Deck 7: Global Markets in Action
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/138
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 7: Global Markets in Action
1
Which of the following statements about Canada's international trade in 2013 is correct?
A)The value of Canada's imports exceeded the value of Canada's exports.
B)The value of Canada's exports was about 45 percent of the value of total expenditure in Canada.
C)Canada imported only goods.
D)Canada was the world's second largest trader.
E)Canada exported only goods.
A)The value of Canada's imports exceeded the value of Canada's exports.
B)The value of Canada's exports was about 45 percent of the value of total expenditure in Canada.
C)Canada imported only goods.
D)Canada was the world's second largest trader.
E)Canada exported only goods.
A
2
Compared to the situation before international trade, after Canada imports a good, production in Canada ________ and consumption in Canada ________.
A)increases; increases
B)increases; decreases
C)decreases; increases
D)decreases; decreases
E)does not change; increases
A)increases; increases
B)increases; decreases
C)decreases; increases
D)decreases; decreases
E)does not change; increases
C
3
Suppose that the world price of eggs is $1 a dozen, Canada does not trade internationally, and the equilibrium price of eggs in Canada is $3 a dozen.Then Canada begins to trade internationally. Canadian farmers produce ________ eggs.Canada ________ eggs.
A)more; imports
B)more; exports
C)less; exports
D)less; imports
E)the same quantity of; imports
A)more; imports
B)more; exports
C)less; exports
D)less; imports
E)the same quantity of; imports
D
4
A country
A)imports those goods in which it has a comparative advantage.
B)exports those goods in which it has a comparative advantage.
C)imports goods produced in countries with lower wage rates.
D)exports goods produced by domestic industries with low wages relative to its trading partners.
E)exports those goods in which it has an absolute advantage.
A)imports those goods in which it has a comparative advantage.
B)exports those goods in which it has a comparative advantage.
C)imports goods produced in countries with lower wage rates.
D)exports goods produced by domestic industries with low wages relative to its trading partners.
E)exports those goods in which it has an absolute advantage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Goods and services that we buy from other countries are our
A)balance of payments.
B)exports.
C)imports.
D)terms of trade.
E)comparative goods and services.
A)balance of payments.
B)exports.
C)imports.
D)terms of trade.
E)comparative goods and services.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The fundamental force that drives international trade is
A)comparative advantage.
B)absolute advantage.
C)a countries' desire to increase their trade surplus.
D)cheap labour in countries like China and India.
E)unemployment of factors of production.
A)comparative advantage.
B)absolute advantage.
C)a countries' desire to increase their trade surplus.
D)cheap labour in countries like China and India.
E)unemployment of factors of production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The fundamental force that drives international trade is
A)absolute advantage.
B)importation duties.
C)the advantage of execution.
D)export advantage.
E)comparative advantage.
A)absolute advantage.
B)importation duties.
C)the advantage of execution.
D)export advantage.
E)comparative advantage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Canada has a comparative advantage in producing hardwood if the Canadian price of hardwood before international trade is ________ the world price.
A)equal to
B)greater than
C)not comparable to
D)at least double
E)less than
A)equal to
B)greater than
C)not comparable to
D)at least double
E)less than

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Canada has a comparative advantage in producing airplanes if
A)it can produce them at a lower dollar cost than another country.
B)it can produce a larger quantity than another country.
C)it has a larger quantity of skilled workers than another country.
D)it can produce them at a higher opportunity cost than another country.
E)it can produce them at a lower opportunity cost than another country.
A)it can produce them at a lower dollar cost than another country.
B)it can produce a larger quantity than another country.
C)it has a larger quantity of skilled workers than another country.
D)it can produce them at a higher opportunity cost than another country.
E)it can produce them at a lower opportunity cost than another country.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Prior to international trade, if the price of good X is lower in country A than in country B,
A)country B has an absolute advantage in the production of good X.
B)country B has a comparative advantage in the production of good X.
C)country A has an absolute advantage in the production of good X.
D)country A has a comparative advantage in the production of good X.
E)country B should stop producing good X.
A)country B has an absolute advantage in the production of good X.
B)country B has a comparative advantage in the production of good X.
C)country A has an absolute advantage in the production of good X.
D)country A has a comparative advantage in the production of good X.
E)country B should stop producing good X.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Choose the correct statement.
A)Exports include goods and services.
B)Imports include goods but not services.
C)Imports include services but not goods.
D)Exports include goods but not services.
E)Exports include services but not goods.
A)Exports include goods and services.
B)Imports include goods but not services.
C)Imports include services but not goods.
D)Exports include goods but not services.
E)Exports include services but not goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Table 7.1.1
Glazeland's Doughnut Market

Table 7.1.1 shows Glazeland's doughnut market before international trade.Glazeland opens up to international trade.If the world price is $0.60 a doughnut then Glazeland will produce ________ doughnuts and will ________ doughnuts.
A)2 million; import 3 million
B)4 million; import 1 million
C)4 million; export 1 million
D)5 million; import 3 million
E)5 million; export 3 million
Glazeland's Doughnut Market

Table 7.1.1 shows Glazeland's doughnut market before international trade.Glazeland opens up to international trade.If the world price is $0.60 a doughnut then Glazeland will produce ________ doughnuts and will ________ doughnuts.
A)2 million; import 3 million
B)4 million; import 1 million
C)4 million; export 1 million
D)5 million; import 3 million
E)5 million; export 3 million

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
In one year, Brazil exported more than 1.8 billion kilograms of coffee to the rest of the world.We can conclude that
A)Brazil has comparative advantage in coffee production.
B)Brazil has an absolute advantage in coffee production.
C)the rest of the world has a comparative advantage in coffee production.
D)the rest of the world has an absolute advantage in coffee production.
E)Brazil's government has placed a tariff on coffee.
A)Brazil has comparative advantage in coffee production.
B)Brazil has an absolute advantage in coffee production.
C)the rest of the world has a comparative advantage in coffee production.
D)the rest of the world has an absolute advantage in coffee production.
E)Brazil's government has placed a tariff on coffee.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Canada produces both lumber and wine.Canada exports lumber and imports wine.The rest of the world imports Canadian lumber and exports wine to Canada.Canada has a comparative advantage in producing ________.The rest of the world has a comparative advantage in producing ________.
A)lumber; wine
B)wine; lumber
C)wine; wine
D)lumber; lumber
E)a good other than lumber or wine; wine
A)lumber; wine
B)wine; lumber
C)wine; wine
D)lumber; lumber
E)a good other than lumber or wine; wine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Compared to the situation before international trade, after Canada exports a good, production in Canada ________ and consumption in Canada ________.
A)increases; increases
B)increases; decreases
C)decreases; increases
D)decreases; decreases
E)increases; does not change
A)increases; increases
B)increases; decreases
C)decreases; increases
D)decreases; decreases
E)increases; does not change

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Canada produces both lumber and wine.Canada exports lumber and imports wine.The rest of the world imports Canadian lumber and exports wine to Canada.If Canada did not trade with the rest of the world, then the equilibrium price of lumber would be ________ in Canada than the rest of the world, and the equilibrium price of wine would be ________ in Canada than the rest of the world.
A)lower; higher
B)higher; lower
C)higher; higher
D)lower; lower
E)the same or lower; the same or higher
A)lower; higher
B)higher; lower
C)higher; higher
D)lower; lower
E)the same or lower; the same or higher

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Table 7.1.1
Glazeland's Doughnut Market

Table 7.1.1 shows Glazeland's doughnut market before international trade.Glazeland opens up to international trade.If the world price is $0.40 a doughnut then Glazeland will produce ________ doughnuts and will ________ doughnuts.
A)3 million; import 3 million
B)3 million; export 3 million
C)4 million; import 1 million
D)4 million; export 1 million
E)6 million; export 3 million
Glazeland's Doughnut Market

Table 7.1.1 shows Glazeland's doughnut market before international trade.Glazeland opens up to international trade.If the world price is $0.40 a doughnut then Glazeland will produce ________ doughnuts and will ________ doughnuts.
A)3 million; import 3 million
B)3 million; export 3 million
C)4 million; import 1 million
D)4 million; export 1 million
E)6 million; export 3 million

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following is a Canadian service export?
A)a Canadian buys dinner while travelling in Switzerland
B)a Swiss buys dinner while travelling in Canada
C)a Canadian buys a clock made in Switzerland
D)a Swiss buys a computer made in Canada
E)a Canadian buys a Canadian computer in Switzerland
A)a Canadian buys dinner while travelling in Switzerland
B)a Swiss buys dinner while travelling in Canada
C)a Canadian buys a clock made in Switzerland
D)a Swiss buys a computer made in Canada
E)a Canadian buys a Canadian computer in Switzerland

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The goods and services we sell to people in other countries are our
A)tariffs.
B)quotas.
C)exports.
D)imports.
E)investment goods and services.
A)tariffs.
B)quotas.
C)exports.
D)imports.
E)investment goods and services.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Suppose that the world price of eggs is $1 a dozen, Canada does not trade internationally, and the equilibrium price of eggs in Canada is $3 a dozen.Then Canada begins to trade internationally. The price of eggs in Canada ________.Canadian consumers buy ________ eggs.
A)rises; more
B)rises; less
C)falls; more
D)falls; less
E)rises; the same quantity of
A)rises; more
B)rises; less
C)falls; more
D)falls; less
E)rises; the same quantity of

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Refer to the figure below to answer the following questions.
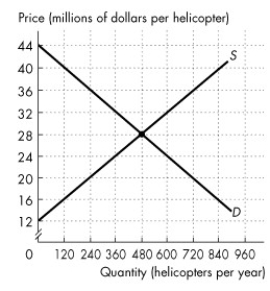
Figure 7.2.2
The figure shows the market for helicopters in Canada, where D is the domestic demand curve and S is the domestic supply curve. Canada trades helicopters with the rest of the world at a price of $36 million per helicopter.
In Figure 7.2.2, with international trade, Canadian firms buy ________ helicopters per year.
A)240
B)480
C)720
D)360
E)600

Figure 7.2.2
The figure shows the market for helicopters in Canada, where D is the domestic demand curve and S is the domestic supply curve. Canada trades helicopters with the rest of the world at a price of $36 million per helicopter.
In Figure 7.2.2, with international trade, Canadian firms buy ________ helicopters per year.
A)240
B)480
C)720
D)360
E)600

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Consider a country that sells some of its goods as exports.Who does NOT benefit?
A)domestic consumers
B)domestic producers
C)workers in the domestic industry
D)foreign consumers
E)everyone benefits
A)domestic consumers
B)domestic producers
C)workers in the domestic industry
D)foreign consumers
E)everyone benefits

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Refer to the figure below to answer the following questions.
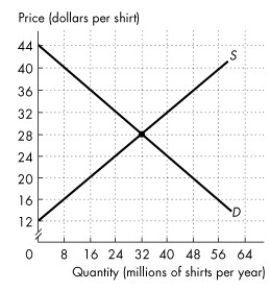
Figure 7.2.1
The figure shows the market for shirts in Canada, where D is the domestic demand curve and S is the domestic supply curve. The world price is $20 per shirt.
In Figure 7.2.1, international trade ________ producer surplus in Canada by ________.
A)increases; $320 million
B)decreases; $192 million
C)increases; $192 million
D)decreases; $320 million
E)decreases; $256 million

Figure 7.2.1
The figure shows the market for shirts in Canada, where D is the domestic demand curve and S is the domestic supply curve. The world price is $20 per shirt.
In Figure 7.2.1, international trade ________ producer surplus in Canada by ________.
A)increases; $320 million
B)decreases; $192 million
C)increases; $192 million
D)decreases; $320 million
E)decreases; $256 million

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
A country opens up to trade and becomes an exporter of a good.Consumer surplus ________ and producer surplus ________.
A)decreases; increases
B)increases; decreases
C)remains unchanged; decreases
D)remains unchanged; increases
E)decreases; decreases
A)decreases; increases
B)increases; decreases
C)remains unchanged; decreases
D)remains unchanged; increases
E)decreases; decreases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
A country opens up to trade and becomes an importer of some good.Consumer surplus ________, and producer surplus ________.
A)increases; decreases
B)decreases; decreases
C)decreases; increases
D)increases; increases
E)increases; does not change
A)increases; decreases
B)decreases; decreases
C)decreases; increases
D)increases; increases
E)increases; does not change

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Refer to the figure below to answer the following questions.

Figure 7.2.1
The figure shows the market for shirts in Canada, where D is the domestic demand curve and S is the domestic supply curve. The world price is $20 per shirt.
In Figure 7.2.1, with international trade, Canada ________ million shirts per year.
A)imports 32
B)imports 48
C)exports 16
D)exports 32
E)imports 16

Figure 7.2.1
The figure shows the market for shirts in Canada, where D is the domestic demand curve and S is the domestic supply curve. The world price is $20 per shirt.
In Figure 7.2.1, with international trade, Canada ________ million shirts per year.
A)imports 32
B)imports 48
C)exports 16
D)exports 32
E)imports 16

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Refer to the figure below to answer the following questions.

Figure 7.2.1
The figure shows the market for shirts in Canada, where D is the domestic demand curve and S is the domestic supply curve. The world price is $20 per shirt.
In Figure 7.2.1, international trade ________ consumer surplus in Canada by ________.
A)increases; $320 million
B)decreases; $192 million
C)increases; $192 million
D)decreases; $320 million
E)increases; $576 million

Figure 7.2.1
The figure shows the market for shirts in Canada, where D is the domestic demand curve and S is the domestic supply curve. The world price is $20 per shirt.
In Figure 7.2.1, international trade ________ consumer surplus in Canada by ________.
A)increases; $320 million
B)decreases; $192 million
C)increases; $192 million
D)decreases; $320 million
E)increases; $576 million

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Table 7.2.1
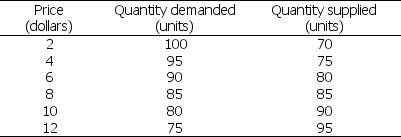
Table 7.2.1 shows a country's demand and supply schedules.Based on Table 7.2.1, suppose the world price is $4 a unit.The country
A)imports 20 units.
B)exports 20 units.
C)imports 10 units.
D)exports 10 units.
E)imports 30 units.

Table 7.2.1 shows a country's demand and supply schedules.Based on Table 7.2.1, suppose the world price is $4 a unit.The country
A)imports 20 units.
B)exports 20 units.
C)imports 10 units.
D)exports 10 units.
E)imports 30 units.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Refer to the figure below to answer the following questions.

Figure 7.2.2
The figure shows the market for helicopters in Canada, where D is the domestic demand curve and S is the domestic supply curve. Canada trades helicopters with the rest of the world at a price of $36 million per helicopter.
In Figure 7.2.2, with international trade, ________ helicopters per year are produced in Canada.
A)360
B)480
C)720
D)240
E)600

Figure 7.2.2
The figure shows the market for helicopters in Canada, where D is the domestic demand curve and S is the domestic supply curve. Canada trades helicopters with the rest of the world at a price of $36 million per helicopter.
In Figure 7.2.2, with international trade, ________ helicopters per year are produced in Canada.
A)360
B)480
C)720
D)240
E)600

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Table 7.2.2
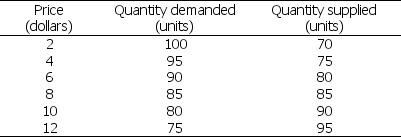
Table 7.2.2 shows a country's demand and supply schedules.Based on Table 7.2.2, at what world price would the country export?
A)at only $8 a unit
B)any price below $8
C)a price of $6 a unit
D)a price of $4 a unit
E)any price above $8 a unit

Table 7.2.2 shows a country's demand and supply schedules.Based on Table 7.2.2, at what world price would the country export?
A)at only $8 a unit
B)any price below $8
C)a price of $6 a unit
D)a price of $4 a unit
E)any price above $8 a unit

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Refer to the figure below to answer the following questions.

Figure 7.2.2
The figure shows the market for helicopters in Canada, where D is the domestic demand curve and S is the domestic supply curve. Canada trades helicopters with the rest of the world at a price of $36 million per helicopter.
In Figure 7.2.2, international trade ________ consumer surplus in Canada by ________.
A)decreases; $2.88 billion
B)decreases; $1.92 billion
C)increases; $2.88 billion
D)increases; $4.8 billion
E)increases; $1.92 billion

Figure 7.2.2
The figure shows the market for helicopters in Canada, where D is the domestic demand curve and S is the domestic supply curve. Canada trades helicopters with the rest of the world at a price of $36 million per helicopter.
In Figure 7.2.2, international trade ________ consumer surplus in Canada by ________.
A)decreases; $2.88 billion
B)decreases; $1.92 billion
C)increases; $2.88 billion
D)increases; $4.8 billion
E)increases; $1.92 billion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Refer to the figure below to answer the following questions.

Figure 7.2.2
The figure shows the market for helicopters in Canada, where D is the domestic demand curve and S is the domestic supply curve. Canada trades helicopters with the rest of the world at a price of $36 million per helicopter.
In Figure 7.2.2, Canada ________ helicopters per year.
A)exports 480
B)exports 720
C)imports 480
D)imports 240
E)exports 240

Figure 7.2.2
The figure shows the market for helicopters in Canada, where D is the domestic demand curve and S is the domestic supply curve. Canada trades helicopters with the rest of the world at a price of $36 million per helicopter.
In Figure 7.2.2, Canada ________ helicopters per year.
A)exports 480
B)exports 720
C)imports 480
D)imports 240
E)exports 240

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
A country opens up to trade.In an export industry, surplus has been redistributed from
A)consumers to producers.
B)producers to consumers.
C)producers to government.
D)government to consumers.
E)government to producers.
A)consumers to producers.
B)producers to consumers.
C)producers to government.
D)government to consumers.
E)government to producers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
A country opens up to trade.In an import industry, surplus has been redistributed from
A)producers to consumers.
B)consumers to producers.
C)government to consumers.
D)producers to government.
E)government to producers.
A)producers to consumers.
B)consumers to producers.
C)government to consumers.
D)producers to government.
E)government to producers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Refer to the figure below to answer the following questions.

Figure 7.2.1
The figure shows the market for shirts in Canada, where D is the domestic demand curve and S is the domestic supply curve. The world price is $20 per shirt.
In Figure 7.2.1, international trade ________ total surplus in Canada by ________.
A)increases; $128 million
B)decreases; $192 million
C)increases; $320 million
D)decreases; $256 million
E)decreases; $128 million

Figure 7.2.1
The figure shows the market for shirts in Canada, where D is the domestic demand curve and S is the domestic supply curve. The world price is $20 per shirt.
In Figure 7.2.1, international trade ________ total surplus in Canada by ________.
A)increases; $128 million
B)decreases; $192 million
C)increases; $320 million
D)decreases; $256 million
E)decreases; $128 million

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Refer to the figure below to answer the following questions.

Figure 7.2.1
The figure shows the market for shirts in Canada, where D is the domestic demand curve and S is the domestic supply curve. The world price is $20 per shirt.
In Figure 7.2.1, with international trade, Canadians buy ________ million shirts per year.
A)48
B)32
C)16
D)24
E)56

Figure 7.2.1
The figure shows the market for shirts in Canada, where D is the domestic demand curve and S is the domestic supply curve. The world price is $20 per shirt.
In Figure 7.2.1, with international trade, Canadians buy ________ million shirts per year.
A)48
B)32
C)16
D)24
E)56

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Table 7.2.1

Table 7.2.1 shows a country's demand and supply schedules.Based on Table 7.2.1, at what world price would the country import?
A)at exactly $8 a unit
B)any price above $8 a unit
C)a price of $10 a unit
D)a price of $20 a unit
E)a price below $8 a unit

Table 7.2.1 shows a country's demand and supply schedules.Based on Table 7.2.1, at what world price would the country import?
A)at exactly $8 a unit
B)any price above $8 a unit
C)a price of $10 a unit
D)a price of $20 a unit
E)a price below $8 a unit

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
A market is open to international trade.At the world price, the quantity demanded is 150 units and the quantity supplied is 200 units.This country will
A)import 50 units.
B)export 200 units.
C)import 150 units.
D)import 200 units.
E)export 50 units.
A)import 50 units.
B)export 200 units.
C)import 150 units.
D)import 200 units.
E)export 50 units.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Who benefits from imports?
A)domestic consumers
B)domestic producers
C)foreign consumers
D)domestic workers in the industry
E)everyone benefits
A)domestic consumers
B)domestic producers
C)foreign consumers
D)domestic workers in the industry
E)everyone benefits

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Refer to the figure below to answer the following questions.

Figure 7.2.1
The figure shows the market for shirts in Canada, where D is the domestic demand curve and S is the domestic supply curve. The world price is $20 per shirt.
In Figure 7.2.1, with international trade, ________ million shirts per year are produced in Canada.
A)48
B)32
C)20
D)56
E)16

Figure 7.2.1
The figure shows the market for shirts in Canada, where D is the domestic demand curve and S is the domestic supply curve. The world price is $20 per shirt.
In Figure 7.2.1, with international trade, ________ million shirts per year are produced in Canada.
A)48
B)32
C)20
D)56
E)16

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
A country moves from a situation of no trade to a situation where it exports a good.Which of the following does not occur in the market for this good in the exporting country?
A)Deadweight loss increases.
B)Consumer surplus decreases.
C)Producer surplus increases.
D)Workers in the domestic industry gain.
E)Total surplus increases.
A)Deadweight loss increases.
B)Consumer surplus decreases.
C)Producer surplus increases.
D)Workers in the domestic industry gain.
E)Total surplus increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
In one year, Brazil exported more than 1.8 billion kilograms of coffee to the rest of the world.We can conclude that
A)Brazil's coffee producers lose from this trade.
B)coffee consumers in the rest of the world lose from this trade.
C)Brazil's coffee consumers lose from this trade.
D)coffee producers in the rest of the world gain from this trade.
E)the deadweight loss in Brazil's coffee market is large and growing.
A)Brazil's coffee producers lose from this trade.
B)coffee consumers in the rest of the world lose from this trade.
C)Brazil's coffee consumers lose from this trade.
D)coffee producers in the rest of the world gain from this trade.
E)the deadweight loss in Brazil's coffee market is large and growing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Refer to the figure below to answer the following question.
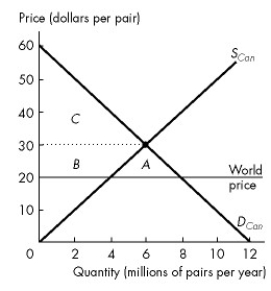
Figure 7.2.3
Refer to Figure 7.2.3.The graph shows the market for shoes in Canada.The world price of a pair of shoes is $20.With free international trade, Canadian consumer surplus ________ and Canadian producer surplus ________.
A)increases by area A + B; decreases by area B
B)increases by area B; decreases by area B
C)increases by area A; decreases by area B
D)decreases by area A + B; increases by area B
E)decreases by area B; increases by area A

Figure 7.2.3
Refer to Figure 7.2.3.The graph shows the market for shoes in Canada.The world price of a pair of shoes is $20.With free international trade, Canadian consumer surplus ________ and Canadian producer surplus ________.
A)increases by area A + B; decreases by area B
B)increases by area B; decreases by area B
C)increases by area A; decreases by area B
D)decreases by area A + B; increases by area B
E)decreases by area B; increases by area A

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
When Canada exports a good, Canada's consumer surplus ________ and Canada's total surplus ________.
A)increases; increases
B)increases; decreases
C)decreases; increases
D)decreases; decreases
E)decreases and Canada's producer surplus increases; does not change
A)increases; increases
B)increases; decreases
C)decreases; increases
D)decreases; decreases
E)decreases and Canada's producer surplus increases; does not change

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
If Canada imposes a tariff on imported cars,
A)Canada's demand curve for cars shifts rightward.
B)Canada's demand curve for cars shifts leftward.
C)Canada's supply curve of cars shifts rightward.
D)Canada's supply curve of cars shifts leftward.
E)the price of a car in Canada rises but neither Canada's demand curve nor Canada's supply curve shifts.
A)Canada's demand curve for cars shifts rightward.
B)Canada's demand curve for cars shifts leftward.
C)Canada's supply curve of cars shifts rightward.
D)Canada's supply curve of cars shifts leftward.
E)the price of a car in Canada rises but neither Canada's demand curve nor Canada's supply curve shifts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Canada exports athletic coaching services and imports computer tech support.The price of athletic coaching services in Canada is ________ with international trade than without international trade.As a result of trade in athletic coaching services, the Canadian producer surplus from athletic coaching services ________.
A)higher; does not change
B)lower; increases
C)lower; decreases
D)higher; increases
E)higher; decreases
A)higher; does not change
B)lower; increases
C)lower; decreases
D)higher; increases
E)higher; decreases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Tariffs and import quotas differ in that
A)one is a form of trade restriction, while the other is not.
B)one is a tax, while the other is a limit.
C)one is imposed by the government, while the other is imposed by the private sector.
D)one is legal, while the other is not.
E)one increases imports, while the other decreases imports.
A)one is a form of trade restriction, while the other is not.
B)one is a tax, while the other is a limit.
C)one is imposed by the government, while the other is imposed by the private sector.
D)one is legal, while the other is not.
E)one increases imports, while the other decreases imports.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Canada's producer surplus ________ when Canada imports a good, and Canada's producer surplus ________ when Canada exports a good.
A)increases; increases
B)increases; decreases
C)decreases; increases
D)decreases; decreases
E)does not change; does not change
A)increases; increases
B)increases; decreases
C)decreases; increases
D)decreases; decreases
E)does not change; does not change

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Refer to the figure below to answer the following question.
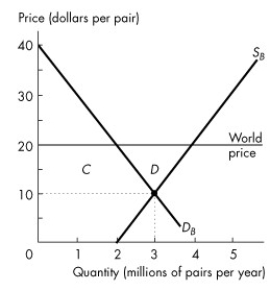
Figure 7.2.4
Refer to Figure 7.2.4.The graph shows the demand for shoes in Brazil, DB, the supply of shoes produced in Brazil, SB, and the market equilibrium in Brazil when it does not trade internationally.If the world price of a pair of shoes is $20 and Brazil opens up and trades internationally, producer surplus in Brazil ________ and consumer surplus in Brazil ________.
A)increases by area C + D; decreases by area C
B)increases by area C; decreases by area C and a deadweight loss equal to area D arises
C)increases by area D; decreases by area D
D)decreases by area C; increases by area C + D
E)decreases by area C + D; increases by area C

Figure 7.2.4
Refer to Figure 7.2.4.The graph shows the demand for shoes in Brazil, DB, the supply of shoes produced in Brazil, SB, and the market equilibrium in Brazil when it does not trade internationally.If the world price of a pair of shoes is $20 and Brazil opens up and trades internationally, producer surplus in Brazil ________ and consumer surplus in Brazil ________.
A)increases by area C + D; decreases by area C
B)increases by area C; decreases by area C and a deadweight loss equal to area D arises
C)increases by area D; decreases by area D
D)decreases by area C; increases by area C + D
E)decreases by area C + D; increases by area C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
International trade benefits the
A)exporting country but not the importing country.
B)importing country but not the exporting country.
C)government of the importing country.
D)government of the exporting country.
E)exporting country and the importing country.
A)exporting country but not the importing country.
B)importing country but not the exporting country.
C)government of the importing country.
D)government of the exporting country.
E)exporting country and the importing country.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
When Canada exports a good, the amount of the ________ in Canada's consumer surplus is ________ the amount of the increase in Canada's producer surplus.
A)increase; smaller than
B)increase; larger than
C)decrease; smaller than
D)decrease; equal to
E)decrease; larger than
A)increase; smaller than
B)increase; larger than
C)decrease; smaller than
D)decrease; equal to
E)decrease; larger than

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
A tariff is a tax that is imposed by the ________ country when an ________ good crosses its international boundary.
A)exporting; imported
B)importing; exported
C)exporting; exported
D)importing; imported
E)importing or exporting; imported or exported
A)exporting; imported
B)importing; exported
C)exporting; exported
D)importing; imported
E)importing or exporting; imported or exported

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Tariffs and import quotas both result in
A)lower levels of domestic production.
B)the domestic government gaining revenue.
C)lower levels of imports.
D)higher levels of domestic consumption.
E)the elimination of deadweight loss.
A)lower levels of domestic production.
B)the domestic government gaining revenue.
C)lower levels of imports.
D)higher levels of domestic consumption.
E)the elimination of deadweight loss.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
In a market that moves from a situation of no trade to a situation where a good is imported, in the importing country the price of the good ________, and producer surplus ________.
A)rises; increases
B)falls; decreases
C)does not change; increases
D)does not change; decreases
E)rises; decreases
A)rises; increases
B)falls; decreases
C)does not change; increases
D)does not change; decreases
E)rises; decreases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Refer to the figure below to answer the following questions.

Figure 7.2.2
The figure shows the market for helicopters in Canada, where D is the domestic demand curve and S is the domestic supply curve. Canada trades helicopters with the rest of the world at a price of $36 million per helicopter.
In Figure 7.2.2, international trade ________ total surplus in Canada by ________.
A)decreases; $2.56 billion
B)increases; $4.8 billion
C)decreases; $3.6 billion
D)decreases; $1.92 billion
E)increases; $1.92 billion

Figure 7.2.2
The figure shows the market for helicopters in Canada, where D is the domestic demand curve and S is the domestic supply curve. Canada trades helicopters with the rest of the world at a price of $36 million per helicopter.
In Figure 7.2.2, international trade ________ total surplus in Canada by ________.
A)decreases; $2.56 billion
B)increases; $4.8 billion
C)decreases; $3.6 billion
D)decreases; $1.92 billion
E)increases; $1.92 billion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
A tax that is imposed by the importing country when an imported good crosses its international boundary is called
A)an import quota.
B)dumping.
C)a voluntary export restraint.
D)a tariff.
E)a sales tax.
A)an import quota.
B)dumping.
C)a voluntary export restraint.
D)a tariff.
E)a sales tax.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Refer to the figure below to answer the following questions.

Figure 7.2.2
The figure shows the market for helicopters in Canada, where D is the domestic demand curve and S is the domestic supply curve. Canada trades helicopters with the rest of the world at a price of $36 million per helicopter.
In Figure 7.2.2, international trade ________ producer surplus in Canada by ________.
A)decreases; $2.88 billion
B)decreases; $1.92 billion
C)increases; $4.8 billion
D)increases; $3.6 billion
E)decreases; $4.8 billion

Figure 7.2.2
The figure shows the market for helicopters in Canada, where D is the domestic demand curve and S is the domestic supply curve. Canada trades helicopters with the rest of the world at a price of $36 million per helicopter.
In Figure 7.2.2, international trade ________ producer surplus in Canada by ________.
A)decreases; $2.88 billion
B)decreases; $1.92 billion
C)increases; $4.8 billion
D)increases; $3.6 billion
E)decreases; $4.8 billion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
A country moves from a situation of no trade to a situation where it imports a good.Which of the following does not occur in the market for this good in the importing country?
A)Deadweight loss decreases.
B)Consumer surplus increases.
C)Producer surplus decreases.
D)Workers in the domestic industry lose.
E)Total surplus increases.
A)Deadweight loss decreases.
B)Consumer surplus increases.
C)Producer surplus decreases.
D)Workers in the domestic industry lose.
E)Total surplus increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Canada exports athletic coaching services and imports computer tech support.The price of computer tech support in Canada is ________ with international trade than without international trade.As a result of trade in computer tech support, the Canadian producer surplus from computer tech support ________.
A)higher; increases
B)lower; decreases
C)lower; does not change
D)higher; decreases
E)lower; increases
A)higher; increases
B)lower; decreases
C)lower; does not change
D)higher; decreases
E)lower; increases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
In a market that moves from a situation of no trade to a situation where a good is exported, in the exporting country the price of the good ________, and producer surplus ________.
A)rises; increases
B)falls; decreases
C)does not change; increases
D)does not change; decreases
E)rises; decreases
A)rises; increases
B)falls; decreases
C)does not change; increases
D)does not change; decreases
E)rises; decreases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Reducing a tariff ________ the domestic production of the good and ________ the total domestic consumption of the good.
A)increases; increases
B)increases; decreases
C)decreases; increases
D)decreases; decreases
E)does not change; increases
A)increases; increases
B)increases; decreases
C)decreases; increases
D)decreases; decreases
E)does not change; increases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Refer to the figure below to answer the following questions.
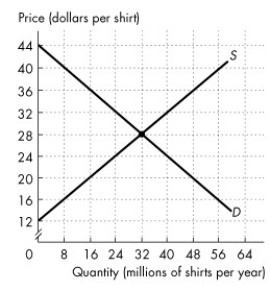
Figure 7.3.1
The figure shows the market for shirts in Canada, where D is the domestic demand curve and S is the domestic supply curve. The world price is $20 per shirt. Canada imposes a tariff on imported shirts of $4 per shirt.
Refer to Figure 7.3.1.With the tariff, Canadians buy ________ million shirts per year.
A)48
B)32
C)16
D)24
E)40

Figure 7.3.1
The figure shows the market for shirts in Canada, where D is the domestic demand curve and S is the domestic supply curve. The world price is $20 per shirt. Canada imposes a tariff on imported shirts of $4 per shirt.
Refer to Figure 7.3.1.With the tariff, Canadians buy ________ million shirts per year.
A)48
B)32
C)16
D)24
E)40

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Canada imports cars from Japan.If Canada imposes a tariff on cars imported from Japan, Canadian
A)consumers will lose and Japanese producers will gain.
B)tariff revenue will equal the loss of Canadian consumer surplus.
C)consumers will lose and Canadian producers will gain.
D)car manufacturers will gain revenue equal to the revenue lost by Japanese car manufacturers.
E)producers will lose and Japanese consumers will gain.
A)consumers will lose and Japanese producers will gain.
B)tariff revenue will equal the loss of Canadian consumer surplus.
C)consumers will lose and Canadian producers will gain.
D)car manufacturers will gain revenue equal to the revenue lost by Japanese car manufacturers.
E)producers will lose and Japanese consumers will gain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Increasing a tariff ________ the domestic quantity consumed of the good and ________ the domestic production of the good.
A)increases; increases
B)increases; decreases
C)decreases; increases
D)decreases; decreases
E)decreases; does not change
A)increases; increases
B)increases; decreases
C)decreases; increases
D)decreases; decreases
E)decreases; does not change

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
A tariff is imposed on imports.Surplus will be redistributed from
A)consumers to producers only.
B)consumers to government only.
C)government to producers only.
D)government to consumers only.
E)consumers to producers and government.
A)consumers to producers only.
B)consumers to government only.
C)government to producers only.
D)government to consumers only.
E)consumers to producers and government.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Tariffs
A)generate revenue for consumers.
B)generate revenue for the government.
C)encourage domestic consumers to buy more imports.
D)encourage domestic producers to produce less.
E)lower prices for consumers.
A)generate revenue for consumers.
B)generate revenue for the government.
C)encourage domestic consumers to buy more imports.
D)encourage domestic producers to produce less.
E)lower prices for consumers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The winners from a tariff on imports are
A)producers and government.
B)producers only.
C)consumers only.
D)consumers, producers, and government.
E)government only.
A)producers and government.
B)producers only.
C)consumers only.
D)consumers, producers, and government.
E)government only.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Which of the following statements concerning tariffs is NOT true?
A)A tariff results in a deadweight loss.
B)A tariff creates revenue for the government.
C)A tariff decreases international trade.
D)A tariff leaves the price of imports unchanged.
E)A tariff decreases consumer surplus.
A)A tariff results in a deadweight loss.
B)A tariff creates revenue for the government.
C)A tariff decreases international trade.
D)A tariff leaves the price of imports unchanged.
E)A tariff decreases consumer surplus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Refer to the figure below to answer the following questions.

Figure 7.3.1
The figure shows the market for shirts in Canada, where D is the domestic demand curve and S is the domestic supply curve. The world price is $20 per shirt. Canada imposes a tariff on imported shirts of $4 per shirt.
Refer to Figure 7.3.1.With the tariff, Canada imports ________ million shirts per year.
A)24
B)8
C)32
D)16
E)40

Figure 7.3.1
The figure shows the market for shirts in Canada, where D is the domestic demand curve and S is the domestic supply curve. The world price is $20 per shirt. Canada imposes a tariff on imported shirts of $4 per shirt.
Refer to Figure 7.3.1.With the tariff, Canada imports ________ million shirts per year.
A)24
B)8
C)32
D)16
E)40

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
If a country imposes a tariff on an imported good, the tariff ________ the price in the importing country and ________ the quantity of imports.
A)raises; increases
B)raises; does not change
C)lowers; does not change
D)lowers; increases
E)raises; decreases
A)raises; increases
B)raises; does not change
C)lowers; does not change
D)lowers; increases
E)raises; decreases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
A Canadian tariff imposed on items that can be produced more cheaply abroad
A)benefits Canadians by making these goods cheaper.
B)makes the goods more expensive in foreign markets.
C)creates a deadweight loss.
D)equalizes the cost of production between Canada and foreign producers.
E)increases total surplus.
A)benefits Canadians by making these goods cheaper.
B)makes the goods more expensive in foreign markets.
C)creates a deadweight loss.
D)equalizes the cost of production between Canada and foreign producers.
E)increases total surplus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Suppose the country of Mooland imposes tariffs on imported beef from the country of Aqualand.As a result of the tariffs, the
A)price of beef in Mooland falls.
B)quantity of beef exported by Mooland increases.
C)quantity of beef imported by Mooland decreases.
D)quantity of beef imported by Mooland increases.
E)price of beef in Mooland does not change.
A)price of beef in Mooland falls.
B)quantity of beef exported by Mooland increases.
C)quantity of beef imported by Mooland decreases.
D)quantity of beef imported by Mooland increases.
E)price of beef in Mooland does not change.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Refer to the figure below to answer the following questions.

Figure 7.3.1
The figure shows the market for shirts in Canada, where D is the domestic demand curve and S is the domestic supply curve. The world price is $20 per shirt. Canada imposes a tariff on imported shirts of $4 per shirt.
Refer to Figure 7.3.1.The tariff ________ Canada's imports of shirts by ________ million shirts per year.
A)decreases; 16
B)decreases; 8
C)increases; 8
D)increases; 4
E)increases; 16

Figure 7.3.1
The figure shows the market for shirts in Canada, where D is the domestic demand curve and S is the domestic supply curve. The world price is $20 per shirt. Canada imposes a tariff on imported shirts of $4 per shirt.
Refer to Figure 7.3.1.The tariff ________ Canada's imports of shirts by ________ million shirts per year.
A)decreases; 16
B)decreases; 8
C)increases; 8
D)increases; 4
E)increases; 16

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
A tariff is imposed on a good.This ________ producer surplus and ________ total surplus in importing country.
A)increases; does not change
B)increases; increases
C)decreases; increases
D)decreases; decreases
E)increases; decreases
A)increases; does not change
B)increases; increases
C)decreases; increases
D)decreases; decreases
E)increases; decreases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Refer to the figure below to answer the following questions.

Figure 7.3.1
The figure shows the market for shirts in Canada, where D is the domestic demand curve and S is the domestic supply curve. The world price is $20 per shirt. Canada imposes a tariff on imported shirts of $4 per shirt.
Refer to Figure 7.3.1.The Canadian government's revenue from the tariff is ________.
A)$64 million
B)$32 million
C)$128 million
D)$48 million
E)$480 million

Figure 7.3.1
The figure shows the market for shirts in Canada, where D is the domestic demand curve and S is the domestic supply curve. The world price is $20 per shirt. Canada imposes a tariff on imported shirts of $4 per shirt.
Refer to Figure 7.3.1.The Canadian government's revenue from the tariff is ________.
A)$64 million
B)$32 million
C)$128 million
D)$48 million
E)$480 million

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
If Canada imposes a tariff of $1 per imported shirt, the tariff results in all of the following except it
A)raises the price of a shirt paid by Canadian consumers.
B)benefits Canadian shirt producers.
C)decreases imports of shirts into Canada.
D)creates a deadweight loss.
E)increases total surplus.
A)raises the price of a shirt paid by Canadian consumers.
B)benefits Canadian shirt producers.
C)decreases imports of shirts into Canada.
D)creates a deadweight loss.
E)increases total surplus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
A tariff is imposed on a good.This ________ the quantity supplied and ________ the quantity demanded in the importing country.
A)increases; decreases
B)increases; does not change
C)increases; increases
D)decreases; decreases
E)decreases; increases
A)increases; decreases
B)increases; does not change
C)increases; increases
D)decreases; decreases
E)decreases; increases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
If Canada imposes a tariff on imported steel, the tariff
A)raises the Canadian price of imported steel.
B)decreases the Canadian production of steel.
C)increases the total Canadian consumption of steel.
D)decreases employment in the Canadian steel industry.
E)increases Canadian consumer surplus.
A)raises the Canadian price of imported steel.
B)decreases the Canadian production of steel.
C)increases the total Canadian consumption of steel.
D)decreases employment in the Canadian steel industry.
E)increases Canadian consumer surplus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
A tariff imposed by Canada on Japanese cars ________ the price of cars in Canada and ________ the quantity of Japanese cars imported into Canada.
A)raises; increases
B)raises; decreases
C)lowers; increases
D)lowers; decreases
E)raises; does not change
A)raises; increases
B)raises; decreases
C)lowers; increases
D)lowers; decreases
E)raises; does not change

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Refer to the figure below to answer the following questions.

Figure 7.3.1
The figure shows the market for shirts in Canada, where D is the domestic demand curve and S is the domestic supply curve. The world price is $20 per shirt. Canada imposes a tariff on imported shirts of $4 per shirt.
Refer to Figure 7.3.1.The tariff ________ the domestic production of shirts in Canada by ________ per year.
A)increases; 8 million
B)decreases; 16 million
C)increases; 4 million
D)decreases; 8 million
E)increases; 24 million

Figure 7.3.1
The figure shows the market for shirts in Canada, where D is the domestic demand curve and S is the domestic supply curve. The world price is $20 per shirt. Canada imposes a tariff on imported shirts of $4 per shirt.
Refer to Figure 7.3.1.The tariff ________ the domestic production of shirts in Canada by ________ per year.
A)increases; 8 million
B)decreases; 16 million
C)increases; 4 million
D)decreases; 8 million
E)increases; 24 million

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



