Deck 16: Monopolistic Competition
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/191
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 16: Monopolistic Competition
1
Which statement explains the characteristics of a monopolistically competitive market
A)There are only a few sellers.
B)Each firm takes the price of its product as given.
C)Firms can enter or exit the market without restriction.
D)Each firm produces a product that is essentially identical to the products of other firms in the market.
A)There are only a few sellers.
B)Each firm takes the price of its product as given.
C)Firms can enter or exit the market without restriction.
D)Each firm produces a product that is essentially identical to the products of other firms in the market.
Firms can enter or exit the market without restriction.
2
What is the profit-maximizing rule for a firm in a monopolistically competitive market
A)Select the quantity at which marginal revenue is equal to marginal cost.
B)Select the quantity at which average total cost is equal to marginal revenue.
C)Select the quantity at which average total cost is at its minimum value.
D)Select the quantity at which average revenue exceeds average total cost.
A)Select the quantity at which marginal revenue is equal to marginal cost.
B)Select the quantity at which average total cost is equal to marginal revenue.
C)Select the quantity at which average total cost is at its minimum value.
D)Select the quantity at which average revenue exceeds average total cost.
Select the quantity at which marginal revenue is equal to marginal cost.
3
Why does each firm in a monopolistically competitive market face a downward-sloping demand curve
A)There are many other sellers in the market.
B)There are very few other sellers in the market.
C)That firm's product is different from those offered by other firms in the market.
D)That firm faces the threat of entry into the market by new firms.
A)There are many other sellers in the market.
B)There are very few other sellers in the market.
C)That firm's product is different from those offered by other firms in the market.
D)That firm faces the threat of entry into the market by new firms.
That firm's product is different from those offered by other firms in the market.
4
Which statement describes a characteristic of a monopolistic competitive market
A)It has some features of monopoly and some features of competition.
B)It has one large, dominant firm and many other smaller firms.
C)It has barriers to entry.
D)It sells homogeneous products.
A)It has some features of monopoly and some features of competition.
B)It has one large, dominant firm and many other smaller firms.
C)It has barriers to entry.
D)It sells homogeneous products.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which goods are NOT sold in a monopolistically competitive market
A)shoes
B)books
C)cookies
D)wheat
A)shoes
B)books
C)cookies
D)wheat

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
In a monopolistically competitive industry,how does price compare with marginal cost
A)Price is equal to marginal cost since each firm is a price taker.
B)Price is below marginal cost since each firm is a price taker.
C)Price is above marginal cost since each firm is a price setter.
D)Price is a fraction of marginal cost since each firm is a price setter.
A)Price is equal to marginal cost since each firm is a price taker.
B)Price is below marginal cost since each firm is a price taker.
C)Price is above marginal cost since each firm is a price setter.
D)Price is a fraction of marginal cost since each firm is a price setter.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
In the short run,a firm in a monopolistically competitive market operates much like what type of firm
A)a perfectly competitive firm
B)an oligopoly firm
C)a monopoly
D)a duopoly
A)a perfectly competitive firm
B)an oligopoly firm
C)a monopoly
D)a duopoly

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
In a monopolistically competitive industry,what do firms' demand curves also represent
A)marginal revenue
B)marginal cost
C)average revenue
D)output
A)marginal revenue
B)marginal cost
C)average revenue
D)output

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
What will happen if firms in a monopolistically competitive market are earning positive profits
A)Firms will likely be subject to regulation.
B)Barriers to entry will be strengthened.
C)Some firms must exit the market.
D)New firms will enter the market.
A)Firms will likely be subject to regulation.
B)Barriers to entry will be strengthened.
C)Some firms must exit the market.
D)New firms will enter the market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
A profit-maximizing firm in a monopolistically competitive market is characterized by which attribute
A)Average revenue exceeds marginal revenue.
B)Marginal revenue exceeds average revenue.
C)Average revenue is equal to marginal revenue.
D)Total revenue is maximized along with profit.
A)Average revenue exceeds marginal revenue.
B)Marginal revenue exceeds average revenue.
C)Average revenue is equal to marginal revenue.
D)Total revenue is maximized along with profit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following is an example of a monopolistically competitive market
A)the market for hair cuts
B)the market for soybeans
C)the market for silver
D)the market for cable TV
A)the market for hair cuts
B)the market for soybeans
C)the market for silver
D)the market for cable TV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following is unique to a monopolistically competitive firm when compared to an oligopoly
A)It advertises.
B)It produces a quantity of output that falls short of the socially optimal level.
C)It produces identical products.
D)Monopolistic competition features many sellers.
A)It advertises.
B)It produces a quantity of output that falls short of the socially optimal level.
C)It produces identical products.
D)Monopolistic competition features many sellers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
What is one way in which a profit-maximizing firm in a monopolistically competitive market differs from a firm in a perfectly competitive market
A)The firm in the monopolistically competitive market is characterized by market share maximization.
B)The firm in the monopolistically competitive market has no barriers to entry.
C)The firm in the monopolistically competitive market faces a downward-sloping demand curve for its product.
D)The firm in the monopolistically competitive market faces a horizontal marginal revenue curve at the market clearing price.
A)The firm in the monopolistically competitive market is characterized by market share maximization.
B)The firm in the monopolistically competitive market has no barriers to entry.
C)The firm in the monopolistically competitive market faces a downward-sloping demand curve for its product.
D)The firm in the monopolistically competitive market faces a horizontal marginal revenue curve at the market clearing price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which goods are sold in a monopolistically competitive market
A)shoes
B)wheat
C)corn
D)postage stamps
A)shoes
B)wheat
C)corn
D)postage stamps

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which situation is least likely to apply to a monopolistically competitive firm
A)Profit is positive in the short run.
B)Total cost exceeds total revenue in the short run.
C)Profit is positive in the long run.
D)Total revenue equals total cost in the long run.
A)Profit is positive in the short run.
B)Total cost exceeds total revenue in the short run.
C)Profit is positive in the long run.
D)Total revenue equals total cost in the long run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
What statement describes both perfect competition and monopolistic competition
A)Each firm is, in many ways, like a monopoly.
B)Each firm sells a product that is at least slightly different from those of other firms.
C)Each firm faces a downward-sloping demand curve.
D)Each firm has competition in the market.
A)Each firm is, in many ways, like a monopoly.
B)Each firm sells a product that is at least slightly different from those of other firms.
C)Each firm faces a downward-sloping demand curve.
D)Each firm has competition in the market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which value does a monopolistically competitive firm choose
A)the quantity of output to produce, but the market determines price
B)the price, but competition in the market determines the quantity
C)the price, but output is determined by a cartel production quota
D)the quantity of output to produce and the price at which it will sell its output
A)the quantity of output to produce, but the market determines price
B)the price, but competition in the market determines the quantity
C)the price, but output is determined by a cartel production quota
D)the quantity of output to produce and the price at which it will sell its output

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Long-run profit earned by a monopolistically competitive firm is driven to the competitive level due to which factor
A)a change in the technology that the firm utilizes
B)new firms entering the market causing a shift of its demand curve
C)new firms entering the market causing a shift of its supply curve
D)increased product differentiation
A)a change in the technology that the firm utilizes
B)new firms entering the market causing a shift of its demand curve
C)new firms entering the market causing a shift of its supply curve
D)increased product differentiation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
A monopolistically competitive firm's choice of output level is virtually identical to the choice made by what other type of firm
A)a perfectly competitive firm
B)a duopolist
C)a monopolist
D)an oligopolist
A)a perfectly competitive firm
B)a duopolist
C)a monopolist
D)an oligopolist

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
When a new firm enters a monopolistically competitive market,what will happen to the individual demand curves faced by all existing firms in that market
A)They will shift to the left.
B)They will shift to the right.
C)They will remain unchanged, but the quantity demanded will increase.
D)They will remain unchanged, but the quantity demanded will decrease.
A)They will shift to the left.
B)They will shift to the right.
C)They will remain unchanged, but the quantity demanded will increase.
D)They will remain unchanged, but the quantity demanded will decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Scenario 16-3
A monopolistically competitive firm has the following cost structure:
The firm faces the following demand curve:
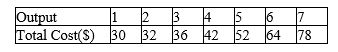
Refer to Scenario 16-3.If the government forces this firm to produce at its efficient scale,how many units will it produce and for what profit or loss
A)produce 3 units and make $9
B)produce 4 units and make $6
C)produce 5 units and lose $5
D)produce 6 units and lose $29
A monopolistically competitive firm has the following cost structure:
The firm faces the following demand curve:

Refer to Scenario 16-3.If the government forces this firm to produce at its efficient scale,how many units will it produce and for what profit or loss
A)produce 3 units and make $9
B)produce 4 units and make $6
C)produce 5 units and lose $5
D)produce 6 units and lose $29

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
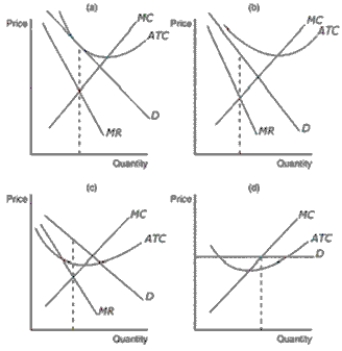
Figure 16-1
Lines in the figures below reflect the potential effect of entry and exit in a monopolistically competitive market on the demand and/or marginal-cost curves of incumbent firms.
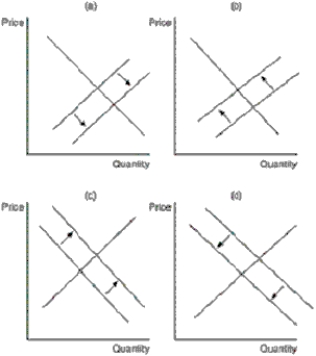
Refer to Figure 16-1.Which of the diagrams depicts the effect on incumbent firms of some existing firms leaving the market
A)panel (a)
B)panel (b)
C)panel (c)
D)panel (d)
Lines in the figures below reflect the potential effect of entry and exit in a monopolistically competitive market on the demand and/or marginal-cost curves of incumbent firms.

Refer to Figure 16-1.Which of the diagrams depicts the effect on incumbent firms of some existing firms leaving the market
A)panel (a)
B)panel (b)
C)panel (c)
D)panel (d)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
As some incumbent firms exit a monopolistically competitive market,what happens to profits of existing firms and product diversity in the market
A)Profits of existing firms decline and product diversity in the market decreases.
B)Profits of existing firms decline and product diversity in the market increases.
C)Profits of existing firms rise and product diversity in the market decreases.
D)Profits of existing firms rise and product diversity in the market increases.
A)Profits of existing firms decline and product diversity in the market decreases.
B)Profits of existing firms decline and product diversity in the market increases.
C)Profits of existing firms rise and product diversity in the market decreases.
D)Profits of existing firms rise and product diversity in the market increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Table 16-2
A firm has the following cost structure:
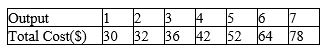
Refer to Table 16-2.If this firm is in a typical monopolistically competitive market,when marginal revenue is $10 and price is $12,how many units of output will it likely produce in the short run
A)less than 4 units of output
B)4 units of output
C)5 units of output
D)more than 5 units of output
A firm has the following cost structure:

Refer to Table 16-2.If this firm is in a typical monopolistically competitive market,when marginal revenue is $10 and price is $12,how many units of output will it likely produce in the short run
A)less than 4 units of output
B)4 units of output
C)5 units of output
D)more than 5 units of output

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Table 16-1
A monopolistically competitive firm faces the following demand curve for its product:
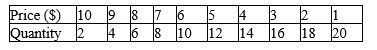
Refer to Table 16-1.The firm has total fixed costs of $20 and a constant marginal cost of $5 per unit.What will the firm do
A)It will produce 2 units; firms will exit the market in the long run.
B)It will produce 4 units; firms will exit the market in the long run.
C)It will produce 6 units; firms will exit the market in the long run.
D)It will produce 8 units; firms will exit the market in the long run.
A monopolistically competitive firm faces the following demand curve for its product:

Refer to Table 16-1.The firm has total fixed costs of $20 and a constant marginal cost of $5 per unit.What will the firm do
A)It will produce 2 units; firms will exit the market in the long run.
B)It will produce 4 units; firms will exit the market in the long run.
C)It will produce 6 units; firms will exit the market in the long run.
D)It will produce 8 units; firms will exit the market in the long run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Table 16-2
A firm has the following cost structure:

Refer to Table 16-2.If this firm is in a typical perfectly competitive market,when marginal revenue is $8 and price is $9,how many units of output will it likely produce in the long run
A)0 units of output
B)4 units of output
C)5 units of output
D)6 units of output
A firm has the following cost structure:

Refer to Table 16-2.If this firm is in a typical perfectly competitive market,when marginal revenue is $8 and price is $9,how many units of output will it likely produce in the long run
A)0 units of output
B)4 units of output
C)5 units of output
D)6 units of output

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which two curves are tangent to one another in a monopolistically competitive market with zero economic profit
A)demand and average variable cost
B)demand and average total cost
C)marginal revenue and average variable cost
D)marginal revenue and average total cost
A)demand and average variable cost
B)demand and average total cost
C)marginal revenue and average variable cost
D)marginal revenue and average total cost

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
As new firms enter a monopolistically competitive market,what happens to profits of existing firms and product diversity in the market
A)Profits of existing firms rise and product diversity in the market increases.
B)Profits of existing firms rise and product diversity in the market decreases.
C)Profits of existing firms decline and product diversity in the market increases.
D)Profits of existing firms decline and product diversity in the market decreases.
A)Profits of existing firms rise and product diversity in the market increases.
B)Profits of existing firms rise and product diversity in the market decreases.
C)Profits of existing firms decline and product diversity in the market increases.
D)Profits of existing firms decline and product diversity in the market decreases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
What does a monopolistically competitive firm do to maximize profit
A)It takes the price as given and it chooses its quantity, just as a competitive firm does.
B)It takes the price as given and chooses its quantity, just as a colluding oligopolist does.
C)It chooses its quantity and price, just as a competitive firm does.
D)It chooses its quantity and price, just as a monopoly does.
A)It takes the price as given and it chooses its quantity, just as a competitive firm does.
B)It takes the price as given and chooses its quantity, just as a colluding oligopolist does.
C)It chooses its quantity and price, just as a competitive firm does.
D)It chooses its quantity and price, just as a monopoly does.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
What does the free entry and exit of firms in a monopolistically competitive market guarantee
A)Both economic profits and economic losses can persist into the long run.
B)Both economic profits and economic losses disappear in the long run.
C)Both economic profits and economic losses increase in the long run.
D)Both economic profits and economic losses decrease in the long run.
A)Both economic profits and economic losses can persist into the long run.
B)Both economic profits and economic losses disappear in the long run.
C)Both economic profits and economic losses increase in the long run.
D)Both economic profits and economic losses decrease in the long run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Figure 16-1
Lines in the figures below reflect the potential effect of entry and exit in a monopolistically competitive market on the demand and/or marginal-cost curves of incumbent firms.

Refer to Figure 16-1.Panel (d) in the set of figures shown depicts the effect on incumbent firms of which circumstance
A)long-run economic losses
B)a decrease in the diversity of products offered in the market
C)new entrants in the market
D)existing firms exiting the market
Lines in the figures below reflect the potential effect of entry and exit in a monopolistically competitive market on the demand and/or marginal-cost curves of incumbent firms.

Refer to Figure 16-1.Panel (d) in the set of figures shown depicts the effect on incumbent firms of which circumstance
A)long-run economic losses
B)a decrease in the diversity of products offered in the market
C)new entrants in the market
D)existing firms exiting the market

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Table 16-1
A monopolistically competitive firm faces the following demand curve for its product:

Refer to Table 16-1.The firm has total fixed costs of $40 and a constant marginal cost of $2 per unit.Which outcome will result
A)Firms will exit this market.
B)Firms will enter this market.
C)This market is in long-run equilibrium.
D)This firm is operating at efficient scale.
A monopolistically competitive firm faces the following demand curve for its product:

Refer to Table 16-1.The firm has total fixed costs of $40 and a constant marginal cost of $2 per unit.Which outcome will result
A)Firms will exit this market.
B)Firms will enter this market.
C)This market is in long-run equilibrium.
D)This firm is operating at efficient scale.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
In monopolistically competitive markets,what is the role that economic profits play
A)They signal some incumbent firms to exit the market.
B)They signal new firms to enter the market.
C)They are maintained through government-imposed barriers to entry.
D)They show that they are price takers in the market.
A)They signal some incumbent firms to exit the market.
B)They signal new firms to enter the market.
C)They are maintained through government-imposed barriers to entry.
D)They show that they are price takers in the market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Scenario 16-3
A monopolistically competitive firm has the following cost structure:
The firm faces the following demand curve:

Refer to Scenario 16-3.To maximize profit (or minimize losses),how many units will the firm produce
A)2 units
B)3 units
C)4 units
D)5 units
A monopolistically competitive firm has the following cost structure:
The firm faces the following demand curve:

Refer to Scenario 16-3.To maximize profit (or minimize losses),how many units will the firm produce
A)2 units
B)3 units
C)4 units
D)5 units

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
If firms in a monopolistically competitive market are earning economic profits,which scenario would best reflect the change facing incumbent firms as the market adjusts to its new equilibrium
A)an increase in demand
B)a decrease in demand
C)a downward shift in their marginal-cost curve
D)an upward shift in their marginal-cost curve
A)an increase in demand
B)a decrease in demand
C)a downward shift in their marginal-cost curve
D)an upward shift in their marginal-cost curve

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Table 16-1
A monopolistically competitive firm faces the following demand curve for its product:

Refer to Table 16-1.The firm has total fixed costs of $20 and a constant marginal cost of $3 per unit.What will the firm do
A)It will produce 8 units; firms will enter the market in the long run.
B)It will produce 10 units; firms will enter the market in the long run.
C)It will produce 10 units; firms will exit the market in the long run.
D)It will produce 12 units; firms will enter the market in the long run.
A monopolistically competitive firm faces the following demand curve for its product:

Refer to Table 16-1.The firm has total fixed costs of $20 and a constant marginal cost of $3 per unit.What will the firm do
A)It will produce 8 units; firms will enter the market in the long run.
B)It will produce 10 units; firms will enter the market in the long run.
C)It will produce 10 units; firms will exit the market in the long run.
D)It will produce 12 units; firms will enter the market in the long run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
In monopolistically competitive markets,what is the role that economic losses play
A)They signal some incumbent firms to exit the market.
B)They signal new firms to enter the market.
C)They are maintained through government-imposed barriers to exit.
D)They show that they are price takers in the market.
A)They signal some incumbent firms to exit the market.
B)They signal new firms to enter the market.
C)They are maintained through government-imposed barriers to exit.
D)They show that they are price takers in the market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Suppose that monopolistically competitive firms in a certain market are earning positive profits.What happens in the transition from this initial situation to a long-run equilibrium
A)The number of firms in the market decreases.
B)Each incumbent firm experiences a decrease in demand for its product.
C)Marginal revenue will increase.
D)Average revenue will increase.
A)The number of firms in the market decreases.
B)Each incumbent firm experiences a decrease in demand for its product.
C)Marginal revenue will increase.
D)Average revenue will increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
If firms in a monopolistically competitive market are incurring economic losses,which scenario would best reflect the change facing incumbent firms as the market adjusts to its new equilibrium
A)a downward shift in their marginal-cost curve
B)an upward shift in their marginal-cost curve
C)a decrease in demand
D)an increase in demand
A)a downward shift in their marginal-cost curve
B)an upward shift in their marginal-cost curve
C)a decrease in demand
D)an increase in demand

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Suppose that monopolistically competitive firms in a certain market are experiencing losses.What happens in the transition from this initial situation to a long-run equilibrium
A)The number of firms in the market decreases.
B)Each incumbent firm experiences a decrease in demand for its product.
C)Marginal cost and average total cost will increase.
D)Product variety increases.
A)The number of firms in the market decreases.
B)Each incumbent firm experiences a decrease in demand for its product.
C)Marginal cost and average total cost will increase.
D)Product variety increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
When a firm's demand (average-revenue) curve is tangent to its average-total-cost curve,which is the result regarding economic profits/losses
A)The firm's economic profit is zero.
B)The firm must be earning economic profits.
C)The firm must be incurring economic losses.
D)The firm must be operating in a monopolistically competitive market.
A)The firm's economic profit is zero.
B)The firm must be earning economic profits.
C)The firm must be incurring economic losses.
D)The firm must be operating in a monopolistically competitive market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Figure 16-4
Refer to Figure 16-4.Panel (b) in the set of figures shown is consistent with a firm in a monopolistically competitive market that is in which of the following positions
A)It suffers a loss in the short-run equilibrium.
B)It earns economic profits in the short-run equilibrium.
C)It suffers a loss in the long-run equilibrium.
D)It earns economic profits in the long-run equilibrium.

Refer to Figure 16-4.Panel (b) in the set of figures shown is consistent with a firm in a monopolistically competitive market that is in which of the following positions
A)It suffers a loss in the short-run equilibrium.
B)It earns economic profits in the short-run equilibrium.
C)It suffers a loss in the long-run equilibrium.
D)It earns economic profits in the long-run equilibrium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
What is an important difference between the situations faced by a profit-maximizing monopolistically competitive firm in the short run and in the long run
A)In the short run, price may exceed marginal revenue; in the long run, price equals marginal revenue.
B)In the short run, price may exceed marginal cost; in the long run, price equals marginal cost.
C)In the short run, price may exceed average total cost; in the long run, price equals average total cost.
D)In the short run, price may exceed average variable cost; in the long run, price equals average variable cost.
A)In the short run, price may exceed marginal revenue; in the long run, price equals marginal revenue.
B)In the short run, price may exceed marginal cost; in the long run, price equals marginal cost.
C)In the short run, price may exceed average total cost; in the long run, price equals average total cost.
D)In the short run, price may exceed average variable cost; in the long run, price equals average variable cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Figure 16-2
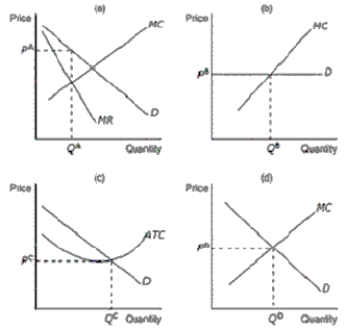
Refer to Figure 16-2.If a firm in a monopolistically competitive market was producing the level of output depicted as QD in panel (d),what would it experience
A)It would not be maximizing its profit.
B)It would be minimizing its losses.
C)It would be losing market share to other firms in the market.
D)It would be operating at excess capacity.

Refer to Figure 16-2.If a firm in a monopolistically competitive market was producing the level of output depicted as QD in panel (d),what would it experience
A)It would not be maximizing its profit.
B)It would be minimizing its losses.
C)It would be losing market share to other firms in the market.
D)It would be operating at excess capacity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Product differentiation in monopolistically competitive markets ensures that,for profit-maximizing firms,what will result
A)Marginal revenue will equal average total cost.
B)Price will exceed marginal cost.
C)Marginal cost will exceed average revenue.
D)Average variable cost will exceed average revenue.
A)Marginal revenue will equal average total cost.
B)Price will exceed marginal cost.
C)Marginal cost will exceed average revenue.
D)Average variable cost will exceed average revenue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
What is one way in which monopolistic competition differs from perfect competition
A)In monopolistically competitive markets there are barriers to entry.
B)In monopolistically competitive markets all firms produce at the efficient scale in the long run.
C)In monopolistically competitive markets each of the sellers offers a somewhat different product.
D)In monopolistically competitive markets strategic interactions between firms are vitally important.
A)In monopolistically competitive markets there are barriers to entry.
B)In monopolistically competitive markets all firms produce at the efficient scale in the long run.
C)In monopolistically competitive markets each of the sellers offers a somewhat different product.
D)In monopolistically competitive markets strategic interactions between firms are vitally important.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
In monopolistically competitive markets,what does the property of free entry and exit suggest
A)The market structure will eventually be characterized by perfect competition in the long run.
B)All firms earn zero economic profits in the long run.
C)Some firms will be able to earn economic profits in the long run.
D)Some firms will be forced to incur economic losses in the long run.
A)The market structure will eventually be characterized by perfect competition in the long run.
B)All firms earn zero economic profits in the long run.
C)Some firms will be able to earn economic profits in the long run.
D)Some firms will be forced to incur economic losses in the long run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Entry and exit drive each firm in a monopolistically competitive market to a point of tangency between which of its curves
A)marginal-revenue curve and its total-cost curve
B)marginal-revenue curve and its average-total-cost curve
C)demand curve and its total-cost curve
D)demand curve and its average-total-cost curve
A)marginal-revenue curve and its total-cost curve
B)marginal-revenue curve and its average-total-cost curve
C)demand curve and its total-cost curve
D)demand curve and its average-total-cost curve

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
When a market is monopolistically competitive,what is the typical firm in the market likely to experience in the short and long run
A)positive profit in the short run and in the long run
B)positive or negative profit in the short run and a zero profit in the long run
C)zero profit in the short run and a positive or negative profit in the long run
D)zero profit in the short run and in the long run
A)positive profit in the short run and in the long run
B)positive or negative profit in the short run and a zero profit in the long run
C)zero profit in the short run and a positive or negative profit in the long run
D)zero profit in the short run and in the long run

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
New firms will necessarily enter a monopolistically competitive market when price exceeds what amount
A)marginal revenue
B)average variable cost
C)marginal cost
D)average total cost
A)marginal revenue
B)average variable cost
C)marginal cost
D)average total cost

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Figure 16-4

Refer to Figure 16-4.Which of the panels depicts a firm in a monopolistically competitive market earning economic profits
A)panel (a)
B)panel (b)
C)panel (c)
D)panel (d)

Refer to Figure 16-4.Which of the panels depicts a firm in a monopolistically competitive market earning economic profits
A)panel (a)
B)panel (b)
C)panel (c)
D)panel (d)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
What is one way in which monopolistic competition differs from oligopoly
A)There are no barriers to entry in oligopolies.
B)In oligopoly markets there are only a few sellers.
C)All oligopoly firms eventually earn zero economic profits.
D)Strategic interactions between firms are rarely evident in oligopolies.
A)There are no barriers to entry in oligopolies.
B)In oligopoly markets there are only a few sellers.
C)All oligopoly firms eventually earn zero economic profits.
D)Strategic interactions between firms are rarely evident in oligopolies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
What happens when a profit-maximizing firm in a monopolistically competitive market is in long-run equilibrium
A)The demand curve will be perfectly elastic.
B)Price exceeds marginal cost.
C)Marginal cost is falling.
D)Marginal revenue exceeds marginal cost.
A)The demand curve will be perfectly elastic.
B)Price exceeds marginal cost.
C)Marginal cost is falling.
D)Marginal revenue exceeds marginal cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
What type of demand curve does product differentiation cause the seller of a good to face
A)downward-sloping
B)upward-sloping
C)horizontal
D)vertical
A)downward-sloping
B)upward-sloping
C)horizontal
D)vertical

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Figure 16-3
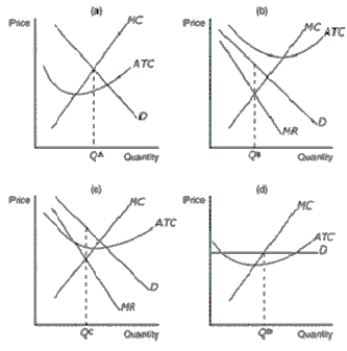
Refer to Figure 16-3.Which of the graphs shown would be consistent with a firm in a monopolistically competitive market that is doing its best but still losing money
A)panel (a)
B)panel (b)
C)panel (c)
D)panel (d)

Refer to Figure 16-3.Which of the graphs shown would be consistent with a firm in a monopolistically competitive market that is doing its best but still losing money
A)panel (a)
B)panel (b)
C)panel (c)
D)panel (d)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
When a firm exits a monopolistically competitive market,what will happen to the individual demand curves faced by all existing firms in that market
A)They will remain unchanged but the quantity of demand will increase.
B)They will shift to the right.
C)They will remain unchanged but the quantity of demand will decrease.
D)They will shift to the left.
A)They will remain unchanged but the quantity of demand will increase.
B)They will shift to the right.
C)They will remain unchanged but the quantity of demand will decrease.
D)They will shift to the left.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Figure 16-2

Refer to Figure 16-2.Which of the graphs would most likely represent a profit-maximizing firm in a monopolistically competitive market
A)panel (a)
B)panel (b)
C)panel (c)
D)panel (d)

Refer to Figure 16-2.Which of the graphs would most likely represent a profit-maximizing firm in a monopolistically competitive market
A)panel (a)
B)panel (b)
C)panel (c)
D)panel (d)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Figure 16-3

Refer to Figure 16-3.Which of the graphs shown would be consistent with a firm in a monopolistically competitive market that is earning a positive profit
A)panel (a)
B)panel (b)
C)panel (c)
D)panel (d)

Refer to Figure 16-3.Which of the graphs shown would be consistent with a firm in a monopolistically competitive market that is earning a positive profit
A)panel (a)
B)panel (b)
C)panel (c)
D)panel (d)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
To maximize its profit,a monopolistically competitive firm chooses its level of output by looking for which of the following
A)the intersection of the demand curve and the marginal-cost curve
B)the intersection of the marginal-revenue curve and the marginal-cost curve
C)the level of output at which marginal revenue equals zero
D)the level of output at which average total cost is minimized
A)the intersection of the demand curve and the marginal-cost curve
B)the intersection of the marginal-revenue curve and the marginal-cost curve
C)the level of output at which marginal revenue equals zero
D)the level of output at which average total cost is minimized

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
When a profit-maximizing firm in a monopolistically competitive market is producing the long-run equilibrium quantity,what is the result
A)Its average revenue will equal its marginal cost.
B)Its marginal revenue will be tangent to its marginal cost.
C)It will be earning positive economic profits.
D)Its demand curve will be tangent to its average-total-cost curve.
A)Its average revenue will equal its marginal cost.
B)Its marginal revenue will be tangent to its marginal cost.
C)It will be earning positive economic profits.
D)Its demand curve will be tangent to its average-total-cost curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Which statement defines business-stealing externality
A)It is the positive externality associated with the gains of consumer surplus in a monopolistically competitive market.
B)It occurs when one firm attempts to exactly duplicate exactly the product of another firm.
C)It is considered to be an explicit cost of business in monopolistically competitive markets.
D)It is the negative externality associated with entry of new firms in a monopolistically competitive market.
A)It is the positive externality associated with the gains of consumer surplus in a monopolistically competitive market.
B)It occurs when one firm attempts to exactly duplicate exactly the product of another firm.
C)It is considered to be an explicit cost of business in monopolistically competitive markets.
D)It is the negative externality associated with entry of new firms in a monopolistically competitive market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Why is a profit-maximizing firm in a monopolistically competitive market eager for another customer
A)to maintain the equality between price and marginal cost
B)to markup where price exceeds marginal cost?c to continue to operate at the efficient scale?d.to earn zero economic profits in the long run
A)to maintain the equality between price and marginal cost
B)to markup where price exceeds marginal cost?c to continue to operate at the efficient scale?d.to earn zero economic profits in the long run

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
For profit-maximizing firms in a monopolistically competitive market,what results from gaining another customer
A)no change in profit
B)more profit
C)potential economic losses
D)marginal cost potentially in excess of price
A)no change in profit
B)more profit
C)potential economic losses
D)marginal cost potentially in excess of price

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
In the long run,a profit-maximizing firm in a monopolistically competitive market operates at which of the following
A)a level of output at which marginal revenue is rising
B)a level of output at which marginal cost is falling
C)a level of output at which average total cost is falling
D)a level of output at which average total cost is rising
A)a level of output at which marginal revenue is rising
B)a level of output at which marginal cost is falling
C)a level of output at which average total cost is falling
D)a level of output at which average total cost is rising

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
In a situation of long-run equilibrium,which statement explains the differences between a perfectly competitive firm and a monopolistically competitive firm
A)A perfectly competitive firm operates at excess capacity.
B)A monopolistically competitive firm does not operate at its efficient scale.
C)A competitive firm charges a markup over marginal cost.
D)A perfectly competitive firm operates at an inefficient scale.
A)A perfectly competitive firm operates at excess capacity.
B)A monopolistically competitive firm does not operate at its efficient scale.
C)A competitive firm charges a markup over marginal cost.
D)A perfectly competitive firm operates at an inefficient scale.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Why is excess capacity undesirable
A)It reduces product differentiation in a market.
B)It is the primary source of market inefficiency in monopolistically competitive markets.
C)It is a characteristic of rising average-total-cost curves.
D)It illustrates the unlimited market power of a monopolist in the market.
A)It reduces product differentiation in a market.
B)It is the primary source of market inefficiency in monopolistically competitive markets.
C)It is a characteristic of rising average-total-cost curves.
D)It illustrates the unlimited market power of a monopolist in the market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
When the loss from a business-stealing externality exceeds the gain from a product-variety externality,what do we expect will happen
A)Firms are more likely to operate at efficient scale.
B)There are likely to be too many firms in a monopolistically competitive market.
C)Market efficiency is likely to be enhanced by the entry of new firms.
D)The market structure is likely to be in transition.
A)Firms are more likely to operate at efficient scale.
B)There are likely to be too many firms in a monopolistically competitive market.
C)Market efficiency is likely to be enhanced by the entry of new firms.
D)The market structure is likely to be in transition.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
In the long run,what do we know about the scale at which a perfectly competitive firm operates,compared to a monopolistically competitive firm
A)A perfectly competitive firm and a monopolistically competitive firm both operate at the efficient scale.
B)A perfectly competitive firm operates at an efficient scale and a monopolistically competitive firm operates with excess capacity.
C)A perfectly competitive firm and a monopolistically competitive firm both operate with excess capacity.
D)A perfectly competitive firm operates with excess capacity and a monopolistically competitive firm operates at the efficient scale.
A)A perfectly competitive firm and a monopolistically competitive firm both operate at the efficient scale.
B)A perfectly competitive firm operates at an efficient scale and a monopolistically competitive firm operates with excess capacity.
C)A perfectly competitive firm and a monopolistically competitive firm both operate with excess capacity.
D)A perfectly competitive firm operates with excess capacity and a monopolistically competitive firm operates at the efficient scale.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
On an average night,80 percent of hotel rooms are occupied in large Canadian cities.What type of market is this kind of excess capacity indicative
A)monopoly
B)perfect competition
C)monopolistic competition
D)oligopoly
A)monopoly
B)perfect competition
C)monopolistic competition
D)oligopoly

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Firm A is a perfectly competitive firm.Firm B is a monopolistically competitive firm.Both firms are currently maximizing their respective profits.Which of the statement best explains the differences between the two firms' sales strategies
A)Firm A will set the price for its products and Firm B will not set the price.
B)Firm A will not set the price for its products and Firm B will set the price.
C)Firm B would be eager to make an additional sale, but Firm A would not care whether it made an additional sale or not.
D)Firm A would be eager to make an additional sale, but Firm B would not care whether it made an additional sale or not.
A)Firm A will set the price for its products and Firm B will not set the price.
B)Firm A will not set the price for its products and Firm B will set the price.
C)Firm B would be eager to make an additional sale, but Firm A would not care whether it made an additional sale or not.
D)Firm A would be eager to make an additional sale, but Firm B would not care whether it made an additional sale or not.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The phenomenon of product differentiation contrasts sharply with which of the following
A)homogeneous products
B)monopolistic competition
C)product integration
D)non-price competition
A)homogeneous products
B)monopolistic competition
C)product integration
D)non-price competition

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
When incumbent firms lose customers and profits due to entry of a new competitor,what type of externality occurs
A)a predatory pricing externality
B)a production externality
C)a business-stealing externality
D)a product-variety externality
A)a predatory pricing externality
B)a production externality
C)a business-stealing externality
D)a product-variety externality

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
What type of externalities accompany the entry of new firms into a monopolistically competitive market
A)the product-variety externality as a positive externality and the business-stealing externality as a negative externality
B)the product-variety externality as a negative externality and the business-stealing externality as a positive externality
C)the business-variety externality as a positive externality and the product-stealing externality as a negative externality
D)the business-variety externality as a negative externality and the product-stealing externality as a positive externality
A)the product-variety externality as a positive externality and the business-stealing externality as a negative externality
B)the product-variety externality as a negative externality and the business-stealing externality as a positive externality
C)the business-variety externality as a positive externality and the product-stealing externality as a negative externality
D)the business-variety externality as a negative externality and the product-stealing externality as a positive externality

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
When a firm operates at the efficient scale,what explains the characteristic of the average-total-cost-curve
A)Its average revenue must be less than the minimum of average total cost.
B)Its average revenue must be equal to the minimum of average total cost.
C)The average-total-cost curve must be falling.
D)The average-total-cost curve must be rising.
A)Its average revenue must be less than the minimum of average total cost.
B)Its average revenue must be equal to the minimum of average total cost.
C)The average-total-cost curve must be falling.
D)The average-total-cost curve must be rising.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
In the long run,a monopolistically competitive firm produces a quantity that is which of the following
A)equal to the efficient scale
B)less than the efficient scale
C)greater than the efficient scale
D)consistent with diseconomies of scale
A)equal to the efficient scale
B)less than the efficient scale
C)greater than the efficient scale
D)consistent with diseconomies of scale

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Which statement best explains the relationship between demand and output capacity of a firm in a monopolistically competitive market
A)Because it faces a downward-sloping demand curve, it will generally operate with excess capacity.
B)Because it faces a downward-sloping demand curve, it will generally operate at the efficient scale.
C)Because it faces a perfectly elastic demand curve, it will generally operate with excess capacity.
D)Because it faces a perfectly inelastic demand curve, it will generally operate at the efficient scale.
A)Because it faces a downward-sloping demand curve, it will generally operate with excess capacity.
B)Because it faces a downward-sloping demand curve, it will generally operate at the efficient scale.
C)Because it faces a perfectly elastic demand curve, it will generally operate with excess capacity.
D)Because it faces a perfectly inelastic demand curve, it will generally operate at the efficient scale.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Why could a monopolistically competitive market be considered inefficient
A)because marginal revenue exceeds average revenue
B)because price exceeds marginal cost
C)because efficient scale is realized in the long run, but not in the short run
D)because markup pricing does not occur in any other market structure
A)because marginal revenue exceeds average revenue
B)because price exceeds marginal cost
C)because efficient scale is realized in the long run, but not in the short run
D)because markup pricing does not occur in any other market structure

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Under what circumstances does a firm operate with excess capacity
A)when additional production would lower the average total cost
B)when additional production would increase average total cost
C)only if it is a perfectly competitive firm in the long run
D)only if it is a monopolistically competitive firm in the short run
A)when additional production would lower the average total cost
B)when additional production would increase average total cost
C)only if it is a perfectly competitive firm in the long run
D)only if it is a monopolistically competitive firm in the short run

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Because a monopolistically competitive firm has some market power,in the long-run what does the price of its good exceed
A)its average revenue
B)its average total cost
C)its marginal cost
D)its profit per unit
A)its average revenue
B)its average total cost
C)its marginal cost
D)its profit per unit

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Where does a firm in a monopolistically competitive market operate
A)where marginal revenue is zero
B)where price is equal to marginal cost
C)on the rising portion of its average-total-cost curve
D)on the declining portion of its average-total-cost curve
A)where marginal revenue is zero
B)where price is equal to marginal cost
C)on the rising portion of its average-total-cost curve
D)on the declining portion of its average-total-cost curve

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



