Deck 10: Macroeconomic Measures
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/111
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 10: Macroeconomic Measures
1
The national income accounting system is used by
A) only the United States
B) only industrialized nations
C) only developing countries
D) all countries
E) members of the World Trade Organization
A) only the United States
B) only industrialized nations
C) only developing countries
D) all countries
E) members of the World Trade Organization
all countries
2
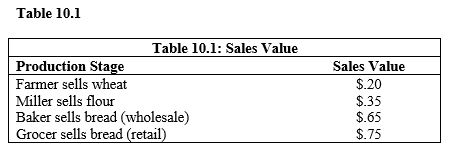
According to Table 10.1, the contribution to GDP from the production of one loaf of bread is
A) $1.95.
B) $1.20.
C) $0.75.
D) $0.65.
E) $0.10.
$0.75.
3
If GDP included intermediate goods and services, then
A) GDP would be understated.
B) we would obtain a more realistic GDP value.
C) we would be undercounting.
D) we would be double counting.
E) final goods and services would have to be subtracted to obtain the true GDP value.
A) GDP would be understated.
B) we would obtain a more realistic GDP value.
C) we would be undercounting.
D) we would be double counting.
E) final goods and services would have to be subtracted to obtain the true GDP value.
we would be double counting.
4
Gross domestic product constitutes the
A) total quantitative output in an economy.
B) current market value of all goods and services produced in a given year.
C) total spending in an economy.
D) total monetary transactions in an economy.
E) current market value of all final goods and services produced in a given year within a country's borders.
A) total quantitative output in an economy.
B) current market value of all goods and services produced in a given year.
C) total spending in an economy.
D) total monetary transactions in an economy.
E) current market value of all final goods and services produced in a given year within a country's borders.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
National income accounting can best be characterized as a
A) set of rules to summarize economic activity over a given period of time.
B) system for comparing different political systems.
C) microeconomic model used by the Federal Reserve.
D) statistical measure of the income received by consumers as opposed to businesses.
E) standardized economic report written by politicians.
A) set of rules to summarize economic activity over a given period of time.
B) system for comparing different political systems.
C) microeconomic model used by the Federal Reserve.
D) statistical measure of the income received by consumers as opposed to businesses.
E) standardized economic report written by politicians.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The concept of value added refers to the
A) increase in the value of a product that occurs at each stage of production.
B) amount subtracted from the value of the goods because of inflation.
C) total value of all intermediate goods used in the production of the final good.
D) amount paid in the final sale of a product or service.
E) amount subtracted from the value of resources because of depreciation.
A) increase in the value of a product that occurs at each stage of production.
B) amount subtracted from the value of the goods because of inflation.
C) total value of all intermediate goods used in the production of the final good.
D) amount paid in the final sale of a product or service.
E) amount subtracted from the value of resources because of depreciation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Gross domestic product (GDP)
A) is gross national product (GNP) less income earned by foreigners working domestically.
B) is different from GNP because GDP includes domestically owned resources in foreign countries.
C) is different from GNP because GDP measures only output produced domestically.
D) counts all income received by foreign citizens.
E) is gross national product (GNP) plus domestic income from abroad.
A) is gross national product (GNP) less income earned by foreigners working domestically.
B) is different from GNP because GDP includes domestically owned resources in foreign countries.
C) is different from GNP because GDP measures only output produced domestically.
D) counts all income received by foreign citizens.
E) is gross national product (GNP) plus domestic income from abroad.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The stock of unsold goods held by a firm is called
A) capital stock.
B) inventory.
C) reservoir.
D) backup.
E) depreciation.
A) capital stock.
B) inventory.
C) reservoir.
D) backup.
E) depreciation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
National income accounting does not
A) provide a framework for discussing macroeconomics.
B) measure the output of an entire economy as well as the flows between sectors
C) summarize the level of production in an economy over a specific period of time.
D) estimate the amount of activity that occurs.
E) None of these - national income accounting does all of these.
A) provide a framework for discussing macroeconomics.
B) measure the output of an entire economy as well as the flows between sectors
C) summarize the level of production in an economy over a specific period of time.
D) estimate the amount of activity that occurs.
E) None of these - national income accounting does all of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
A cotton farmer sells cotton to a textile mill for $3; the textile mill sells cloth to a shirt manufacturer, adding $2 to the value of the final shirt; the manufacturer sells the shirt to the retail store, adding $10 to the value of the final shirt; the retail store sells to a customer , adding $12 to the value of the final shirt. What is the retail price of the shirt, the price the customer pays?
A) $12
B) $22
C) $24
D) $27
E) $30
A) $12
B) $22
C) $24
D) $27
E) $30

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Changes in inventory are applied by economists to measure
A) changes in business capital.
B) the total value of goods produced and sold in a year.
C) the total value of sold products.
D) changes in planned investment.
E) the total value of goods produced but not sold in a year.
A) changes in business capital.
B) the total value of goods produced and sold in a year.
C) the total value of sold products.
D) changes in planned investment.
E) the total value of goods produced but not sold in a year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12

According to Table 10.1, the value added by the grocer is
A) $.10.
B) $.15.
C) $.30.
D) $.65.
E) $.75.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Changes in inventory
A) are always planned.
B) are always unplanned.
C) count in GDP.
D) depend on government regulations.
E) count as output that is produced and sold in a given year.
A) are always planned.
B) are always unplanned.
C) count in GDP.
D) depend on government regulations.
E) count as output that is produced and sold in a given year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Productive activity in the underground economy
A) results in an overstatement of actual income and production in the national accounting system.
B) consists of unrecorded cash transactions.
C) is fully estimated and included in the national income accounting system.
D) poses no problems for the measurement of gross domestic product.
E) does not affect GDP, but it is included in the value-added computations.
A) results in an overstatement of actual income and production in the national accounting system.
B) consists of unrecorded cash transactions.
C) is fully estimated and included in the national income accounting system.
D) poses no problems for the measurement of gross domestic product.
E) does not affect GDP, but it is included in the value-added computations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
National income accounting is
A) used by business firms to determine the level of profit during a given year.
B) used by accountants to figure household tax obligations.
C) a system of accounts designed to measure macroeconomic activity.
D) a system of measures that indicates when an economy is experiencing inflation.
E) a system of microeconomic measures that indicates equilibrium conditions for individual markets.
A) used by business firms to determine the level of profit during a given year.
B) used by accountants to figure household tax obligations.
C) a system of accounts designed to measure macroeconomic activity.
D) a system of measures that indicates when an economy is experiencing inflation.
E) a system of microeconomic measures that indicates equilibrium conditions for individual markets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16

The total value added in Table 10.1 is the same as the
A) value of the wheat before the miller turned it into flour.
B) retail value of the loaf of bread minus the wholesale value of the bread.
C) sum of all sales transactions.
D) final retail price of the loaf of bread.
E) wholesale value of the loaf of bread plus the final market value of the bread.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following economic activities is not be counted as part of GDP?
A) A student working part-time
B) A housewife selling cherry pies in the corner store
C) A gang member selling illegal drugs
D) The government buying computers for public schools
E) None - all of these are counted in GDP.
A) A student working part-time
B) A housewife selling cherry pies in the corner store
C) A gang member selling illegal drugs
D) The government buying computers for public schools
E) None - all of these are counted in GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
GDP can be calculated as
A) output.
B) expenditures.
C) income.
D) output and income only.
E) output, expenditures, and income.
A) output.
B) expenditures.
C) income.
D) output and income only.
E) output, expenditures, and income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
What is the importance of not including intermediate goods when calculating GDP?
A) Avoiding single product counting
B) Restricting GDP to important goods
C) Maintaining a constant consumer price index definition
D) Avoiding double counting
E) Restricting GDP to goods that can be priced
A) Avoiding single product counting
B) Restricting GDP to important goods
C) Maintaining a constant consumer price index definition
D) Avoiding double counting
E) Restricting GDP to goods that can be priced

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following will count in this year's GDP?
A) The value of a house built last year
B) The real estate broker's fee on the sale of the house this year
C) The value of a new Toshiba built-in home theatre system installed to help sell the house
D) All of these would be counted in this year's GDP.
E) All of these would not be counted in this year's GDP.
A) The value of a house built last year
B) The real estate broker's fee on the sale of the house this year
C) The value of a new Toshiba built-in home theatre system installed to help sell the house
D) All of these would be counted in this year's GDP.
E) All of these would not be counted in this year's GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which of the following is subtracted from GNP when calculating net national product?
A) Interest
B) Capital consumption allowance
C) Rent
D) Indirect business taxes
E) Consumption
A) Interest
B) Capital consumption allowance
C) Rent
D) Indirect business taxes
E) Consumption

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
What is a consumer price index?
A) A measure of the price at which consumers sell their resources
B) A measure of the average price level of goods and services purchased by consumers
C) A measure of the average prices received by producers
D) A measure of the average price at which consumers sell their resources
E) A measure of the prices of goods and services included in the gross domestic product
A) A measure of the price at which consumers sell their resources
B) A measure of the average price level of goods and services purchased by consumers
C) A measure of the average prices received by producers
D) A measure of the average price at which consumers sell their resources
E) A measure of the prices of goods and services included in the gross domestic product

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following is included in figuring GDP as income?
A) Consumption
B) Profits
C) Investment
D) Government spending
E) Imports
A) Consumption
B) Profits
C) Investment
D) Government spending
E) Imports

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
C + I + G + X equals
A) net national product.
B) disposable personal income.
C) national income.
D) personal income.
E) gross domestic product.
A) net national product.
B) disposable personal income.
C) national income.
D) personal income.
E) gross domestic product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Historically, nominal GDP in the United States has been increasing faster than real GDP because
A) technology has been increasing, resulting in more efficient production.
B) the general price level has been decreasing.
C) indirect business taxes have been increasing.
D) the general price level has been increasing.
E) total output in the economy has been decreasing.
A) technology has been increasing, resulting in more efficient production.
B) the general price level has been decreasing.
C) indirect business taxes have been increasing.
D) the general price level has been increasing.
E) total output in the economy has been decreasing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Net national product is defined as
A) national income plus statistical discrepancy.
B) GNP minus proprietors' income and corporate profits.
C) national income plus capital consumption allowance.
D) GNP minus indirect business taxes.
E) disposable income plus personal tax payments.
A) national income plus statistical discrepancy.
B) GNP minus proprietors' income and corporate profits.
C) national income plus capital consumption allowance.
D) GNP minus indirect business taxes.
E) disposable income plus personal tax payments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Nominal GDP
A) has been adjusted for changes in the general price level.
B) measures the real level of output in the economy.
C) measures national output on the basis of the current year's prices.
D) tends to rise by a smaller amount than real GDP when the general price level increases.
E) measures changes in the output of intermediate goods and services.
A) has been adjusted for changes in the general price level.
B) measures the real level of output in the economy.
C) measures national output on the basis of the current year's prices.
D) tends to rise by a smaller amount than real GDP when the general price level increases.
E) measures changes in the output of intermediate goods and services.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
We face taxes every day. Sales, excise, and income taxes are some of the most common. Which of these taxes is (are) considered indirect business taxes?
A) Only excise and income taxes
B) Only income tax
C) Only income and sales taxes
D) Only excise and sales taxes
E) Excise, sales, and income taxes are all forms of indirect business taxes.
A) Only excise and income taxes
B) Only income tax
C) Only income and sales taxes
D) Only excise and sales taxes
E) Excise, sales, and income taxes are all forms of indirect business taxes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Gross domestic product is the sum of
A) consumption spending, investment spending, government purchases, and net exports.
B) the value of output produced at all stages of production, including intermediate goods.
C) consumption spending, saving, investment, and net exports.
D) consumption spending, saving, investment, government spending, taxes, and net exports.
E) the value of all monetary transactions in the economy.
A) consumption spending, investment spending, government purchases, and net exports.
B) the value of output produced at all stages of production, including intermediate goods.
C) consumption spending, saving, investment, and net exports.
D) consumption spending, saving, investment, government spending, taxes, and net exports.
E) the value of all monetary transactions in the economy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
GDP can be calculated by adding
A) wages, rent, interest, and profits.
B) consumption, gross investment, depreciation, and net exports.
C) depreciation, net factor income from abroad, and indirect business taxes.
D) gross investment, wages, profits, rent, and indirect business taxes.
E) consumption, profits, interest, rent, and net exports.
A) wages, rent, interest, and profits.
B) consumption, gross investment, depreciation, and net exports.
C) depreciation, net factor income from abroad, and indirect business taxes.
D) gross investment, wages, profits, rent, and indirect business taxes.
E) consumption, profits, interest, rent, and net exports.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Real GDP measures
A) personal income adjusted for taxes paid to the government.
B) national output adjusted for changes in the quality of products.
C) national output adjusted for price-level changes.
D) nominal output adjusted for changes in national income because of economic booms.
E) national output adjusted for unemployment.
A) personal income adjusted for taxes paid to the government.
B) national output adjusted for changes in the quality of products.
C) national output adjusted for price-level changes.
D) nominal output adjusted for changes in national income because of economic booms.
E) national output adjusted for unemployment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The price index for the current year is 180, which means that, on average, prices in the current year are
A) $.80 higher than prices in the base year.
B) $1.80 higher than prices in the base year.
C) 80 percent of prices in the base year.
D) 180 percent higher than prices in the base year.
E) 80 percent higher than prices in the base year.
A) $.80 higher than prices in the base year.
B) $1.80 higher than prices in the base year.
C) 80 percent of prices in the base year.
D) 180 percent higher than prices in the base year.
E) 80 percent higher than prices in the base year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Consider GDP calculated as expenditures. GDP would increase if
A) imports decreased.
B) consumption decreased.
C) exports decreased.
D) investment decreased.
E) government spending decreased.
A) imports decreased.
B) consumption decreased.
C) exports decreased.
D) investment decreased.
E) government spending decreased.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
For a hypothetical economy in a given year, GDP was $1,171, consumption equaled $482, investment equaled $286, goods exported equaled $198, and goods imported equaled $57. What was government spending equal to?
A) $148
B) $403
C) $262
D) $544
E) None of these numbers are correct.
A) $148
B) $403
C) $262
D) $544
E) None of these numbers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
A reduction in the value of capital goods over time due to their use in production is called
A) waste of finite resources.
B) erosion.
C) consumption.
D) investment.
E) depreciation.
A) waste of finite resources.
B) erosion.
C) consumption.
D) investment.
E) depreciation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
What is an indirect business tax?
A) A tax that is collected by businesses for a government agency
B) A foreign tax that affects the consumer indirectly
C) A foreign tax collected by the local government
D) A local tax intended to tax different goods than the ones that end up being taxed
E) A tax that affects only those businesses that deal with indirect goods
A) A tax that is collected by businesses for a government agency
B) A foreign tax that affects the consumer indirectly
C) A foreign tax collected by the local government
D) A local tax intended to tax different goods than the ones that end up being taxed
E) A tax that affects only those businesses that deal with indirect goods

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
World GDP is ____ World GNP.
A) more than
B) less than
C) equal to
D) sometimes more than and sometimes less than
E) cannot be calculated
A) more than
B) less than
C) equal to
D) sometimes more than and sometimes less than
E) cannot be calculated

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The difference between gross investment and net investment is defined as
A) net national product.
B) net exports.
C) capital consumption allowance.
D) indirect business taxes.
E) national income.
A) net national product.
B) net exports.
C) capital consumption allowance.
D) indirect business taxes.
E) national income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
GDP can be calculated by all of the following except:
A) summing the market value of all final goods and services produced in a year
B) summing the value added at each stage of production
C) adding total expenditures on goods and services
D) using the total income earned in the production of goods and services, subtracting net factor income from abroad, and adding depreciation and indirect business taxes
E) None - all of these can be used to calculate GDP.
A) summing the market value of all final goods and services produced in a year
B) summing the value added at each stage of production
C) adding total expenditures on goods and services
D) using the total income earned in the production of goods and services, subtracting net factor income from abroad, and adding depreciation and indirect business taxes
E) None - all of these can be used to calculate GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
National income is
A) personal income plus personal tax payments.
B) net national product plus or minus statistical discrepancies.
C) wages, transfer payments, interest paid to businesses, and tax revenue.
D) NNP plus the capital consumption allowance.
E) consumption, investment, government spending, and net exports.
A) personal income plus personal tax payments.
B) net national product plus or minus statistical discrepancies.
C) wages, transfer payments, interest paid to businesses, and tax revenue.
D) NNP plus the capital consumption allowance.
E) consumption, investment, government spending, and net exports.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
If 1 U.S. dollar = 11.76 shillings, then one schilling equals
A) $11.76.
B) $3.92.
C) $0.008.
D) $0.085.
E) $.111.
A) $11.76.
B) $3.92.
C) $0.008.
D) $0.085.
E) $.111.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Foreign exchange constitutes
A) foreign stock market activity.
B) the balance of payments.
C) trade agreement(s) with foreign countries.
D) currency and bank deposits that are denominated in foreign money.
E) a trade commodity of foreign countries.
A) foreign stock market activity.
B) the balance of payments.
C) trade agreement(s) with foreign countries.
D) currency and bank deposits that are denominated in foreign money.
E) a trade commodity of foreign countries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The foreign exchange market
A) is located at the New York Stock Exchange.
B) depends on the actual movement of currency.
C) is based exclusively on the exchange of bank notes.
D) is a global market in which foreign-currency-denominated deposits are traded.
E) is a currency exchange system limited to tourism and illegal transactions.
A) is located at the New York Stock Exchange.
B) depends on the actual movement of currency.
C) is based exclusively on the exchange of bank notes.
D) is a global market in which foreign-currency-denominated deposits are traded.
E) is a currency exchange system limited to tourism and illegal transactions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The idea that total expenditures equal total income earned is illustrated in the
A) double-entry accounting system.
B) intermediate value-added system.
C) circular flow diagram.
D) personal and national income accounts diagram.
E) cost of living adjustment to the balance of payments.
A) double-entry accounting system.
B) intermediate value-added system.
C) circular flow diagram.
D) personal and national income accounts diagram.
E) cost of living adjustment to the balance of payments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
If the U.S. dollar appreciated against the British pound, other things being equal, we would expect
A) the British demand for U.S. products to increase.
B) a reduction in trade between the United States and Britain.
C) the U.S. demand for British products to decrease.
D) the U.S. demand for British products to increase.
E) an increase in trade between the United States and Britain.
A) the British demand for U.S. products to increase.
B) a reduction in trade between the United States and Britain.
C) the U.S. demand for British products to decrease.
D) the U.S. demand for British products to increase.
E) an increase in trade between the United States and Britain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The producer price index
A) is a measure of average prices received by producers.
B) fluctuates more than the GDP price index.
C) is also referred to as the wholesale price index.
D) is more volatile than the CPI.
E) is all of these.
A) is a measure of average prices received by producers.
B) fluctuates more than the GDP price index.
C) is also referred to as the wholesale price index.
D) is more volatile than the CPI.
E) is all of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The demand for foreign currency in the United States is based on the demand for
A) domestic goods and services.
B) domestic exports.
C) gold.
D) foreign goods and services.
E) U.S. dollars.
A) domestic goods and services.
B) domestic exports.
C) gold.
D) foreign goods and services.
E) U.S. dollars.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Which of the following transactions would not necessitate foreign exchange?
A) a student from Japan buying a hamburger at the snack bar on an American college campus
B) an American college student purchasing a new mobile telephone device in the United States.
C) an American tourist who purchases a beer with U.S. dollars at a pub in Tijuana, Mexico.
D) the Japanese investor buying stock in "The Walt Disney Company"
E) None-all of these transactions involve foreign exchange.
A) a student from Japan buying a hamburger at the snack bar on an American college campus
B) an American college student purchasing a new mobile telephone device in the United States.
C) an American tourist who purchases a beer with U.S. dollars at a pub in Tijuana, Mexico.
D) the Japanese investor buying stock in "The Walt Disney Company"
E) None-all of these transactions involve foreign exchange.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
GDP is a measure of total
A) expenditures.
B) income.
C) income and expenditures.
D) income but not expenditures.
E) expenditures but not income.
A) expenditures.
B) income.
C) income and expenditures.
D) income but not expenditures.
E) expenditures but not income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Foreign exchange rates are necessary to
A) compare the demand and supply of goods traded internationally.
B) balance imports and exports in the international market.
C) ensure cultural exchanges across countries.
D) compare prices stated in foreign currency.
E) allow Americans to travel abroad.
A) compare the demand and supply of goods traded internationally.
B) balance imports and exports in the international market.
C) ensure cultural exchanges across countries.
D) compare prices stated in foreign currency.
E) allow Americans to travel abroad.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
A foreign exchange rate constitutes the
A) price of foreign currency as it is determined by the World Bank.
B) price of one country's currency in terms of another country's currency.
C) dollar value of imports and exports undertaken in the world economy during one year.
D) price of foreign currency as it is established by the relative amount of tourism.
E) dollar value of U.S. international trade.
A) price of foreign currency as it is determined by the World Bank.
B) price of one country's currency in terms of another country's currency.
C) dollar value of imports and exports undertaken in the world economy during one year.
D) price of foreign currency as it is established by the relative amount of tourism.
E) dollar value of U.S. international trade.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
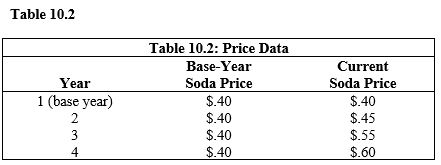
In Table 10.2, the price of soda at the end of four years had
A) decreased 15 percent.
B) decreased 20 percent.
C) increased 60 percent.
D) increased 20 percent.
E) increased 50 percent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Which of the following is not a form of foreign exchange?
A) Foreign bank notes
B) Bank deposits denominated in foreign currency
C) Domestic currency
D) Checking accounts denominated in foreign currency
E) None - all of these are a form of foreign exchange
A) Foreign bank notes
B) Bank deposits denominated in foreign currency
C) Domestic currency
D) Checking accounts denominated in foreign currency
E) None - all of these are a form of foreign exchange

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
A price index is ____, while a base year ____ is.
A) the year against which other years are measured; a measure of the average price level in an economy
B) a broad measure of the prices of goods and services included in the gross domestic product; the year against which other years are measured
C) a measure of the average price of goods and services purchased by the typical household; the year against which other years are measured
D) a measure of the average price level in an economy; the year against which other years are measured
E) an automatic increase in wages that matches increases in items; the year against which other years are measured
A) the year against which other years are measured; a measure of the average price level in an economy
B) a broad measure of the prices of goods and services included in the gross domestic product; the year against which other years are measured
C) a measure of the average price of goods and services purchased by the typical household; the year against which other years are measured
D) a measure of the average price level in an economy; the year against which other years are measured
E) an automatic increase in wages that matches increases in items; the year against which other years are measured

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Given an exchange rate of 80 yen = $1, what is the U.S. dollar price of 1 yen?
A) $0.125
B) $0.0125
C) 80 yen
D) $80
E) $1.25
A) $0.125
B) $0.0125
C) 80 yen
D) $80
E) $1.25

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
On December 29, a skiing trip to Norway cost 7,000 krone. Two weeks later, the U.S. dollar devalued against the Norwegian krone. If the price of the trip in Norway remains the same, a skier living in Florida will now view this trip as
A) cheaper.
B) more expensive.
C) of equal value as before.
D) a more affordable choice.
E) The amount cannot be determined from the information given.
A) cheaper.
B) more expensive.
C) of equal value as before.
D) a more affordable choice.
E) The amount cannot be determined from the information given.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
What is a COLA?
A) A measure of the quality of living
B) A consumer price adjustment
C) An increase in wages to match consumer price increases
D) Another name for a price index
E) The brand name of a soft drink
A) A measure of the quality of living
B) A consumer price adjustment
C) An increase in wages to match consumer price increases
D) Another name for a price index
E) The brand name of a soft drink

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58

In Table 10.2, what is the price index for the base year?
A) 100
B) 112.5
C) 125
D) 137.5
E) 150

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
When talking about price indexes, the term COLAs appears. COLAs stands for
A) community-operated living arrangements.
B) cost of operations in Libya aggression.
C) cost of operating lesser adjustments.
D) cost of living adjustments.
E) cooperative ordinance of Los Angeles.
A) community-operated living arrangements.
B) cost of operations in Libya aggression.
C) cost of operating lesser adjustments.
D) cost of living adjustments.
E) cooperative ordinance of Los Angeles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60

Refer to Table 10.2. What is the price index for the third year?
A) 100
B) 112.5
C) 125
D) 137.5
E) 150

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The financial account is
A) the value of services provided by capital in foreign countries.
B) the record in the balance of payments of the flow of financial assets into and out of a country.
C) the amount of dollars held abroad.
D) the amount of foreign currency held domestically.
E) a record of the dollar amount of exported and imported services.
A) the value of services provided by capital in foreign countries.
B) the record in the balance of payments of the flow of financial assets into and out of a country.
C) the amount of dollars held abroad.
D) the amount of foreign currency held domestically.
E) a record of the dollar amount of exported and imported services.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
If there is a current account surplus in the U.S. balance of payments, then
A) there will necessarily be a surplus in the financial account.
B) the sum of deficit accounts exceeds the sum of surplus accounts in the current account.
C) the sum of surplus accounts in the current account exceeds the sum of deficit accounts in the financial account.
D) the net balance of the balance of payments will equal zero.
E) the United States is a net debtor to the rest of the world.
A) there will necessarily be a surplus in the financial account.
B) the sum of deficit accounts exceeds the sum of surplus accounts in the current account.
C) the sum of surplus accounts in the current account exceeds the sum of deficit accounts in the financial account.
D) the net balance of the balance of payments will equal zero.
E) the United States is a net debtor to the rest of the world.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The average household in Australia spends A$460 on groceries per month. What would this grocery bill amount to in U.S. dollars if the current exchange rate were A$1.27 per dollar?
A) $946.40
B) $584.20
C) $447.91
D) $362.20
E) $222.00
A) $946.40
B) $584.20
C) $447.91
D) $362.20
E) $222.00

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Depreciation of the dollar means all except
A) dollar is now cheaper in terms of other currencies.
B) demand for U.S. products will rise.
C) general price level in the United States has increased.
D) dollar value is higher in terms of other currencies.
E) price of U.S. exports will fall in terms of foreign currencies.
A) dollar is now cheaper in terms of other currencies.
B) demand for U.S. products will rise.
C) general price level in the United States has increased.
D) dollar value is higher in terms of other currencies.
E) price of U.S. exports will fall in terms of foreign currencies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
The balance of payments is
A) the difference between the dollar value of exports and the dollar value of imports.
B) the same as the sum of the merchandise and services accounts.
C) a record of a country's trade in goods, services, and financial assets with the rest of the world.
D) a summary statement of the merchandise, services, and unilateral transfers accounts.
E) a record of the amount of U.S. dollars held abroad.
A) the difference between the dollar value of exports and the dollar value of imports.
B) the same as the sum of the merchandise and services accounts.
C) a record of a country's trade in goods, services, and financial assets with the rest of the world.
D) a summary statement of the merchandise, services, and unilateral transfers accounts.
E) a record of the amount of U.S. dollars held abroad.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
What is a unilateral transfer?
A) A merchandise export
B) A retirement pension sent to another country
C) A royalty receipt on a foreign patent
D) A salary earned abroad
E) All of these are examples of unilateral transfers.
A) A merchandise export
B) A retirement pension sent to another country
C) A royalty receipt on a foreign patent
D) A salary earned abroad
E) All of these are examples of unilateral transfers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
If the exchange rate moves from $.08 = 1 peso to $.12 = 1 peso, then
A) the peso has depreciated.
B) 1 dollar will buy more Mexican pesos than before.
C) the U.S. dollar has appreciated.
D) the prices of U.S. imports from Mexico are more expensive.
E) Mexicans will demand fewer U.S. products, other things being equal.
A) the peso has depreciated.
B) 1 dollar will buy more Mexican pesos than before.
C) the U.S. dollar has appreciated.
D) the prices of U.S. imports from Mexico are more expensive.
E) Mexicans will demand fewer U.S. products, other things being equal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The balance of payments is a record divided into categories, or accounts, including all of the following categories except
A) merchandise.
B) financial assets.
C) profits.
D) services.
E) investment income.
A) merchandise.
B) financial assets.
C) profits.
D) services.
E) investment income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Which of the following statements is false with respect to the net balance of the balance of payments?
A) It cannot show a surplus.
B) It cannot show a deficit.
C) It is zero because the sum of credits equals the sum of debits.
D) It can show either a surplus or a deficit.
E) A deficit in the current account would be offset by a surplus in the financial account, thus ensuring a zero net balance.
A) It cannot show a surplus.
B) It cannot show a deficit.
C) It is zero because the sum of credits equals the sum of debits.
D) It can show either a surplus or a deficit.
E) A deficit in the current account would be offset by a surplus in the financial account, thus ensuring a zero net balance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Which of the following is not one of the subaccounts that add up to the current account?
A) Unilateral transfers
B) Statistical discrepancy
C) Services
D) Merchandise
E) Investment income
A) Unilateral transfers
B) Statistical discrepancy
C) Services
D) Merchandise
E) Investment income

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
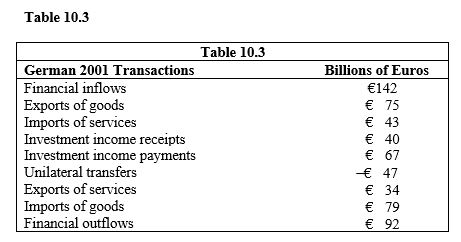
In Table 10.3, the financial account balance for Germany is
A) €80.
B) €17.
C) €4.
D) €50.
E) None of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
A ____ in the value of a currency is called an appreciation of the currency; a ____ in the value of a currency is called a depreciation of the currency.
A) rise; rise
B) rise; fall
C) fall; fall
D) fall; rise
E) The answer cannot be determined from the information given.
A) rise; rise
B) rise; fall
C) fall; fall
D) fall; rise
E) The answer cannot be determined from the information given.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73

-In Table 10.3, the current account balance for Germany is
A) €172.
B) -€87.
C) -€13.
D) €47.
E) none of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The merchandise trade balance
A) indicates the difference between the dollar value of U.S. exported goods and that of U.S. imported goods.
B) includes services and financial assets.
C) is not included in the U.S. balance of payments.
D) will always be in balance.
E) includes U.S. interest earned on foreign asset holdings.
A) indicates the difference between the dollar value of U.S. exported goods and that of U.S. imported goods.
B) includes services and financial assets.
C) is not included in the U.S. balance of payments.
D) will always be in balance.
E) includes U.S. interest earned on foreign asset holdings.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
If the U.S. dollar appreciates against the Japanese yen, then
A) it takes fewer Japanese yen to buy one dollar.
B) Japanese products are less expensive to U.S. residents.
C) the Japanese yen has also appreciated against the U.S. dollar.
D) the prices of U.S. imports from Japan are more expensive.
E) it takes more U.S. dollars to buy a given amount of Japanese yen.
A) it takes fewer Japanese yen to buy one dollar.
B) Japanese products are less expensive to U.S. residents.
C) the Japanese yen has also appreciated against the U.S. dollar.
D) the prices of U.S. imports from Japan are more expensive.
E) it takes more U.S. dollars to buy a given amount of Japanese yen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
A negative balance in the merchandise account would be indicated by
A) exports that exceed imports.
B) imports that exceed exports.
C) a current account deficit.
D) decreasing transfer payments.
E) a deficit balance on investment income.
A) exports that exceed imports.
B) imports that exceed exports.
C) a current account deficit.
D) decreasing transfer payments.
E) a deficit balance on investment income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Appreciation of the U.S. dollar means that the
A) dollar is now cheaper in terms of other currencies.
B) demand for U.S. products will rise.
C) general price level in the United States has increased.
D) dollar value is higher in terms of other currencies.
E) price of U.S. exports will fall.
A) dollar is now cheaper in terms of other currencies.
B) demand for U.S. products will rise.
C) general price level in the United States has increased.
D) dollar value is higher in terms of other currencies.
E) price of U.S. exports will fall.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
A country that is a net creditor
A) shows a deficit in its current account.
B) receives more tax revenue from its citizens than it returns in transfer payments.
C) lends more funds to foreigners than it borrows.
D) shows a surplus in its financial account.
E) sells more bonds to the rest of the world than it buys from the rest of the world.
A) shows a deficit in its current account.
B) receives more tax revenue from its citizens than it returns in transfer payments.
C) lends more funds to foreigners than it borrows.
D) shows a surplus in its financial account.
E) sells more bonds to the rest of the world than it buys from the rest of the world.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79

-In Table 10.3, the merchandise trade balance for Germany is
A) €4.
B) €13.
C) -€4.
D) -€13.
E) none of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
A U.S. financial account deficit means that the dollar amount of
A) U.S. purchases of foreign financial assets and real property abroad exceeds foreign purchases of U.S. financial assets and real property in the United States.
B) foreign investments in the United States exceeds the dollar amount of U.S. investments abroad.
C) U.S. purchases of foreign financial assets and real property abroad is less than foreign purchases of U.S. financial assets and real property in the United States..
D) imported goods exceeds that of exported goods.
E) U.S. gifts to foreigners exceeds the amount of unilateral transfers Americans receive from abroad.
A) U.S. purchases of foreign financial assets and real property abroad exceeds foreign purchases of U.S. financial assets and real property in the United States.
B) foreign investments in the United States exceeds the dollar amount of U.S. investments abroad.
C) U.S. purchases of foreign financial assets and real property abroad is less than foreign purchases of U.S. financial assets and real property in the United States..
D) imported goods exceeds that of exported goods.
E) U.S. gifts to foreigners exceeds the amount of unilateral transfers Americans receive from abroad.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



