Deck 22: Frontiers of Microeconomics
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/141
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 22: Frontiers of Microeconomics
1
Which action would NOT be an example of a principal trying to deal with a moral-hazard problem
A)The parents of an infant secretly place video cameras in their house before the babysitter arrives.
B)An insurance company checks police records to determine if its policyholders have received traffic citations.
C)An employer examines his workers' output on a daily basis.
D)An employer agrees to lower daily output quotas.
A)The parents of an infant secretly place video cameras in their house before the babysitter arrives.
B)An insurance company checks police records to determine if its policyholders have received traffic citations.
C)An employer examines his workers' output on a daily basis.
D)An employer agrees to lower daily output quotas.
An employer agrees to lower daily output quotas.
2
How can employers try to overcome the moral hazard problem involving their employees
A)by paying their employees more often
B)by paying their employees minimum wage
C)by better monitoring of their employees' work efforts
D)by paying their employees in cash
A)by paying their employees more often
B)by paying their employees minimum wage
C)by better monitoring of their employees' work efforts
D)by paying their employees in cash
by better monitoring of their employees' work efforts
3
What characteristic best describes asymmetric information
A)It is rare in economic transactions, but it is common in other aspects of life.
B)It can take the form of a hidden action or a hidden characteristic.
C)It always involves an employer-employee relationship.
D)It is a larger problem for firms than for consumers.
A)It is rare in economic transactions, but it is common in other aspects of life.
B)It can take the form of a hidden action or a hidden characteristic.
C)It always involves an employer-employee relationship.
D)It is a larger problem for firms than for consumers.
It can take the form of a hidden action or a hidden characteristic.
4
What is the problem called that arises when one person performs a task on behalf of another person
A)the hidden characteristics problem
B)the "lemons" problem
C)moral hazard
D)adverse selection
A)the hidden characteristics problem
B)the "lemons" problem
C)moral hazard
D)adverse selection

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which reason is a plausible explanation for a firm paying above-equilibrium wages to its workers
A)It increases the probability that a worker who shirks will be caught.
B)It discourages workers from shirking.
C)It pays a premium for workers to work overtime.
D)It increases their costs but lowers their net taxes due.
A)It increases the probability that a worker who shirks will be caught.
B)It discourages workers from shirking.
C)It pays a premium for workers to work overtime.
D)It increases their costs but lowers their net taxes due.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
What type of problem is the temptation of imperfectly monitored workers to shirk their responsibilities
A)an adverse-selection problem
B)a lemons problem
C)a problem in which the employer is the principal and the worker is the agent
D)a problem of high risk life insurance
A)an adverse-selection problem
B)a lemons problem
C)a problem in which the employer is the principal and the worker is the agent
D)a problem of high risk life insurance

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
When does the moral hazard problem arise
A)when an agent performs a task on behalf of a principal
B)when a principal performs a task on behalf of an agent
C)when a moral person trusts an immoral person to perform a task for him
D)when an immoral person bribes a moral person to perform a task for her
A)when an agent performs a task on behalf of a principal
B)when a principal performs a task on behalf of an agent
C)when a moral person trusts an immoral person to perform a task for him
D)when an immoral person bribes a moral person to perform a task for her

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which statement best explains the relationship of moral hazard,adverse selection,hidden actions,and asymmetric information
A)The moral hazard problem is a problem involving hidden actions.
B)Adverse selection is a problem involving hidden actions.
C)Adverse selection is a problem involving principals and agents.
D)Moral hazard always involves asymmetric information; asymmetric information always involves adverse selection.
A)The moral hazard problem is a problem involving hidden actions.
B)Adverse selection is a problem involving hidden actions.
C)Adverse selection is a problem involving principals and agents.
D)Moral hazard always involves asymmetric information; asymmetric information always involves adverse selection.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which relationship involves asymmetric information
A)An employee knows more than his employer knows about his work effort.
B)A lender knows more than the borrower about his ability to repay the loan.
C)The buyer of a 30-year-old house knows more than the seller about the condition of the house.
D)A consumer knows more about a product than the employee who assembled it.
A)An employee knows more than his employer knows about his work effort.
B)A lender knows more than the borrower about his ability to repay the loan.
C)The buyer of a 30-year-old house knows more than the seller about the condition of the house.
D)A consumer knows more about a product than the employee who assembled it.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Moral hazard is a problem that arises when which situation occurs
A)There is a misunderstanding rising from differences of opinion.
B)There is a hidden characteristic.
C)There is a risk of inappropriate behaviour by one of the parties to a transaction or agreement.
D)There is a risk of a "lemon."
A)There is a misunderstanding rising from differences of opinion.
B)There is a hidden characteristic.
C)There is a risk of inappropriate behaviour by one of the parties to a transaction or agreement.
D)There is a risk of a "lemon."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
In the relationship between a worker and her employer,which of the following are potential problems
A)Asymmetric information is a potential problem, but moral hazard is not a potential problem.
B)Asymmetric information is a potential problem, but adverse selection is not a potential problem.
C)Moral hazard is a potential problem, but asymmetric information is not a potential problem.
D)Adverse selection is a potential problem, but asymmetric information is not a potential problem.
A)Asymmetric information is a potential problem, but moral hazard is not a potential problem.
B)Asymmetric information is a potential problem, but adverse selection is not a potential problem.
C)Moral hazard is a potential problem, but asymmetric information is not a potential problem.
D)Adverse selection is a potential problem, but asymmetric information is not a potential problem.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A realtor knows more than the buyer about a house the realtor's selling.What is this an example of
A)an information asymmetry; specifically, it is an example of a hidden action
B)an information asymmetry; specifically, it is an example of a hidden characteristic
C)a hidden action; specifically, it is an example of a hidden characteristic
D)a hidden characteristic; specifically, it is an example of a hidden action
A)an information asymmetry; specifically, it is an example of a hidden action
B)an information asymmetry; specifically, it is an example of a hidden characteristic
C)a hidden action; specifically, it is an example of a hidden characteristic
D)a hidden characteristic; specifically, it is an example of a hidden action

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which practice would indicate that an employer is trying to overcome a moral hazard problem with respect to her employees
A)The employer pays wages to her workers that are unusually high for the industry and region.
B)The employer has voluntarily removed video cameras from the factory floor.
C)The employer has discontinued the practice of giving year-end bonuses to her employees.
D)The employer has hired a mediator to resolve union grievances.
A)The employer pays wages to her workers that are unusually high for the industry and region.
B)The employer has voluntarily removed video cameras from the factory floor.
C)The employer has discontinued the practice of giving year-end bonuses to her employees.
D)The employer has hired a mediator to resolve union grievances.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
A seller of a used car knows more than the buyer about the car's condition.What is this an example of
A)a hidden action; specifically, it is an example of a hidden characteristic
B)a hidden characteristic; specifically, it is an example of a hidden action
C)an information asymmetry; specifically, it is an example of a hidden action
D)an information asymmetry; specifically, it is an example of a hidden characteristic
A)a hidden action; specifically, it is an example of a hidden characteristic
B)a hidden characteristic; specifically, it is an example of a hidden action
C)an information asymmetry; specifically, it is an example of a hidden action
D)an information asymmetry; specifically, it is an example of a hidden characteristic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The 2001 Nobel Prize in Economics was awarded to George Akerlof,Michael Spence,and Joseph Stiglitz.The subject of their work described how actors on one side of the market had much better information than those on the other side.What is this topic called
A)asymmetric information
B)monopoly knowledge
C)information disequilibrium
D)asymmetric labour markets
A)asymmetric information
B)monopoly knowledge
C)information disequilibrium
D)asymmetric labour markets

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
In the worker-employer relationship,how may inappropriate or immoral behaviour best be characterized
A)It generally takes the form of workers shirking their responsibilities.
B)It generally takes the form of employers being unfair to their workers.
C)It is not generally regarded as a significant problem.
D)It is generally regarded as a significant problem, but it does not arise from asymmetric information.
A)It generally takes the form of workers shirking their responsibilities.
B)It generally takes the form of employers being unfair to their workers.
C)It is not generally regarded as a significant problem.
D)It is generally regarded as a significant problem, but it does not arise from asymmetric information.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
When asymmetric information affects a relationship between two parties,what is always the case
A)Neither party is well informed.
B)One party is better informed than the other party.
C)Both parties are equally well informed.
D)The government is better informed than either of the two parties.
A)Neither party is well informed.
B)One party is better informed than the other party.
C)Both parties are equally well informed.
D)The government is better informed than either of the two parties.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
What is the classic example of moral hazard
A)the market for used cars
B)the market for new houses
C)the relationship between a buyer and a seller
D)the relationship between a worker and his employer
A)the market for used cars
B)the market for new houses
C)the relationship between a buyer and a seller
D)the relationship between a worker and his employer

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The buyer runs a risk of being sold a low quality good when which type of problem is present
A)principal-agent problem
B)moral-hazard problem
C)problem involving hidden actions
D)problem involving hidden characteristics
A)principal-agent problem
B)moral-hazard problem
C)problem involving hidden actions
D)problem involving hidden characteristics

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
In economics,which term refers to a difference in access to relevant knowledge
A)a behavioural gap
B)a concealment gap
C)an information asymmetry
D)an access imperfection
A)a behavioural gap
B)a concealment gap
C)an information asymmetry
D)an access imperfection

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Francesca owns a small clothing business in Victoria.She travels a lot,meeting with important customers,attending fashion shows,and the like.Francesca hired Renaldo to work in the Victoria office as the day-to-day general manager of the business.Which statement best characterizes this principal and agent problem
A)There is an adverse-selection risk in that perhaps Renaldo will not work as hard as Francesca would like.
B)With respect to the potential risk involving Francesca and Renaldo, Francesca is the principal and Renaldo is the agent.
C)It is common for employers such as Francesca to pay managers such as Renaldo below-equilibrium wages and salaries because they know managers shirk their responsibilities.
D)Renaldo may withhold information from Francesca, creating a moral hazard problem.
A)There is an adverse-selection risk in that perhaps Renaldo will not work as hard as Francesca would like.
B)With respect to the potential risk involving Francesca and Renaldo, Francesca is the principal and Renaldo is the agent.
C)It is common for employers such as Francesca to pay managers such as Renaldo below-equilibrium wages and salaries because they know managers shirk their responsibilities.
D)Renaldo may withhold information from Francesca, creating a moral hazard problem.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
What are the two basic problems involving asymmetric information
A)moral dilemma and inverse-risk selection
B)moral dilemma and adverse selection
C)moral hazard and inverse-risk selection
D)moral hazard and adverse selection
A)moral dilemma and inverse-risk selection
B)moral dilemma and adverse selection
C)moral hazard and inverse-risk selection
D)moral hazard and adverse selection

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
XYZ Company pays its workers very well.The wages of workers at XYZ significantly exceed regional and national averages for people who do similar work.In fact,all indications are that XYZ workers' wages are well above equilibrium levels.What might explain the fact that XYZ pays its workers so well
A)There is no problem of asymmetric information at XYZ between the company's management and its workers.
B)Workers at XYZ have never demonstrated any tendency to shirk.
C)XYZ wants to maintain a good mix of workers in terms of their true abilities.
D)XYZ is not worried about lemons.
A)There is no problem of asymmetric information at XYZ between the company's management and its workers.
B)Workers at XYZ have never demonstrated any tendency to shirk.
C)XYZ wants to maintain a good mix of workers in terms of their true abilities.
D)XYZ is not worried about lemons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
"Signalling" refers to actions by an informed party for what sole purpose
A)telling another party that the signaller has information to reveal, without actually revealing that information
B)conveying false information
C)confusing another party
D)credibly revealing private information
A)telling another party that the signaller has information to reveal, without actually revealing that information
B)conveying false information
C)confusing another party
D)credibly revealing private information

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Shawn buys automobile insurance from Safe-T Insurance Company.If Shawn avoids having an accident for three years,Safe-T will reduce the price he has to pay for his insurance.Nevertheless,he routinely drives fast and with reckless abandon.Which statement best characterizes this principal and agent problem
A)It would make sense for Safe-T to reduce Shawn's price of insurance now, rather than waiting to see if he has an accident in the next three years.
B)Shawn's behaviour is an example of adverse selection.
C)Safe-T Insurance Company is a principal; Shawn is an agent.
D)Shawn should avoid reporting any accidents to Safe-T.
A)It would make sense for Safe-T to reduce Shawn's price of insurance now, rather than waiting to see if he has an accident in the next three years.
B)Shawn's behaviour is an example of adverse selection.
C)Safe-T Insurance Company is a principal; Shawn is an agent.
D)Shawn should avoid reporting any accidents to Safe-T.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which phenomenon does the lemons problem likely explain
A)For several months after it is purchased, the price of a new car falls very little.
B)Almost no one favours government-provided health insurance.
C)People in average health may be discouraged from buying health insurance due to the high price.
D)Employers are reluctant to monitor the activities of their workers, fearing that some of the workers may take legal action against the employers.
A)For several months after it is purchased, the price of a new car falls very little.
B)Almost no one favours government-provided health insurance.
C)People in average health may be discouraged from buying health insurance due to the high price.
D)Employers are reluctant to monitor the activities of their workers, fearing that some of the workers may take legal action against the employers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Because people with hidden health problems are more likely to buy health insurance than are other people,which outcome is the result
A)The price of health insurance reflects the costs of a sicker-than-average person.
B)The price of health insurance is too low, relative to the socially optimal price.
C)People in average health may be encouraged to buy too much health insurance, relative to the socially optimal quantity.
D)People in higher risk may be buying too little insurance due to the higher cost.
A)The price of health insurance reflects the costs of a sicker-than-average person.
B)The price of health insurance is too low, relative to the socially optimal price.
C)People in average health may be encouraged to buy too much health insurance, relative to the socially optimal quantity.
D)People in higher risk may be buying too little insurance due to the higher cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
How can signalling theory explain the advertising strategies of a firm that produces a good quality product
A)It is not a good example of asymmetric information.
B)It has more to gain by signalling (advertising) than does a firm with an inferior product.
C)It will never signal (advertise), regardless of the cost of the signal.
D)It will signal (advertise) only if the cost of the signal is very low.
A)It is not a good example of asymmetric information.
B)It has more to gain by signalling (advertising) than does a firm with an inferior product.
C)It will never signal (advertise), regardless of the cost of the signal.
D)It will signal (advertise) only if the cost of the signal is very low.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which characterization best describes the phenomenon of signalling
A)It refers to actions taken by an informed party to conceal private information.
B)It plays a role in certain theories of education.
C)It is the same as the phenomenon of screening.
D)It is unrelated to problems of asymmetric information.
A)It refers to actions taken by an informed party to conceal private information.
B)It plays a role in certain theories of education.
C)It is the same as the phenomenon of screening.
D)It is unrelated to problems of asymmetric information.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Employers may choose to pay their workers a wage that exceeds the equilibrium wage according to which theory
A)efficiency-wage theories
B)minimum-wage theories
C)monitoring theory
D)signalling theory
A)efficiency-wage theories
B)minimum-wage theories
C)monitoring theory
D)signalling theory

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
How can we use the theories of asymmetric information to explain the fact that year-end bonuses are often paid to workers
A)It may be evidence of the validity of efficiency-wage theories.
B)It may in some cases be a response by employers to the moral hazard problem.
C)It may in some cases be a response by employers to the lemons problem.
D)It may in some cases be a response by employers to a hidden characteristic problem.
A)It may be evidence of the validity of efficiency-wage theories.
B)It may in some cases be a response by employers to the moral hazard problem.
C)It may in some cases be a response by employers to the lemons problem.
D)It may in some cases be a response by employers to a hidden characteristic problem.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which outcome may well result from severe adverse-selection problems
A)Too few good used cars are offered for sale.
B)Wages are too low relative to equilibrium levels.
C)Too many good drivers buy too much automobile insurance.
D)Prices for inferior goods are too low.
A)Too few good used cars are offered for sale.
B)Wages are too low relative to equilibrium levels.
C)Too many good drivers buy too much automobile insurance.
D)Prices for inferior goods are too low.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Why do private markets not provide adequate amounts of medical insurance for everyone
A)Only low-risk people will buy insurance.
B)High-risk people will not buy insurance because the premium is too high.
C)People in average health will buy insurance due to the low cost.
D)Higher risk people will buy insurance but not the lower risk people.
A)Only low-risk people will buy insurance.
B)High-risk people will not buy insurance because the premium is too high.
C)People in average health will buy insurance due to the low cost.
D)Higher risk people will buy insurance but not the lower risk people.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
When new professors are hired,their job performance is monitored closely.If they meet their institution's standards,they will eventually receive tenure.After receiving tenure,professors' job performance is less closely monitored,and they become difficult to fire.What does tenure create
A)adverse selection
B)Condorcet's paradox
C)a screening paradox
D)moral hazard
A)adverse selection
B)Condorcet's paradox
C)a screening paradox
D)moral hazard

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
How do hidden actions and hidden characteristics relate to the moral hazard and adverse selection problems
A)Hidden actions and hidden characteristics are both associated with the moral hazard problem.
B)Hidden actions and hidden characteristics are both associated with the adverse-selection problem.
C)Hidden actions are associated with the moral hazard problem, whereas hidden characteristics are associated with the adverse-selection problem.
D)Hidden actions are associated with the adverse-selection problem, whereas hidden characteristics are associated with the moral hazard problem.
A)Hidden actions and hidden characteristics are both associated with the moral hazard problem.
B)Hidden actions and hidden characteristics are both associated with the adverse-selection problem.
C)Hidden actions are associated with the moral hazard problem, whereas hidden characteristics are associated with the adverse-selection problem.
D)Hidden actions are associated with the adverse-selection problem, whereas hidden characteristics are associated with the moral hazard problem.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
What problem does the Latin term caveat emptor,meaning "let the buyer beware," bring to mind
A)the problem of hidden actions
B)the problem of adverse selection
C)the problem of principals and agents
D)the problem of moral hazard
A)the problem of hidden actions
B)the problem of adverse selection
C)the problem of principals and agents
D)the problem of moral hazard

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
How is the signalling theory of education related to other theories that explain the determinants of wages
A)It contrasts with efficiency-wage theories.
B)It closely parallels efficiency-wage theories.
C)It contrasts with the human-capital theory.
D)It closely parallels the human-capital theory.
A)It contrasts with efficiency-wage theories.
B)It closely parallels efficiency-wage theories.
C)It contrasts with the human-capital theory.
D)It closely parallels the human-capital theory.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Lisa,a homeowner,buys fewer fire extinguishers than her insurance company would prefer.What can we infer from this behaviour
A)There is an adverse-selection problem.
B)There is a moral hazard problem.
C)Lisa can be regarded as a principal; her insurance company can be regarded as an agent.
D)Lisa must be regarded as irrational in that her benefits from buying fire extinguishers are just as great as the insurance company's benefits.
A)There is an adverse-selection problem.
B)There is a moral hazard problem.
C)Lisa can be regarded as a principal; her insurance company can be regarded as an agent.
D)Lisa must be regarded as irrational in that her benefits from buying fire extinguishers are just as great as the insurance company's benefits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Robert borrowed $15,000 from Granite Bank,telling the loan officer that he intended to use the money to make repairs to his home.After getting the loan,Robert and his girlfriend immediately took the $15,000 and headed to Las Vegas for a weekend of gambling and entertainment.Which statement best characterizes this principal and agent problem
A)This is a problem of moral hazard, but it is not a problem of asymmetric information.
B)This is a problem of asymmetric information, but it is not a problem of moral hazard.
C)From the given information, it is correct to say that Robert is a principal and that his girlfriend is an agent.
D)From the given information, it is correct to say that Granite Bank is a principal and that Robert is an agent.
A)This is a problem of moral hazard, but it is not a problem of asymmetric information.
B)This is a problem of asymmetric information, but it is not a problem of moral hazard.
C)From the given information, it is correct to say that Robert is a principal and that his girlfriend is an agent.
D)From the given information, it is correct to say that Granite Bank is a principal and that Robert is an agent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
What is the classic example of adverse selection
A)the market for used cars
B)the market for new houses
C)the relationship between husband and wife
D)the relationship between a worker and his employer
A)the market for used cars
B)the market for new houses
C)the relationship between husband and wife
D)the relationship between a worker and his employer

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
What effect have recent developments in political economy shown
A)They have rendered much of the traditional field of political science obsolete.
B)They have rendered much of the traditional field of economics obsolete.
C)They have reaffirmed the good qualities of majority voting.
D)They have pointed to the fact that government is a less-than-perfect institution.
A)They have rendered much of the traditional field of political science obsolete.
B)They have rendered much of the traditional field of economics obsolete.
C)They have reaffirmed the good qualities of majority voting.
D)They have pointed to the fact that government is a less-than-perfect institution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
What does the Condorcet paradox show
A)preferential voting based on majority rule are inefficient in all cases.
B)problems in counting votes can negate legitimate democratic outcomes.
C)the order in which items are voted on can affect the result.
D)transitive preferences are inconsistent with rationality.
A)preferential voting based on majority rule are inefficient in all cases.
B)problems in counting votes can negate legitimate democratic outcomes.
C)the order in which items are voted on can affect the result.
D)transitive preferences are inconsistent with rationality.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Normally,what property do we expect voters' preferences to exhibit
A)transitivity
B)homogeneity
C)normality
D)universality
A)transitivity
B)homogeneity
C)normality
D)universality

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
When does screening occur
A)when an informed party acts to reveal his private information
B)when an informed party acts to conceal his private information
C)when an uninformed party acts to induce the informed party to reveal private information
D)when one informed party acts to prevent another informed party from revealing private information
A)when an informed party acts to reveal his private information
B)when an informed party acts to conceal his private information
C)when an uninformed party acts to induce the informed party to reveal private information
D)when one informed party acts to prevent another informed party from revealing private information

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The Feel Better Health Insurance Company is thinking about raising its rates for insurance.Which outcome is the least likely to happen if it does
A)The percentage of its customers who are generally healthy will fall.
B)The number of its customers with hidden health problems will fall.
C)The number of customers who are generally healthy will fall.
D)The firm's profit per customer will rise.
A)The percentage of its customers who are generally healthy will fall.
B)The number of its customers with hidden health problems will fall.
C)The number of customers who are generally healthy will fall.
D)The firm's profit per customer will rise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
On car insurance policies,Prairie Ranch Insurance Company offers drivers an option: Policy 1 features a deductible of $2000 and it requires a driver to pay an annual premium of $500; Policy 2 features a deductible of $500 and it requires a driver to pay an annual premium of $750.Why does the company offer two policies
A)In offering these two policies, Prairie Ranch is engaging in price discrimination.
B)In offering these two policies, Prairie Ranch is attempting to sort out the safe drivers from the risky drivers.
C)In offering these two policies, Prairie Ranch can earn a higher profit on Policy 2 if it is bought by safe drivers.
D)In offering these two policies, Prairie Ranch can earn a higher profit because only risky drivers will buy a policy.
A)In offering these two policies, Prairie Ranch is engaging in price discrimination.
B)In offering these two policies, Prairie Ranch is attempting to sort out the safe drivers from the risky drivers.
C)In offering these two policies, Prairie Ranch can earn a higher profit on Policy 2 if it is bought by safe drivers.
D)In offering these two policies, Prairie Ranch can earn a higher profit because only risky drivers will buy a policy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
What can we say about the problem of asymmetric information
A)It always arises from government intervention in private markets.
B)It serves as a possible rationale for government intervention in private markets.
C)It always amounts to a moral hazard problem.
D)It does not affect prices consumers are willing to pay in the market.
A)It always arises from government intervention in private markets.
B)It serves as a possible rationale for government intervention in private markets.
C)It always amounts to a moral hazard problem.
D)It does not affect prices consumers are willing to pay in the market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Under majority rule,what can we say about the order in which items are voted on
A)It is unimportant, and this is a lesson of the Condorcet paradox.
B)It is unimportant, and this has nothing to do with the Condorcet paradox.
C)It is important, and this is a lesson of the Condorcet paradox.
D)It is important, and this has nothing to do with the Condorcet paradox.
A)It is unimportant, and this is a lesson of the Condorcet paradox.
B)It is unimportant, and this has nothing to do with the Condorcet paradox.
C)It is important, and this is a lesson of the Condorcet paradox.
D)It is important, and this has nothing to do with the Condorcet paradox.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Table 22-1
Three long-time friends, Sam, Denise, and Carlos, are deciding how they will spend their Saturday evening.They all agree that they should do one of three things: go to a movie, go bowling, or go out to dinner.They also agree that they will have two pairwise votes to determine how to spend their evening, with the majority determining the outcome on each vote.The first, second, and third choices for each person are as indicated in the table below.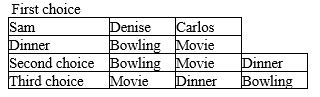
Refer to Table 22-1.If (1) the first vote pits "dinner" against "movie," and (2) the second vote pits "bowling" against the winner of the first vote,what is the outcome
A)"Dinner" wins the first vote and "dinner" wins the second vote, so they go to dinner.
B)"Dinner" wins the first vote and "bowling" wins the second vote, so they go bowling.
C)"Movie" wins the first vote and "movie" wins the second vote, so they go to a movie.
D)"Movie" wins the first vote and "bowling" wins the second vote, so they go bowling.
Three long-time friends, Sam, Denise, and Carlos, are deciding how they will spend their Saturday evening.They all agree that they should do one of three things: go to a movie, go bowling, or go out to dinner.They also agree that they will have two pairwise votes to determine how to spend their evening, with the majority determining the outcome on each vote.The first, second, and third choices for each person are as indicated in the table below.

Refer to Table 22-1.If (1) the first vote pits "dinner" against "movie," and (2) the second vote pits "bowling" against the winner of the first vote,what is the outcome
A)"Dinner" wins the first vote and "dinner" wins the second vote, so they go to dinner.
B)"Dinner" wins the first vote and "bowling" wins the second vote, so they go bowling.
C)"Movie" wins the first vote and "movie" wins the second vote, so they go to a movie.
D)"Movie" wins the first vote and "bowling" wins the second vote, so they go bowling.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The Condorcet voting paradox is that democratic outcomes do not always obey which of the following properties
A)homogeneity of preferences
B)concavity of preferences
C)asymmetry of preferences
D)transitivity of preferences
A)homogeneity of preferences
B)concavity of preferences
C)asymmetry of preferences
D)transitivity of preferences

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Table 22-1
Three long-time friends, Sam, Denise, and Carlos, are deciding how they will spend their Saturday evening.They all agree that they should do one of three things: go to a movie, go bowling, or go out to dinner.They also agree that they will have two pairwise votes to determine how to spend their evening, with the majority determining the outcome on each vote.The first, second, and third choices for each person are as indicated in the table below.
Refer to Table 22-1.If (1) the first vote pits "dinner" against "bowling," and (2) the second vote pits "movie" against the winner of the first vote,what is the outcome
A)"Dinner" wins the first vote and "dinner" wins the second vote, so they go to dinner.
B)"Dinner" wins the first vote and "movie" wins the second vote, so they go to a movie.
C)"Bowling" wins the first vote and "bowling" wins the second vote, so they go bowling.
D)"Bowling" wins the first vote and "movie" wins the second vote, so they go to a movie.
Three long-time friends, Sam, Denise, and Carlos, are deciding how they will spend their Saturday evening.They all agree that they should do one of three things: go to a movie, go bowling, or go out to dinner.They also agree that they will have two pairwise votes to determine how to spend their evening, with the majority determining the outcome on each vote.The first, second, and third choices for each person are as indicated in the table below.

Refer to Table 22-1.If (1) the first vote pits "dinner" against "bowling," and (2) the second vote pits "movie" against the winner of the first vote,what is the outcome
A)"Dinner" wins the first vote and "dinner" wins the second vote, so they go to dinner.
B)"Dinner" wins the first vote and "movie" wins the second vote, so they go to a movie.
C)"Bowling" wins the first vote and "bowling" wins the second vote, so they go bowling.
D)"Bowling" wins the first vote and "movie" wins the second vote, so they go to a movie.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Which action best exemplifies the concept of signalling
A)A college student's parents, having learned that their child is short of money, send her a cheque for $1000.
B)A woman, who is trying to win the love of a certain man, buys him a very personal gift.
C)A grocery store maintains a policy of examining the driver's licence of everyone who writes a personal cheque to purchase their groceries.
D)A university maintains a policy of considering for admission only those students who graduated among the top 10 percent of their high school class.
A)A college student's parents, having learned that their child is short of money, send her a cheque for $1000.
B)A woman, who is trying to win the love of a certain man, buys him a very personal gift.
C)A grocery store maintains a policy of examining the driver's licence of everyone who writes a personal cheque to purchase their groceries.
D)A university maintains a policy of considering for admission only those students who graduated among the top 10 percent of their high school class.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
What does the field of political economy apply
A)It applies government intervention and casts aside most of the standard methods of economic analysis.
B)It applies the methods of economics to study how government works.
C)It applies the methods of economics to study how the financial sector works.
D)It applies the conclusion that democratic principles never lead to desirable economic outcomes.
A)It applies government intervention and casts aside most of the standard methods of economic analysis.
B)It applies the methods of economics to study how government works.
C)It applies the methods of economics to study how the financial sector works.
D)It applies the conclusion that democratic principles never lead to desirable economic outcomes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
In view of the possible need for government action in markets where asymmetric information is a problem,which consideration is most valid
A)The government almost always has more information than the private parties.
B)Private markets have no means of dealing with information asymmetries on their own.
C)The government is itself an imperfect institution.
D)Government intervention will exacerbate any market failures.
A)The government almost always has more information than the private parties.
B)Private markets have no means of dealing with information asymmetries on their own.
C)The government is itself an imperfect institution.
D)Government intervention will exacerbate any market failures.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Table 22-1
Three long-time friends, Sam, Denise, and Carlos, are deciding how they will spend their Saturday evening.They all agree that they should do one of three things: go to a movie, go bowling, or go out to dinner.They also agree that they will have two pairwise votes to determine how to spend their evening, with the majority determining the outcome on each vote.The first, second, and third choices for each person are as indicated in the table below.
Refer to Table 22-1.Which statement regarding the Condorcet paradox and the results of pairwise voting by Sam,Denise,and Carlos is most accurate
A)The paradox implies that pairwise voting never produces transitive preferences, and so the voting by Sam, Denise, and Carlos fails to produce transitive preferences.
B)The paradox implies that pairwise voting sometimes (but not always) produces transitive preferences, and the voting by Sam, Denise, and Carlos does produce transitive preferences.
C)The paradox implies that pairwise voting sometimes (but not always) fails to produce transitive preferences, and the voting by Sam, Denise, and Carlos fails to produce transitive preferences.
D)The paradox implies that pairwise voting almost never produces transitive preferences, but the voting by Sam, Denise, and Carlos does produce transitive preferences.
Three long-time friends, Sam, Denise, and Carlos, are deciding how they will spend their Saturday evening.They all agree that they should do one of three things: go to a movie, go bowling, or go out to dinner.They also agree that they will have two pairwise votes to determine how to spend their evening, with the majority determining the outcome on each vote.The first, second, and third choices for each person are as indicated in the table below.

Refer to Table 22-1.Which statement regarding the Condorcet paradox and the results of pairwise voting by Sam,Denise,and Carlos is most accurate
A)The paradox implies that pairwise voting never produces transitive preferences, and so the voting by Sam, Denise, and Carlos fails to produce transitive preferences.
B)The paradox implies that pairwise voting sometimes (but not always) produces transitive preferences, and the voting by Sam, Denise, and Carlos does produce transitive preferences.
C)The paradox implies that pairwise voting sometimes (but not always) fails to produce transitive preferences, and the voting by Sam, Denise, and Carlos fails to produce transitive preferences.
D)The paradox implies that pairwise voting almost never produces transitive preferences, but the voting by Sam, Denise, and Carlos does produce transitive preferences.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Which statement best captures the meaning of transitivity of preferences
A)If A is preferred to B, then B is less preferred than A.
B)If A is preferred to B and B is preferred to C, then A is preferred to C.
C)If A is preferred to B and B is preferred to C, then the preference for A over B is stronger than the preference for B over C.
D)If A is preferred to C, then there exists B such that A is preferred to B and B is preferred to C.
A)If A is preferred to B, then B is less preferred than A.
B)If A is preferred to B and B is preferred to C, then A is preferred to C.
C)If A is preferred to B and B is preferred to C, then the preference for A over B is stronger than the preference for B over C.
D)If A is preferred to C, then there exists B such that A is preferred to B and B is preferred to C.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
An insurance company that writes automobile policies tries to separate safe drivers from risky drivers by offering policies that feature different deductibles and different premiums.What is this an example of
A)screening
B)signing
C)underwriting
D)signalling
A)screening
B)signing
C)underwriting
D)signalling

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which type of voting does the Condorcet paradox apply to
A)pairwise majority voting
B)a vote that requires unanimous consent by all voters
C)preferential voting
D)a Borda count
A)pairwise majority voting
B)a vote that requires unanimous consent by all voters
C)preferential voting
D)a Borda count

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The Condorcet voting paradox applies to situations in which voters do which of the following things
A)They decide between exactly two possible similar outcomes.
B)They decide among more than two possible outcomes.
C)They decide to make a choice between two possible outcomes.
D)They decide between exactly two very different outcomes.
A)They decide between exactly two possible similar outcomes.
B)They decide among more than two possible outcomes.
C)They decide to make a choice between two possible outcomes.
D)They decide between exactly two very different outcomes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Table 22-1
Three long-time friends, Sam, Denise, and Carlos, are deciding how they will spend their Saturday evening.They all agree that they should do one of three things: go to a movie, go bowling, or go out to dinner.They also agree that they will have two pairwise votes to determine how to spend their evening, with the majority determining the outcome on each vote.The first, second, and third choices for each person are as indicated in the table below.
Refer to Table 22-1.If Sam,Denise,and Carlos use a Borda count,rather than pairwise majority voting,to decide how to spend their evening,what will they do
A)go to a movie
B)go bowling
C)go out to dinner
D)go their separate ways
Three long-time friends, Sam, Denise, and Carlos, are deciding how they will spend their Saturday evening.They all agree that they should do one of three things: go to a movie, go bowling, or go out to dinner.They also agree that they will have two pairwise votes to determine how to spend their evening, with the majority determining the outcome on each vote.The first, second, and third choices for each person are as indicated in the table below.

Refer to Table 22-1.If Sam,Denise,and Carlos use a Borda count,rather than pairwise majority voting,to decide how to spend their evening,what will they do
A)go to a movie
B)go bowling
C)go out to dinner
D)go their separate ways

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
What do we know about the Arrow impossibility theorem in the history of political economy
A)It was proved by Arrow mathematically and definitively.
B)It has not been taken seriously since the 1970s.
C)It was overturned by the median voter theorem in the 1990s.
D)It runs counter to most people's intuition in that it establishes the "relevance of irrelevant alternatives."
A)It was proved by Arrow mathematically and definitively.
B)It has not been taken seriously since the 1970s.
C)It was overturned by the median voter theorem in the 1990s.
D)It runs counter to most people's intuition in that it establishes the "relevance of irrelevant alternatives."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Economist Kenneth Arrow wrote a famous book in 1951 in which he took up what question
A)Is there a perfect voting system?
B)Are preferences transitive?
C)Is government an imperfect institution?
D)Should politicians face fixed terms?
A)Is there a perfect voting system?
B)Are preferences transitive?
C)Is government an imperfect institution?
D)Should politicians face fixed terms?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
What is the relationship of the Condorcet paradox to the Arrow impossibility theorem
A)It proved that the Arrow impossibility theorem is wrong.
B)It was proved wrong by the Arrow impossibility theorem.
C)It serves as an example of the Arrow impossibility theorem.
D)It pertains to voting systems, whereas Arrow's impossibility theorem does not.
A)It proved that the Arrow impossibility theorem is wrong.
B)It was proved wrong by the Arrow impossibility theorem.
C)It serves as an example of the Arrow impossibility theorem.
D)It pertains to voting systems, whereas Arrow's impossibility theorem does not.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
What does the Arrow impossibility theorem show
A)Democracy should be abandoned as a form of government.
B)It is impossible to improve upon democratic voting methods as a mechanism for social choice.
C)All voting systems are flawed as mechanisms for social choice.
D)It is impossible to identify the median voter.
A)Democracy should be abandoned as a form of government.
B)It is impossible to improve upon democratic voting methods as a mechanism for social choice.
C)All voting systems are flawed as mechanisms for social choice.
D)It is impossible to identify the median voter.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Table 22-2
Voters are deciding how they will spend the City of Elmongary's budget surplus.They have enough money to build one of three projects: build a school, build a skate park, or build a bike lane for commuters.They agree that they will have two pairwise votes to determine how to spend their budget, with the majority determining the outcome on each vote.The first, second, and third choices for each project are as indicated in the table below.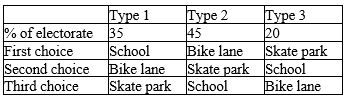
Refer to Table 22-2.What is a possible outcome in a pairwise election
A)In a pairwise election, "school" beats "bike lane."
B)In a pairwise election, "bike lane" beats "skate park."
C)In a pairwise election, "school" beats "skate park."
D)In a pairwise election, "skate park" beats "school."
Voters are deciding how they will spend the City of Elmongary's budget surplus.They have enough money to build one of three projects: build a school, build a skate park, or build a bike lane for commuters.They agree that they will have two pairwise votes to determine how to spend their budget, with the majority determining the outcome on each vote.The first, second, and third choices for each project are as indicated in the table below.

Refer to Table 22-2.What is a possible outcome in a pairwise election
A)In a pairwise election, "school" beats "bike lane."
B)In a pairwise election, "bike lane" beats "skate park."
C)In a pairwise election, "school" beats "skate park."
D)In a pairwise election, "skate park" beats "school."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Table 22-2
Voters are deciding how they will spend the City of Elmongary's budget surplus.They have enough money to build one of three projects: build a school, build a skate park, or build a bike lane for commuters.They agree that they will have two pairwise votes to determine how to spend their budget, with the majority determining the outcome on each vote.The first, second, and third choices for each project are as indicated in the table below.
Refer to Table 22-2.Which statement regarding the Condorcet paradox and the results of pairwise voting in Elmongary is most accurate
A)The paradox implies that pairwise voting never produces transitive preferences, and so the voting in Elmongary fails to produce transitive preferences.
B)The paradox implies that pairwise voting sometimes (but not always) produces transitive preferences, and the voting in Elmongary does produce transitive preferences.
C)The paradox implies that pairwise voting sometimes (but not always) fails to produce transitive preferences, and the voting in Elmongary fails to produce transitive preferences.
D)The paradox implies that pairwise voting almost never produces transitive preferences, but the voting in Elmongary does produce transitive preferences.
Voters are deciding how they will spend the City of Elmongary's budget surplus.They have enough money to build one of three projects: build a school, build a skate park, or build a bike lane for commuters.They agree that they will have two pairwise votes to determine how to spend their budget, with the majority determining the outcome on each vote.The first, second, and third choices for each project are as indicated in the table below.

Refer to Table 22-2.Which statement regarding the Condorcet paradox and the results of pairwise voting in Elmongary is most accurate
A)The paradox implies that pairwise voting never produces transitive preferences, and so the voting in Elmongary fails to produce transitive preferences.
B)The paradox implies that pairwise voting sometimes (but not always) produces transitive preferences, and the voting in Elmongary does produce transitive preferences.
C)The paradox implies that pairwise voting sometimes (but not always) fails to produce transitive preferences, and the voting in Elmongary fails to produce transitive preferences.
D)The paradox implies that pairwise voting almost never produces transitive preferences, but the voting in Elmongary does produce transitive preferences.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Table 22-2
Voters are deciding how they will spend the City of Elmongary's budget surplus.They have enough money to build one of three projects: build a school, build a skate park, or build a bike lane for commuters.They agree that they will have two pairwise votes to determine how to spend their budget, with the majority determining the outcome on each vote.The first, second, and third choices for each project are as indicated in the table below.
Refer to Table 22-2.If (1) the first vote pits "school" against "bike lane," and (2) the second vote pits "skate park" against the winner of the first vote,what is the outcome
A)"School" wins the first vote and "school" wins the second vote, so they build a school.
B)"School" wins the first vote and "skate park" wins the second vote, so they build a skate park.
C)"Bike lane" wins the first vote and "bike lane" wins the second vote, so they build a bike lane.
D)"Bike lane" wins the first vote and "skate park" wins the second vote, so they build a skate park.
Voters are deciding how they will spend the City of Elmongary's budget surplus.They have enough money to build one of three projects: build a school, build a skate park, or build a bike lane for commuters.They agree that they will have two pairwise votes to determine how to spend their budget, with the majority determining the outcome on each vote.The first, second, and third choices for each project are as indicated in the table below.

Refer to Table 22-2.If (1) the first vote pits "school" against "bike lane," and (2) the second vote pits "skate park" against the winner of the first vote,what is the outcome
A)"School" wins the first vote and "school" wins the second vote, so they build a school.
B)"School" wins the first vote and "skate park" wins the second vote, so they build a skate park.
C)"Bike lane" wins the first vote and "bike lane" wins the second vote, so they build a bike lane.
D)"Bike lane" wins the first vote and "skate park" wins the second vote, so they build a skate park.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
In his 1951 book Social Choice and Individual Values,what does Kenneth Arrow use the term "unanimity" to mean
A)A beats B only if everyone prefers A to B.
B)If everyone prefers A to B, then A beats B.
C)He uses it to mean the same thing as transitivity.
D)Everyone who is eligible to vote must vote; otherwise, the outcome is invalid.
A)A beats B only if everyone prefers A to B.
B)If everyone prefers A to B, then A beats B.
C)He uses it to mean the same thing as transitivity.
D)Everyone who is eligible to vote must vote; otherwise, the outcome is invalid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
In polls that rank sports teams (giving 1 point for last place,2 points for second to last,and so on),what count is often used
A)a Condorcet count
B)a Borda count
C)an Arrow count
D)a median voter count
A)a Condorcet count
B)a Borda count
C)an Arrow count
D)a median voter count

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
The statement that political platforms compete for the middle refers directly to the result established by which proposition
A)the Arrow impossibility theorem
B)the Condorcet paradox
C)the median voter theorem
D)the Borda mechanism
A)the Arrow impossibility theorem
B)the Condorcet paradox
C)the median voter theorem
D)the Borda mechanism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The Borda count fails to satisfy which of Kenneth Arrow's properties of a perfect voting system
A)no dictator
B)unanimity
C)transitivity
D)independence of irrelevant alternatives
A)no dictator
B)unanimity
C)transitivity
D)independence of irrelevant alternatives

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
When each voter has a most-preferred outcome in terms of the expenditure on a particular government program,which outcome will majority rule produce
A)the outcome preferred by the mean (average) voter
B)the outcome preferred by the median voter
C)the outcome that causes the ruling political party to increase its power
D)the outcome preferred by the poorest voter
A)the outcome preferred by the mean (average) voter
B)the outcome preferred by the median voter
C)the outcome that causes the ruling political party to increase its power
D)the outcome preferred by the poorest voter

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Assume there are nine voters in a certain small town and let x = preferred number of dollars spent per person per month on garbage collection.For Voters 1,2,and 3,x = $10; for Voter 4,x = $15; for Voter 5,x = $18; and for Voters 6,7,8 and 9,x = $20.Who is a median voter
A)Voter 3
B)Voter 4
C)Voter 5
D)Voter 6
A)Voter 3
B)Voter 4
C)Voter 5
D)Voter 6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
As an alternative to pairwise majority voting,each voter could be asked to rank the possible outcomes,giving 1 point to her lowest choice,2 points to her second-lowest choice,3 points to her third-lowest choice,and so on.What is this voting method called
A)a median voter theorem
B)a pairwise minority vote
C)a Borda count
D)an Arrow count
A)a median voter theorem
B)a pairwise minority vote
C)a Borda count
D)an Arrow count

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Table 22-2
Voters are deciding how they will spend the City of Elmongary's budget surplus.They have enough money to build one of three projects: build a school, build a skate park, or build a bike lane for commuters.They agree that they will have two pairwise votes to determine how to spend their budget, with the majority determining the outcome on each vote.The first, second, and third choices for each project are as indicated in the table below.
Refer to Table 22-2.If the citizens of Elmongary use a Borda count,rather than pairwise majority voting,to decide what to build,what will they build
A)a new school
B)a new skate park
C)a new bike lane
D)nothing
Voters are deciding how they will spend the City of Elmongary's budget surplus.They have enough money to build one of three projects: build a school, build a skate park, or build a bike lane for commuters.They agree that they will have two pairwise votes to determine how to spend their budget, with the majority determining the outcome on each vote.The first, second, and third choices for each project are as indicated in the table below.

Refer to Table 22-2.If the citizens of Elmongary use a Borda count,rather than pairwise majority voting,to decide what to build,what will they build
A)a new school
B)a new skate park
C)a new bike lane
D)nothing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Table 22-2
Voters are deciding how they will spend the City of Elmongary's budget surplus.They have enough money to build one of three projects: build a school, build a skate park, or build a bike lane for commuters.They agree that they will have two pairwise votes to determine how to spend their budget, with the majority determining the outcome on each vote.The first, second, and third choices for each project are as indicated in the table below.
Refer to Table 22-2.If (1) the first vote pits "school" against "skate park," and (2) the second vote pits "bike lane" against the winner of the first vote,what is the outcome
A)"School" wins the first vote and "school" wins the second vote, so they build a school.
B)"School" wins the first vote and "bike lane" wins the second vote, so they build a bike lane.
C)"Skate park" wins the first vote and "skate park" wins the second vote, so they build a skate park.
D)"Skate park" wins the first vote and "bike lane" wins the second vote, so they build a bike lane.
Voters are deciding how they will spend the City of Elmongary's budget surplus.They have enough money to build one of three projects: build a school, build a skate park, or build a bike lane for commuters.They agree that they will have two pairwise votes to determine how to spend their budget, with the majority determining the outcome on each vote.The first, second, and third choices for each project are as indicated in the table below.

Refer to Table 22-2.If (1) the first vote pits "school" against "skate park," and (2) the second vote pits "bike lane" against the winner of the first vote,what is the outcome
A)"School" wins the first vote and "school" wins the second vote, so they build a school.
B)"School" wins the first vote and "bike lane" wins the second vote, so they build a bike lane.
C)"Skate park" wins the first vote and "skate park" wins the second vote, so they build a skate park.
D)"Skate park" wins the first vote and "bike lane" wins the second vote, so they build a bike lane.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Majority rule will produce the outcome most preferred by the median voter,as demonstrated by which proposition
A)the Arrow impossibility theorem
B)the Condorcet paradox
C)the pairwise voting proposition
D)the median voter theorem
A)the Arrow impossibility theorem
B)the Condorcet paradox
C)the pairwise voting proposition
D)the median voter theorem

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Arrow's impossibility theorem is disturbing in the sense that it proves which of the following
A)No voting system is perfect.
B)Only a dictator can produce a desirable social outcome.
C)The preferences of the wealthy should be given more weight than the preferences of the poor.
D)The centuries-old Condorcet paradox was not a paradox after all.
A)No voting system is perfect.
B)Only a dictator can produce a desirable social outcome.
C)The preferences of the wealthy should be given more weight than the preferences of the poor.
D)The centuries-old Condorcet paradox was not a paradox after all.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Table 22-2
Voters are deciding how they will spend the City of Elmongary's budget surplus.They have enough money to build one of three projects: build a school, build a skate park, or build a bike lane for commuters.They agree that they will have two pairwise votes to determine how to spend their budget, with the majority determining the outcome on each vote.The first, second, and third choices for each project are as indicated in the table below.
Refer to Table 22-2.What is a possible outcome in a pairwise election
A)In a pairwise election, "bike lane" beats "skate park."
B)In a pairwise election, "school" beats "bike lane."
C)In a pairwise election, "skate park" beats "bike lane."
D)In a pairwise election, "skate park" beats "school."
Voters are deciding how they will spend the City of Elmongary's budget surplus.They have enough money to build one of three projects: build a school, build a skate park, or build a bike lane for commuters.They agree that they will have two pairwise votes to determine how to spend their budget, with the majority determining the outcome on each vote.The first, second, and third choices for each project are as indicated in the table below.

Refer to Table 22-2.What is a possible outcome in a pairwise election
A)In a pairwise election, "bike lane" beats "skate park."
B)In a pairwise election, "school" beats "bike lane."
C)In a pairwise election, "skate park" beats "bike lane."
D)In a pairwise election, "skate park" beats "school."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
One property of Kenneth Arrow's perfect voting system is that the ranking between any two outcomes A and B should not depend on whether some third outcome C is also available.What did Arrow call this property
A)transitivity
B)unanimity
C)independence of irrelevant alternatives
D)individual preference
A)transitivity
B)unanimity
C)independence of irrelevant alternatives
D)individual preference

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



