Deck 17: Public Goods and Common Resources
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/98
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 17: Public Goods and Common Resources
1
Which one of the following goods exhibits nonexcludability?
A)a cheeseburger
B)the Internet
C)rides on the U.S. Space Shuttle
D)cable TV
E)air traffic control
A)a cheeseburger
B)the Internet
C)rides on the U.S. Space Shuttle
D)cable TV
E)air traffic control
E
2
Which of the following quotations describes a nonexcludable and nonrival good?
A)"Mom, Ashley is looking at me."
B)"Mom, Morgan won't let me watch the Backyardigans because she is watching Dora the Explorer."
C)"Mom, Harrison won't let me in his room."
D)"Mom, Taylor told me on the phone that he is also watching the Backyardigans on TV at his house, but I'm not allowed to go over there."
E)"Mom said everyone in this house gets to enjoy the flowers in the garden."
A)"Mom, Ashley is looking at me."
B)"Mom, Morgan won't let me watch the Backyardigans because she is watching Dora the Explorer."
C)"Mom, Harrison won't let me in his room."
D)"Mom, Taylor told me on the phone that he is also watching the Backyardigans on TV at his house, but I'm not allowed to go over there."
E)"Mom said everyone in this house gets to enjoy the flowers in the garden."
E
3
When a good is nonrival and nonexcludable, it is a
A)natural monopoly good.
B)private good.
C)regulated good.
D)public good.
E)common resource.
A)natural monopoly good.
B)private good.
C)regulated good.
D)public good.
E)common resource.
D
4
When a city street is not congested, it is
A)a common resource
B)rival and excludable.
C)rival and nonexcludable.
D)a private good.
E)a public good.
A)a common resource
B)rival and excludable.
C)rival and nonexcludable.
D)a private good.
E)a public good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A good that is rival and nonexcludable is a
A)private good.
B)public good.
C)government good.
D)regulated good.
E)common resource.
A)private good.
B)public good.
C)government good.
D)regulated good.
E)common resource.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which one of the following goods is nonexcludable?
A)a taxi
B)a toll bridge
C)the atmosphere
D)an art museum
E)cable TV
A)a taxi
B)a toll bridge
C)the atmosphere
D)an art museum
E)cable TV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following quotations describes a rival good?
A)"Mom, Ashley is looking at me."
B)"Mom, Morgan won't let me watch the Backyardigans because she is watching Dora the Explorer."
C)"Mom, Harrison won't let me in his room."
D)"Mom, Taylor told me on the phone that he is also watching the Backyardigans on TV at his house."
E)"Mom said everyone in this house gets to enjoy the flowers in the garden."
A)"Mom, Ashley is looking at me."
B)"Mom, Morgan won't let me watch the Backyardigans because she is watching Dora the Explorer."
C)"Mom, Harrison won't let me in his room."
D)"Mom, Taylor told me on the phone that he is also watching the Backyardigans on TV at his house."
E)"Mom said everyone in this house gets to enjoy the flowers in the garden."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
An example of a public good is
A)national defence.
B)a Ford truck.
C)a loaf of bread.
D)a home computer.
E)a television.
A)national defence.
B)a Ford truck.
C)a loaf of bread.
D)a home computer.
E)a television.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which one of the following goods is excludable?
A)a city bus
B)a bridge that does not charge a toll
C)the atmosphere
D)protection from the police force
E)air traffic control
A)a city bus
B)a bridge that does not charge a toll
C)the atmosphere
D)protection from the police force
E)air traffic control

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
A good that is nonrival and excludable is a
A)private good.
B)public good.
C)government good.
D)natural monopoly good.
E)common resource.
A)private good.
B)public good.
C)government good.
D)natural monopoly good.
E)common resource.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A public good is
A)nonrival and nonexcludable.
B)produced by monopolies.
C)rival and excludable.
D)rival and nonexcludable.
E)nonrival and excludable.
A)nonrival and nonexcludable.
B)produced by monopolies.
C)rival and excludable.
D)rival and nonexcludable.
E)nonrival and excludable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Private goods are
A)nonrival and excludable.
B)nonrival and nonexcludable.
C)always produced in a non-regulated market.
D)rival and excludable.
E)rival and nonexcludable.
A)nonrival and excludable.
B)nonrival and nonexcludable.
C)always produced in a non-regulated market.
D)rival and excludable.
E)rival and nonexcludable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
If a good is a public good,
A)anyone can be excluded from enjoying its benefits.
B)no one can be excluded from enjoying its benefits.
C)consumers must pay a high price to enjoy its benefits.
D)it is rival and excludable.
E)economies of scale exist over the entire range of output for which there is a demand.
A)anyone can be excluded from enjoying its benefits.
B)no one can be excluded from enjoying its benefits.
C)consumers must pay a high price to enjoy its benefits.
D)it is rival and excludable.
E)economies of scale exist over the entire range of output for which there is a demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
A common resource is
A)rival and either excludable or nonexcludable.
B)excludable and either rival or nonrival.
C)rival and excludable.
D)rival and nonexcludable.
E)nonexcludable and either rival or nonrival.
A)rival and either excludable or nonexcludable.
B)excludable and either rival or nonrival.
C)rival and excludable.
D)rival and nonexcludable.
E)nonexcludable and either rival or nonrival.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
When a city street is congested, it is
A)a common resource.
B)nonrival and nonexcludable.
C)nonrival and excludable.
D)a private good.
E)a public good.
A)a common resource.
B)nonrival and nonexcludable.
C)nonrival and excludable.
D)a private good.
E)a public good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A natural monopoly good is
A)nonrival.
B)excludable.
C)rival.
D)nonexcludable.
E)both A and B.
A)nonrival.
B)excludable.
C)rival.
D)nonexcludable.
E)both A and B.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
A common resource is
A)regulated and excludable.
B)rival and nonexcludable.
C)nonrival and excludable.
D)rival and excludable.
E)nonrival and nonexcludable.
A)regulated and excludable.
B)rival and nonexcludable.
C)nonrival and excludable.
D)rival and excludable.
E)nonrival and nonexcludable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
When a good is rival and excludable, it is a
A)natural monopoly good.
B)public good.
C)regulated good.
D)private good.
E)common resource.
A)natural monopoly good.
B)public good.
C)regulated good.
D)private good.
E)common resource.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Suppose Bryan Adams wants to perform a concert in the City Park in Corner Brook Newfoundland.The city officials argue that the only way the concert can be given permission to be performed in the City Park is if it is free of charge.If Bryan Adams agrees to performing free of charge, then the concert is
A)excludable.
B)a private good.
C)nonexcludable.
D)rival.
E)rival and nonexcludable.
A)excludable.
B)a private good.
C)nonexcludable.
D)rival.
E)rival and nonexcludable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
An example of common resource is
A)fish in the ocean.
B)air traffic control.
C)the Ambassador Bridge which goes between Windsor Ontario and Detroit.
D)the Internet.
E)national defence.
A)fish in the ocean.
B)air traffic control.
C)the Ambassador Bridge which goes between Windsor Ontario and Detroit.
D)the Internet.
E)national defence.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The economy's demand curve for a public good is obtained by summing the individual
A)marginal cost curves horizontally.
B)marginal cost curves vertically.
C)marginal benefit curves horizontally.
D)marginal benefit curves vertically.
E)benefit curves diagonally.
A)marginal cost curves horizontally.
B)marginal cost curves vertically.
C)marginal benefit curves horizontally.
D)marginal benefit curves vertically.
E)benefit curves diagonally.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The efficient scale of provision of a public good occurs where
A)total benefit is at a maximum.
B)total benefit is at a minimum.
C)marginal social benefit is at a maximum.
D)marginal social benefit minus marginal social cost equals zero.
E)marginal social cost is at a minimum.
A)total benefit is at a maximum.
B)total benefit is at a minimum.
C)marginal social benefit is at a maximum.
D)marginal social benefit minus marginal social cost equals zero.
E)marginal social cost is at a minimum.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Public goods are provided by government because
A)governments are more efficient than private firms at producing public goods.
B)free-rider problems result in underproduction by private markets.
C)people value national defence very highly.
D)private firms will make an economic profit.
E)private firms do not take into account the impact of external costs.
A)governments are more efficient than private firms at producing public goods.
B)free-rider problems result in underproduction by private markets.
C)people value national defence very highly.
D)private firms will make an economic profit.
E)private firms do not take into account the impact of external costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
If the marginal social cost of producing a public good is greater than the marginal social benefit, then
A)more than the efficient quantity of the public good is being produced.
B)less than the efficient quantity of the public good is being produced.
C)the efficient quantity of the public good is being produced.
D)the public good is being produced by a private firm.
E)the public good must be a common resource.
A)more than the efficient quantity of the public good is being produced.
B)less than the efficient quantity of the public good is being produced.
C)the efficient quantity of the public good is being produced.
D)the public good is being produced by a private firm.
E)the public good must be a common resource.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Use the figure below to answer the following questions.
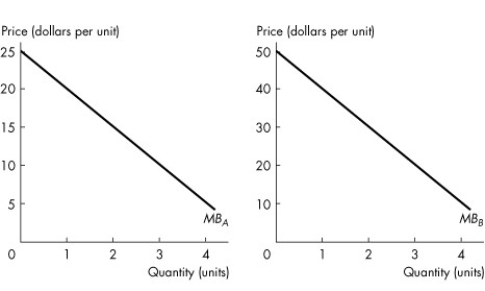
Figure 17.2.1
Refer to Figure 17.2.1.Curve MBA is Andrew's marginal benefit curve for a public good and curve MBB is Betty's marginal benefit curve for the same public good.If Andrew and Betty are the only two consumers in the economy, which point would be on the economy's marginal social benefit curve?
A)price of $20, quantity of 3
B)price of $20, quantity of 4
C)price of $10, quantity of 4
D)price of $30, quantity of 0
E)price of $60, quantity of 1

Figure 17.2.1
Refer to Figure 17.2.1.Curve MBA is Andrew's marginal benefit curve for a public good and curve MBB is Betty's marginal benefit curve for the same public good.If Andrew and Betty are the only two consumers in the economy, which point would be on the economy's marginal social benefit curve?
A)price of $20, quantity of 3
B)price of $20, quantity of 4
C)price of $10, quantity of 4
D)price of $30, quantity of 0
E)price of $60, quantity of 1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
For a private good, the economy's marginal social benefit curve is the ________ sum of the individual marginal benefit curves and for a public good, the economy's marginal social benefit curve is the ________ sum of the individual marginal benefit curves.
A)vertical; vertical
B)vertical; horizontal
C)horizontal; vertical
D)horizontal; horizontal
E)horizontal and vertical; vertical and horizontal
A)vertical; vertical
B)vertical; horizontal
C)horizontal; vertical
D)horizontal; horizontal
E)horizontal and vertical; vertical and horizontal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The quantity of a public good produced by private provision
A)is less than the efficient quantity.
B)is equal to the efficient quantity.
C)is greater than the efficient quantity.
D)maximizes total public benefit.
E)maximizes net public benefit.
A)is less than the efficient quantity.
B)is equal to the efficient quantity.
C)is greater than the efficient quantity.
D)maximizes total public benefit.
E)maximizes net public benefit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
A Big Mac is
A)excludable and rival.
B)nonexcludable and nonrival.
C)nonexcludable and rival.
D)excludable and nonrival.
E)a private good in North America but a natural monopoly good in other countries.
A)excludable and rival.
B)nonexcludable and nonrival.
C)nonexcludable and rival.
D)excludable and nonrival.
E)a private good in North America but a natural monopoly good in other countries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Use the figure below to answer the following questions.

Figure 17.2.1
Refer to Figure 17.2.1.Curve MBA is Andrew's marginal benefit curve for a private good and curve MBB is Betty's marginal benefit curve for the same private good.If Andrew and Betty are the only two consumers in the economy, which point would be on the economy's marginal social benefit curve?
A)price of $20, quantity of 3 units
B)price of $20, quantity of 4 units
C)price of $10, quantity of 4 units
D)price of $30, quantity of 0 units
E)price of $60, quantity of 1 units

Figure 17.2.1
Refer to Figure 17.2.1.Curve MBA is Andrew's marginal benefit curve for a private good and curve MBB is Betty's marginal benefit curve for the same private good.If Andrew and Betty are the only two consumers in the economy, which point would be on the economy's marginal social benefit curve?
A)price of $20, quantity of 3 units
B)price of $20, quantity of 4 units
C)price of $10, quantity of 4 units
D)price of $30, quantity of 0 units
E)price of $60, quantity of 1 units

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Public choice theory predicts that government
A)acts to promote the redistribution of wealth and income.
B)acts to maximize the amount of campaign contributions.
C)acts to eliminate waste and promote an efficient allocation of resources.
D)makes choices that result in efficient provision of public goods.
E)makes choices that result in inefficient overprovision of public goods.
A)acts to promote the redistribution of wealth and income.
B)acts to maximize the amount of campaign contributions.
C)acts to eliminate waste and promote an efficient allocation of resources.
D)makes choices that result in efficient provision of public goods.
E)makes choices that result in inefficient overprovision of public goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Private provision of public goods
A)fails because the private firm will always go broke.
B)succeeds because public provision is often more costly.
C)succeeds if consumers expect to obtain a benefit from the consumption of the public good.
D)fails because of the free-rider problem.
E)fails because private firms generally charge higher prices than public firms, and therefore lose customers.
A)fails because the private firm will always go broke.
B)succeeds because public provision is often more costly.
C)succeeds if consumers expect to obtain a benefit from the consumption of the public good.
D)fails because of the free-rider problem.
E)fails because private firms generally charge higher prices than public firms, and therefore lose customers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Free riding can occur if a good is
A)excludable and rival.
B)excludable and nonrival.
C)a private good.
D)nonexcludable and rival.
E)nonexcludable and nonrival.
A)excludable and rival.
B)excludable and nonrival.
C)a private good.
D)nonexcludable and rival.
E)nonexcludable and nonrival.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
A view of the sunset is
A)excludable and rival.
B)nonexcludable and nonrival.
C)nonexcludable and rival.
D)excludable and nonrival.
E)a private good.
A)excludable and rival.
B)nonexcludable and nonrival.
C)nonexcludable and rival.
D)excludable and nonrival.
E)a private good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Although both cable television and air traffic control are nonrival, they differ from each other because
A)cable television is a private good and air traffic control is a public good.
B)cable television is a public good and air traffic control is a private good.
C)cable television is nonexcludable and air traffic control is a public good.
D)cable television is nonexcludable and air traffic control is excludable.
E)cable television is excludable and air traffic control is nonexcludable.
A)cable television is a private good and air traffic control is a public good.
B)cable television is a public good and air traffic control is a private good.
C)cable television is nonexcludable and air traffic control is a public good.
D)cable television is nonexcludable and air traffic control is excludable.
E)cable television is excludable and air traffic control is nonexcludable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The marginal social benefit curve for a public good is derived by
A)adding the marginal benefits of all individuals at each quantity.
B)adding the quantities demanded by all individuals at each price.
C)surveying consumers and asking how much they use a certain good or service.
D)adding the total benefits for all consumers for a given quantity of the good.
E)finding the maximum amount someone is willing to pay for one more unit of the good.
A)adding the marginal benefits of all individuals at each quantity.
B)adding the quantities demanded by all individuals at each price.
C)surveying consumers and asking how much they use a certain good or service.
D)adding the total benefits for all consumers for a given quantity of the good.
E)finding the maximum amount someone is willing to pay for one more unit of the good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The air in the atmosphere is
A)nonrival and nonexcludable.
B)rival and nonexcludable.
C)nonrival and excludable.
D)rival and excludable.
E)a private good.
A)nonrival and nonexcludable.
B)rival and nonexcludable.
C)nonrival and excludable.
D)rival and excludable.
E)a private good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
An economy's marginal social benefit curve for a private good is obtained by summing the individual marginal
A)cost curves horizontally.
B)cost curves vertically.
C)benefit curves horizontally.
D)benefit curves vertically.
E)benefit curves diagonally.
A)cost curves horizontally.
B)cost curves vertically.
C)benefit curves horizontally.
D)benefit curves vertically.
E)benefit curves diagonally.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Cable television and air traffic control are similar to each other because both of them are
A)excludable.
B)nonexcludable.
C)nonrival.
D)rival.
E)private services.
A)excludable.
B)nonexcludable.
C)nonrival.
D)rival.
E)private services.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Suppose in a country there are only two persons.Person A is willing to pay $50 to have one unit of a public good produced; person B is willing to pay $60 to have one unit of a public good produced and $50 to have two units produced.A point on the country's marginal social benefit curve for this public good is a price of ________ and quantity demanded of ________.
A)$50; 1 unit
B)$60; 1 unit
C)$110; 2 units
D)$110; 1 unit
E)$55; 1 unit
A)$50; 1 unit
B)$60; 1 unit
C)$110; 2 units
D)$110; 1 unit
E)$55; 1 unit

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Governments provide public goods such as national defence because
A)governments are more efficient than private firms at producing public goods.
B)of the free-rider problem, which results in underproduction by private firms.
C)people do not value national defence very highly.
D)of the potential that private firms will make excess profit.
E)of external costs.
A)governments are more efficient than private firms at producing public goods.
B)of the free-rider problem, which results in underproduction by private firms.
C)people do not value national defence very highly.
D)of the potential that private firms will make excess profit.
E)of external costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Competition between two political parties will cause those parties to propose policies
A)that are quite different.
B)that are quite similar.
C)of rational ignorance.
D)that reduce the well-being of middle-income families and increasing the well-being of the rich and the poor.
E)that equate total costs and total benefits.
A)that are quite different.
B)that are quite similar.
C)of rational ignorance.
D)that reduce the well-being of middle-income families and increasing the well-being of the rich and the poor.
E)that equate total costs and total benefits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The budget of a government department is likely to be efficient if
A)voters are well informed.
B)there is rational voter ignorance combined with special interest lobbying.
C)the political equilibrium can be described in terms of public choice theory.
D)bureaucrats are rationally ignorant.
E)there are negative externalities.
A)voters are well informed.
B)there is rational voter ignorance combined with special interest lobbying.
C)the political equilibrium can be described in terms of public choice theory.
D)bureaucrats are rationally ignorant.
E)there are negative externalities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The budget of a government department is likely to increase beyond the efficient quantity if
A)voters are well informed.
B)there is rational voter ignorance combined with special interest lobbying.
C)the political equilibrium can be described in terms of social interest theory.
D)bureaucrats are rationally ignorant.
E)there are negative externalities.
A)voters are well informed.
B)there is rational voter ignorance combined with special interest lobbying.
C)the political equilibrium can be described in terms of social interest theory.
D)bureaucrats are rationally ignorant.
E)there are negative externalities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
If voters are rationally ignorant, the quantity of national defence provided by the government will be
A)greater than the efficient quantity.
B)less than the efficient quantity.
C)the least costly quantity.
D)the quantity that maximizes the budget of the Department of National Defence.
E)both A and D are correct.
A)greater than the efficient quantity.
B)less than the efficient quantity.
C)the least costly quantity.
D)the quantity that maximizes the budget of the Department of National Defence.
E)both A and D are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Competitors who make themselves identical to appeal to the maximum number of voters illustrate the
A)principle of maximum differentiation.
B)principle of minimum differentiation.
C)principle of rational ignorance.
D)principle of nonrivalry.
E)principle of excludability.
A)principle of maximum differentiation.
B)principle of minimum differentiation.
C)principle of rational ignorance.
D)principle of nonrivalry.
E)principle of excludability.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Public choice theory assumes those involved in the political process are motivated by
A)self-interest.
B)the desire to achieve efficiency.
C)dishonesty.
D)public spirit.
E)the desire for maximum profit.
A)self-interest.
B)the desire to achieve efficiency.
C)dishonesty.
D)public spirit.
E)the desire for maximum profit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Use the table below to answer the following questions.
Table 17.2.1
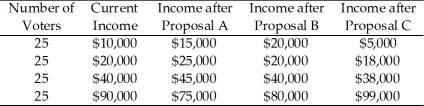
In Table 17.2.1, which one of the proposals will have the greatest support?
A)Current income distribution
B)Proposal A
C)Proposal B
D)Proposal C
E)Proposal A or C
Table 17.2.1

In Table 17.2.1, which one of the proposals will have the greatest support?
A)Current income distribution
B)Proposal A
C)Proposal B
D)Proposal C
E)Proposal A or C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
All of the following statements regarding rational ignorance are true except
A)it results when the cost of information exceeds the expected benefit of acquiring the information.
B)it allows special interest groups to exert political influence.
C)combined with special interest groups, it yields inefficiency in the provision of public goods.
D)it leads to an efficient outcome.
E)it results in voters having little knowledge about issues that have little effect on their economic welfare.
A)it results when the cost of information exceeds the expected benefit of acquiring the information.
B)it allows special interest groups to exert political influence.
C)combined with special interest groups, it yields inefficiency in the provision of public goods.
D)it leads to an efficient outcome.
E)it results in voters having little knowledge about issues that have little effect on their economic welfare.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Minimum differentiation among the political parties suggests that
A)the parties will have few ideas in common on their platforms.
B)the parties will offer few ideas on minimizing the size and scope of government.
C)the platforms of the parties will tend to become similar as they try to appeal to a majority of voters.
D)the platforms of the parties will tend to become dissimilar as they try to appeal to a loyal majority of voters.
E)the platforms of the parties will tend to have few, if any, new ideas.
A)the parties will have few ideas in common on their platforms.
B)the parties will offer few ideas on minimizing the size and scope of government.
C)the platforms of the parties will tend to become similar as they try to appeal to a majority of voters.
D)the platforms of the parties will tend to become dissimilar as they try to appeal to a loyal majority of voters.
E)the platforms of the parties will tend to have few, if any, new ideas.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Use the table below to answer the following questions.
Table 17.2.1

In Table 17.2.1, which of the proposals would be supported by political parties according to the principle of minimum differentiation?
A)Current income distribution
B)Proposal A
C)Proposal B
D)Proposal C
E)Proposal A or C
Table 17.2.1

In Table 17.2.1, which of the proposals would be supported by political parties according to the principle of minimum differentiation?
A)Current income distribution
B)Proposal A
C)Proposal B
D)Proposal C
E)Proposal A or C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Rational ignorance suggests that a voter should stop acquiring more information about an issue when
A)the marginal benefit from acquiring the information equals zero.
B)the total cost of acquiring the information is minimized.
C)the total benefit from acquiring the information is maximized.
D)the marginal cost of acquiring the information is equal to the marginal benefit derived from the information.
E)the marginal cost of acquiring the information is greater than zero.
A)the marginal benefit from acquiring the information equals zero.
B)the total cost of acquiring the information is minimized.
C)the total benefit from acquiring the information is maximized.
D)the marginal cost of acquiring the information is equal to the marginal benefit derived from the information.
E)the marginal cost of acquiring the information is greater than zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The idea that the platforms of the political parties will tend to become similar over time is
A)not a reflection of reality.
B)true in theory but not true in actuality.
C)called the principle of minimum differentiation.
D)called the principle of minimal political confrontation.
E)the result of intense lobbying pressure.
A)not a reflection of reality.
B)true in theory but not true in actuality.
C)called the principle of minimum differentiation.
D)called the principle of minimal political confrontation.
E)the result of intense lobbying pressure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Rational ignorance suggests that voters will
A)understand defence technology before voting for defence policy.
B)understand the auditing procedures of the Canada Revenue Agency before voting for tax reform.
C)understand the chemistry of the atmosphere before voting for a clean-air act.
D)vote without complete information on many issues.
E)vote based on their complete trust in politicians and bureaucrats.
A)understand defence technology before voting for defence policy.
B)understand the auditing procedures of the Canada Revenue Agency before voting for tax reform.
C)understand the chemistry of the atmosphere before voting for a clean-air act.
D)vote without complete information on many issues.
E)vote based on their complete trust in politicians and bureaucrats.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
To attract a majority of voters, a political party will
A)aim its message at the most enthusiastic groups.
B)aim its message at a small but loyal following.
C)present a political package aimed at making the wealthier voters better off.
D)present a political package aimed at making a majority of voters better off.
E)respond strongest to the most vigorous lobbyists.
A)aim its message at the most enthusiastic groups.
B)aim its message at a small but loyal following.
C)present a political package aimed at making the wealthier voters better off.
D)present a political package aimed at making a majority of voters better off.
E)respond strongest to the most vigorous lobbyists.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Use the table below to answer the following questions.
Table 17.2.1

In Table 17.2.1, which one of the proposals will have the least support?
A)Current income distribution
B)Proposal A
C)Proposal B
D)Proposal C
E)Proposal A or C
Table 17.2.1

In Table 17.2.1, which one of the proposals will have the least support?
A)Current income distribution
B)Proposal A
C)Proposal B
D)Proposal C
E)Proposal A or C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Public choice theory predicts that
A)voters are fully informed about the effects of policies.
B)voters are rationally ignorant.
C)governments make choices that achieve an efficient provision of public goods.
D)votes are based on reality, not perceptions.
E)votes are based on lobbyists' viewpoints.
A)voters are fully informed about the effects of policies.
B)voters are rationally ignorant.
C)governments make choices that achieve an efficient provision of public goods.
D)votes are based on reality, not perceptions.
E)votes are based on lobbyists' viewpoints.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
According to public choice theory, a voter will tend to be well informed if the issue in question
A)is complicated and difficult to understand.
B)affects everyone a little.
C)is of special interest to a small group to which the voter does not belong.
D)has a large direct effect on the voter.
E)is important even if it does not directly affect the voter.
A)is complicated and difficult to understand.
B)affects everyone a little.
C)is of special interest to a small group to which the voter does not belong.
D)has a large direct effect on the voter.
E)is important even if it does not directly affect the voter.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
According to public choice theory, government failure occurs because
A)government officials do not listen to the pleading of special interest groups.
B)lobbyists write legislation.
C)government officials act in their own self-interest.
D)voters are fully informed about the effects of policies.
E)government cannot calculate the levels of externalities because there is no market for them.
A)government officials do not listen to the pleading of special interest groups.
B)lobbyists write legislation.
C)government officials act in their own self-interest.
D)voters are fully informed about the effects of policies.
E)government cannot calculate the levels of externalities because there is no market for them.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Rational ignorance suggests that
A)all voters are ignorant.
B)all voters will be ignorant on issues that are not of special interest to them.
C)all voters will pursue information about each issue before voting.
D)low voter turnout is due to a lack of understanding of the importance of the political platforms.
E)it is easier to aim at the median voter because it is a less costly strategy for the politicians.
A)all voters are ignorant.
B)all voters will be ignorant on issues that are not of special interest to them.
C)all voters will pursue information about each issue before voting.
D)low voter turnout is due to a lack of understanding of the importance of the political platforms.
E)it is easier to aim at the median voter because it is a less costly strategy for the politicians.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
If all voters are well informed about national defence, the quantity of national defence provided by the government will be
A)greater than the efficient quantity.
B)less than the efficient quantity.
C)the least costly quantity.
D)the efficient quantity.
E)the quantity that maximizes the budget of the Department of National Defence.
A)greater than the efficient quantity.
B)less than the efficient quantity.
C)the least costly quantity.
D)the efficient quantity.
E)the quantity that maximizes the budget of the Department of National Defence.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Which of the following achieves the efficient use of a common resource?
A)property rights, production quotas, and individual transferable quotas
B)property rights, individual transferable quotas, and subsidies
C)property rights, production quotas, and subsidies
D)individual transferable quotas and copyrights
E)production quotas, individual transferable quotas, and copyrights
A)property rights, production quotas, and individual transferable quotas
B)property rights, individual transferable quotas, and subsidies
C)property rights, production quotas, and subsidies
D)individual transferable quotas and copyrights
E)production quotas, individual transferable quotas, and copyrights

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
John receives a marginal benefit of $80 from one satellite.Nick receives a marginal benefit of $50 from one satellite.Christina receives a marginal benefit of $65 from one satellite.John, Nick, and Christina are the only people in the economy What is the economy's marginal social benefit from one satellite?
A)$30
B)$195
C)$15
D)$80
E)$65
A)$30
B)$195
C)$15
D)$80
E)$65

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
In the equilibrium for a common resource with no government regulation,
A)marginal social benefit is greater than marginal social cost.
B)marginal social benefit equals marginal social cost.
C)marginal social benefit is less than marginal cost.
D)marginal social benefit is greater than marginal cost.
E)marginal social benefit equals marginal cost.
A)marginal social benefit is greater than marginal social cost.
B)marginal social benefit equals marginal social cost.
C)marginal social benefit is less than marginal cost.
D)marginal social benefit is greater than marginal cost.
E)marginal social benefit equals marginal cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
According to ________ theory, governments make choices that result in an ________ provision of public goods.This outcome occurs in ________.
A)public choice; efficient; political markets in which voters are rationally ignorant
B)social interest; efficient; a perfect political system in which voters are fully informed about the effects of policies
C)social interest; efficient; political markets in which voters are rationally ignorant
D)public choice; inefficient; a perfect political system in which voters are full informed about the effects of policies
E)social interest; inefficient; political markets in which voters are rationally ignorant
A)public choice; efficient; political markets in which voters are rationally ignorant
B)social interest; efficient; a perfect political system in which voters are fully informed about the effects of policies
C)social interest; efficient; political markets in which voters are rationally ignorant
D)public choice; inefficient; a perfect political system in which voters are full informed about the effects of policies
E)social interest; inefficient; political markets in which voters are rationally ignorant

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Common resources are overused because
A)the marginal private benefit of operating a boat is the quantity of fish a boat can catch.
B)the social benefits outweigh the private benefits.
C)the marginal private benefit will always exceed the marginal social cost.
D)external costs are not considered.
E)social costs are controlled by production quotas.
A)the marginal private benefit of operating a boat is the quantity of fish a boat can catch.
B)the social benefits outweigh the private benefits.
C)the marginal private benefit will always exceed the marginal social cost.
D)external costs are not considered.
E)social costs are controlled by production quotas.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
An individual transferable quota is a production limit that
A)has a price equal to marginal cost.
B)is assigned to every producer in the industry at a predetermined price.
C)is assigned to an individual who must transfer the quota to anyone the government assigns.
D)is assigned to an individual who is free to transfer the quota to someone else.
E)has a price equal to marginal benefit.
A)has a price equal to marginal cost.
B)is assigned to every producer in the industry at a predetermined price.
C)is assigned to an individual who must transfer the quota to anyone the government assigns.
D)is assigned to an individual who is free to transfer the quota to someone else.
E)has a price equal to marginal benefit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The absence of incentives to prevent the overuse of a common resource that arises when its users have no incentive to conserve it and use it sustainably is referred to as
A)unsustainable production.
B)sustainable production.
C)the tragedy of the commons.
D)rational ignorance.
E)irrational production.
A)unsustainable production.
B)sustainable production.
C)the tragedy of the commons.
D)rational ignorance.
E)irrational production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The "tragedy of the commons" refers to
A)the inability of lower income groups to achieve a higher level of education.
B)the absence of incentives to prevent the overuse of a common resource that arises when its users have no incentive to conserve it and use it sustainably.
C)the acceptance of deplorable working conditions by those who lack the human capital to obtain a better job.
D)the tendency for bureaucrats to maximize their budget.
E)farmers who allow their livestock to overgraze their fields.
A)the inability of lower income groups to achieve a higher level of education.
B)the absence of incentives to prevent the overuse of a common resource that arises when its users have no incentive to conserve it and use it sustainably.
C)the acceptance of deplorable working conditions by those who lack the human capital to obtain a better job.
D)the tendency for bureaucrats to maximize their budget.
E)farmers who allow their livestock to overgraze their fields.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Rational ignorance
A)results when the cost of acquiring information exceeds the benefit of acquiring the information.
B)allows special interest groups to exert political influence.
C)combined with special-interest groups can yield inefficient provision of public goods.
D)results in all of the above.
E)results in none of the above.
A)results when the cost of acquiring information exceeds the benefit of acquiring the information.
B)allows special interest groups to exert political influence.
C)combined with special-interest groups can yield inefficient provision of public goods.
D)results in all of the above.
E)results in none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
One way to alleviate the tragedy of the commons is to
A)eliminate production quotas for using the common resource.
B)make the resource private property.
C)allow all individuals to use the common resource free of charge.
D)distribute common resources among those individuals who really need the resource free of charge.
E)set a price of $1 per unit of the common resource because it is an affordable price.
A)eliminate production quotas for using the common resource.
B)make the resource private property.
C)allow all individuals to use the common resource free of charge.
D)distribute common resources among those individuals who really need the resource free of charge.
E)set a price of $1 per unit of the common resource because it is an affordable price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Use the figure below to answer the following question.
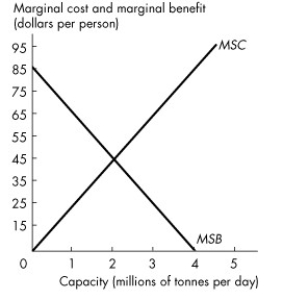
Figure 17.2.2
Refer to Figure 17.2.2.The graph shows the marginal social benefit and marginal social cost of a garbage disposal system in a city of 1 million people.If voters are well informed about the costs and benefits of the garbage disposal system, the political equilibrium of garbage is
A)2.0 million tonnes a day.
B)1.5 million tonnes a day.
C)2.5 million tonnes a day.
D)4.0 million tonnes a day.
E)0 million tonnes a day.

Figure 17.2.2
Refer to Figure 17.2.2.The graph shows the marginal social benefit and marginal social cost of a garbage disposal system in a city of 1 million people.If voters are well informed about the costs and benefits of the garbage disposal system, the political equilibrium of garbage is
A)2.0 million tonnes a day.
B)1.5 million tonnes a day.
C)2.5 million tonnes a day.
D)4.0 million tonnes a day.
E)0 million tonnes a day.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
According to public choice theory, a voter will favour a candidate whose political program is
A)perceived by the voter to be in his self-interest.
B)best for the majority of the people.
C)closest to efficiency.
D)favoured by the median voter.
E)efficient.
A)perceived by the voter to be in his self-interest.
B)best for the majority of the people.
C)closest to efficiency.
D)favoured by the median voter.
E)efficient.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Sustainable production is
A)the rate of production that can be maintained indefinitely.
B)the production output with the lowest average total cost.
C)the production output where MC = ATC.
D)the rate of production that maximizes marginal private benefit.
E)the rate of production where MB = MC.
A)the rate of production that can be maintained indefinitely.
B)the production output with the lowest average total cost.
C)the production output where MC = ATC.
D)the rate of production that maximizes marginal private benefit.
E)the rate of production where MB = MC.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Sharing downloaded music
A)has a free-rider problem that cannot be eliminated because once music is downloaded, it is nonexcludable.
B)has a free-rider problem that can be eliminated by charging people to download music.
C)is a private good.
D)does not have a free-rider problem.
E)is a common resource.
A)has a free-rider problem that cannot be eliminated because once music is downloaded, it is nonexcludable.
B)has a free-rider problem that can be eliminated by charging people to download music.
C)is a private good.
D)does not have a free-rider problem.
E)is a common resource.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
The construction of the economy's marginal social benefit curve for a public good reflects the fact that
A)all the individuals can consume the same unit of the good.
B)the government can supply a public good at a lower cost than can a private supplier.
C)more than one supplier can provide the good.
D)the same unit of the good cannot be simultaneously shared by more than one person at a time.
E)demand for a public good is perfectly elastic.
A)all the individuals can consume the same unit of the good.
B)the government can supply a public good at a lower cost than can a private supplier.
C)more than one supplier can provide the good.
D)the same unit of the good cannot be simultaneously shared by more than one person at a time.
E)demand for a public good is perfectly elastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Use the information below to answer the following question.
Fact 17.2.1 Should Childhood Vaccines Be Mandatory?
While Canadian vaccination rates are high, the outbreaks of measles in five provinces during 2014 show that not everyone is getting them. There is no national policy making vaccinations mandatory, although Ontario, New Brunswick and Manitoba require public school students to show their immunization records to attend school.
Source: CBC Radio, April 15, 2014
Refer to Fact 17.2.1.Someone who doesn't get vaccinated against measles is a "free rider" because if everyone in a neighbourhood except one person gets vaccinated, then the unvaccinated person
A)defeats the principle of minimum differentiation.
B)benefits from the neighbours' vaccinations.
C)increases the risk of his neighbours getting measles.
D)changes the measles vaccination into a natural monopoly good.
E)changes the measles vaccination into a common resource.
Fact 17.2.1 Should Childhood Vaccines Be Mandatory?
While Canadian vaccination rates are high, the outbreaks of measles in five provinces during 2014 show that not everyone is getting them. There is no national policy making vaccinations mandatory, although Ontario, New Brunswick and Manitoba require public school students to show their immunization records to attend school.
Source: CBC Radio, April 15, 2014
Refer to Fact 17.2.1.Someone who doesn't get vaccinated against measles is a "free rider" because if everyone in a neighbourhood except one person gets vaccinated, then the unvaccinated person
A)defeats the principle of minimum differentiation.
B)benefits from the neighbours' vaccinations.
C)increases the risk of his neighbours getting measles.
D)changes the measles vaccination into a natural monopoly good.
E)changes the measles vaccination into a common resource.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Use the figure below to answer the following question.
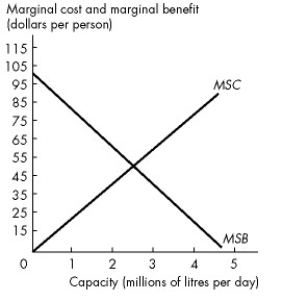
Figure 17.2.3
Refer to Figure 17.2.3.The graph provides information about a waste disposal system in a city of 1 million people.If the city installs the efficient capacity, then each person pays ________ in taxes.
A)$125
B)$62.50
C)$250
D)zero
E)$31.25

Figure 17.2.3
Refer to Figure 17.2.3.The graph provides information about a waste disposal system in a city of 1 million people.If the city installs the efficient capacity, then each person pays ________ in taxes.
A)$125
B)$62.50
C)$250
D)zero
E)$31.25

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
A Canada Day fireworks display
A)does not have a free-rider problem.
B)has a free-rider problem that cannot be eliminated.
C)has a free-rider problem that can be eliminated by using taxes paid by area residents to finance the display.
D)is a private good.
E)is a natural monopoly good.
A)does not have a free-rider problem.
B)has a free-rider problem that cannot be eliminated.
C)has a free-rider problem that can be eliminated by using taxes paid by area residents to finance the display.
D)is a private good.
E)is a natural monopoly good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Your city council is contemplating upgrading its traffic control system and the council believes that the bigger the computer it installs, the better job it can do.Elected officials want to install the scale of the system that will win the most votes.The city bureaucrats want to maximize the budget.Suppose that you are an economist and your job is to calculate the scale of the system that uses resources efficiently.Public choice theory predicts that the quantity chosen will result in ________.As an informed voter, you can attempt to influence the choice of the correct system by encouraging other voters to ________.
A)overprovision that maximizes the budget of the bureaucrats; vote only for officials that will provide the smaller efficient quantity
B)overprovision that maximizes the budget of the bureaucrats; increase their income elasticity of demand for the new traffic control system
C)the efficient quantity; decrease their income elasticity of demand for the new traffic control system
D)the efficient quantity; increase their income elasticity of demand for the new traffic control system
E)overprovision that minimizes the income elasticity of demand of bureaucrats; decrease their elasticity of demand for the new traffic control system
A)overprovision that maximizes the budget of the bureaucrats; vote only for officials that will provide the smaller efficient quantity
B)overprovision that maximizes the budget of the bureaucrats; increase their income elasticity of demand for the new traffic control system
C)the efficient quantity; decrease their income elasticity of demand for the new traffic control system
D)the efficient quantity; increase their income elasticity of demand for the new traffic control system
E)overprovision that minimizes the income elasticity of demand of bureaucrats; decrease their elasticity of demand for the new traffic control system

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Growing voter income can lead to the growth of the government sector because
A)public goods are income elastic.
B)public goods are income inelastic.
C)richer voters are more likely to be rationally ignorant.
D)richer voters do not care about overprovision of government goods.
E)as income increases, more public goods become private goods.
A)public goods are income elastic.
B)public goods are income inelastic.
C)richer voters are more likely to be rationally ignorant.
D)richer voters do not care about overprovision of government goods.
E)as income increases, more public goods become private goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



