Deck 7: Business, Society, and the Government
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/157
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 7: Business, Society, and the Government
1
Figure 7.3
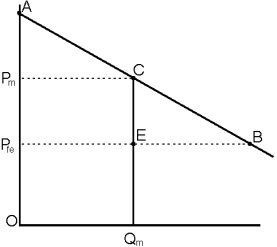
Refer to Figure 7.3. When the monopoly firm raises the price from Pfe to Pm, the deadweight loss is:
A) ACPm
B) ABPfe
C) CEB
D) PmPfeEC
E) QmCPm0

Refer to Figure 7.3. When the monopoly firm raises the price from Pfe to Pm, the deadweight loss is:
A) ACPm
B) ABPfe
C) CEB
D) PmPfeEC
E) QmCPm0
CEB
2
Figure 7.1
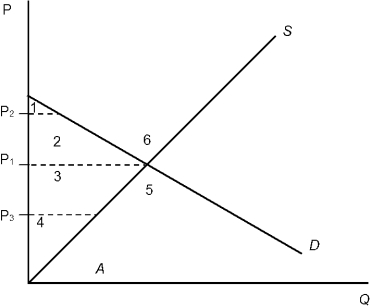
Refer to Figure 7.1. At a price of P1, the consumer surplus is represented by areas:
A) 1
B) 1 + 2
C) 1 + 2 + 3 + 4
D) 1 + 2 + 3 + 5
E) 1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + 5 + 6

Refer to Figure 7.1. At a price of P1, the consumer surplus is represented by areas:
A) 1
B) 1 + 2
C) 1 + 2 + 3 + 4
D) 1 + 2 + 3 + 5
E) 1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + 5 + 6
1 + 2
3
If a consumer can gain extra satisfaction, to the extent of receiving more satisfaction than he or she is paying for, the consumer is obtaining
A) a good deal.
B) negative utility.
C) consumer surplus.
D) the demand factor.
E) consumer sovereignty.
A) a good deal.
B) negative utility.
C) consumer surplus.
D) the demand factor.
E) consumer sovereignty.
consumer surplus.
4
In a competitive market situation, when a firm is earning significant positive economic profit,
A) government will intervene and establish greater regulation.
B) other firms will enter the market.
C) government will likely increase the tax rate on this firm in the long run.
D) competitors are more likely to cooperate with the leading firms.
E) common property ownership will likely be created with the economic profits.
A) government will intervene and establish greater regulation.
B) other firms will enter the market.
C) government will likely increase the tax rate on this firm in the long run.
D) competitors are more likely to cooperate with the leading firms.
E) common property ownership will likely be created with the economic profits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
In a market system, the primary goal of a business is
A) to earn the largest economic profit possible.
B) benefit society.
C) encourage employment.
D) charge the highest possible price.
E) satisfy the needs of taxpayers and politicians in their market area.
A) to earn the largest economic profit possible.
B) benefit society.
C) encourage employment.
D) charge the highest possible price.
E) satisfy the needs of taxpayers and politicians in their market area.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Suppose Bill receives a consumer surplus of $3 on his purchase of a pizza, for which he paid $9. The price Bill was willing and able to pay is
A) $15
B) $12
C) $9
D) $6
E) $3
A) $15
B) $12
C) $9
D) $6
E) $3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
If all consumers pay the same price for a good, that price represents the
A) average value.
B) average surplus.
C) value they place on the last unit purchased.
D) average value they place on units purchased.
E) highest price per unit they would be willing to pay.
A) average value.
B) average surplus.
C) value they place on the last unit purchased.
D) average value they place on units purchased.
E) highest price per unit they would be willing to pay.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
When shopping in some countries, bargaining is standard. The sellers ask for a high price to start, and then decrease the price until the sale is made. This is due to
A) prices changing so quickly that it doesn't make sense to make price tags.
B) consumers trying to gain as much consumer surplus as they can.
C) producers trying to gain as much consumer surplus as they can.
D) the market unable to reach equilibrium.
E) no government control.
A) prices changing so quickly that it doesn't make sense to make price tags.
B) consumers trying to gain as much consumer surplus as they can.
C) producers trying to gain as much consumer surplus as they can.
D) the market unable to reach equilibrium.
E) no government control.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Figure 7.2
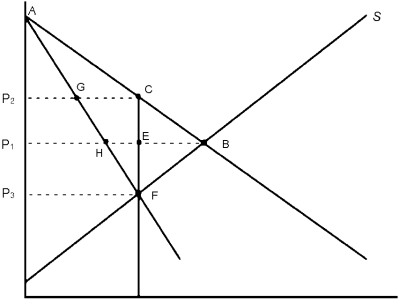
Refer to Figure 7.2. If industry is just one firm, then the area ____ represents the consumer surplus that is transferred to the one firm when it raises its price.
A) P1P2CB
B) P1P2CE
C) CBF
D) ACP2
E) ACEP1

Refer to Figure 7.2. If industry is just one firm, then the area ____ represents the consumer surplus that is transferred to the one firm when it raises its price.
A) P1P2CB
B) P1P2CE
C) CBF
D) ACP2
E) ACEP1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Figure 7.1

Disneyland, Sea World, and other amusement parks commonly charge for admission but not for rides or exhibits inside the park. This is an example of
A) a partially competitive firm practicing price discrimination.
B) an attempt by the producers to collect the entire consumer surplus.
C) the law of diminishing marginal utility.
D) a product for which there is no consumer surplus.
E) products for which there are no substitutes.

Disneyland, Sea World, and other amusement parks commonly charge for admission but not for rides or exhibits inside the park. This is an example of
A) a partially competitive firm practicing price discrimination.
B) an attempt by the producers to collect the entire consumer surplus.
C) the law of diminishing marginal utility.
D) a product for which there is no consumer surplus.
E) products for which there are no substitutes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Figure 7.2

In Figure 7.2, consumer surplus in the case where there is just one firm is the area
A) AP2C.
B) BCF.
C) 0FQ1.
D) ACFP3.
E) P1P2CE.

In Figure 7.2, consumer surplus in the case where there is just one firm is the area
A) AP2C.
B) BCF.
C) 0FQ1.
D) ACFP3.
E) P1P2CE.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Economists like to illustrate the benefits of competition by comparing the results of a(n) ____ with the results of a(n) ____.
A) supply; demand
B) commodity market; monopoly
C) oligopolist; perfect competitor
D) monopolistic competitor; perfect competitor
E) profit-making firm; firm that incurs negative profit
A) supply; demand
B) commodity market; monopoly
C) oligopolist; perfect competitor
D) monopolistic competitor; perfect competitor
E) profit-making firm; firm that incurs negative profit

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Consumer surplus is
A) equivalent to value in use.
B) equivalent to value in exchange.
C) total expenditure divided by the price per unit.
D) the difference between what consumers would be willing to pay and what they have to pay.
E) the difference between total expenditure and what consumers have to pay per unit.
A) equivalent to value in use.
B) equivalent to value in exchange.
C) total expenditure divided by the price per unit.
D) the difference between what consumers would be willing to pay and what they have to pay.
E) the difference between total expenditure and what consumers have to pay per unit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Suppose Kim is willing to pay $5 for her first ice cream sundae, $4 for a second ice cream sundae, and $2 for a third ice cream sundae. If Kim is able to buy all three ice cream sundaes for $2 each, she has realized a consumer surplus of
A) $6.
B) $5.
C) $4.
D) $2.
E) $0.
A) $6.
B) $5.
C) $4.
D) $2.
E) $0.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Figure 7.3

Refer to Figure 7.3. When the monopoly firm raises the price from Pfe to Pm, the consumer surplus that is transferred to the monopolist is
A) ACPm
B) ABPfe
C) CEB
D) PmPfeEC
E) QmCPm0

Refer to Figure 7.3. When the monopoly firm raises the price from Pfe to Pm, the consumer surplus that is transferred to the monopolist is
A) ACPm
B) ABPfe
C) CEB
D) PmPfeEC
E) QmCPm0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
If you pay a total of $10 to purchase 2 units of a good and would have been willing to pay $14, then
A) you receive a producer surplus of $2.
B) your receive a producer surplus of $4.
C) you do not have consumer sovereignty.
D) you receive a consumer surplus of $4.
E) you receive a consumer surplus of $2.
A) you receive a producer surplus of $2.
B) your receive a producer surplus of $4.
C) you do not have consumer sovereignty.
D) you receive a consumer surplus of $4.
E) you receive a consumer surplus of $2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
In general, the market system is the most efficient allocation mechanism because
A) government oversight ensures market efficiency.
B) no monopolies are allowed to be created.
C) everyone has an equal part in determining the market outcome.
D) in pursuing their self-interest, people create efficiency.
E) of all of these.
A) government oversight ensures market efficiency.
B) no monopolies are allowed to be created.
C) everyone has an equal part in determining the market outcome.
D) in pursuing their self-interest, people create efficiency.
E) of all of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
When ____ can occur, no firm can get away with anything.
A) free exit
B) free entry
C) advertising
D) positive economic profits
E) product differentiation
A) free exit
B) free entry
C) advertising
D) positive economic profits
E) product differentiation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Figure 7.3

Refer to Figure 7.3. The market price is Pfe. The consumer surplus is the region
A) ACPm
B) ABPfe
C) CEB
D) PmPfeEC
E) QmCPm0

Refer to Figure 7.3. The market price is Pfe. The consumer surplus is the region
A) ACPm
B) ABPfe
C) CEB
D) PmPfeEC
E) QmCPm0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
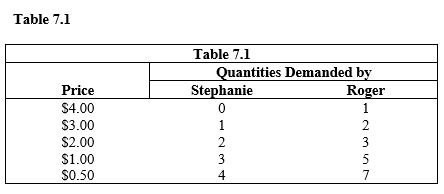
Assume that Stephanie and Roger are the only consumers, and are willing and able to purchase one unit each. According to Table 7.1, at a price of $3, the total consumer surplus is
A) $4.
B) $11.
C) $3.
D) $2.
E) $1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
One reason government intervenes in the market process is to enhance competition, often referred to as
A) "sticking to your guns."
B) "let it be."
C) "all is fair in love and war."
D) "don't shoot until you see the whites of their eyes."
E) "creating a level playing field."
A) "sticking to your guns."
B) "let it be."
C) "all is fair in love and war."
D) "don't shoot until you see the whites of their eyes."
E) "creating a level playing field."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Government action has not resulted in
A) IBM controlling its higher price on the central processing unit
B) IBM controlling its higher price on peripherals-disk drives, programs, and other components
C) AT&T to be broken into AT&T (the long-distance company) and seven local calling companies.
D) Microsoft agreeing to license its technology so that other firms could produce equipment that would seamlessly communicate with Windows.
E) All these are a result of government action.
A) IBM controlling its higher price on the central processing unit
B) IBM controlling its higher price on peripherals-disk drives, programs, and other components
C) AT&T to be broken into AT&T (the long-distance company) and seven local calling companies.
D) Microsoft agreeing to license its technology so that other firms could produce equipment that would seamlessly communicate with Windows.
E) All these are a result of government action.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Government does not:
A) build highways
B) decide which airline can fly to which city
C) provide medical insurance
D) tell power companies what prices they can charge for electricity
E) Governments provide all of these.
A) build highways
B) decide which airline can fly to which city
C) provide medical insurance
D) tell power companies what prices they can charge for electricity
E) Governments provide all of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following is an antitrust question?
A) Is an agreement by FedEx Kinko's to use only Kodak paper anticompetitive?
B) Does Walmart use unfair practices to compete against small local firms?
C) Is Apple competing unfairly by making iPods incompatible with MP3 systems?
D) Would the merger of AT&T and T-Mobile USA significantly reduce competition?
E) All of these are antitrust questions.
A) Is an agreement by FedEx Kinko's to use only Kodak paper anticompetitive?
B) Does Walmart use unfair practices to compete against small local firms?
C) Is Apple competing unfairly by making iPods incompatible with MP3 systems?
D) Would the merger of AT&T and T-Mobile USA significantly reduce competition?
E) All of these are antitrust questions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Antitrust policy is the term used to describe government policies and programs designed to
A) promote the creation of trusts, or combinations of independent firms.
B) control the growth of monopoly and enhance competition.
C) deal with the threat of competitive practices to the public interest.
D) create an environment in which firms will trust the government.
E) create an environment in which firms will distrust the government.
A) promote the creation of trusts, or combinations of independent firms.
B) control the growth of monopoly and enhance competition.
C) deal with the threat of competitive practices to the public interest.
D) create an environment in which firms will trust the government.
E) create an environment in which firms will distrust the government.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
According to the survey reported in the text, the least number of people believe that health-related goods and services should be allocated by the ____ allocation mechanism.
A) price
B) first-come, first-served
C) government
D) random
E) private
A) price
B) first-come, first-served
C) government
D) random
E) private

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
If the market system is so efficient, why is it not universally used?
A) The rich get richer, and the poor get poorer.
B) Goods and services cannot freely move from one part of the world to another.
C) People are evading taxes, so not all transactions go through the market.
D) The market does not work very well in all situations.
E) Some governments want to control every aspect on their country's economy.
A) The rich get richer, and the poor get poorer.
B) Goods and services cannot freely move from one part of the world to another.
C) People are evading taxes, so not all transactions go through the market.
D) The market does not work very well in all situations.
E) Some governments want to control every aspect on their country's economy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
All of the following are examples of a first-come, first-served system of allocation except:
A) medical care
B) classes at school
C) access to highways
D) tickets to concerts
E) All of these are examples allocated by a first-come, first-served system.
A) medical care
B) classes at school
C) access to highways
D) tickets to concerts
E) All of these are examples allocated by a first-come, first-served system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
According to the survey reported in the text, most people believe that health-related goods and services should be allocated by the ____ allocation mechanism.
A) price
B) first-come, first-served
C) government
D) random
E) private
A) price
B) first-come, first-served
C) government
D) random
E) private

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
In the case of a natural monopoly where cost conditions lead to a sole supplier, regulation is used to ensure that
A) competition can be enhanced.
B) the monopolist does not oversupply the market.
C) price and output are more beneficial for consumers than would be the case without government interference.
D) the monopolist does not attempt to further increase market share.
E) the monopolist does not try to expand internationally.
A) competition can be enhanced.
B) the monopolist does not oversupply the market.
C) price and output are more beneficial for consumers than would be the case without government interference.
D) the monopolist does not attempt to further increase market share.
E) the monopolist does not try to expand internationally.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Some people do not like market allocation because
A) some people lose their jobs as their skills are no longer needed.
B) people who are not willing and able to pay for something do not get that something.
C) people who need certain goods and services (e.g., medical care) are not able to obtain them.
D) some people experience a loss of income as their resources become replaced.
E) All of these are reasons why people oppose market allocation.
A) some people lose their jobs as their skills are no longer needed.
B) people who are not willing and able to pay for something do not get that something.
C) people who need certain goods and services (e.g., medical care) are not able to obtain them.
D) some people experience a loss of income as their resources become replaced.
E) All of these are reasons why people oppose market allocation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
A firm charges a lower price in another country than it does for the same product in its home country may be a simple case of price discrimination. (For example, "international editions" of textbooks are much lower than the American edition.) To prove dumping, it must be shown that
A) the consumers in the home country have a lower price elasticity of demand than consumers in the foreign country.
B) the government in the home country did not subsidize production of the good.
C) the item can be produced in the foreign country.
D) the cost of production is higher than the price the firm charges for the good.
E) All of these could be used to prove dumping.
A) the consumers in the home country have a lower price elasticity of demand than consumers in the foreign country.
B) the government in the home country did not subsidize production of the good.
C) the item can be produced in the foreign country.
D) the cost of production is higher than the price the firm charges for the good.
E) All of these could be used to prove dumping.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
It is ____ that transfer(s) consumer surplus to producers and create(s) deadweight losses.
A) perfect competition
B) restrictions to entry
C) the commodity market
D) government
E) the allocation mechanism
A) perfect competition
B) restrictions to entry
C) the commodity market
D) government
E) the allocation mechanism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Research indicates that, with regard to health care, American consumers prefer a ____ market allocation mechanism.
A) price
B) first-come first-served
C) socialism
D) random
E) government
A) price
B) first-come first-served
C) socialism
D) random
E) government

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which of the following is not a common market allocation mechanism in the United States?
A) Price
B) First-come, first-served
C) Socialism
D) Random
E) Government
A) Price
B) First-come, first-served
C) Socialism
D) Random
E) Government

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
It is ____ that generate(s) the benefits of the market system
A) government
B) monopoly power
C) entry and competition
D) consumer surplus
E) advertising
A) government
B) monopoly power
C) entry and competition
D) consumer surplus
E) advertising

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The goal of a business is to:
A) earn a profit
B) restrict competition
C) limit entry
D) charge consumers higher prices
E) all of these are goals of a business
A) earn a profit
B) restrict competition
C) limit entry
D) charge consumers higher prices
E) all of these are goals of a business

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Antitrust laws are designed to
A) enhance the trustworthiness of government.
B) create trust between consumers and businesses.
C) prevent monopolization of a market.
D) make natural monopolies unnatural.
E) bail out large firms and keep them from failing, to ensure a stable economy.
A) enhance the trustworthiness of government.
B) create trust between consumers and businesses.
C) prevent monopolization of a market.
D) make natural monopolies unnatural.
E) bail out large firms and keep them from failing, to ensure a stable economy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The international agency involved in business behavior, and studies cases in which an industry in one country accuses competitors in another country of dumping is the
A) CIA
B) WTO
C) Department of Justice
D) EU
E) NATO
A) CIA
B) WTO
C) Department of Justice
D) EU
E) NATO

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
According to the survey reported in the text, most people believe that non-health-related goods and services should be allocated by the ____ allocation mechanism.
A) price
B) first-come, first-served
C) government
D) random
E) private
A) price
B) first-come, first-served
C) government
D) random
E) private

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Which of the following is not one of the problems associated with common ownership of resources and a job that needed to be done?
A) Everybody was sure Somebody would do it.
B) Nobody realized that Everybody wouldn't do it.
C) Everybody blamed Somebody.
D) Zimbody paid Bigbody to do Antibody's job.
E) Anybody could have done it, but Nobody did it.
A) Everybody was sure Somebody would do it.
B) Nobody realized that Everybody wouldn't do it.
C) Everybody blamed Somebody.
D) Zimbody paid Bigbody to do Antibody's job.
E) Anybody could have done it, but Nobody did it.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
When 95% of the students in your economics receive a flu shot, the remaining 5% have less chance of getting sick with the flu. This is an example of a(n)
A) positive externality
B) negative externality
C) common good
D) adverse selection
E) moral hazard
A) positive externality
B) negative externality
C) common good
D) adverse selection
E) moral hazard

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
If the owners of SUVs are not forced to compensate the people affected by their pollution, the market result will be
A) a lower equilibrium price.
B) a higher level of demand.
C) a price that is too low and too many SUVs being driven.
D) a price that is too high and too few SUVS being driven.
E) impossible to determine from the information provided.
A) a lower equilibrium price.
B) a higher level of demand.
C) a price that is too low and too many SUVs being driven.
D) a price that is too high and too few SUVS being driven.
E) impossible to determine from the information provided.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
By September 2008, ____ of all U.S., mortgages outstanding were either delinquent or in foreclosure.
A) 3%
B) 6%
C) 10%
D) 14%
E) 19%
A) 3%
B) 6%
C) 10%
D) 14%
E) 19%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Several years ago, schoolchildren began mailing the Styrofoam containers from McDonald's meals they had purchased back to McDonald's headquarters. The schoolchildren wanted McDonald's to stop using Styrofoam and instead use biodegradable packaging, which the company did. From an economic perspective, the schoolchildren were pressuring McDonald's to
A) increase the supply of nutritional meals.
B) create a positive externality.
C) compete fairly with other fast-food chains.
D) reduce their negative externality.
E) reduce global warming.
A) increase the supply of nutritional meals.
B) create a positive externality.
C) compete fairly with other fast-food chains.
D) reduce their negative externality.
E) reduce global warming.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Situations where the market does not work efficiently or does not allocate resources to their highest valued uses are called
A) unnatural monopolies.
B) moral hazards.
C) adverse selections.
D) market failures.
E) most-favored customers.
A) unnatural monopolies.
B) moral hazards.
C) adverse selections.
D) market failures.
E) most-favored customers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
If taxpayers are forced to pay for the schools needed to meet the needs created by a new real estate development in an area,
A) a positive externality has been created.
B) the developers have transferred the negative externality to taxpayers.
C) a public good situation arises.
D) private property rights have been violated.
E) common ownership resulted in adverse selection.
A) a positive externality has been created.
B) the developers have transferred the negative externality to taxpayers.
C) a public good situation arises.
D) private property rights have been violated.
E) common ownership resulted in adverse selection.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Several politicians have proposed a "guzzler" tax that would be added to the cost of few-miles-per-gallon vehicles. If enacted, this tax would most likely
A) reduce the equilibrium price.
B) increase the equilibrium output.
C) increase U.S. dependency on foreign oil supplies.
D) shift the supply curve (for automobiles) inward.
E) do all of these.
A) reduce the equilibrium price.
B) increase the equilibrium output.
C) increase U.S. dependency on foreign oil supplies.
D) shift the supply curve (for automobiles) inward.
E) do all of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The immediate cause of the 2006-2010 economic crisis was:
A) the failure of Enron
B) greedy financial advisors on Wall Street
C) the increase in imports from China
D) the bursting of the U.S. housing bubble
E) the decrease in the value of the U.S. dollar, compared with the Euro.
A) the failure of Enron
B) greedy financial advisors on Wall Street
C) the increase in imports from China
D) the bursting of the U.S. housing bubble
E) the decrease in the value of the U.S. dollar, compared with the Euro.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
A situation where everybody owns something but nobody takes care of it illustrates the market failure problem associated with
A) private property rights.
B) collusion.
C) social regulation.
D) common ownership.
E) situational dysfunctionality.
A) private property rights.
B) collusion.
C) social regulation.
D) common ownership.
E) situational dysfunctionality.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
"Too big to fail" is a term used to describe a firm
A) whose assets are so large that it could never fail.
B) whose failure would cause a major ripple effect throughout the economy, causing other firms to fail.
C) which is a natural monopoly.
D) that produces products which are necessities.
E) that produces bombs and other items for national security.
A) whose assets are so large that it could never fail.
B) whose failure would cause a major ripple effect throughout the economy, causing other firms to fail.
C) which is a natural monopoly.
D) that produces products which are necessities.
E) that produces bombs and other items for national security.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
A subprime loan is a loan ____, while an ARM is a loan ____.
A) that has a low initial interest rate, but the interest rate adjusts according to market conditions; made to individuals with a high risk of default.
B) that has low an interest rate made to low-risk borrowers; that has a low initial interest rate, but the interest rate adjusts according to market conditions.
C) that has a low initial interest rate, but the interest rate adjusts according to market conditions; made to low-risk borrowers.
D) made to individuals with a low risk of default, that has a low initial interest rate, but the interest rate adjusts according to market conditions
E) made to individuals with high risk of default; that has a low initial interest rate, but the interest rate adjusts according to market conditions.
A) that has a low initial interest rate, but the interest rate adjusts according to market conditions; made to individuals with a high risk of default.
B) that has low an interest rate made to low-risk borrowers; that has a low initial interest rate, but the interest rate adjusts according to market conditions.
C) that has a low initial interest rate, but the interest rate adjusts according to market conditions; made to low-risk borrowers.
D) made to individuals with a low risk of default, that has a low initial interest rate, but the interest rate adjusts according to market conditions
E) made to individuals with high risk of default; that has a low initial interest rate, but the interest rate adjusts according to market conditions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Monopoly regulation occurs primarily because
A) there are no natural monopolies in the real world.
B) monopolies are especially guilty of unsafe industrial practices.
C) monopolies do not typically follow occupational and safety rules.
D) by comparison with competitive firms, monopolies tend to restrict output and raise prices.
E) most economists believe that most industries should conform to the purely competitive model.
A) there are no natural monopolies in the real world.
B) monopolies are especially guilty of unsafe industrial practices.
C) monopolies do not typically follow occupational and safety rules.
D) by comparison with competitive firms, monopolies tend to restrict output and raise prices.
E) most economists believe that most industries should conform to the purely competitive model.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Between 1997 and 2006, the price of the typical American house increased by ____, a rate significantly higher than at any other time during the previous decades.
A) 48%
B) 82%
C) 103%
D) 124%
E) 167%
A) 48%
B) 82%
C) 103%
D) 124%
E) 167%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
To reduce road congestion in Singapore, cars traveling into certain districts at specified times pay a toll. This attempts to address a(n)
A) unnatural monopoly.
B) moral hazard.
C) adverse selection.
D) market failure.
E) government budget deficit.
A) unnatural monopoly.
B) moral hazard.
C) adverse selection.
D) market failure.
E) government budget deficit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Lojack anti-theft devices installed on some cars located the stolen cars and helped shut down chop shops, where thieves cut up stolen cars and resold the parts. This reduced car theft in general, creating a(n)
A) moral hazard.
B) positive externality.
C) adverse selection.
D) discrimination against cars most likely to be stolen.
E) logrolling.
A) moral hazard.
B) positive externality.
C) adverse selection.
D) discrimination against cars most likely to be stolen.
E) logrolling.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
An externality is a cost or benefit created by a transaction that
A) is outside the firm's ability to control.
B) is a result of regulatory market failure.
C) reduces antitrust concerns.
D) substitutes most-favored-customer prices for cost-plus markups.
E) is not paid for or enjoyed by those involved directly in the transaction.
A) is outside the firm's ability to control.
B) is a result of regulatory market failure.
C) reduces antitrust concerns.
D) substitutes most-favored-customer prices for cost-plus markups.
E) is not paid for or enjoyed by those involved directly in the transaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which of the following is the best example of a negative externality?
A) A real estate developer pollutes a stream, thus making the fish inedible.
B) A trucking company converts its fleet to hydrogen-driven engines.
C) The cost of agricultural products increases as farmers apply less fertilizer.
D) The tuition at public colleges is subsidized by taxpayers.
E) Consumers purchase fewer SUVs.
A) A real estate developer pollutes a stream, thus making the fish inedible.
B) A trucking company converts its fleet to hydrogen-driven engines.
C) The cost of agricultural products increases as farmers apply less fertilizer.
D) The tuition at public colleges is subsidized by taxpayers.
E) Consumers purchase fewer SUVs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which of the following is not in the category of economic regulation?
A) Setting price levels for a natural monopoly
B) Setting output levels for a natural monopoly
C) Setting price and output levels for a particular industry
D) Setting price levels for an industry that is not a natural monopoly
E) Setting output and job standards that apply across several industries
A) Setting price levels for a natural monopoly
B) Setting output levels for a natural monopoly
C) Setting price and output levels for a particular industry
D) Setting price levels for an industry that is not a natural monopoly
E) Setting output and job standards that apply across several industries

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Nobel Prize-winning economist Ronald Coase perceives market failures as a problem associated with
A) property rights.
B) most-favored customers.
C) facilitating practices.
D) synthetic coalitions.
E) public goods.
A) property rights.
B) most-favored customers.
C) facilitating practices.
D) synthetic coalitions.
E) public goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Pollution permits are an example of
A) government creation of public goods.
B) a market approach to internalizing negative externalities.
C) replacing a natural monopoly with a regulated monopoly.
D) social regulation of the environment.
E) offsetting collusion with a government-sponsored cartel.
A) government creation of public goods.
B) a market approach to internalizing negative externalities.
C) replacing a natural monopoly with a regulated monopoly.
D) social regulation of the environment.
E) offsetting collusion with a government-sponsored cartel.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Police and fire protection are often provided by government because
A) if you don't pay, you don't get to use them.
B) if you don't pay, you cannot be excluded from using them.
C) a private company providing these services would make too much profit.
D) adverse selection would result.
E) if government did not provide these services, too many people would be involved in these activities.
A) if you don't pay, you don't get to use them.
B) if you don't pay, you cannot be excluded from using them.
C) a private company providing these services would make too much profit.
D) adverse selection would result.
E) if government did not provide these services, too many people would be involved in these activities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The civil defense sirens warning Hawaii residents of a tsunami resulting from an earthquake in Japan are classified as
A) common goods
B) pubic goods
C) private goods
D) positive externalities
E) moral hazards
A) common goods
B) pubic goods
C) private goods
D) positive externalities
E) moral hazards

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
The practice of legislators supporting one another's projects in order to ensure support for their own is called
A) democracy
B) partisanship
C) logrolling
D) wasteful
E) social regulation
A) democracy
B) partisanship
C) logrolling
D) wasteful
E) social regulation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
____ are goods that are available free to all consumers once they are produced.
A) Most-favored outcomes
B) Socially acceptable goods
C) Public goods
D) Commodities
E) Logrolls
A) Most-favored outcomes
B) Socially acceptable goods
C) Public goods
D) Commodities
E) Logrolls

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Which of the following statements about social regulation is false?
A) There are enormous costs and benefits to social regulation.
B) The cost-benefit test for regulation would expand regulations designed to benefit a very few at the cost of many.
C) The government should regulate industry whenever the benefits of regulation exceed the costs.
D) Many economists contend that the cost-benefit test for regulation should include the opportunity costs implied by interfering with the free market.
E) Some economists argue that any regulation costing more than $10 million per life saved should not be implemented.
A) There are enormous costs and benefits to social regulation.
B) The cost-benefit test for regulation would expand regulations designed to benefit a very few at the cost of many.
C) The government should regulate industry whenever the benefits of regulation exceed the costs.
D) Many economists contend that the cost-benefit test for regulation should include the opportunity costs implied by interfering with the free market.
E) Some economists argue that any regulation costing more than $10 million per life saved should not be implemented.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The total cost imposed on the U.S. economy from federal government regulations is estimated to be more than ____ a year.
A) $50 billion
B) $200 billion
C) $600 billion
D) $1 trillion
E) $12 trillion
A) $50 billion
B) $200 billion
C) $600 billion
D) $1 trillion
E) $12 trillion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
When hurricanes approach, Dave never prepares his house, stating "I'm insured." Dave's behavior is an example of
A) adverse selection.
B) common ownership.
C) social regulation.
D) private property rights.
E) moral hazard.
A) adverse selection.
B) common ownership.
C) social regulation.
D) private property rights.
E) moral hazard.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Which of the following agencies is concerned with protecting workers against injuries and illnesses associated with their jobs?
A) Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC)
B) Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA)
C) Food and Drug Administration (FDA)
D) Environmental Protection Agency (EPA)
E) Consumer Products Safety Commission (CPSC)
A) Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC)
B) Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA)
C) Food and Drug Administration (FDA)
D) Environmental Protection Agency (EPA)
E) Consumer Products Safety Commission (CPSC)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
When you have to pay a deductible when you file a car accident claim, you are more likely to drive carefully. This is an example of reducing the ____ problem.
A) moral hazard
B) adverse selection
C) common property
D) social regulation
E) externalities
A) moral hazard
B) adverse selection
C) common property
D) social regulation
E) externalities

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
A primary cause of inefficiency in government is that
A) markets interfere with governments.
B) the gains from government projects are often concentrated, while the costs are dispersed among all taxpayers.
C) government employees tend to be lazier than private-sector employees.
D) antitrust is applied to government policies as well as market situations.
E) all of these are true.
A) markets interfere with governments.
B) the gains from government projects are often concentrated, while the costs are dispersed among all taxpayers.
C) government employees tend to be lazier than private-sector employees.
D) antitrust is applied to government policies as well as market situations.
E) all of these are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
One of the problems associated with government's use of taxes and subsidies to address externalities is
A) that higher tax rates discourage adverse selection.
B) that subsidies create moral hazards.
C) determining the socially optimal level of output.
D) that logrolling interferes with a natural market solution.
E) that the government must facilitate free riders.
A) that higher tax rates discourage adverse selection.
B) that subsidies create moral hazards.
C) determining the socially optimal level of output.
D) that logrolling interferes with a natural market solution.
E) that the government must facilitate free riders.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Consumers who benefit from a public good or service without paying for it are called
A) free loafers.
B) thieves.
C) amoral hazards.
D) free riders.
E) externals.
A) free loafers.
B) thieves.
C) amoral hazards.
D) free riders.
E) externals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
All of the following are examples of social regulation except:
A) a new drug available in Canada but not in the United States.
B) lead-painted toys not allowed to be imported into the United States.
C) an elderly vice president replaced by a young college-graduate.
D) noxious fumes at a workplace.
E) the dentist obtaining a license to practice.
A) a new drug available in Canada but not in the United States.
B) lead-painted toys not allowed to be imported into the United States.
C) an elderly vice president replaced by a young college-graduate.
D) noxious fumes at a workplace.
E) the dentist obtaining a license to practice.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
A situation where bad quality drives good quality out of a market is known as
A) private property rights.
B) adverse selection.
C) social regulation.
D) common ownership.
E) moral hazard.
A) private property rights.
B) adverse selection.
C) social regulation.
D) common ownership.
E) moral hazard.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
For a market to work, someone has to
A) own the good or resource.
B) be in charge.
C) ask government to provide market-clearing prices.
D) replace cost-plus-markup pricing with most-favored-customer pricing.
E) reduce consumer-producer interdependence.
A) own the good or resource.
B) be in charge.
C) ask government to provide market-clearing prices.
D) replace cost-plus-markup pricing with most-favored-customer pricing.
E) reduce consumer-producer interdependence.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
In some African countries, the elephant population increased significantly when the government facilitated
A) substitution of African elephants for Indian elephants.
B) a shift from common ownership to private property rights.
C) social regulation of elephant breeding.
D) a shift from private ownership to public ownership.
E) the creation of a natural monopoly.
A) substitution of African elephants for Indian elephants.
B) a shift from common ownership to private property rights.
C) social regulation of elephant breeding.
D) a shift from private ownership to public ownership.
E) the creation of a natural monopoly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
The senator from Iowa supports funding for a freeway in Hawaii, because
A) the senator wants to go on a Hawaiian vacation.
B) the senator wants the Hawaii senator to support an Iowa project.
C) the freeway in Hawaii will help Iowa tourists in Hawaii.
D) the senator knows new construction jobs will benefit Iowa construction companies
E) all of these.
A) the senator wants to go on a Hawaiian vacation.
B) the senator wants the Hawaii senator to support an Iowa project.
C) the freeway in Hawaii will help Iowa tourists in Hawaii.
D) the senator knows new construction jobs will benefit Iowa construction companies
E) all of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Which of the following agencies is not concerned with social regulation?
A) Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA)
B) Consumer Products Safety Commission (CPSC)
C) Food and Drug Administration (FDA)
D) Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA)
E) Environmental Protection Agency (EPA)
A) Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA)
B) Consumer Products Safety Commission (CPSC)
C) Food and Drug Administration (FDA)
D) Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA)
E) Environmental Protection Agency (EPA)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
According to the text, the primary issue regarding the blow-up of the British Petroleum (BP) oil derrick forty miles out to sea, at a depth of about one mile, in April 2010 is
A) BP because their emergency measures failed to work.
B) the U.S. government because it did not regulate the drilling tightly enough.
C) the special interest group(s) benefitting from forcing the drilling so far off shore and so deep.
D) both BP and the U.S. government
E) Who knows? They are still debating this.
A) BP because their emergency measures failed to work.
B) the U.S. government because it did not regulate the drilling tightly enough.
C) the special interest group(s) benefitting from forcing the drilling so far off shore and so deep.
D) both BP and the U.S. government
E) Who knows? They are still debating this.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 157 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



