Deck 17: Oligopoly
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/198
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 17: Oligopoly
1
What is one characteristic of an oligopoly market structure
A)Firms in the industry are typically characterized by very diverse product lines.
B)Firms in the industry have some degree of market power.
C)Products typically sell at a price that reflects their marginal cost of production.
D)The actions of one seller have no impact on the profitability of other sellers.
A)Firms in the industry are typically characterized by very diverse product lines.
B)Firms in the industry have some degree of market power.
C)Products typically sell at a price that reflects their marginal cost of production.
D)The actions of one seller have no impact on the profitability of other sellers.
Firms in the industry have some degree of market power.
2
What are markets with only a few sellers,each offering a product similar or identical to the others,typically called
A)competitive markets
B)monopoly markets
C)monopolistically competitive markets
D)oligopoly markets
A)competitive markets
B)monopoly markets
C)monopolistically competitive markets
D)oligopoly markets
oligopoly markets
3
The typical firm in the economy has which characteristic
A)It has some degree of market power.
B)It sells its product for a price that is equal to the marginal cost of producing the last unit.
C)It is perfectly competitive.
D)It is an oligopoly.
A)It has some degree of market power.
B)It sells its product for a price that is equal to the marginal cost of producing the last unit.
C)It is perfectly competitive.
D)It is an oligopoly.
It has some degree of market power.
4
What would oligopolists do regarding their cooperation in the market
A)The oligopolists are best off cooperating and behaving like a monopolist.
B)Collusive agreements will always prevail.
C)Collective profits are always lower with cartel arrangements than they are without cartel arrangements.
D)Pursuit of self-interest by profit-maximizing firms always maximizes collective profits in the market.
A)The oligopolists are best off cooperating and behaving like a monopolist.
B)Collusive agreements will always prevail.
C)Collective profits are always lower with cartel arrangements than they are without cartel arrangements.
D)Pursuit of self-interest by profit-maximizing firms always maximizes collective profits in the market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
What is a special kind of imperfectly competitive market that has only two firms called
A)a monopsony
B)an incidental monopoly
C)a doublet
D)a duopoly
A)a monopsony
B)an incidental monopoly
C)a doublet
D)a duopoly

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
What is the basic characteristic of a market that is characterized by imperfect competition
A)Firms are price takers.
B)There are generally a large number of firms.
C)There are at least a few firms that compete with one another.
D)The actions of one firm in the market have no impact on the other firms' profits.
A)Firms are price takers.
B)There are generally a large number of firms.
C)There are at least a few firms that compete with one another.
D)The actions of one firm in the market have no impact on the other firms' profits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
What are the two types of imperfectly competitive markets
A)monopoly and monopolistic competition
B)monopoly and oligopoly
C)monopolistic competition and oligopoly
D)monopolistic competition and cartels
A)monopoly and monopolistic competition
B)monopoly and oligopoly
C)monopolistic competition and oligopoly
D)monopolistic competition and cartels

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
What is one key difference between an oligopoly market and a competitive market
A)Oligopolistic firms are price takers while competitive firms are not.
B)Oligopolistic firms are interdependent while competitive firms are not.
C)Oligopolistic firms sell completely unrelated products while competitive firms do not.
D)Oligopolistic firms sell their product at a price equal to marginal cost while competitive firms do not.
A)Oligopolistic firms are price takers while competitive firms are not.
B)Oligopolistic firms are interdependent while competitive firms are not.
C)Oligopolistic firms sell completely unrelated products while competitive firms do not.
D)Oligopolistic firms sell their product at a price equal to marginal cost while competitive firms do not.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Firms in industries that have competitors but,at the same time,do not face so much competition that they are price takers,are operating in either of which types of markets
A)oligopoly or perfectly competitive market
B)oligopoly or monopoly market
C)oligopoly or monopolistically competitive market
D)monopoly or monopolistically competitive market
A)oligopoly or perfectly competitive market
B)oligopoly or monopoly market
C)oligopoly or monopolistically competitive market
D)monopoly or monopolistically competitive market

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
When an industry has many firms,the industry may be which of the following
A)It is an oligopoly if the firms sell differentiated products; it is monopolistically competitive if the firms sell identical products.
B)It is an oligopoly if the firms sell differentiated products; it is perfectly competitive if the firms sell identical products.
C)It is monopolistically competitive if the firms sell differentiated products; it is perfectly competitive if the firms sell identical products.
D)It is perfectly competitive if the firms sell differentiated products; it is monopolistically competitive if the firms sell identical products.
A)It is an oligopoly if the firms sell differentiated products; it is monopolistically competitive if the firms sell identical products.
B)It is an oligopoly if the firms sell differentiated products; it is perfectly competitive if the firms sell identical products.
C)It is monopolistically competitive if the firms sell differentiated products; it is perfectly competitive if the firms sell identical products.
D)It is perfectly competitive if the firms sell differentiated products; it is monopolistically competitive if the firms sell identical products.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which characterization typically applies to monopolistically competitive firms
A)many firms selling products that are similar, but not identical
B)many firms selling identical products
C)a few firms selling products that are similar, but not identical
D)a few firms selling highly different products
A)many firms selling products that are similar, but not identical
B)many firms selling identical products
C)a few firms selling products that are similar, but not identical
D)a few firms selling highly different products

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
What are typical firms in our economy classified as
A)perfectly competitive firms
B)imperfectly competitive firms
C)oligopolists
D)free trade firms
A)perfectly competitive firms
B)imperfectly competitive firms
C)oligopolists
D)free trade firms

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Noncooperative outcomes typically imply what kind of outcome
A)one that is better for both parties to the "game"
B)one that is worse for both parties to the "game"
C)one in which society is generally worse off
D)one in which society is generally better off
A)one that is better for both parties to the "game"
B)one that is worse for both parties to the "game"
C)one in which society is generally worse off
D)one in which society is generally better off

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
What is the role that the Competition Act plays in our market economy
A)It was passed to encourage judicial leniency in the review of cooperative agreements.
B)It was concerned with self-interest-dominated Nash equilibriums in prisoners' dilemma games.
C)It enhanced the ability to enforce cartel agreements.
D)It restricted the ability of competitors to engage in cooperative agreements.
A)It was passed to encourage judicial leniency in the review of cooperative agreements.
B)It was concerned with self-interest-dominated Nash equilibriums in prisoners' dilemma games.
C)It enhanced the ability to enforce cartel agreements.
D)It restricted the ability of competitors to engage in cooperative agreements.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
In which way would a group of oligopolists generally be better off acting collectively
A)as if they were each seeking to maximize their own individual profits
B)in a manner that would prohibit collusive agreements
C)as a single monopolist
D)as a single perfectly competitive firm
A)as if they were each seeking to maximize their own individual profits
B)in a manner that would prohibit collusive agreements
C)as a single monopolist
D)as a single perfectly competitive firm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Given that there are approximately 12 companies currently selling cars in Canada,what is the car market classified as
A)perfectly competitive
B)monopolistically competitive
C)oligopolistic
D)monopoly
A)perfectly competitive
B)monopolistically competitive
C)oligopolistic
D)monopoly

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
If there are many firms participating in a market,what could the market be
A)either an oligopoly or monopolistically competitive
B)either perfectly competitive or monopolistically competitive
C)either an oligopoly or perfectly competitive
D)either an oligopoly or monopoly
A)either an oligopoly or monopolistically competitive
B)either perfectly competitive or monopolistically competitive
C)either an oligopoly or perfectly competitive
D)either an oligopoly or monopoly

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
What is an oligopoly
A)a market in which there are only a few sellers, each offering a product similar or identical to the others
B)a market in which firms are price takers and do not advertise
C)a market in which firms are price takers and advertise
D)a market in which the actions of one seller in the market have no impact on the other sellers' profits
A)a market in which there are only a few sellers, each offering a product similar or identical to the others
B)a market in which firms are price takers and do not advertise
C)a market in which firms are price takers and advertise
D)a market in which the actions of one seller in the market have no impact on the other sellers' profits

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
In which market is economic profit driven to zero in the long run
A)oligopoly
B)monopoly
C)monopolistically competitive market
D)duopoly
A)oligopoly
B)monopoly
C)monopolistically competitive market
D)duopoly

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
What is the general term for market structures that fall somewhere in between monopoly and perfect competition
A)mid-markets
B)imperfectly competitive markets
C)oligopoly markets
D)monopolistically competitive markets
A)mid-markets
B)imperfectly competitive markets
C)oligopoly markets
D)monopolistically competitive markets

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Table 17-2
The information in the table depicts the total demand for wireless Internet subscriptions in a small urban market. Assume that each wireless Internet operator pays a fixed cost of $100,000 (per year) to provide wireless Internet in the market area and that the marginal cost of providing the wireless Internet service to a household is zero.
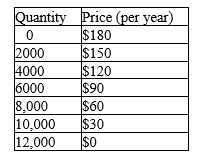
Refer to Table 17-2.Assume that there are two profit-maximizing wireless Internet companies operating in this market.Further assume that they are not able to "collude" on price and quantity of wireless Internet subscriptions to sell.How many wireless Internet subscriptions will be collectively sold (by both firms) when this market reaches a Nash equilibrium
A)2000
B)4000
C)6000
D)58000
The information in the table depicts the total demand for wireless Internet subscriptions in a small urban market. Assume that each wireless Internet operator pays a fixed cost of $100,000 (per year) to provide wireless Internet in the market area and that the marginal cost of providing the wireless Internet service to a household is zero.

Refer to Table 17-2.Assume that there are two profit-maximizing wireless Internet companies operating in this market.Further assume that they are not able to "collude" on price and quantity of wireless Internet subscriptions to sell.How many wireless Internet subscriptions will be collectively sold (by both firms) when this market reaches a Nash equilibrium
A)2000
B)4000
C)6000
D)58000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
In what type of market do the actions of any one seller have a significant impact on the profits of all other sellers
A)a monopoly market
B)a perfectly competitive market
C)a monopolistically competitive market
D)an oligopoly
A)a monopoly market
B)a perfectly competitive market
C)a monopolistically competitive market
D)an oligopoly

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Table 17-1
Imagine a small town in which only two residents, Matthew and Anna, own wells that produce water for safe drinking. Each Saturday, Matthew and Anna work together to decide how many litres of water to pump, bring the water to town, and sell it at whatever price the market will bear. To keep things simple, suppose that Matthew and Anna can pump as much water as they want without cost; therefore, the marginal cost of water equals zero.
The weekly town demand schedule and total revenue schedule for water is reflected in the table.
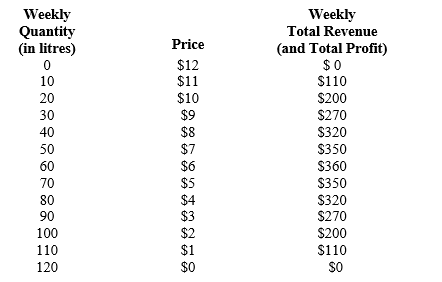
Refer to Table 17-1.Since Matthew and Anna operate as a profit-maximizing monopoly in the market for water,what price will they charge to sell 80 litres of water
A)$2
B)$4
C)$6
D)$7
Imagine a small town in which only two residents, Matthew and Anna, own wells that produce water for safe drinking. Each Saturday, Matthew and Anna work together to decide how many litres of water to pump, bring the water to town, and sell it at whatever price the market will bear. To keep things simple, suppose that Matthew and Anna can pump as much water as they want without cost; therefore, the marginal cost of water equals zero.
The weekly town demand schedule and total revenue schedule for water is reflected in the table.
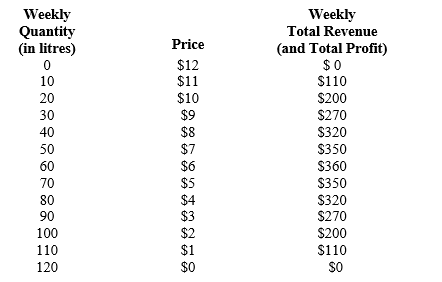
Refer to Table 17-1.Since Matthew and Anna operate as a profit-maximizing monopoly in the market for water,what price will they charge to sell 80 litres of water
A)$2
B)$4
C)$6
D)$7

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Table 17-2
The information in the table depicts the total demand for wireless Internet subscriptions in a small urban market. Assume that each wireless Internet operator pays a fixed cost of $100,000 (per year) to provide wireless Internet in the market area and that the marginal cost of providing the wireless Internet service to a household is zero.

Refer to Table 17-2.If there is only one wireless internet company in this market,what price would it charge for a wireless Internet subscription to maximize its profit
A)$60
B)$90
C)$120
D)$150
The information in the table depicts the total demand for wireless Internet subscriptions in a small urban market. Assume that each wireless Internet operator pays a fixed cost of $100,000 (per year) to provide wireless Internet in the market area and that the marginal cost of providing the wireless Internet service to a household is zero.

Refer to Table 17-2.If there is only one wireless internet company in this market,what price would it charge for a wireless Internet subscription to maximize its profit
A)$60
B)$90
C)$120
D)$150

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
There are two types of markets in which firms face some competition yet are still able to have some control over the prices of their products.What are the names given to these market structures
A)monopolistic competition and oligopoly
B)duopoly and triopoly
C)perfect competition and monopolistic competition
D)duopoly and perfect competition
A)monopolistic competition and oligopoly
B)duopoly and triopoly
C)perfect competition and monopolistic competition
D)duopoly and perfect competition

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Once a cartel is formed,what structure in effect serves the market
A)a monopoly
B)an oligopoly
C)imperfect competition
D)monopolistic competition
A)a monopoly
B)an oligopoly
C)imperfect competition
D)monopolistic competition

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
If duopolists individually pursue their own self-interest when deciding how much to produce,how will the amount they produce collectively compare with the monopoly quantity
A)It will be less than the monopoly quantity.
B)It will be equal to the monopoly quantity.
C)It will be greater than the monopoly quantity.
D)It will be unrelated to the monopoly quantity.
A)It will be less than the monopoly quantity.
B)It will be equal to the monopoly quantity.
C)It will be greater than the monopoly quantity.
D)It will be unrelated to the monopoly quantity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Table 17-1
Imagine a small town in which only two residents, Matthew and Anna, own wells that produce water for safe drinking. Each Saturday, Matthew and Anna work together to decide how many litres of water to pump, bring the water to town, and sell it at whatever price the market will bear. To keep things simple, suppose that Matthew and Anna can pump as much water as they want without cost; therefore, the marginal cost of water equals zero.
The weekly town demand schedule and total revenue schedule for water is reflected in the table.
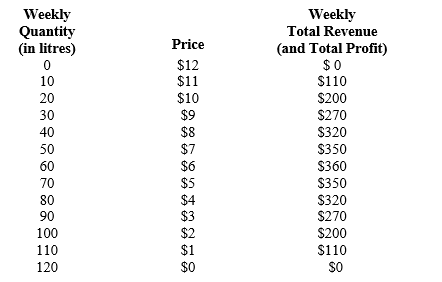
Refer to Table 17-1.What would be the socially efficient level of water supplied to the market
A)40 litres
B)60 litres
C)80 litres
D)120 litres
Imagine a small town in which only two residents, Matthew and Anna, own wells that produce water for safe drinking. Each Saturday, Matthew and Anna work together to decide how many litres of water to pump, bring the water to town, and sell it at whatever price the market will bear. To keep things simple, suppose that Matthew and Anna can pump as much water as they want without cost; therefore, the marginal cost of water equals zero.
The weekly town demand schedule and total revenue schedule for water is reflected in the table.
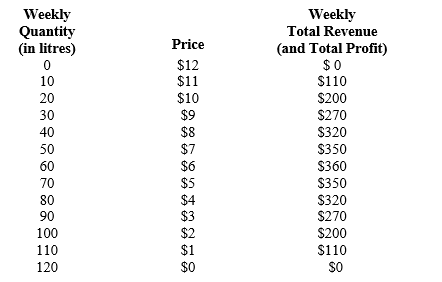
Refer to Table 17-1.What would be the socially efficient level of water supplied to the market
A)40 litres
B)60 litres
C)80 litres
D)120 litres

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Because each oligopolist cares about its own profit rather than the collective profit of all the oligopolists,what is the result
A)They have incentives to cheat.
B)Each firm's profit ends up being zero.
C)Society is worse off.
D)Collusion is necessary.
A)They have incentives to cheat.
B)Each firm's profit ends up being zero.
C)Society is worse off.
D)Collusion is necessary.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Table 17-1
Imagine a small town in which only two residents, Matthew and Anna, own wells that produce water for safe drinking. Each Saturday, Matthew and Anna work together to decide how many litres of water to pump, bring the water to town, and sell it at whatever price the market will bear. To keep things simple, suppose that Matthew and Anna can pump as much water as they want without cost; therefore, the marginal cost of water equals zero.
The weekly town demand schedule and total revenue schedule for water is reflected in the table.
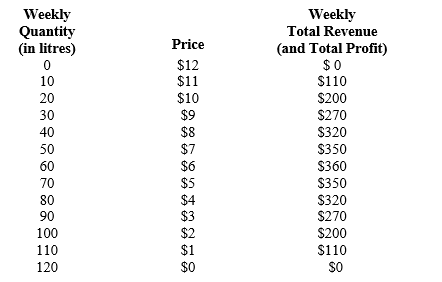
Refer to Table 17-1.If the market for water was perfectly competitive instead of monopolistic,how many litres of water would be produced and sold
A)70
B)80
C)90
D)120
Imagine a small town in which only two residents, Matthew and Anna, own wells that produce water for safe drinking. Each Saturday, Matthew and Anna work together to decide how many litres of water to pump, bring the water to town, and sell it at whatever price the market will bear. To keep things simple, suppose that Matthew and Anna can pump as much water as they want without cost; therefore, the marginal cost of water equals zero.
The weekly town demand schedule and total revenue schedule for water is reflected in the table.
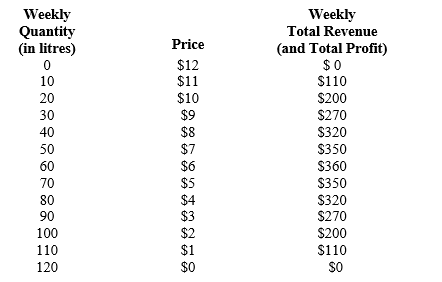
Refer to Table 17-1.If the market for water was perfectly competitive instead of monopolistic,how many litres of water would be produced and sold
A)70
B)80
C)90
D)120

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
If duopolists individually pursue their own self-interest when deciding how much to produce,what do we know about the price they are able to charge for their product
A)It will be less than the monopoly price.
B)It will be equal to the monopoly price.
C)It will be less than the perfectly competitive market price.
D)It will be equal to the perfectly competitive market price.
A)It will be less than the monopoly price.
B)It will be equal to the monopoly price.
C)It will be less than the perfectly competitive market price.
D)It will be equal to the perfectly competitive market price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Table 17-1
Imagine a small town in which only two residents, Matthew and Anna, own wells that produce water for safe drinking. Each Saturday, Matthew and Anna work together to decide how many litres of water to pump, bring the water to town, and sell it at whatever price the market will bear. To keep things simple, suppose that Matthew and Anna can pump as much water as they want without cost; therefore, the marginal cost of water equals zero.
The weekly town demand schedule and total revenue schedule for water is reflected in the table.
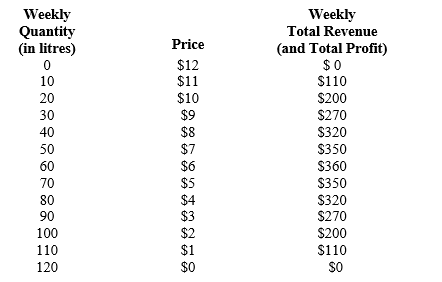
Refer to Table 17-1.Suppose the town enacts new competition laws that prohibit Matthew and Anna from operating as a monopolist.What will the new price of water end up being once the Nash equilibrium is reached
A)$3
B)$4
C)$5
D)$6
Imagine a small town in which only two residents, Matthew and Anna, own wells that produce water for safe drinking. Each Saturday, Matthew and Anna work together to decide how many litres of water to pump, bring the water to town, and sell it at whatever price the market will bear. To keep things simple, suppose that Matthew and Anna can pump as much water as they want without cost; therefore, the marginal cost of water equals zero.
The weekly town demand schedule and total revenue schedule for water is reflected in the table.
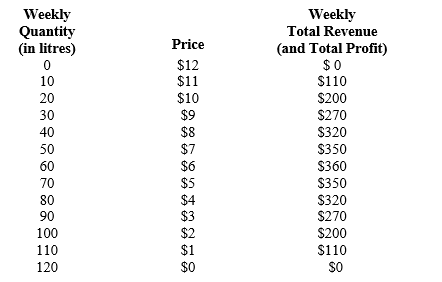
Refer to Table 17-1.Suppose the town enacts new competition laws that prohibit Matthew and Anna from operating as a monopolist.What will the new price of water end up being once the Nash equilibrium is reached
A)$3
B)$4
C)$5
D)$6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Table 17-2
The information in the table depicts the total demand for wireless Internet subscriptions in a small urban market. Assume that each wireless Internet operator pays a fixed cost of $100,000 (per year) to provide wireless Internet in the market area and that the marginal cost of providing the wireless Internet service to a household is zero.

Refer to Table 17-2.Assume that there are two profit-maximizing wireless Internet companies operating in this market.Further assume that they are not able to "collude" on price and quantity of wireless Internet subscriptions to sell.How much profit will each firm earn when this market reaches a Nash equilibrium
A)$0
B)$140,000
C)$170,000
D)$220,000
The information in the table depicts the total demand for wireless Internet subscriptions in a small urban market. Assume that each wireless Internet operator pays a fixed cost of $100,000 (per year) to provide wireless Internet in the market area and that the marginal cost of providing the wireless Internet service to a household is zero.

Refer to Table 17-2.Assume that there are two profit-maximizing wireless Internet companies operating in this market.Further assume that they are not able to "collude" on price and quantity of wireless Internet subscriptions to sell.How much profit will each firm earn when this market reaches a Nash equilibrium
A)$0
B)$140,000
C)$170,000
D)$220,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
How does the Competition Act prohibit price-fixing
A)Competing executives cannot even talk about fixing prices.
B)Competing executives can talk about fixing prices, but they cannot take action to fix prices.
C)A price-fixing agreement can lead to prosecution provided the government can show that the public was not well-served by the agreement.
D)Activities such as bid rigging price discrimination and predatory pricing are all subject to prosecution but resale price maintenance is allowed.
A)Competing executives cannot even talk about fixing prices.
B)Competing executives can talk about fixing prices, but they cannot take action to fix prices.
C)A price-fixing agreement can lead to prosecution provided the government can show that the public was not well-served by the agreement.
D)Activities such as bid rigging price discrimination and predatory pricing are all subject to prosecution but resale price maintenance is allowed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Table 17-2
The information in the table depicts the total demand for wireless Internet subscriptions in a small urban market. Assume that each wireless Internet operator pays a fixed cost of $100,000 (per year) to provide wireless Internet in the market area and that the marginal cost of providing the wireless Internet service to a household is zero.

Refer to Table 17-2.Assume that there are two wireless Internet companies operating in this market.If they are able to "collude" on price and quantity of subscriptions to sell,what price (P) will they charge,and what quantity (Q) of subscriptions will they collectively sell
A)P = $60, Q = 8000
B)P = $90, Q = 6000
C)P = $120, Q = 4000
D)P = $150, Q = 2000
The information in the table depicts the total demand for wireless Internet subscriptions in a small urban market. Assume that each wireless Internet operator pays a fixed cost of $100,000 (per year) to provide wireless Internet in the market area and that the marginal cost of providing the wireless Internet service to a household is zero.

Refer to Table 17-2.Assume that there are two wireless Internet companies operating in this market.If they are able to "collude" on price and quantity of subscriptions to sell,what price (P) will they charge,and what quantity (Q) of subscriptions will they collectively sell
A)P = $60, Q = 8000
B)P = $90, Q = 6000
C)P = $120, Q = 4000
D)P = $150, Q = 2000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Table 17-2
The information in the table depicts the total demand for wireless Internet subscriptions in a small urban market. Assume that each wireless Internet operator pays a fixed cost of $100,000 (per year) to provide wireless Internet in the market area and that the marginal cost of providing the wireless Internet service to a household is zero.

Refer to Table 17-2.Assume that there are two profit-maximizing wireless Internet companies operating in this market.Further assume that they are not able to "collude" on price and quantity of wireless Internet subscriptions to sell.What price will wireless Internet subscriptions be sold at when this market reaches a Nash equilibrium
A)$60
B)$90
C)$120
D)$150
The information in the table depicts the total demand for wireless Internet subscriptions in a small urban market. Assume that each wireless Internet operator pays a fixed cost of $100,000 (per year) to provide wireless Internet in the market area and that the marginal cost of providing the wireless Internet service to a household is zero.

Refer to Table 17-2.Assume that there are two profit-maximizing wireless Internet companies operating in this market.Further assume that they are not able to "collude" on price and quantity of wireless Internet subscriptions to sell.What price will wireless Internet subscriptions be sold at when this market reaches a Nash equilibrium
A)$60
B)$90
C)$120
D)$150

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Table 17-1
Imagine a small town in which only two residents, Matthew and Anna, own wells that produce water for safe drinking. Each Saturday, Matthew and Anna work together to decide how many litres of water to pump, bring the water to town, and sell it at whatever price the market will bear. To keep things simple, suppose that Matthew and Anna can pump as much water as they want without cost; therefore, the marginal cost of water equals zero.
The weekly town demand schedule and total revenue schedule for water is reflected in the table.
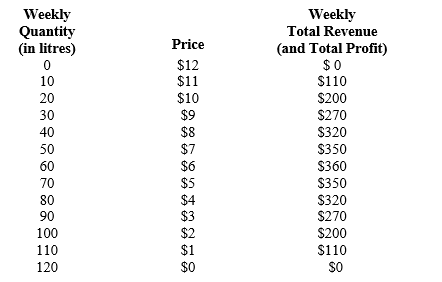
Refer to Table 17-1.As long as Matthew and Anna operate as a profit-maximizing monopoly,what will their weekly revenue equal
A)$200
B)$270
C)$320
D)$360
Imagine a small town in which only two residents, Matthew and Anna, own wells that produce water for safe drinking. Each Saturday, Matthew and Anna work together to decide how many litres of water to pump, bring the water to town, and sell it at whatever price the market will bear. To keep things simple, suppose that Matthew and Anna can pump as much water as they want without cost; therefore, the marginal cost of water equals zero.
The weekly town demand schedule and total revenue schedule for water is reflected in the table.
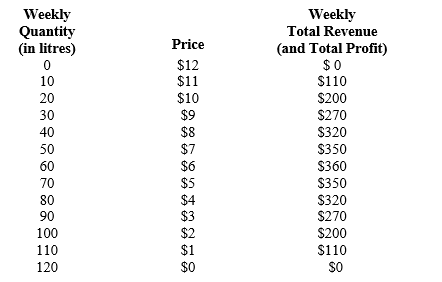
Refer to Table 17-1.As long as Matthew and Anna operate as a profit-maximizing monopoly,what will their weekly revenue equal
A)$200
B)$270
C)$320
D)$360

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Assuming that oligopolists do not have the opportunity to collude,once they have reached the Nash equilibrium,what actions will they take next
A)It is generally in their best interest to raise the price of the product.
B)It is generally in their best interest to supply less to the market.
C)It is generally in their best interest to leave their quantities supplied unchanged.
D)It is generally in their best interest to lower the price of the product.
A)It is generally in their best interest to raise the price of the product.
B)It is generally in their best interest to supply less to the market.
C)It is generally in their best interest to leave their quantities supplied unchanged.
D)It is generally in their best interest to lower the price of the product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
As a group,how would oligopolists generally be better off
A)if they would produce the perfectly competitive quantity of output
B)if they would produce more than the perfectly competitive quantity of output
C)if they would charge the same price that a monopolist would charge if the market were a monopoly
D)if they would operate according to their own individual self-interests
A)if they would produce the perfectly competitive quantity of output
B)if they would produce more than the perfectly competitive quantity of output
C)if they would charge the same price that a monopolist would charge if the market were a monopoly
D)if they would operate according to their own individual self-interests

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Table 17-2
The information in the table depicts the total demand for wireless Internet subscriptions in a small urban market. Assume that each wireless Internet operator pays a fixed cost of $100,000 (per year) to provide wireless Internet in the market area and that the marginal cost of providing the wireless Internet service to a household is zero.

Refer to Table 17-2.Assume that there are two profit-maximizing wireless Internet companies operating in this market.Further assume that they are able to "collude" on price and quantity of wireless Internet subscriptions to sell.As part of their collusive agreement they decide to take an equal share of the market.How much profit will each company make
A)$40,000
B)$170,000
C)$210,000
D)$380,000
The information in the table depicts the total demand for wireless Internet subscriptions in a small urban market. Assume that each wireless Internet operator pays a fixed cost of $100,000 (per year) to provide wireless Internet in the market area and that the marginal cost of providing the wireless Internet service to a household is zero.

Refer to Table 17-2.Assume that there are two profit-maximizing wireless Internet companies operating in this market.Further assume that they are able to "collude" on price and quantity of wireless Internet subscriptions to sell.As part of their collusive agreement they decide to take an equal share of the market.How much profit will each company make
A)$40,000
B)$170,000
C)$210,000
D)$380,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
As the number of firms in a cartel increases,what happens
A)The monopoly outcome becomes more likely.
B)The magnitude of the price effect increases.
C)Each seller becomes more concerned about its own impact on the market price.
D)The monopoly outcome becomes less likely.
A)The monopoly outcome becomes more likely.
B)The magnitude of the price effect increases.
C)Each seller becomes more concerned about its own impact on the market price.
D)The monopoly outcome becomes less likely.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Suppose a perfectly competitive market is taken over by three or four firms.What result would we expect regarding market output and the price of the product
A)an increase in market output and an increase in the price of the product
B)an increase in market output and an decrease in the price of the product
C)a decrease in market output and an increase in the price of the product
D)a decrease in market output and a decrease in the price of the product
A)an increase in market output and an increase in the price of the product
B)an increase in market output and an decrease in the price of the product
C)a decrease in market output and an increase in the price of the product
D)a decrease in market output and a decrease in the price of the product

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Oligopolists are aware that increases in the quantity of output they produce will do which of the following
A)reduce the price of their product, and in this respect they are like monopolists
B)reduce the price of their product, and in this respect they are like competitive firms
C)increase the price of their product, and in this respect they are like monopolists
D)increase the price of their product, and in this respect they are like competitive firms
A)reduce the price of their product, and in this respect they are like monopolists
B)reduce the price of their product, and in this respect they are like competitive firms
C)increase the price of their product, and in this respect they are like monopolists
D)increase the price of their product, and in this respect they are like competitive firms

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The concept of a Nash equilibrium,when applied to an oligopoly,relies on the notion that Firm A in an oligopoly chooses its own best strategy based on which consideration
A)based on the strategies that other firms have chosen
B)based on the knowledge that other firms are likely to choose their strategies in response to Firm A's choice of a strategy
C)based on the objective of maximizing the collective profits of all firms in the industry
D)based on the internal financial information of Firm A
A)based on the strategies that other firms have chosen
B)based on the knowledge that other firms are likely to choose their strategies in response to Firm A's choice of a strategy
C)based on the objective of maximizing the collective profits of all firms in the industry
D)based on the internal financial information of Firm A

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Like monopolists,what do oligopolists know about the result of an increase in the quantity of output
A)It reduces the price of their product.
B)It reduces their profit.
C)It reduces their revenue.
D)It reduces productivity.
A)It reduces the price of their product.
B)It reduces their profit.
C)It reduces their revenue.
D)It reduces productivity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
As the number of firms in an oligopoly market grows larger,what will the price approach
A)marginal cost
B)average variable cost
C)zero
D)the monopoly price
A)marginal cost
B)average variable cost
C)zero
D)the monopoly price

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
In a particular town,Xpressdata and Blazedata are the only two providers of wireless Internet service.What do Xpressdata and Blazedata constitute
A)a duopoly, whether they collude or not
B)a cartel, whether they collude or not
C)a Nash industry, whether they collude or not
D)a monopolistically competitive industry, whether they collude or not
A)a duopoly, whether they collude or not
B)a cartel, whether they collude or not
C)a Nash industry, whether they collude or not
D)a monopolistically competitive industry, whether they collude or not

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Which of these situations produces the largest profits for oligopolists
A)They reach a Nash equilibrium.
B)They reach the monopoly outcome.
C)They reach the competitive outcome.
D)They produce a quantity of output that lies between the competitive outcome and the monopoly outcome.
A)They reach a Nash equilibrium.
B)They reach the monopoly outcome.
C)They reach the competitive outcome.
D)They produce a quantity of output that lies between the competitive outcome and the monopoly outcome.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
What,essentially,is an oligopoly if it has a large number of firms
A)a large monopolist
B)a large monopolistically competitive market
C)a group of competitive firms
D)a group of monopolistic firms
A)a large monopolist
B)a large monopolistically competitive market
C)a group of competitive firms
D)a group of monopolistic firms

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
What will happen when an oligopoly market reaches a Nash equilibrium
A)The market price will be different for each firm.
B)Firms will not behave as profit maximizers.
C)A firm will choose its best pricing strategy, given the strategies that it observes other firms taking.
D)A firm will not take into account the strategies of competing firms.
A)The market price will be different for each firm.
B)Firms will not behave as profit maximizers.
C)A firm will choose its best pricing strategy, given the strategies that it observes other firms taking.
D)A firm will not take into account the strategies of competing firms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
What is a situation called in which economic actors.interacting with one another,each choose their best strategy,given the strategies the others have chosen
A)a cartel
B)an open market solution
C)a socially optimal solution
D)a Nash equilibrium
A)a cartel
B)an open market solution
C)a socially optimal solution
D)a Nash equilibrium

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
In order to be successful,what must a cartel do
A)They must find a way to encourage their members to produce more than they would otherwise produce.
B)They must agree on the total level of production for the cartel, but they need not agree on the amount produced by each member.
C)They must agree on the total level of production and on the amount produced by each member.
D)They must agree on the prices charged by each member, but they need not agree on amounts produced.
A)They must find a way to encourage their members to produce more than they would otherwise produce.
B)They must agree on the total level of production for the cartel, but they need not agree on the amount produced by each member.
C)They must agree on the total level of production and on the amount produced by each member.
D)They must agree on the prices charged by each member, but they need not agree on amounts produced.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
For a duopoly,what is the result of the logic of self-interest
A)The total output level equals the output level that would prevail in a competitive market.
B)The total output level equals the output level that would prevail in a monopoly.
C)The total output level exceeds the monopoly level, but falls short of the competitive level.
D)The total output level falls short of the monopoly level.
A)The total output level equals the output level that would prevail in a competitive market.
B)The total output level equals the output level that would prevail in a monopoly.
C)The total output level exceeds the monopoly level, but falls short of the competitive level.
D)The total output level falls short of the monopoly level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
When firms have agreements among themselves on the quantity to produce and the price at which to sell output,what is their form of organization called
A)a Nash arrangement
B)a cartel
C)a monopolistically competitive oligopoly
D)a perfectly competitive oligopoly
A)a Nash arrangement
B)a cartel
C)a monopolistically competitive oligopoly
D)a perfectly competitive oligopoly

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
How do equilibrium prices in markets characterized by oligopoly compare with those in monopolies and perfectly competitive markets
A)They are higher than in monopoly markets and higher than in perfectly competitive markets.
B)They are higher than in monopoly markets and lower than in perfectly competitive markets.
C)They are lower than in monopoly markets and higher than in perfectly competitive markets.
D)They are lower than in monopoly markets and lower than in perfectly competitive markets.
A)They are higher than in monopoly markets and higher than in perfectly competitive markets.
B)They are higher than in monopoly markets and lower than in perfectly competitive markets.
C)They are lower than in monopoly markets and higher than in perfectly competitive markets.
D)They are lower than in monopoly markets and lower than in perfectly competitive markets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Assume that oligopoly firms are profit maximizers,do not form a cartel,and take other firms' production levels as given.How does the output effect compare with the price effect
A)The output effect must dominate the price effect.
B)The output effect must be smaller than the price effect.
C)The output effect must balance with the price effect.
D)The output effect can be larger or smaller than the price effect.
A)The output effect must dominate the price effect.
B)The output effect must be smaller than the price effect.
C)The output effect must balance with the price effect.
D)The output effect can be larger or smaller than the price effect.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
As the number of firms change in an oligopoly market,what will it become
A)As the number of firms decreases, the market approaches a cartel equilibrium.
B)As the number of firms decreases, the market approaches a socially optimal equilibrium.
C)As the number of firms increases, the market approaches a competitive market equilibrium.
D)As the number of firms increases, the market approaches a monopoly market equilibrium.
A)As the number of firms decreases, the market approaches a cartel equilibrium.
B)As the number of firms decreases, the market approaches a socially optimal equilibrium.
C)As the number of firms increases, the market approaches a competitive market equilibrium.
D)As the number of firms increases, the market approaches a monopoly market equilibrium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
How does equilibrium quantity in markets characterized by oligopoly compare with that in monopolies and perfectly competitive markets
A)It is higher than in monopoly markets and higher than in perfectly competitive markets.
B)It is higher than in monopoly markets and lower than in perfectly competitive markets.
C)It is lower than in monopoly markets and higher than in perfectly competitive markets.
D)It is lower than in monopoly markets and lower than in perfectly competitive markets.
A)It is higher than in monopoly markets and higher than in perfectly competitive markets.
B)It is higher than in monopoly markets and lower than in perfectly competitive markets.
C)It is lower than in monopoly markets and higher than in perfectly competitive markets.
D)It is lower than in monopoly markets and lower than in perfectly competitive markets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
When oligopolistic firms interacting with one another,each choose their best strategy given the strategies chosen by other firms in the market,what do we have
A)a cartel
B)a socially optimal outcome
C)a Nash equilibrium
D)a collusion
A)a cartel
B)a socially optimal outcome
C)a Nash equilibrium
D)a collusion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
How are oligopolists generally best off,in terms of their profits
A)operating in a Nash equilibrium
B)producing a total quantity of output that falls short of the Nash-equilibrium total quantity
C)producing a total quantity of output that exceeds the Nash-equilibrium total quantity
D)charging a price that falls short of the Nash-equilibrium price
A)operating in a Nash equilibrium
B)producing a total quantity of output that falls short of the Nash-equilibrium total quantity
C)producing a total quantity of output that exceeds the Nash-equilibrium total quantity
D)charging a price that falls short of the Nash-equilibrium price

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Why are cartels difficult to maintain
A)Competition laws are difficult to enforce.
B)Cartel agreements are conducive to monopoly outcomes.
C)There is inevitable tension between cooperation and self-interest in a cartel.
D)Collusion is an unspoken agreement.
A)Competition laws are difficult to enforce.
B)Cartel agreements are conducive to monopoly outcomes.
C)There is inevitable tension between cooperation and self-interest in a cartel.
D)Collusion is an unspoken agreement.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
As the number of firms in an oligopolistic market grows larger,what does the price approach
A)average total cost
B)marginal cost
C)marginal revenue
D)the monopoly price
A)average total cost
B)marginal cost
C)marginal revenue
D)the monopoly price

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
As the number of firms in an oligopoly increases,what happens
A)Each seller becomes more concerned about its impact on the market price.
B)The output effect decreases.
C)The quantity of output becomes closer to the socially efficient quantity.
D)The price of the firms' products and services increases.
A)Each seller becomes more concerned about its impact on the market price.
B)The output effect decreases.
C)The quantity of output becomes closer to the socially efficient quantity.
D)The price of the firms' products and services increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
In a typical cartel agreement,when does the cartel maximize profit
A)when it behaves as a monopolist
B)when it behaves as a duopolist
C)when it behaves as a monopolistically competitive firm
D)when it behaves as a perfectly competitive firm
A)when it behaves as a monopolist
B)when it behaves as a duopolist
C)when it behaves as a monopolistically competitive firm
D)when it behaves as a perfectly competitive firm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Firms do not need to be concerned about striking a balance between the price effect and the output effect when making production decisions in which type of markets
A)oligopolies
B)duopolies
C)monopolies
D)competitive markets
A)oligopolies
B)duopolies
C)monopolies
D)competitive markets

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
When will profit-maximizing production decisions drive price to equal marginal cost
A)when many sellers sell products that are slightly differentiated
B)when many sellers sell products that are identical
C)when there is only one seller
D)when there are only a few sellers
A)when many sellers sell products that are slightly differentiated
B)when many sellers sell products that are identical
C)when there is only one seller
D)when there are only a few sellers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
If nations such as Germany,Japan,and Canada prohibited international trade in automobiles,what would a likely effect be
A)The price effect would become a more significant consideration for each firm that makes automobiles.
B)The excess of price over marginal cost would become less pronounced in the automobile market.
C)All countries would become better off because all automakers would be earning higher profits.
D)The competition would increase within each country, which would keep prices closer to marginal cost.
A)The price effect would become a more significant consideration for each firm that makes automobiles.
B)The excess of price over marginal cost would become less pronounced in the automobile market.
C)All countries would become better off because all automakers would be earning higher profits.
D)The competition would increase within each country, which would keep prices closer to marginal cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Oligopolies can end up looking like competitive markets if the number and behaviour of firms is which of the following
A)large and cooperative
B)large and noncooperative
C)small and cooperative
D)small and noncooperative
A)large and cooperative
B)large and noncooperative
C)small and cooperative
D)small and noncooperative

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
What happens when an oligopoly grows very large
A)The output effect disappears.
B)The price effect disappears.
C)The input effect disappears.
D)The cost effect disappears.
A)The output effect disappears.
B)The price effect disappears.
C)The input effect disappears.
D)The cost effect disappears.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
As the number of firms in an oligopoly grows larger,what does an oligopolistic market look more and more like
A)a competitive market
B)a monopoly
C)a duopoly
D)a monopolistically competitive market
A)a competitive market
B)a monopoly
C)a duopoly
D)a monopolistically competitive market

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
An oligopolist will increase production if the output effect is which of the following
A)less than the price effect
B)equal to the price effect
C)greater than the price effect
D)greater than or equal to the price effect
A)less than the price effect
B)equal to the price effect
C)greater than the price effect
D)greater than or equal to the price effect

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Game theory is important for the understanding of which type of markets
A)competitive markets
B)monopolies
C)oligopolies
D)foreign markets
A)competitive markets
B)monopolies
C)oligopolies
D)foreign markets

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
For the oligopolist that does not collude with its competitors,there are two factors that affect the decision to raise production.What are these factors
A)the input effect and the output effect
B)the production effect and the cost effect
C)the output effect and the price effect
D)the cost effect and the price effect
A)the input effect and the output effect
B)the production effect and the cost effect
C)the output effect and the price effect
D)the cost effect and the price effect

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
When price is above marginal cost,selling one more unit of output at the going price will increase profit.What is this concept called
A)income effect
B)price effect
C)output effect
D)cost effect
A)income effect
B)price effect
C)output effect
D)cost effect

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
What is the profit-maximizing price for monopoly firms
A)a price that exceeds marginal cost
B)a price that exceeds fixed costs
C)a price that exceeds average revenue
D)a price that equals marginal revenue
A)a price that exceeds marginal cost
B)a price that exceeds fixed costs
C)a price that exceeds average revenue
D)a price that equals marginal revenue

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
What is a group of firms that are acting in unison to maximize collective profits called
A)a market structure
B)a coalition
C)a cartel
D)a Nash market
A)a market structure
B)a coalition
C)a cartel
D)a Nash market

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
When strategic interactions are important to pricing and production decisions,what will a typical firm do
A)It will set the price of its product equal to marginal cost.
B)It will consider how competing firms might respond to its actions.
C)It will generally operate as if it is a monopolist.
D)It will consider exiting the market.
A)It will set the price of its product equal to marginal cost.
B)It will consider how competing firms might respond to its actions.
C)It will generally operate as if it is a monopolist.
D)It will consider exiting the market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
When firms are faced with making strategic choices in order to maximize profit,what do economists typically use to model their behaviour
A)the theory of monopoly
B)the theory of aggressive competition
C)game theory
D)cartel theory
A)the theory of monopoly
B)the theory of aggressive competition
C)game theory
D)cartel theory

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Binding agreements concerning production levels between oligopolists can lead the involved firms to what outcome
A)monopoly profit
B)lower prices and more profit
C)zero profit
D)higher prices and less profit
A)monopoly profit
B)lower prices and more profit
C)zero profit
D)higher prices and less profit

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Increasing production will increase quantity sold,which will decrease the price of all units sold.What is this concept known as
A)income effect
B)input effect
C)output effect
D)price effect
A)income effect
B)input effect
C)output effect
D)price effect

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



