Deck 9: A: Price Takers and the Competitive Process
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/237
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 9: A: Price Takers and the Competitive Process
1
Which of the following is a primary difference between price takers and price searchers that operate in markets with low barriers to entry?
A)The price searchers will maximize profits in the short run, but price takers will not. Price takers can only maximize profits in the long run.
B)The price searchers will have to search for the price, while price takers will have to take the price determined in the market.
C)The price searchers will be able to earn profit in the long run, but the price takers will not.
D)The price searchers may be able to earn profit in the short run, but the price takers will not be able to do so.
A)The price searchers will maximize profits in the short run, but price takers will not. Price takers can only maximize profits in the long run.
B)The price searchers will have to search for the price, while price takers will have to take the price determined in the market.
C)The price searchers will be able to earn profit in the long run, but the price takers will not.
D)The price searchers may be able to earn profit in the short run, but the price takers will not be able to do so.
B
2
When the price of a product rises, the increase in quantity supplied will generally be greater in the long run than the short run because
A)producers maximize short-run, not long-run, profits.
B)over time, new firms will enter the industry and old firms will expand their operations in response to the price increase.
C)consumers are less resistant to higher prices in the long run than in the short run because they have fewer options in the long run.
D)consumer income will expand in the long run, causing resource prices to rise, which will induce producers to increase output.
A)producers maximize short-run, not long-run, profits.
B)over time, new firms will enter the industry and old firms will expand their operations in response to the price increase.
C)consumers are less resistant to higher prices in the long run than in the short run because they have fewer options in the long run.
D)consumer income will expand in the long run, causing resource prices to rise, which will induce producers to increase output.
B
3
A firm that is a price taker can
A)substantially change the market price of its product by changing its level of production.
B)sell all of its output at the market price.
C)sell some of its output at a price higher than the market price.
D)decide what price to charge for its product.
A)substantially change the market price of its product by changing its level of production.
B)sell all of its output at the market price.
C)sell some of its output at a price higher than the market price.
D)decide what price to charge for its product.
B
4
In price-taker markets, individual firms have no control over price. Therefore, the firm's marginal revenue curve is
A)a downward-sloping curve.
B)indeterminate.
C)constant at the market price of the product.
D)precisely the same as the firm's total revenue curve.
A)a downward-sloping curve.
B)indeterminate.
C)constant at the market price of the product.
D)precisely the same as the firm's total revenue curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 237 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
In competitive price-taker markets, firms
A)can sell all of their output at the market price.
B)produce differentiated products.
C)can influence the market price by altering their output level.
D)are large relative to the total market.
A)can sell all of their output at the market price.
B)produce differentiated products.
C)can influence the market price by altering their output level.
D)are large relative to the total market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 237 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Firms that can choose what price they will charge for their product and can increase the number of units sold by reducing price are called
A)price searchers.
B)price leaders.
C)purely competitive.
D)price takers.
A)price searchers.
B)price leaders.
C)purely competitive.
D)price takers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 237 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following business decisions will be made by firms that are price searchers but not those that are price takers?
A)What combination of resources should be used to produce a product that is supplied?
B)What output should be produced?
C)What price should be charged?
D)What legal structure of business organization (for example, a proprietorship or corporation) should be used?
A)What combination of resources should be used to produce a product that is supplied?
B)What output should be produced?
C)What price should be charged?
D)What legal structure of business organization (for example, a proprietorship or corporation) should be used?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 237 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
When market conditions in a price-taker market are such that firms cannot cover their production costs,
A)the firms will suffer long-run economic losses.
B)the firms will suffer short-run economic losses that will be exactly offset by long-run economic profits.
C)some firms will go out of business, causing prices to rise until the remaining firms can cover their production costs.
D)all firms will go out of business, since consumers will not pay prices that enable firms to cover their production costs.
A)the firms will suffer long-run economic losses.
B)the firms will suffer short-run economic losses that will be exactly offset by long-run economic profits.
C)some firms will go out of business, causing prices to rise until the remaining firms can cover their production costs.
D)all firms will go out of business, since consumers will not pay prices that enable firms to cover their production costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 237 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Competition as a dynamic process implies that the individual firms in an industry
A)face a perfectly elastic demand curve.
B)utilize a variety of techniques, such as product, style, and price, to win the dollar votes of consumers.
C)produce a homogeneous product.
D)cooperate, attempting to establish a price and output structure so each firm can survive and continue to serve the consumer.
A)face a perfectly elastic demand curve.
B)utilize a variety of techniques, such as product, style, and price, to win the dollar votes of consumers.
C)produce a homogeneous product.
D)cooperate, attempting to establish a price and output structure so each firm can survive and continue to serve the consumer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 237 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The main difference between a firm that is a price searcher and a firm that is a price taker is that a
A)price searcher produces products that are identical to its competitors' products.
B)price taker can decide what price to charge for its product.
C)price searcher cannot decide what price to charge for its product.
D)price searcher will still be able to sell some of its product if it increases its price.
A)price searcher produces products that are identical to its competitors' products.
B)price taker can decide what price to charge for its product.
C)price searcher cannot decide what price to charge for its product.
D)price searcher will still be able to sell some of its product if it increases its price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 237 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A firm in a price-taker market
A)must take the price that is determined in the market.
B)must reduce its price if it wants to sell a larger quantity.
C)must be large relative to the total market.
D)can exert a major influence on the market price.
A)must take the price that is determined in the market.
B)must reduce its price if it wants to sell a larger quantity.
C)must be large relative to the total market.
D)can exert a major influence on the market price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 237 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
If marginal revenue exceeds marginal cost, a price-taker firm should
A)expand output.
B)reduce output.
C)lower its price.
D)do both a and c.
A)expand output.
B)reduce output.
C)lower its price.
D)do both a and c.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 237 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Suppose a restaurant that is highly profitable during the summer months is unable to cover its total cost during the winter months. If it wants to maximize profits, the restaurant should
A)shut down during the winter, even if it is able to cover its variable costs during that period.
B)continue operating during the winter months if it is able to cover its variable costs.
C)go a out of business immediately; losses should never be tolerated.
D)lower its prices during the summer months.
A)shut down during the winter, even if it is able to cover its variable costs during that period.
B)continue operating during the winter months if it is able to cover its variable costs.
C)go a out of business immediately; losses should never be tolerated.
D)lower its prices during the summer months.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 237 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
When we say that a firm is a price taker, we are indicating that the
A)firm takes the price established in the market then tries to increase that price through advertising.
B)firm can change output levels without having any significant effect on price.
C)demand curve faced by the firm is perfectly inelastic.
D)firm will have to take a lower price if it wants to increase the number of units that it sells.
A)firm takes the price established in the market then tries to increase that price through advertising.
B)firm can change output levels without having any significant effect on price.
C)demand curve faced by the firm is perfectly inelastic.
D)firm will have to take a lower price if it wants to increase the number of units that it sells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 237 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
If occupational safety laws were changed so that firms no longer had to take expensive steps to meet regulatory requirements, we would expect
A)the demand for the products of this industry to increase.
B)the market price of the products of this industry to decrease in the short run but not in the long run.
C)the firms in the industry to make long-run economic profit.
D)competition to force producers to pass the lower production costs on to consumers in the long run.
A)the demand for the products of this industry to increase.
B)the market price of the products of this industry to decrease in the short run but not in the long run.
C)the firms in the industry to make long-run economic profit.
D)competition to force producers to pass the lower production costs on to consumers in the long run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 237 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Firms that are price takers
A)are small relative to the total market.
B)produce products that are different than their competitors.
C)can sell only a portion of their output at the market price.
D)have downward-sloping demand curves.
A)are small relative to the total market.
B)produce products that are different than their competitors.
C)can sell only a portion of their output at the market price.
D)have downward-sloping demand curves.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 237 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following is the best example of a business firm operating in a competitive price-taker market?
A)TGIFriday's, a restaurant chain that operates in numerous locations
B)a bookstore located a few blocks from a major university
C)Ford Motor company, a major manufacturer of automobiles that operates in numerous markets throughout the world
D)an Indiana hog farmer that raises pigs
A)TGIFriday's, a restaurant chain that operates in numerous locations
B)a bookstore located a few blocks from a major university
C)Ford Motor company, a major manufacturer of automobiles that operates in numerous markets throughout the world
D)an Indiana hog farmer that raises pigs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 237 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following is a primary difference between price searchers and price takers?
A)Price searchers maximize profits, but price takers do not.
B)Price searchers have to cut their price to sell additional output, but price takers do not.
C)The market demand for goods produced by price searchers is downward sloping, while the market demand for goods produced by price takers is horizontal.
D)Profit-maximizing price searchers will expand output to the quantity where marginal revenue equals marginal cost, but price takers will not.
A)Price searchers maximize profits, but price takers do not.
B)Price searchers have to cut their price to sell additional output, but price takers do not.
C)The market demand for goods produced by price searchers is downward sloping, while the market demand for goods produced by price takers is horizontal.
D)Profit-maximizing price searchers will expand output to the quantity where marginal revenue equals marginal cost, but price takers will not.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 237 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following is the best example of a business firm operating in a competitive price-taker market?
A)a Midwest farmer producing beef cattle
B)a Laundromat located a few blocks from a major university
C)a pizza parlor located in a major metropolitan area
D)a small brewery supplying a local brand of beer
E)Wal-Mart, a large retailer that competes in many markets
A)a Midwest farmer producing beef cattle
B)a Laundromat located a few blocks from a major university
C)a pizza parlor located in a major metropolitan area
D)a small brewery supplying a local brand of beer
E)Wal-Mart, a large retailer that competes in many markets

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 237 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
When firms in a price-taker market are temporarily able to charge prices that exceed their production costs,
A)the firms will earn long-run economic profit.
B)additional firms will be attracted into the market until price falls to the level of per-unit production cost.
C)the firms will earn short-run economic profits that will be offset by long-run economic losses.
D)the existing firms must be colluding or rigging the market, otherwise, they would be unable to charge such high prices.
A)the firms will earn long-run economic profit.
B)additional firms will be attracted into the market until price falls to the level of per-unit production cost.
C)the firms will earn short-run economic profits that will be offset by long-run economic losses.
D)the existing firms must be colluding or rigging the market, otherwise, they would be unable to charge such high prices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 237 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
When a law is passed that requires businesses to obtain permission from government officials in order to enter a market, this is an example of
A)price-control legislation.
B)a barrier to entry
C)antitrust legislation.
D)the invisible hand principle.
A)price-control legislation.
B)a barrier to entry
C)antitrust legislation.
D)the invisible hand principle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 237 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
If a price-taker firm selling in a competitive market offers its product at a higher price than others, it will
A)increase its profits.
B)maintain its profit base if the demand for the product is inelastic.
C)be able to expand output.
D)not be able to sell any output.
A)increase its profits.
B)maintain its profit base if the demand for the product is inelastic.
C)be able to expand output.
D)not be able to sell any output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 237 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following is a reason to study the decisions of price takers?
A)While there are not many price-taker markets, these few markets dominate the economy.
B)The decision making of both price searchers and price takers is identical.
C)The price-taker model enhances our knowledge of competition as a dynamic process.
D)Price takers are the most common type of business in the real world.
A)While there are not many price-taker markets, these few markets dominate the economy.
B)The decision making of both price searchers and price takers is identical.
C)The price-taker model enhances our knowledge of competition as a dynamic process.
D)Price takers are the most common type of business in the real world.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 237 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Competition as a dynamic process implies that individual firms in a market
A)seek to utilize a variety of techniques, such as product, style, and convenience of location, to win the dollar vote of consumers, but they never use price to compete.
B)use price competition as well as other forms of competition to gain the dollar votes of consumers.
C)produce a homogeneous product.
D)cooperate, attempting to establish a price and output structure so each firm can survive and continue to serve the consumer.
A)seek to utilize a variety of techniques, such as product, style, and convenience of location, to win the dollar vote of consumers, but they never use price to compete.
B)use price competition as well as other forms of competition to gain the dollar votes of consumers.
C)produce a homogeneous product.
D)cooperate, attempting to establish a price and output structure so each firm can survive and continue to serve the consumer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 237 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Harry Smith sells wheat in a price-taker market. With regard to Smith's price and output choices, which of the following is true?
A)Smith will constantly attempt to increase the price of his product so he can increase his total revenue.
B)Since the price of his product is dictated by the market, Smith will not have an incentive to control per-unit cost.
C)Since the price of his product is dictated by the market, Smith has no production decisions to make.
D)It would be senseless for Smith to try to increase sales by lowering the price of his product.
A)Smith will constantly attempt to increase the price of his product so he can increase his total revenue.
B)Since the price of his product is dictated by the market, Smith will not have an incentive to control per-unit cost.
C)Since the price of his product is dictated by the market, Smith has no production decisions to make.
D)It would be senseless for Smith to try to increase sales by lowering the price of his product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 237 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which of the following is a necessary condition for the presence of competition in a market?
A)government regulations that assure firms will make excess profits
B)suppliers that offer a homogeneous product
C)a price that always equals per-unit production costs
D)low barriers to entry into the market
A)government regulations that assure firms will make excess profits
B)suppliers that offer a homogeneous product
C)a price that always equals per-unit production costs
D)low barriers to entry into the market

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 237 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
In short-run equilibrium, a competitive price-taker firm
A)may earn a profit or a loss.
B)always earns a profit.
C)never earns a profit.
D)earns a profit only if the firm has no fixed cost.
A)may earn a profit or a loss.
B)always earns a profit.
C)never earns a profit.
D)earns a profit only if the firm has no fixed cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 237 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Several states require cosmetologists to undertake 1,500 hours or more of training in order to obtain a license to provide hair styling or braiding services. This is an example of
A)antitrust legislation.
B)government action that promotes competition.
C)a barrier to entry
D)the legal structure that is required for the operation of price-taker markets.
A)antitrust legislation.
B)government action that promotes competition.
C)a barrier to entry
D)the legal structure that is required for the operation of price-taker markets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 237 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
"Competitive price-taker markets" and "purely competitive markets" are
A)similar, but competition is stronger in the latter.
B)similar, but products are differentiated in the former.
C)merely alternative names for the same concept.
D)terms used to designate markets in which the firms confront a downward sloping demand curve.
A)similar, but competition is stronger in the latter.
B)similar, but products are differentiated in the former.
C)merely alternative names for the same concept.
D)terms used to designate markets in which the firms confront a downward sloping demand curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 237 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following best explains why price in competitive price-taker markets will tend to be driven to the minimum per-unit cost?
A)homogeneous products.
B)few sellers.
C)firms face downward-sloping demand curves.
D)free entry and exit.
A)homogeneous products.
B)few sellers.
C)firms face downward-sloping demand curves.
D)free entry and exit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 237 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
If a single firm in a price-taker market lowers its price below the market equilibrium price,
A)it will get a larger share of the market.
B)it will lose revenue without increasing the quantity it can sell.
C)other firms will lower their prices.
D)other firms will be driven out of the industry.
A)it will get a larger share of the market.
B)it will lose revenue without increasing the quantity it can sell.
C)other firms will lower their prices.
D)other firms will be driven out of the industry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 237 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The dynamic process of competition
A)provides profit-seeking sellers with little incentive to heed consumer preferences.
B)was shown by Adam Smith to be a major source of economic inefficiency.
C)provides consumers with alternative suppliers and thus a mechanism with which they can discipline sellers.
D)will permit business decision makers to earn long-run economic profit unless they are regulated by government officials.
A)provides profit-seeking sellers with little incentive to heed consumer preferences.
B)was shown by Adam Smith to be a major source of economic inefficiency.
C)provides consumers with alternative suppliers and thus a mechanism with which they can discipline sellers.
D)will permit business decision makers to earn long-run economic profit unless they are regulated by government officials.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 237 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
In the absence of government regulation, which of the following products would most closely fit the competitive price-taker (purely competitive) model?
A)beer because there are many consumers
B)cigarettes because there are several alternative brands that look similar
C)milk because there are many dairy farmers producing a virtually identical product
D)automobiles because there are substantial economies of scale in production
A)beer because there are many consumers
B)cigarettes because there are several alternative brands that look similar
C)milk because there are many dairy farmers producing a virtually identical product
D)automobiles because there are substantial economies of scale in production

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 237 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Competitive price-taker markets are characterized by
A)firms that all produce the same product.
B)a small number of firms in the market.
C)firms that are large relative to the size of the market.
D)widespread use of advertising as a competitive weapon.
A)firms that all produce the same product.
B)a small number of firms in the market.
C)firms that are large relative to the size of the market.
D)widespread use of advertising as a competitive weapon.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 237 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The dynamic process of competition
A)is hindered by the self-interest of business decision makers.
B)puts the profit motive of sellers to work for buyers.
C)conflicts with the interest of consumers when businesses pursue profit rather than the public interest.
D)will permit business decision makers to earn long-run economic profit unless they are regulated by government.
A)is hindered by the self-interest of business decision makers.
B)puts the profit motive of sellers to work for buyers.
C)conflicts with the interest of consumers when businesses pursue profit rather than the public interest.
D)will permit business decision makers to earn long-run economic profit unless they are regulated by government.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 237 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
In a competitive price-taker market,
A)many other sellers are offering a product that is essentially identical.
B)consumers have more influence over the market price than producers do.
C)government intervention prevents firms from influencing price.
D)producers agree not to change the price.
A)many other sellers are offering a product that is essentially identical.
B)consumers have more influence over the market price than producers do.
C)government intervention prevents firms from influencing price.
D)producers agree not to change the price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 237 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which of the following is always true in competitive price-taker markets?
A)There are more sellers than buyers.
B)Barriers to entry into the market are low.
C)The products of firms in the industry are differentiated.
D)The firms never earn economic profit.
A)There are more sellers than buyers.
B)Barriers to entry into the market are low.
C)The products of firms in the industry are differentiated.
D)The firms never earn economic profit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 237 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which of the following is a characteristic of a competitive price-taker market?
A)Profit maximizing firms in the market will expand output until price equals average variable cost.
B)The market demand curve for the product is a horizontal line.
C)There are many firms in the market, each producing a small share of total market output.
D)The product produced by each of the firms is differentiated.
A)Profit maximizing firms in the market will expand output until price equals average variable cost.
B)The market demand curve for the product is a horizontal line.
C)There are many firms in the market, each producing a small share of total market output.
D)The product produced by each of the firms is differentiated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 237 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which of the following best explains why a firm in a competitive price-taker market must take the price determined in the market?
A)The short-run average total costs of firms that are price takers will be constant.
B)If a price taker increased its price, consumers would buy from other suppliers.
C)Firms in a price-taker market will have to advertise in order to increase sales.
D)There are no good substitutes for the product supplied by a firm that is a price taker.
A)The short-run average total costs of firms that are price takers will be constant.
B)If a price taker increased its price, consumers would buy from other suppliers.
C)Firms in a price-taker market will have to advertise in order to increase sales.
D)There are no good substitutes for the product supplied by a firm that is a price taker.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 237 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
In a competitive price-taker market, the actions of any single buyer or seller will
A)have a negligible impact on the market price.
B)have little effect on overall production but will ultimately change final product price.
C)cause a noticeable change in overall production and a change in final product price.
D)adversely affect the profitability of more than one firm in the market.
A)have a negligible impact on the market price.
B)have little effect on overall production but will ultimately change final product price.
C)cause a noticeable change in overall production and a change in final product price.
D)adversely affect the profitability of more than one firm in the market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 237 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Scenario 9-1
Assume a certain competitive price-taker firm is producing Q = 1,000 units of output. At Q = 1,000, the firm's marginal cost equals $15 and its average total cost equals $11. The firm sells its output for $12 per unit.
Refer to Scenario 9-1. At Q = 1,000, the firm's profit amounts to
A)-$200.
B)$1,000.
C)$3,000.
D)$4,000.
Assume a certain competitive price-taker firm is producing Q = 1,000 units of output. At Q = 1,000, the firm's marginal cost equals $15 and its average total cost equals $11. The firm sells its output for $12 per unit.
Refer to Scenario 9-1. At Q = 1,000, the firm's profit amounts to
A)-$200.
B)$1,000.
C)$3,000.
D)$4,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 237 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
In competitive price-taker markets, if one firm raises its price,
A)others will follow
B)that firm will increase its revenues
C)that firm will lose revenues because other firms will not follow
D)all consumers will be adversely affected
E)the market demand curve will shift
A)others will follow
B)that firm will increase its revenues
C)that firm will lose revenues because other firms will not follow
D)all consumers will be adversely affected
E)the market demand curve will shift

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 237 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The Wheeler Wheat Farm sells wheat to a grain broker in Seattle, Washington. Since the market for wheat is generally considered to be competitive, the Wheeler Wheat Farm maximizes its profit by choosing
A)to produce the quantity at which average variable cost is minimized.
B)to produce the quantity at which average fixed cost is minimized.
C)to sell its wheat at a price where marginal cost is equal to average total cost.
D)the quantity at which the farm's marginal cost of production is equal to the market price.
A)to produce the quantity at which average variable cost is minimized.
B)to produce the quantity at which average fixed cost is minimized.
C)to sell its wheat at a price where marginal cost is equal to average total cost.
D)the quantity at which the farm's marginal cost of production is equal to the market price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 237 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Refer to Scenario 9-1. At Q = 999, the firm's total cost amounts to
A)$10,985.
B)$10,990.
C)$10,995.
D)$10,999.
A)$10,985.
B)$10,990.
C)$10,995.
D)$10,999.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 237 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Which of the following statements best reflects the production decision of a profit-maximizing firm in a competitive price-taker market when price falls below the minimum of average variable cost?
A)The firm will continue to produce to attempt to pay fixed costs.
B)The firm will stop production to minimize its losses.
C)The firm will stop production as soon as it is able to pay its sunk costs.
D)The firm will continue to produce in the short run but will likely exit the market in the long run.
A)The firm will continue to produce to attempt to pay fixed costs.
B)The firm will stop production to minimize its losses.
C)The firm will stop production as soon as it is able to pay its sunk costs.
D)The firm will continue to produce in the short run but will likely exit the market in the long run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 237 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The intersection of a firm's marginal revenue and marginal cost curves determines the level of output at which
A)total revenue is equal to variable cost.
B)total revenue is equal to fixed cost.
C)total revenue is equal to total cost.
D)profit is maximized.
A)total revenue is equal to variable cost.
B)total revenue is equal to fixed cost.
C)total revenue is equal to total cost.
D)profit is maximized.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 237 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
If a competitive price-taker firm is currently producing a level of output at which marginal revenue exceeds marginal cost, then
A)a one-unit increase in output will increase the firm's profit.
B)a one-unit decrease in output will increase the firm's profit.
C)total revenue exceeds total cost.
D)total cost exceeds total revenue.
A)a one-unit increase in output will increase the firm's profit.
B)a one-unit decrease in output will increase the firm's profit.
C)total revenue exceeds total cost.
D)total cost exceeds total revenue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 237 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Suppose Thelma and Louise both sell fried green tomatoes in a competitive price-taker market. If Louise increases her output,
A)Thelma must reduce output
B)the price Thelma can charge falls
C)the price Thelma can charge rises
D)the price Thelma can charge is unaffected
E)Thelma's profits must fall
A)Thelma must reduce output
B)the price Thelma can charge falls
C)the price Thelma can charge rises
D)the price Thelma can charge is unaffected
E)Thelma's profits must fall

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 237 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Claude's Copper Clappers sells clappers for $40 each in a competitive price-taker market. At its present rate of output, Claude's marginal cost is $40, average variable cost is $45, and average total cost is $60. Claude should
A)increase output
B)reduce output but not to zero
C)maintain the present rate of output
D)shut down
E)raise the price
A)increase output
B)reduce output but not to zero
C)maintain the present rate of output
D)shut down
E)raise the price

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 237 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Claude's Copper Clappers sells clappers for $40 each in a competitive price-taker market. At its present rate of output, Claude's marginal cost is $39, average variable cost is $25, and average total cost is $45. To improve his profit/loss situation, Claude should
A)increase output
B)reduce output but not to zero
C)maintain the present rate of output
D)shut down
E)raise the price
A)increase output
B)reduce output but not to zero
C)maintain the present rate of output
D)shut down
E)raise the price

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 237 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Competitive price-taker firms respond to changing market conditions by varying their
A)price
B)output
C)market share
D)information
E)advertising campaigns
A)price
B)output
C)market share
D)information
E)advertising campaigns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 237 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Farmer Fanny sells her crops in a competitive price-taker market. If she produces 500 bushels for total revenue of $2,500 and if harvesting the 501st bushel would raise her total cost from $2,500 to $2,505, her
A)revenue will increase by $10 if she harvests the 501st bushel
B)revenue will fall by $5 if she harvests the 501st bushel
C)average fixed cost will rise if she harvests the 501st bushel
D)profit will fall by $10 if she harvests the 501st bushel
E)profit will remain unchanged if she harvests the 501st bushel
A)revenue will increase by $10 if she harvests the 501st bushel
B)revenue will fall by $5 if she harvests the 501st bushel
C)average fixed cost will rise if she harvests the 501st bushel
D)profit will fall by $10 if she harvests the 501st bushel
E)profit will remain unchanged if she harvests the 501st bushel

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 237 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Refer to Scenario 9-1. To maximize its profit, the firm should
A)increase its output.
B)continue to produce 1,000 units.
C)decrease its output, but continue to produce.
D)shut down.
A)increase its output.
B)continue to produce 1,000 units.
C)decrease its output, but continue to produce.
D)shut down.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 237 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Suppose the equilibrium price in a competitive price-taker market is $10 and a firm in the industry charges $9. Which of the following is true?
A)The firm will not be able to sell any output.
B)The firm will sell less output than its competitors.
C)The firm will make more profit than it could at the $10 price.
D)The firm will make less profit than it could at the $10 price.
A)The firm will not be able to sell any output.
B)The firm will sell less output than its competitors.
C)The firm will make more profit than it could at the $10 price.
D)The firm will make less profit than it could at the $10 price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 237 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
For a certain firm, the 100th unit of output that the firm produces has marginal revenue equal to $10 and a marginal cost of $7. It follows that
A)the production of the 100th unit of output increases the firm's profit by $3.
B)the production of the 100th unit of output increases the firm's average total cost by $7.
C)the firm's profit-maximizing level of output is less than 100 units.
D)the production of the 110th unit of output must increase the firm's profit by less than $3.
A)the production of the 100th unit of output increases the firm's profit by $3.
B)the production of the 100th unit of output increases the firm's average total cost by $7.
C)the firm's profit-maximizing level of output is less than 100 units.
D)the production of the 110th unit of output must increase the firm's profit by less than $3.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 237 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
A firm in competitive price-taker market is maximizing profit at Q = 3,000. Then its fixed cost increases. The profit-maximizing output is now
A)greater than 3,000 and profit decreases
B)less than 3,000 and profit decreases
C)greater than 3,000 and profit is unchanged
D)equal to 3,000 and profit decreases
E)equal to 3,000 and profit increases
A)greater than 3,000 and profit decreases
B)less than 3,000 and profit decreases
C)greater than 3,000 and profit is unchanged
D)equal to 3,000 and profit decreases
E)equal to 3,000 and profit increases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 237 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Refer to Scenario 9-1. At Q = 999, the firm's profit amounts to
A)$993.
B)$997.
C)$1,003.
D)$1,007.
A)$993.
B)$997.
C)$1,003.
D)$1,007.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 237 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
When price is greater than marginal cost for a firm in a competitive market,
A)marginal cost must be falling.
B)the firm must be minimizing its losses.
C)there are opportunities to increase profit by increasing production.
D)the firm should decrease output to maximize profit.
A)marginal cost must be falling.
B)the firm must be minimizing its losses.
C)there are opportunities to increase profit by increasing production.
D)the firm should decrease output to maximize profit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 237 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Profit-maximizing firms enter a competitive market when, for existing firms in that market,
A)total revenue exceeds fixed costs.
B)total revenue exceeds total variable costs.
C)average total cost exceeds average revenue.
D)price exceeds average total cost.
A)total revenue exceeds fixed costs.
B)total revenue exceeds total variable costs.
C)average total cost exceeds average revenue.
D)price exceeds average total cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 237 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
If a competitive price-taker firm is currently producing a level of output at which marginal cost exceeds marginal revenue, then
A)average revenue exceeds marginal cost.
B)the firm is earning a positive profit.
C)a one-unit decrease in output would increase the firm's profit.
D)All of the above are correct.
A)average revenue exceeds marginal cost.
B)the firm is earning a positive profit.
C)a one-unit decrease in output would increase the firm's profit.
D)All of the above are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 237 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
If the demand and marginal revenue curves confronting firm A are identical, it may be concluded that firm A is a
A)monopolistic competitor.
B)price taker.
C)price searcher.
D)monopolist.
A)monopolistic competitor.
B)price taker.
C)price searcher.
D)monopolist.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 237 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Within the framework of the price-taker model, a price taker will always produce a quantity of output that
A)minimizes the per-unit cost of production.
B)is expected to provide the largest possible total revenue.
C)maximizes total revenue minus total cost.
D)brings average total cost and price into equality.
A)minimizes the per-unit cost of production.
B)is expected to provide the largest possible total revenue.
C)maximizes total revenue minus total cost.
D)brings average total cost and price into equality.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 237 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
If a firm competing in a price-taker market seeks to maximize profit, the firm should
A)increase output whenever marginal cost is less than average total cost.
B)increase output whenever marginal revenue is less than marginal cost.
C)choose the output where per-unit profit is greatest.
D)increase output whenever price exceeds marginal cost.
A)increase output whenever marginal cost is less than average total cost.
B)increase output whenever marginal revenue is less than marginal cost.
C)choose the output where per-unit profit is greatest.
D)increase output whenever price exceeds marginal cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 237 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
The marginal revenue of a price taker is
A)equal to price.
B)less than price.
C)more than price.
D)unrelated to price.
A)equal to price.
B)less than price.
C)more than price.
D)unrelated to price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 237 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
The usefulness of the price-taker model requires that the firm's decision makers
A)act to maximize their total revenue and fully understand marginal costs and marginal revenues.
B)be able to draw accurate marginal cost and marginal revenue curves.
C)place the social interest of the economy above their individual self interests.
D)seek to maximize the profits of the firm.
A)act to maximize their total revenue and fully understand marginal costs and marginal revenues.
B)be able to draw accurate marginal cost and marginal revenue curves.
C)place the social interest of the economy above their individual self interests.
D)seek to maximize the profits of the firm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 237 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
A profit-maximizing firm will continue to expand output
A)as long as the revenues from the production and sale of an additional unit exceeds the average costs of the unit.
B)until the average cost of producing the good or service is at a minimum.
C)as long as the revenues from the production and sale of an additional unit exceeds the marginal cost of the unit.
D)until the marginal cost of producing a good or service is at a minimum.
A)as long as the revenues from the production and sale of an additional unit exceeds the average costs of the unit.
B)until the average cost of producing the good or service is at a minimum.
C)as long as the revenues from the production and sale of an additional unit exceeds the marginal cost of the unit.
D)until the marginal cost of producing a good or service is at a minimum.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 237 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
In general, firms will produce at a rate of output such that marginal revenue equals marginal cost because this output rate will
A)bring total revenue into equality with total cost.
B)maximize the difference between the revenue received from the last unit and the cost incurred in producing the last unit.
C)result in the lowest possible average total costs of production.
D)maximize the firm's profit.
A)bring total revenue into equality with total cost.
B)maximize the difference between the revenue received from the last unit and the cost incurred in producing the last unit.
C)result in the lowest possible average total costs of production.
D)maximize the firm's profit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 237 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Table 9-1
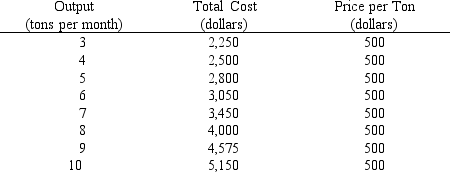
Refer to Table 9-1. If the market price is $500, what is the maximum economic profit per month the Tuckers can earn?
A)-$50
B)zero
C)$50
D)$100
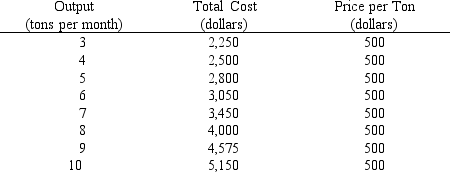
Refer to Table 9-1. If the market price is $500, what is the maximum economic profit per month the Tuckers can earn?
A)-$50
B)zero
C)$50
D)$100

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 237 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Table 9-1
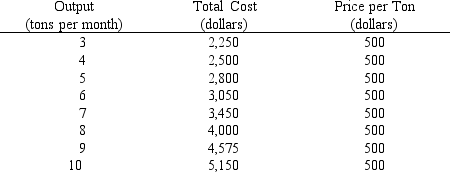
Refer to Table 9-1. If the Tuckers are profit maximizers, how many tomatoes should they produce when the market price is $500 per ton?
A)6
B)7
C)8
D)9
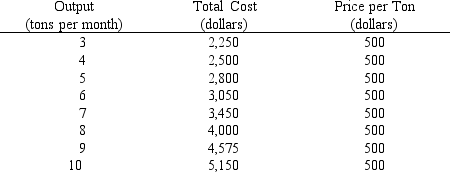
Refer to Table 9-1. If the Tuckers are profit maximizers, how many tomatoes should they produce when the market price is $500 per ton?
A)6
B)7
C)8
D)9

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 237 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Table 9-1
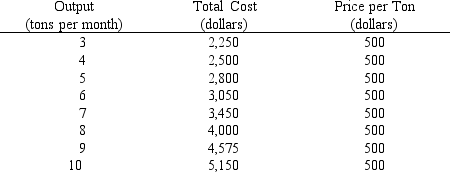
Refer to Table 9-1. If the market price of tomatoes rose to $570 per ton, how many tons per month would the Tuckers produce if they were maximizing profit?
A)6
B)7
C)8
D)9
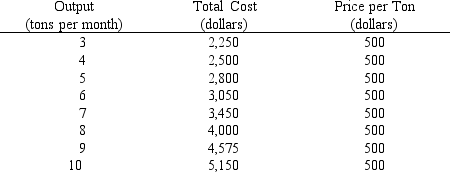
Refer to Table 9-1. If the market price of tomatoes rose to $570 per ton, how many tons per month would the Tuckers produce if they were maximizing profit?
A)6
B)7
C)8
D)9

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 237 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
If a firm is a price taker and wants to earn as much profit as possible, it should expand output
A)to the quantity at which marginal cost is minimized.
B)as long as marginal cost is less than price.
C)to the quantity at which average total costs are minimized.
D)to try to sell all the output it can produce so that its average fixed costs will be minimized.
A)to the quantity at which marginal cost is minimized.
B)as long as marginal cost is less than price.
C)to the quantity at which average total costs are minimized.
D)to try to sell all the output it can produce so that its average fixed costs will be minimized.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 237 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
In the price-taker model, what impact does the individual firm have on the price of its product?
A)The firm must accept the price determined in the market if it is going to sell its product.
B)The firm may raise or lower its price to a small extent, but sales revenues will tend to be the same regardless of price.
C)The firm may raise its price and, thereby, increase its revenues.
D)The firm may raise or lower its price to a considerable extent, but sales revenues will tend to be the same regardless of price.
A)The firm must accept the price determined in the market if it is going to sell its product.
B)The firm may raise or lower its price to a small extent, but sales revenues will tend to be the same regardless of price.
C)The firm may raise its price and, thereby, increase its revenues.
D)The firm may raise or lower its price to a considerable extent, but sales revenues will tend to be the same regardless of price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 237 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
The schedule of total costs for a chair-manufacturing firm is presented in the table below. If the market price of chairs is $100, which of the output levels should this price-taker firm produce in order to maximize profit? 
A)10
B)20
C)30
D)40

A)10
B)20
C)30
D)40

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 237 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
When the marginal cost of a price-taker firm is more than the market price of its product, the firm should
A)expand output.
B)reduce output.
C)maintain output.
D)charge more than the market price.
A)expand output.
B)reduce output.
C)maintain output.
D)charge more than the market price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 237 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
When a firm is operating in a price-taker market, marginal revenue will always equal
A)average total cost.
B)one minus the elasticity of the market demand curve.
C)total revenue.
D)price.
A)average total cost.
B)one minus the elasticity of the market demand curve.
C)total revenue.
D)price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 237 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
The schedule of total costs for a chair-manufacturing firm is presented in the table below. If the market price of chairs is $100, which output should this price-taker firm produce to maximize profit? 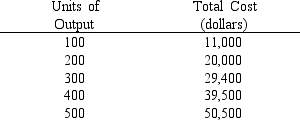
A)200
B)300
C)400
D)500

A)200
B)300
C)400
D)500

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 237 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
The schedule of total costs for a table-manufacturing company is presented in the table below. The firm sells its product in a price-taker market at $120 per table. What is the maximum monthly profit (or minimum loss) that the firm will be able to earn? 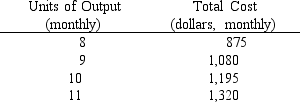
A)$15 loss
B)zero
C)$5 profit
D)$10 profit

A)$15 loss
B)zero
C)$5 profit
D)$10 profit

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 237 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
In the competitive price-taker model, individual firms exert no effect on the market price. Therefore, the firm's marginal revenue curve is
A)indeterminate.
B)an upward-sloping curve.
C)a downward-sloping curve.
D)the same as the firm's demand curve.
A)indeterminate.
B)an upward-sloping curve.
C)a downward-sloping curve.
D)the same as the firm's demand curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 237 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
A profit-maximizing entrepreneur will produce and sell an additional unit of output as long as
A)it lowers the firm's unit costs.
B)it lowers the firm's marginal cost.
C)it adds more to revenue than it adds to cost.
D)there is additional plant capacity to produce.
A)it lowers the firm's unit costs.
B)it lowers the firm's marginal cost.
C)it adds more to revenue than it adds to cost.
D)there is additional plant capacity to produce.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 237 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
A price-taker firm will tend to expand its output so long as its
A)marginal revenue is positive.
B)marginal revenue is greater than the market price.
C)marginal revenue is less than the market price.
D)marginal cost is less than the market price.
A)marginal revenue is positive.
B)marginal revenue is greater than the market price.
C)marginal revenue is less than the market price.
D)marginal cost is less than the market price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 237 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



