Deck 12: Macroeconomic Equilibrium: Aggregate Demand and Supply
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/117
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 12: Macroeconomic Equilibrium: Aggregate Demand and Supply
1
Which of the following is not one of the factors that directly affect how much households spend?
A) Income taxes levied by government
B) Net exports
C) Household wealth
D) Changes in the population of a country
E) Expectations about the future
A) Income taxes levied by government
B) Net exports
C) Household wealth
D) Changes in the population of a country
E) Expectations about the future
Net exports
2
A reduction in resource prices tends to be associated with a
A) rightward shift of the aggregate supply curve.
B) movement up the aggregate supply curve.
C) rightward shift of the aggregate demand curve.
D) movement up the aggregate demand curve.
E) leftward shift of the aggregate supply curve.
A) rightward shift of the aggregate supply curve.
B) movement up the aggregate supply curve.
C) rightward shift of the aggregate demand curve.
D) movement up the aggregate demand curve.
E) leftward shift of the aggregate supply curve.
rightward shift of the aggregate supply curve.
3
Which of the following statements is true?
A) Aggregate demand and aggregate supply determine the equilibrium price and quantity of a single good.
B) The aggregate demand curve indicates a positive relationship between the price level and GDP.
C) The intersection of the aggregate demand and aggregate supply curves determines the equilibrium price and quantity.
D) The intersection of the aggregate demand and aggregate supply curves determines the equilibrium price level and the equilibrium level of real GDP.
E) Other things equal, a downward shift of the aggregate demand curve implies that the economy enters an expansionary phase.
A) Aggregate demand and aggregate supply determine the equilibrium price and quantity of a single good.
B) The aggregate demand curve indicates a positive relationship between the price level and GDP.
C) The intersection of the aggregate demand and aggregate supply curves determines the equilibrium price and quantity.
D) The intersection of the aggregate demand and aggregate supply curves determines the equilibrium price level and the equilibrium level of real GDP.
E) Other things equal, a downward shift of the aggregate demand curve implies that the economy enters an expansionary phase.
The intersection of the aggregate demand and aggregate supply curves determines the equilibrium price level and the equilibrium level of real GDP.
4
Aggregate supply could increase due to all of the following except:
A) an improvement in technology
B) decrease in the price of resources
C) optimistic producers' expectations
D) increase in government spending
E) none - all of these would cause aggregate supply to increase
A) an improvement in technology
B) decrease in the price of resources
C) optimistic producers' expectations
D) increase in government spending
E) none - all of these would cause aggregate supply to increase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Business cycles are linked to the interaction between the
A) foreign exchange rate and the balance of payments account.
B) aggregate demand and aggregate supply curves.
C) demand and supply curves for a particular good.
D) substitution and the wealth effect.
E) long-run aggregate supply curve and the aggregate resource curve.
A) foreign exchange rate and the balance of payments account.
B) aggregate demand and aggregate supply curves.
C) demand and supply curves for a particular good.
D) substitution and the wealth effect.
E) long-run aggregate supply curve and the aggregate resource curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The sum of consumption spending, investment, government spending, and net exports is defined as aggregate
A) supply.
B) demand.
C) equilibrium.
D) expenditures.
E) wealth.
A) supply.
B) demand.
C) equilibrium.
D) expenditures.
E) wealth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Household expenditures increase as a result of
A) population growth.
B) higher personal income taxes.
C) a depreciation of the domestic currency.
D) reduced consumer confidence.
E) a higher domestic price level.
A) population growth.
B) higher personal income taxes.
C) a depreciation of the domestic currency.
D) reduced consumer confidence.
E) a higher domestic price level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following would cause cost-push inflation?
A) lower income tax rates
B) oil-exporting countries restricting oil supplies
C) an increase in government spending
D) depreciation of the domestic currency
E) all of these would cause cost-push inflation
A) lower income tax rates
B) oil-exporting countries restricting oil supplies
C) an increase in government spending
D) depreciation of the domestic currency
E) all of these would cause cost-push inflation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Other things equal, an increase in aggregate demand tends to be associated with
A) cost-push inflation.
B) an economic contraction.
C) a lower level of equilibrium real GDP.
D) demand-pull inflation.
E) an increase in the quality of goods and services produced.
A) cost-push inflation.
B) an economic contraction.
C) a lower level of equilibrium real GDP.
D) demand-pull inflation.
E) an increase in the quality of goods and services produced.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The aggregate demand curve
A) shows total spending in which the economy will engage at alternative price levels.
B) implies an inverse relationship between inflation and unemployment.
C) is identical to the aggregate expenditures curve.
D) has the same slope as a demand curve.
E) relates relative prices to the quantity demanded of a particular good.
A) shows total spending in which the economy will engage at alternative price levels.
B) implies an inverse relationship between inflation and unemployment.
C) is identical to the aggregate expenditures curve.
D) has the same slope as a demand curve.
E) relates relative prices to the quantity demanded of a particular good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Other things equal, a decrease in aggregate demand will result in
A) an economic expansion.
B) lower unemployment and a higher equilibrium price level.
C) an economic contraction.
D) an increase in equilibrium real GDP and a decrease in the equilibrium level of prices.
E) increased economic welfare.
A) an economic expansion.
B) lower unemployment and a higher equilibrium price level.
C) an economic contraction.
D) an increase in equilibrium real GDP and a decrease in the equilibrium level of prices.
E) increased economic welfare.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
When aggregate demand increases, all of the following result except:
A) equilibrium level of real GDP increases
B) unemployment decreases
C) the price level increases
D) cost-push inflation results
E) none -10 all of these result when aggregate demand increases
A) equilibrium level of real GDP increases
B) unemployment decreases
C) the price level increases
D) cost-push inflation results
E) none -10 all of these result when aggregate demand increases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Demand-pull inflation is caused by a(n)
A) increase in aggregate supply.
B) increase in aggregate demand.
C) increase in the demand for a particular good.
D) decrease in the supply of a particular good.
E) decrease in aggregate demand.
A) increase in aggregate supply.
B) increase in aggregate demand.
C) increase in the demand for a particular good.
D) decrease in the supply of a particular good.
E) decrease in aggregate demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
In an attempt to understand an economy's periods of expansion and periods of contraction, economists analyze
A) demand and supply for a single good or service.
B) elasticity.
C) marginal cost and marginal revenue curves.
D) aggregate demand and aggregate supply.
E) the money supply.
A) demand and supply for a single good or service.
B) elasticity.
C) marginal cost and marginal revenue curves.
D) aggregate demand and aggregate supply.
E) the money supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Other things equal, the steeper the aggregate supply curve, the
A) greater the expansionary effect of an increase in aggregate demand.
B) smaller the inflationary effect of an increase in aggregate demand.
C) smaller the recessionary effect of a decrease in aggregate demand.
D) greater the expansionary effect of a decrease in aggregate demand.
E) smaller the recessionary effect of an increase in aggregate demand.
A) greater the expansionary effect of an increase in aggregate demand.
B) smaller the inflationary effect of an increase in aggregate demand.
C) smaller the recessionary effect of a decrease in aggregate demand.
D) greater the expansionary effect of a decrease in aggregate demand.
E) smaller the recessionary effect of an increase in aggregate demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Wealth, income taxes, and demographics are determinants of
A) business spending.
B) household spending.
C) government spending.
D) net exports.
E) technological advancement.
A) business spending.
B) household spending.
C) government spending.
D) net exports.
E) technological advancement.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Cost-push inflation is caused by
A) a leftward shift in the aggregate supply curve.
B) a rightward shift in the aggregate supply curve.
C) a leftward shift in the aggregate demand curve.
D) a rightward shift in the aggregate demand curve.
E) none of these.
A) a leftward shift in the aggregate supply curve.
B) a rightward shift in the aggregate supply curve.
C) a leftward shift in the aggregate demand curve.
D) a rightward shift in the aggregate demand curve.
E) none of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The aggregate supply curve
A) is irrelevant for determining macroeconomic equilibrium.
B) shows the various amounts of real output that the economy will produce of a particular good.
C) has a negative slope.
D) shifts with changes in consumer spending, investment, government spending, and net exports.
E) relates total output of the economy at alternative price levels.
A) is irrelevant for determining macroeconomic equilibrium.
B) shows the various amounts of real output that the economy will produce of a particular good.
C) has a negative slope.
D) shifts with changes in consumer spending, investment, government spending, and net exports.
E) relates total output of the economy at alternative price levels.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following is not one of the four components of the aggregate expenditures of an economy?
A) Government spending
B) Consumption
C) Capitalistic spending
D) Net exports
E) Investment
A) Government spending
B) Consumption
C) Capitalistic spending
D) Net exports
E) Investment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Business cycles result from
A) changes in aggregate demand
B) changes in aggregate supply
C) changes in both aggregate demand and aggregate supply
D) greedy Wall Street executives
E) government intervention
A) changes in aggregate demand
B) changes in aggregate supply
C) changes in both aggregate demand and aggregate supply
D) greedy Wall Street executives
E) government intervention

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
We would expect higher interest rates on business loans to result in a(n)
A) increase in aggregate demand.
B) increase in aggregate supply.
C) increase in investment spending.
D) decrease in government spending.
E) decrease in aggregate expenditures.
A) increase in aggregate demand.
B) increase in aggregate supply.
C) increase in investment spending.
D) decrease in government spending.
E) decrease in aggregate expenditures.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Other things equal, investment spending declines when
A) interest rates are lowered.
B) firms operate at full capacity.
C) profit expectations are rising.
D) capacity utilization is low.
E) the cost of capital falls.
A) interest rates are lowered.
B) firms operate at full capacity.
C) profit expectations are rising.
D) capacity utilization is low.
E) the cost of capital falls.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
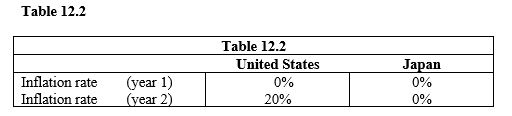
Refer to Table 12.2. Between year 1 and year 2, what happens to the U.S. aggregate demand curve?
A) There is a movement to the right along the aggregate demand curve.
B) The aggregate demand curve shifts to the right.
C) There is a movement to the left along the aggregate demand curve.
D) The aggregate demand curve shifts to the left.
E) There is no movement along, or shift in any direction of, the aggregate demand curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following does not account for a movement along a given aggregate demand curve?
A) The wealth effect
B) The interest-rate effect
C) The real-balance effect
D) The international trade effect
E) The effect of an increase in government spending
A) The wealth effect
B) The interest-rate effect
C) The real-balance effect
D) The international trade effect
E) The effect of an increase in government spending

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The change in aggregate expenditures resulting from a change in the domestic price level that changes the price of domestic goods in relation to foreign goods is known as a(n)
A) international trade effect.
B) international deficit effect.
C) international exchange rate effect.
D) multilateral equilibrium condition.
E) international pricing effect.
A) international trade effect.
B) international deficit effect.
C) international exchange rate effect.
D) multilateral equilibrium condition.
E) international pricing effect.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
If consumers become more optimistic about their future economic well-being, we would expect
A) the aggregate demand curve to shift to the left.
B) the aggregate demand curve to shift to the right.
C) a movement to the left along the aggregate demand curve.
D) a movement to the right along the aggregate demand curve.
E) the aggregate demand curve to be unchanged, but the aggregate supply curve to shift to the right.
A) the aggregate demand curve to shift to the left.
B) the aggregate demand curve to shift to the right.
C) a movement to the left along the aggregate demand curve.
D) a movement to the right along the aggregate demand curve.
E) the aggregate demand curve to be unchanged, but the aggregate supply curve to shift to the right.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which of the following is not a nonprice determinant of demand?
A) Foreign income
B) Foreign prices
C) Increased government spending
D) Relative prices in the same country
E) Lower taxes
A) Foreign income
B) Foreign prices
C) Increased government spending
D) Relative prices in the same country
E) Lower taxes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
All of the following lead to a change in aggregate expenditures except a change in
A) exchange rates.
B) the foreign price level.
C) domestic wealth.
D) the price of apples.
E) interest rates.
A) exchange rates.
B) the foreign price level.
C) domestic wealth.
D) the price of apples.
E) interest rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The wealth effect and the interest rate effect are changes in the price level that
A) bring about a movement along the aggregate demand curve.
B) lead to a shift of the demand curve for a particular good.
C) result in a shift of the aggregate supply curve.
D) help explain the vertical shape of the long-run aggregate supply curve.
E) cause a movement along the aggregate supply curve.
A) bring about a movement along the aggregate demand curve.
B) lead to a shift of the demand curve for a particular good.
C) result in a shift of the aggregate supply curve.
D) help explain the vertical shape of the long-run aggregate supply curve.
E) cause a movement along the aggregate supply curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
When aggregate supply increases, all of the following result except:
A) equilibrium level of real GDP increases
B) unemployment decreases
C) the price level decreases
D) cost-push inflation results
E) none - all of these result when aggregate demand increases
A) equilibrium level of real GDP increases
B) unemployment decreases
C) the price level decreases
D) cost-push inflation results
E) none - all of these result when aggregate demand increases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Other things equal, an increase in government spending
A) increases the slope of the aggregate demand curve.
B) increases the slope of the aggregate supply curve.
C) increases aggregate expenditures.
D) shifts the aggregate demand curve to the left.
E) reduces the equilibrium level of GDP.
A) increases the slope of the aggregate demand curve.
B) increases the slope of the aggregate supply curve.
C) increases aggregate expenditures.
D) shifts the aggregate demand curve to the left.
E) reduces the equilibrium level of GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Investment spending increases with
A) lower interest rates.
B) rapid technological change.
C) a decrease in the price of capital goods.
D) production levels near capacity.
E) all of these.
A) lower interest rates.
B) rapid technological change.
C) a decrease in the price of capital goods.
D) production levels near capacity.
E) all of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33

Refer to Table 12.2. Assume the exchange rate is fixed at 100 yen = $1 and that price changes for cars are identical to the inflation rate in each country. If a U.S. car is sold to Japanese importers for $10,000 in year 1, what is its price in year 2?
A) $9,800
B) $8,000
C) $10,200
D) $12,000
E) $10,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The inverse relationship between the general price level and real GDP is depicted by
A) a downward-sloping demand curve for an individual good.
B) the aggregate demand curve.
C) an upward-sloping demand curve.
D) the aggregate supply curve.
E) a vertical long-run aggregate supply curve.
A) a downward-sloping demand curve for an individual good.
B) the aggregate demand curve.
C) an upward-sloping demand curve.
D) the aggregate supply curve.
E) a vertical long-run aggregate supply curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which of the following will not occur if the level of prices rises?
A) The purchasing power of assets increases.
B) The real value of wealth falls.
C) Aggregate expenditures tend to fall.
D) The real value of assets falls.
E) The purchasing power of money falls.
A) The purchasing power of assets increases.
B) The real value of wealth falls.
C) Aggregate expenditures tend to fall.
D) The real value of assets falls.
E) The purchasing power of money falls.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
All of the following would cause an increase in the aggregate quantity demanded except:
A) real value of assets and wealth rises.
B) increase in purchasing power of money.
C) interest rates fall.
D) higher domestic inflation, relative to other countries.
E) none-all of these would cause an increase in aggregate quantity demanded.
A) real value of assets and wealth rises.
B) increase in purchasing power of money.
C) interest rates fall.
D) higher domestic inflation, relative to other countries.
E) none-all of these would cause an increase in aggregate quantity demanded.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which of the following will not cause net exports to decline?
A) An appreciation of the domestic currency
B) A fall in foreign income
C) Higher foreign tariffs on domestic goods
D) Lower foreign prices
E) None - all of these will cause net exports to decline.
A) An appreciation of the domestic currency
B) A fall in foreign income
C) Higher foreign tariffs on domestic goods
D) Lower foreign prices
E) None - all of these will cause net exports to decline.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
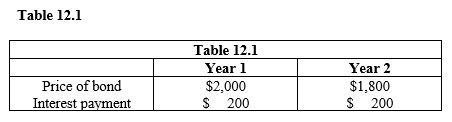
Refer to Table 12.1. The change in the price of the bond is likely to be the result of
A) a decrease in the price of goods and services.
B) an increase in government spending.
C) an increase in the price of goods and services.
D) a decrease in the supply of bonds.
E) none of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39

Refer to Table 12.1. Between year 1 and year 2, the interest rate on the bond
A) did not change.
B) decreased by 1 percentage point.
C) increased by 1 percentage point.
D) decreased by 10 percentage points.
E) increased by 10 percentage points.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following factors least affects net exports?
A) Foreign inflation rates
B) Foreign bank systems
C) Foreign international trade tariffs
D) Foreign income
E) Change in foreign tastes
A) Foreign inflation rates
B) Foreign bank systems
C) Foreign international trade tariffs
D) Foreign income
E) Change in foreign tastes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Consider the following statement: "If the government attempts to raise employment through increased fiscal spending, all it will do is drive up the price level." The proponent of this statement assumes that the aggregate
A) demand curve is a horizontal line.
B) supply curve is a vertical line.
C) supply curve is upward-sloping.
D) supply curve is downward-sloping.
E) supply curve is flat.
A) demand curve is a horizontal line.
B) supply curve is a vertical line.
C) supply curve is upward-sloping.
D) supply curve is downward-sloping.
E) supply curve is flat.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The aggregate demand curve will not shift to the left if
A) people become pessimistic about the future of the economy.
B) there is a decrease in foreign income.
C) the government decreases spending.
D) domestic price levels increase.
E) foreign price levels decrease.
A) people become pessimistic about the future of the economy.
B) there is a decrease in foreign income.
C) the government decreases spending.
D) domestic price levels increase.
E) foreign price levels decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Why is the long-run aggregate supply curve vertical at potential real GDP?
A) Resource costs adjust fully to price changes.
B) Producers' profits are increasing at this point.
C) Unemployment equals zero.
D) There is a very strong relationship between further price changes and output produced.
E) Production costs are at the lowest level possible.
A) Resource costs adjust fully to price changes.
B) Producers' profits are increasing at this point.
C) Unemployment equals zero.
D) There is a very strong relationship between further price changes and output produced.
E) Production costs are at the lowest level possible.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The short-run aggregate supply curve is
A) a horizontal line.
B) positively sloped.
C) negatively sloped.
D) a vertical line.
E) a 45-degree line.
A) a horizontal line.
B) positively sloped.
C) negatively sloped.
D) a vertical line.
E) a 45-degree line.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Figure 12.1
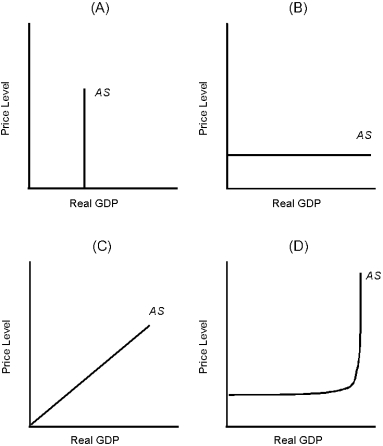
Which of the graphs in Figure 12.1 is consistent with a short-run equilibrium model where prices are variable?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) None of these

Which of the graphs in Figure 12.1 is consistent with a short-run equilibrium model where prices are variable?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) None of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The short-run aggregate supply curve shifts to the left when
A) production technology increases.
B) equipment prices rise.
C) people expect lower inflation rates.
D) productivity increases.
E) wages are reduced.
A) production technology increases.
B) equipment prices rise.
C) people expect lower inflation rates.
D) productivity increases.
E) wages are reduced.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Of the following, which is not held constant in the short run when determining the aggregate supply curve?
A) Profits
B) Wages
C) Rent
D) Interest
E) All of these are held constant when determining the short run aggregate supply curve.
A) Profits
B) Wages
C) Rent
D) Interest
E) All of these are held constant when determining the short run aggregate supply curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
All of the following will cause the short run aggregate supply to shift except for changes in:
A) resource prices
B) technology
C) expectations
D) price level
E) none - changes in all of these will cause the aggregate supply curve to shift
A) resource prices
B) technology
C) expectations
D) price level
E) none - changes in all of these will cause the aggregate supply curve to shift

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Figure 12.1

Which of the graphs in Figure 12.1 is consistent with long-run equilibrium analysis?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) None of these

Which of the graphs in Figure 12.1 is consistent with long-run equilibrium analysis?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) None of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
A leftward shift of the aggregate demand curve can be explained by
A) an increase in raw materials prices.
B) an increase in foreign income.
C) a decline in foreign price levels.
D) inefficient production technology.
E) higher investor optimism.
A) an increase in raw materials prices.
B) an increase in foreign income.
C) a decline in foreign price levels.
D) inefficient production technology.
E) higher investor optimism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The upward-sloping aggregate supply curve represents
A) increases in national output that are accompanied by decreases in the average price level.
B) increases in national output but a fixed price level.
C) increases in the average price level but fixed national output.
D) increases in national output that are accompanied by increases in the average price level.
E) fixed national output and a fixed price level.
A) increases in national output that are accompanied by decreases in the average price level.
B) increases in national output but a fixed price level.
C) increases in the average price level but fixed national output.
D) increases in national output that are accompanied by increases in the average price level.
E) fixed national output and a fixed price level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The less vertical the aggregate supply curve, the
A) faster the price level increases.
B) higher the level of potential GDP.
C) lower the profits earned by businesses.
D) quicker wages adjust to price changes.
E) slower wages adjust to price changes.
A) faster the price level increases.
B) higher the level of potential GDP.
C) lower the profits earned by businesses.
D) quicker wages adjust to price changes.
E) slower wages adjust to price changes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The long-run aggregate supply curve at the potential level of real GDP is a(n)
A) horizontal line.
B) upward-sloping curve.
C) downward-sloping curve.
D) vertical line.
E) combination of a horizontal line, an upward-sloping curve, and a vertical line.
A) horizontal line.
B) upward-sloping curve.
C) downward-sloping curve.
D) vertical line.
E) combination of a horizontal line, an upward-sloping curve, and a vertical line.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
A decline in production costs
A) reduces the amount of output produced.
B) increases the opportunity cost of doing business.
C) reduces the opportunity cost of doing business.
D) reduces business profits.
E) increases business revenues.
A) reduces the amount of output produced.
B) increases the opportunity cost of doing business.
C) reduces the opportunity cost of doing business.
D) reduces business profits.
E) increases business revenues.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
An upward-sloping aggregate supply curve indicates that
A) higher prices lead to less consumption.
B) higher prices lead to increased production.
C) lower prices lead to increased production.
D) the amount of real GDP produced falls as prices increase.
E) lower prices decreases the supply of labor.
A) higher prices lead to less consumption.
B) higher prices lead to increased production.
C) lower prices lead to increased production.
D) the amount of real GDP produced falls as prices increase.
E) lower prices decreases the supply of labor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The short run aggregate supply curve slopes ____because, everything else held constant, higher prices ____ producers' profits, creating an incentive to ____output.
A) up; increase; increase
B) up; decrease; decrease
C) up; increase; decrease
D) down; increase; increase
E) down; decrease; decrease
A) up; increase; increase
B) up; decrease; decrease
C) up; increase; decrease
D) down; increase; increase
E) down; decrease; decrease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Which of the following is true about the economy in the long run?
A) Equilibrium output is always below potential GDP.
B) The aggregate supply curve is horizontal.
C) Structural unemployment and frictional unemployment are nonexistent.
D) Business profits do not increase.
E) Production costs are close to zero.
A) Equilibrium output is always below potential GDP.
B) The aggregate supply curve is horizontal.
C) Structural unemployment and frictional unemployment are nonexistent.
D) Business profits do not increase.
E) Production costs are close to zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which of the following will not shift the short-run aggregate supply curve?
A) A change in technology
B) A change in price expectations
C) A change in wage rates
D) A change in the domestic price level
E) A change in raw material supplies
A) A change in technology
B) A change in price expectations
C) A change in wage rates
D) A change in the domestic price level
E) A change in raw material supplies

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
In the short run, an increase in the average price level causes
A) profits to fall, and thus total production to decline.
B) profits to rise, and thus total production to increase.
C) profits to rise, and thus total production to decline.
D) input costs to fall, and thus total production to rise.
E) input costs to fall, and thus total production to decline.
A) profits to fall, and thus total production to decline.
B) profits to rise, and thus total production to increase.
C) profits to rise, and thus total production to decline.
D) input costs to fall, and thus total production to rise.
E) input costs to fall, and thus total production to decline.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The short-run aggregate supply curve will not shift to the left if
A) there is a significant decrease in worker productivity.
B) workers on fixed-wage contracts expect higher inflation.
C) the price of raw materials increases.
D) the price of capital goods rises.
E) wages rise in anticipation of higher prices.
A) there is a significant decrease in worker productivity.
B) workers on fixed-wage contracts expect higher inflation.
C) the price of raw materials increases.
D) the price of capital goods rises.
E) wages rise in anticipation of higher prices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Long-run aggregate supply increases as
A) new production technology is introduced.
B) the quality of labor declines.
C) the average price level increases.
D) natural resources deplete.
E) corporate wage rates increase.
A) new production technology is introduced.
B) the quality of labor declines.
C) the average price level increases.
D) natural resources deplete.
E) corporate wage rates increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The short-run aggregate supply curve shifts to the right when
A) nominal wage rates fall.
B) nominal wage rates increase.
C) real wage rates increase.
D) real wage rates fall.
E) real wage rates equal nominal wage rates.
A) nominal wage rates fall.
B) nominal wage rates increase.
C) real wage rates increase.
D) real wage rates fall.
E) real wage rates equal nominal wage rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
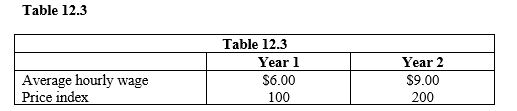
Refer to Table 12.3. Between year 1 and year 2, the real wage
A) decreased by 50 percent.
B) increased by 50 percent.
C) increased by 33.3 percent.
D) decreased by 33.3 percent.
E) decreased by 25 percent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Figure 12.2
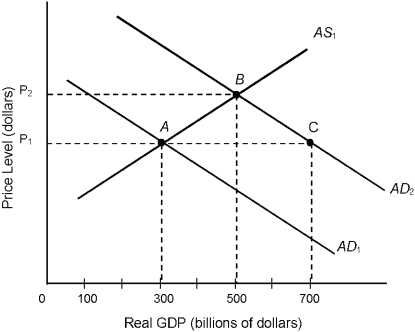
Consider the economy described in Figure 12.2. Assume that equilibrium is at point A. Given AD1, a rightward shift of the aggregate supply curve would cause
A) unemployment to rise.
B) the price level to rise.
C) the equilibrium income level to fall.
D) business production to fall.
E) real GDP to rise.

Consider the economy described in Figure 12.2. Assume that equilibrium is at point A. Given AD1, a rightward shift of the aggregate supply curve would cause
A) unemployment to rise.
B) the price level to rise.
C) the equilibrium income level to fall.
D) business production to fall.
E) real GDP to rise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
In the 1970s, the world price of oil was driven upward due to ____, while in the mid-2000s, the price of oil was driven upward primarily due to ____.
A) increase in demand; decrease in supply
B) increase in demand; increase in supply
C) decrease in demand; decrease in supply
D) decrease in supply; increase in demand
E) decrease in supply; decrease in demand
A) increase in demand; decrease in supply
B) increase in demand; increase in supply
C) decrease in demand; decrease in supply
D) decrease in supply; increase in demand
E) decrease in supply; decrease in demand

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66

Refer to Table 12.3. Assume that labor is a major production cost. In year 2, employers would like to hire
A) more labor because profits are falling.
B) more labor because profits are rising.
C) less labor because profits are falling.
D) less labor because profits are rising.
E) the same amount of labor as in year 1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67

The data in Table 12.3 suggest that, in year 2, aggregate
A) demand increases.
B) demand decreases.
C) supply decreases.
D) supply increases.
E) supply remains constant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
To determine short-run equilibrium in the economy, we use an aggregate supply curve that is
A) downward sloping.
B) vertical.
C) upward sloping.
D) horizontal.
E) circular.
A) downward sloping.
B) vertical.
C) upward sloping.
D) horizontal.
E) circular.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Figure 12.2

Consider the economy described in Figure 12.2. When macroeconomic equilibrium shifts from point A to point B,
A) cyclical unemployment decreases.
B) inflation decreases.
C) productive capacity decreases.
D) business profits decrease.
E) aggregate expenditures decrease.

Consider the economy described in Figure 12.2. When macroeconomic equilibrium shifts from point A to point B,
A) cyclical unemployment decreases.
B) inflation decreases.
C) productive capacity decreases.
D) business profits decrease.
E) aggregate expenditures decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Which of the following statements is true?
A) The long-run aggregate supply curve can never shift to the left.
B) The long-run aggregate supply curve can never shift to the right.
C) The long-run aggregate supply curve can shift to both the left and the right.
D) The long-run aggregate supply curve always stays in the same location because potential real GDP cannot change.
E) New technologies affect only the short-run aggregate supply curve, not the long-run aggregate supply curve.
A) The long-run aggregate supply curve can never shift to the left.
B) The long-run aggregate supply curve can never shift to the right.
C) The long-run aggregate supply curve can shift to both the left and the right.
D) The long-run aggregate supply curve always stays in the same location because potential real GDP cannot change.
E) New technologies affect only the short-run aggregate supply curve, not the long-run aggregate supply curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Figure 12.2

Consider the economy described in Figure 12.2. At point C,
A) businesses produce more than consumers want to spend.
B) inventories deplete, which pushes the price up to its new equilibrium.
C) inventories accumulate, which pushes the price down to its new equilibrium.
D) real GDP is below its equilibrium level.
E) the economy is in equilibrium.

Consider the economy described in Figure 12.2. At point C,
A) businesses produce more than consumers want to spend.
B) inventories deplete, which pushes the price up to its new equilibrium.
C) inventories accumulate, which pushes the price down to its new equilibrium.
D) real GDP is below its equilibrium level.
E) the economy is in equilibrium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
In the mid-2000s, the price of oil was being driven higher by rising demand by
A) Germany
B) the United States
C) China
D) the United States and China
E) Germany, the United States, and China
A) Germany
B) the United States
C) China
D) the United States and China
E) Germany, the United States, and China

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
When we consider an upward-sloping aggregate supply curve and a downward-sloping aggregate demand curve, a decrease in aggregate expenditures is reflected as a
A) leftward shift in the aggregate supply curve, which increases the equilibrium price level and decreases equilibrium income.
B) rightward shift in the aggregate supply curve, which increases both the equilibrium price level and equilibrium income.
C) rightward shift in the aggregate demand curve, which increases both the equilibrium price level and equilibrium income.
D) leftward shift in the aggregate demand curve, which decreases both the equilibrium price level and equilibrium income.
E) leftward shift in the aggregate demand curve, which increases the equilibrium price level and decreases equilibrium income.
A) leftward shift in the aggregate supply curve, which increases the equilibrium price level and decreases equilibrium income.
B) rightward shift in the aggregate supply curve, which increases both the equilibrium price level and equilibrium income.
C) rightward shift in the aggregate demand curve, which increases both the equilibrium price level and equilibrium income.
D) leftward shift in the aggregate demand curve, which decreases both the equilibrium price level and equilibrium income.
E) leftward shift in the aggregate demand curve, which increases the equilibrium price level and decreases equilibrium income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
A simultaneous increase in both unemployment and inflation would most likely be the result of a(n)
A) increase in long-run aggregate supply.
B) increase in short-run aggregate supply.
C) decrease in the aggregate demand curve.
D) increase in the long-run aggregate supply curve and an increase in the aggregate demand curve.
E) decrease in the short-run aggregate supply curve.
A) increase in long-run aggregate supply.
B) increase in short-run aggregate supply.
C) decrease in the aggregate demand curve.
D) increase in the long-run aggregate supply curve and an increase in the aggregate demand curve.
E) decrease in the short-run aggregate supply curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Figure 12.3
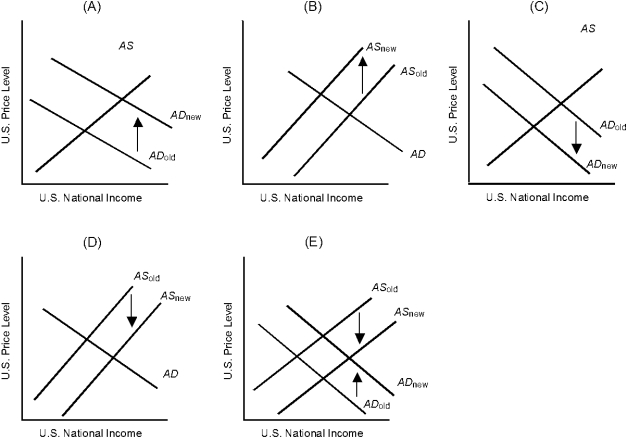
Which of the graphs in Figure 12.3 describes the impact of domestic real wage increases on U.S. equilibrium income and the U.S. equilibrium price level?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

Which of the graphs in Figure 12.3 describes the impact of domestic real wage increases on U.S. equilibrium income and the U.S. equilibrium price level?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
A decline in short-run aggregate supply would be caused by which of the following?
A) The discovery of new mineral deposits in Arizona
B) Higher real wage rates
C) Lower personal income in France
D) Cutbacks in government spending
E) Rapid depreciation of the Swiss franc
A) The discovery of new mineral deposits in Arizona
B) Higher real wage rates
C) Lower personal income in France
D) Cutbacks in government spending
E) Rapid depreciation of the Swiss franc

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Figure 12.2

Consider the economy described in Figure 12.2. At point A, equilibrium income equals
A) P1
B) P2
C) $300 billion.
D) $500 billion.
E) $700 billion.

Consider the economy described in Figure 12.2. At point A, equilibrium income equals
A) P1
B) P2
C) $300 billion.
D) $500 billion.
E) $700 billion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Figure 12.2

Consider the economy described in Figure 12.2. The shift in aggregate demand from AD1 to AD2 could have been initiated by
A) a decrease in the price level.
B) an increase in saving.
C) government budget cuts.
D) an increase in autonomous net exports.
E) lower resource prices.

Consider the economy described in Figure 12.2. The shift in aggregate demand from AD1 to AD2 could have been initiated by
A) a decrease in the price level.
B) an increase in saving.
C) government budget cuts.
D) an increase in autonomous net exports.
E) lower resource prices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Figure 12.3

Which of the graphs in Figure 12.3 best describes the impact of lower real income in Germany on U.S. equilibrium income and the U.S. equilibrium price level?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

Which of the graphs in Figure 12.3 best describes the impact of lower real income in Germany on U.S. equilibrium income and the U.S. equilibrium price level?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
If both aggregate demand and short-run aggregate supply increase at the same time,
A) the price level increases, but the change in equilibrium income is unknown.
B) both the price level and equilibrium income increase.
C) both the price level and equilibrium income decline.
D) equilibrium income increases, but the change in the price level is unknown.
E) the change in both equilibrium income and the price level is ambiguous.
A) the price level increases, but the change in equilibrium income is unknown.
B) both the price level and equilibrium income increase.
C) both the price level and equilibrium income decline.
D) equilibrium income increases, but the change in the price level is unknown.
E) the change in both equilibrium income and the price level is ambiguous.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



