposits as liabilities.
D) required reserves as liabilities.
E) loans from the institution as liabilities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
A depository institution's profit is derived from the difference between the
A) interest rate it receives on loans and the rate it receives on investments in government securities.
B) interest rate it pays on deposits and the rate it receives on loans.
C) difference between its total reserves and its required reserves.
D) difference between its assets and its liabilities.
E) interest rate it receives on domestic loans and the rate it receives on foreign loans.
A) interest rate it receives on loans and the rate it receives on investments in government securities.
B) interest rate it pays on deposits and the rate it receives on loans.
C) difference between its total reserves and its required reserves.
D) difference between its assets and its liabilities.
E) interest rate it receives on domestic loans and the rate it receives on foreign loans.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Banking in the United States is
A) fractional reserve banking.
B) total reserve banking.
C) high-liquidity banking.
D) no-reserve banking.
E) unregulated banking.
A) fractional reserve banking.
B) total reserve banking.
C) high-liquidity banking.
D) no-reserve banking.
E) unregulated banking.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
In developing countries, farmers typically borrow from informal lenders at high interest rates because
A) the government wants to restrict agricultural development.
B) farmers generally have little collateral.
C) formal financial lenders are too risk averse.
D) farmers are good credit risks.
E) none of these.
A) the government wants to restrict agricultural development.
B) farmers generally have little collateral.
C) formal financial lenders are too risk averse.
D) farmers are good credit risks.
E) none of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Which of the following statements is false?
A) The Eurocurrency market is also known as offshore banking.
B) In the Eurocurrency market, the currency used in a banking transaction is generally not the domestic currency.
C) The Eurocurrency market operates with few restrictions.
D) The Eurocurrency market is limited to European currencies.
E) Eurodollars account for most of the deposit and loan activity in the Eurocurrency market.
A) The Eurocurrency market is also known as offshore banking.
B) In the Eurocurrency market, the currency used in a banking transaction is generally not the domestic currency.
C) The Eurocurrency market operates with few restrictions.
D) The Eurocurrency market is limited to European currencies.
E) Eurodollars account for most of the deposit and loan activity in the Eurocurrency market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Which of the following is considered a liability by a depository institution?
A) Reserves
B) Bank loans
C) Government securities
D) Buildings and equipment
E) Time deposits
A) Reserves
B) Bank loans
C) Government securities
D) Buildings and equipment
E) Time deposits

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
In the United States, the reserve requirement is set by the
A) Bank of America.
B) federal government
C) U.S. Treasury.
D) Federal Reserve Board.
E) Department of Commerce.
A) Bank of America.
B) federal government
C) U.S. Treasury.
D) Federal Reserve Board.
E) Department of Commerce.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which of the following is not an asset of a depository institution?
A) Cash
B) Bank loans
C) Securities
D) Reserves
E) Savings deposits
A) Cash
B) Bank loans
C) Securities
D) Reserves
E) Savings deposits

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Bank runs in the United States are unlikely because
A) the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation insures commercial bank deposits.
B) depository institutions operate on a partial-reserve basis.
C) bank failures have been nonexistent since 1932.
D) today's financial institutions cannot lose money.
E) the banking deregulation act of 1980 has prohibited bank failures by law.
A) the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation insures commercial bank deposits.
B) depository institutions operate on a partial-reserve basis.
C) bank failures have been nonexistent since 1932.
D) today's financial institutions cannot lose money.
E) the banking deregulation act of 1980 has prohibited bank failures by law.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The murabaha
A) is a dance.
B) is a popular musical instrument
C) is a popular instrument for financing investments.
D) is used only in Arab nations.
E) is an Islamic bank.
A) is a dance.
B) is a popular musical instrument
C) is a popular instrument for financing investments.
D) is used only in Arab nations.
E) is an Islamic bank.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Gold is the most liquid asset.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Which of the following constitutes a currency drain from the banking system?
A) Purchases of government securities
B) New demand deposits
C) Banks lending out all excess reserves
D) Lost or misplaced currency
E) Lower required reserve holdings
A) Purchases of government securities
B) New demand deposits
C) Banks lending out all excess reserves
D) Lost or misplaced currency
E) Lower required reserve holdings

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Liquidity indicates how easily an asset can be exchanged for goods and services.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
If a bank has deposits of $800,000, total reserves equal $600,000, and the reserve ratio is equal to .25, what is the value of excess reserves?
A) $600,000
B) $100,000
C) $400,000
D) $150,000
E) $500,000
A) $600,000
B) $100,000
C) $400,000
D) $150,000
E) $500,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
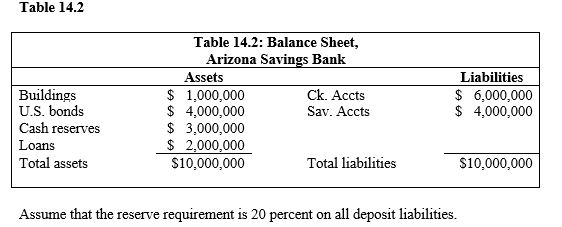
Refer to Table 14.2. How many new loans can Arizona Savings Bank make?
A) $10,000,000
B) $3,000,000
C) $7,000,000
D) $1,000,000
E) $0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
When do we say that a bank is loaned up?
A) When its debtors don't want to pay
B) When it is susceptible to a bank panic
C) When excess reserves equal zero
D) When it is part of a fractional reserve banking system
E) When its required reserves are equal to its excess reserves
A) When its debtors don't want to pay
B) When it is susceptible to a bank panic
C) When excess reserves equal zero
D) When it is part of a fractional reserve banking system
E) When its required reserves are equal to its excess reserves

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
If a bank's required reserves equal $270,000, no excess reserves are held, and the reserve requirement is equal to .18, what is the value of the bank's total deposits?
A) $900,000
B) $1,500,000
C) $48,000
D) $486,000
E) $150,000
A) $900,000
B) $1,500,000
C) $48,000
D) $486,000
E) $150,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
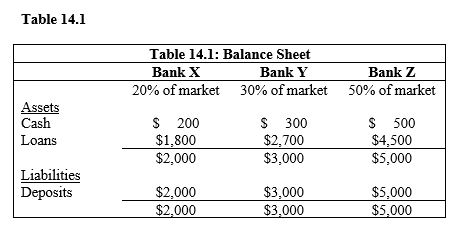
Refer to Table 14.1. Suppose that the current reserves in the three banks all come from one initial deposit. What is the initial deposit that is divided among the three banks that make up the market?
A) $10,000
B) $9,000
C) $5,000
D) $1,800
E) $1,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Money is used by every sector of the economy in all nations; it plays a crucial role in every economy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
If the reserve requirement is 25 percent, what is the deposit expansion multiplier?
A) 100
B) 25
C) 10
D) 4
E) 2
A) 100
B) 25
C) 10
D) 4
E) 2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
If a banking system receives an initial deposit of $85,000 and the reserve requirement is .25, the deposits in the banking system (including the initial deposit) can be expanded by
A) $40,000.
B) $340,000.
C) $21,250.
D) $425,000.
E) $170,000.
A) $40,000.
B) $340,000.
C) $21,250.
D) $425,000.
E) $170,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72

Refer to Table 14.1. What is the reserve requirement if banks have zero excess reserves?
A) 20 percent
B) 15 percent
C) 25 percent
D) 11 percent
E) 10 percent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
The deposit expansion multiplier is equal to
A) the reciprocal of excess reserves.
B) the reciprocal of the reserve requirement.
C) total reserves minus demand deposits.
D) total required reserves.
E) the reciprocal of total reserves.
A) the reciprocal of excess reserves.
B) the reciprocal of the reserve requirement.
C) total reserves minus demand deposits.
D) total required reserves.
E) the reciprocal of total reserves.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Excess reserves are equal to
A) total reserves plus required reserves.
B) cash plus required reserves.
C) total reserves minus cash.
D) total reserves minus required reserves.
E) required reserves minus total reserves.
A) total reserves plus required reserves.
B) cash plus required reserves.
C) total reserves minus cash.
D) total reserves minus required reserves.
E) required reserves minus total reserves.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Assume that the reserve requirement is 25 percent and that the amount of checkable deposits in Federal Bank is $200. If the bank has loaned out $120, then the bank's excess reserves must equal
A) $0.
B) $25.
C) $30.
D) $50.
E) $80.
A) $0.
B) $25.
C) $30.
D) $50.
E) $80.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Which of the following would reduce the deposit expansion multiplier?
A) Increases in the reserve requirement
B) Decreases in excess reserves
C) Increased investor deposits in commercial banks
D) Decreases in the reserve requirement
E) Increased taxes
A) Increases in the reserve requirement
B) Decreases in excess reserves
C) Increased investor deposits in commercial banks
D) Decreases in the reserve requirement
E) Increased taxes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Given a reserve requirement of 10 percent, a new bank loan of $500 can result in a maximum money supply increase in the whole banking system of
A) $500.
B) $1,000.
C) $1,500.
D) $2,500.
E) $5,000.
A) $500.
B) $1,000.
C) $1,500.
D) $2,500.
E) $5,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
The actual expansion of the money supply is likely to be ____ than the amount indicated by the deposit expansion multiplier because ____.
A) greater; of cash injections into the banking system
B) greater; banks prefer to keep excess cash
C) smaller; of cash leakages out of the banking system
D) smaller; banks are not permitted to lend excess reserves
E) greater; people are not willing to borrow at the going interest rate
A) greater; of cash injections into the banking system
B) greater; banks prefer to keep excess cash
C) smaller; of cash leakages out of the banking system
D) smaller; banks are not permitted to lend excess reserves
E) greater; people are not willing to borrow at the going interest rate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79

Refer to Table 14.2. What are Arizona Savings Bank's required reserves?
A) $10,000,000
B) $7,000,000
C) $3,000,000
D) $2,000,000
E) $1,000,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80

Refer to Table 14.2. What are Arizona Savings Bank's excess reserves?
A) $10,000,000
B) $7,000,000
C) $2,000,000
D) $1,000,000
E) $0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



