Deck 6: Efficiency and Fairness of Markets
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/352
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 6: Efficiency and Fairness of Markets
1
Often people trying to withdraw money from their bank must wait in line, which reflects a ________ allocation method.
A)first-come, first-served
B)market price
C)contest
D)majority rule
E)command
A)first-come, first-served
B)market price
C)contest
D)majority rule
E)command
A
2
Canned milk was only rationed to babies and small children during World War 2.This rationing was an example of allocation by
A)market price.
B)first-come, first-served.
C)sharing equally.
D)force.
E)personal characteristics .
A)market price.
B)first-come, first-served.
C)sharing equally.
D)force.
E)personal characteristics .
E
3
Although Jack and Vanessa were equally qualified, Jack was promoted to manager instead of Vanessa because the president of the company thought that the other employees would not respect a female manager.The resource, the management position, was allocated in what manner?
A)sharing equally
B)contest
C)personal characteristics
D)command
E)lottery
A)sharing equally
B)contest
C)personal characteristics
D)command
E)lottery
C
4
Seventy percent of Austin's chess club wanted to purchase new chess sets and thirty percent did not.The club purchased the sets.Which method of allocation best describes the choice to purchase the sets?
A)force
B)sharing equally
C)command
D)majority rule
E)lottery
A)force
B)sharing equally
C)command
D)majority rule
E)lottery

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 352 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Lattes at Starbucks are allocated to individuals in society through what type of method?
A)lottery
B)contest
C)sharing equally
D)market price
E)personal characteristics
A)lottery
B)contest
C)sharing equally
D)market price
E)personal characteristics

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 352 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Honda will sell its vehicles to anyone who wants to and can buy one.Honda is using a ________ allocation method.
A)first-come, first-served
B)market price
C)contest
D)majority rule
E)command
A)first-come, first-served
B)market price
C)contest
D)majority rule
E)command

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 352 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
University of Colorado reserves 5,000 free tickets to each home football game for students.Students must stand in line to receive their ticket.Football tickets are allocated through which method?
A)market price
B)sharing equally
C)personal characteristics
D)first-come, first-served
E)force
A)market price
B)sharing equally
C)personal characteristics
D)first-come, first-served
E)force

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 352 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following situations describing a resource allocation method most resembles the force method?
A)Seventy percent of Austin's chess club wanted to purchase new chess sets and thirty percent did not. The club purchased the sets.
B)Lattes are sold at Starbucks.
C)Food from the Weld County Food Bank is distributed to families in need.
D)Mandy saved her allowance to buy a 12 pack of cream soda. When Mandy's brother saw the soda, he took four.
E)Jose works at Intel. His manager tells him what work needs to be completed each month.
A)Seventy percent of Austin's chess club wanted to purchase new chess sets and thirty percent did not. The club purchased the sets.
B)Lattes are sold at Starbucks.
C)Food from the Weld County Food Bank is distributed to families in need.
D)Mandy saved her allowance to buy a 12 pack of cream soda. When Mandy's brother saw the soda, he took four.
E)Jose works at Intel. His manager tells him what work needs to be completed each month.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 352 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following situations describing a resource allocation method most resembles the market price method?
A)Food from the Weld County Food Bank is distributed to families in need.
B)Lattes are sold at Starbucks.
C)Jose works at Intel. His manager tells him what work needs to be completed each month.
D)Matt's mother had the rule that whoever cuts the cake chooses their slice last.
E)Seventy percent of Austin's chess club wanted to purchase new chess sets and thirty percent did not. The club purchased the sets.
A)Food from the Weld County Food Bank is distributed to families in need.
B)Lattes are sold at Starbucks.
C)Jose works at Intel. His manager tells him what work needs to be completed each month.
D)Matt's mother had the rule that whoever cuts the cake chooses their slice last.
E)Seventy percent of Austin's chess club wanted to purchase new chess sets and thirty percent did not. The club purchased the sets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 352 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
If you split your dessert with your date, you are using a ________ allocation method.
A)first-come, first-served
B)sharing equally
C)contest
D)personal characteristics
E)command
A)first-come, first-served
B)sharing equally
C)contest
D)personal characteristics
E)command

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 352 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Walmart has a limited number of "Black Friday" (the day-after Thanksgiving Day)special items on sale at prices well below their typical price.Walmart opens at 10 PM on Thanksgiving.Walmart is using a ________ allocation method for these items.
A)first-come, first-served
B)market price
C)contest
D)majority rule
E)command
A)first-come, first-served
B)market price
C)contest
D)majority rule
E)command

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 352 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The chair of the Department of Economics at Colorado State University decided that office space is for tenured faculty and that graduate students are required to share cubicles.What method is used to allocate office space?
A)lottery
B)majority rule
C)command
D)first-come, first-served
E)sharing equally
A)lottery
B)majority rule
C)command
D)first-come, first-served
E)sharing equally

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 352 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Allocating resources by the order of someone in authority is a ________ allocation method.
A)first-come, first-served
B)market price
C)contest
D)majority rule
E)command
A)first-come, first-served
B)market price
C)contest
D)majority rule
E)command

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 352 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
When the city of Fresno holds a referendum to determine if taxes will be raised to pay for road repairs, the city is using a ________ allocation method.
A)majority rule
B)market price
C)contest
D)personal characteristics
E)command
A)majority rule
B)market price
C)contest
D)personal characteristics
E)command

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 352 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The resource allocation method used for the online auctions on eBay is
A)market price.
B)lottery.
C)contest.
D)first-come, first-served.
E)sharing equally.
A)market price.
B)lottery.
C)contest.
D)first-come, first-served.
E)sharing equally.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 352 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Auditors working for a large accounting firm are often away from the office.When they are in the office, they are allowed to use any desk that is available.Which method is used to allocate desks?
A)lottery
B)first-come, first-served
C)command
D)contest
E)sharing equally
A)lottery
B)first-come, first-served
C)command
D)contest
E)sharing equally

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 352 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following situations describing a resource allocation method most resembles the majority rule method?
A)Seventy percent of Austin's chess club wanted to purchase new chess sets and thirty percent did not. The club purchased the sets.
B)Lattes are sold at Starbucks.
C)Food from the Weld County Food Bank is distributed to families in need.
D)Jose works at Intel. His manager tells him what work needs to be completed each month.
E)Matt's mother had the rule that whoever cuts the cake chooses their slice last.
A)Seventy percent of Austin's chess club wanted to purchase new chess sets and thirty percent did not. The club purchased the sets.
B)Lattes are sold at Starbucks.
C)Food from the Weld County Food Bank is distributed to families in need.
D)Jose works at Intel. His manager tells him what work needs to be completed each month.
E)Matt's mother had the rule that whoever cuts the cake chooses their slice last.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 352 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Mandy saved her allowance to buy a 12 pack of cream soda.When Mandy's brother saw the soda, he took four.Sodas were allocated between Mandy and her brother through
A)force.
B)majority rule.
C)first-come, first-served.
D)sharing equally.
E)personal characteristics.
A)force.
B)majority rule.
C)first-come, first-served.
D)sharing equally.
E)personal characteristics.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 352 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
If a landlord will rent an apartment only to married couples, the landlord is using a ________ allocation method.
A)majority rule
B)market price
C)contest
D)personal characteristics
E)command
A)majority rule
B)market price
C)contest
D)personal characteristics
E)command

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 352 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Jose works at Intel.His manager tells him what work needs to be completed each month.Jose's resource, labor, is allocated with which of the following methods?
A)command
B)majority rule
C)force
D)personal characteristics
E)lottery
A)command
B)majority rule
C)force
D)personal characteristics
E)lottery

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 352 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Marginal benefit is the benefit that a person receives from consuming
A)a good or service until the person has grown tired of it.
B)only goods and services that are free.
C)one more unit of a good or service.
D)all of the possible units of a good or service that can be consumed.
E)one more unit of a good and is equal to the cost of producing the unit of the good.
A)a good or service until the person has grown tired of it.
B)only goods and services that are free.
C)one more unit of a good or service.
D)all of the possible units of a good or service that can be consumed.
E)one more unit of a good and is equal to the cost of producing the unit of the good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 352 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Marginal benefit
A)increases as more of a good is consumed.
B)decreases as more of a good is consumed.
C)is the total benefit from all units consumed.
D)is constant as more of a good is consumed.
E)is the gain to the producer of producing and selling one more unit of a good.
A)increases as more of a good is consumed.
B)decreases as more of a good is consumed.
C)is the total benefit from all units consumed.
D)is constant as more of a good is consumed.
E)is the gain to the producer of producing and selling one more unit of a good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 352 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
To achieve allocative efficiency, an economy
A)must produce on its PPF.
B)does not necessarily need to be production efficient.
C)must have increases in technology.
D)might leave some resources unemployed.
E)can produce either on or within its PPF.
A)must produce on its PPF.
B)does not necessarily need to be production efficient.
C)must have increases in technology.
D)might leave some resources unemployed.
E)can produce either on or within its PPF.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 352 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
As more of a good is consumed, the marginal benefit of the good
A)increases.
B)decreases.
C)remains constant.
D)is unpredictable.
E)first decreases and then increases.
A)increases.
B)decreases.
C)remains constant.
D)is unpredictable.
E)first decreases and then increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 352 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The principle of decreasing marginal benefit explains why the marginal benefit curve
A)is upward sloping.
B)has an infinite slope.
C)is vertical.
D)is downward sloping.
E)is horizontal.
A)is upward sloping.
B)has an infinite slope.
C)is vertical.
D)is downward sloping.
E)is horizontal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 352 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
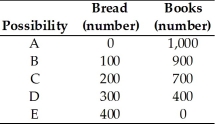
The table above shows the production possibilities for an economy.When the economy produces a combination of 900 books and 50 loaves of bread,
A)production efficiency occurs because resources are not overused.
B)allocative efficiency is achieved because both goods are produced.
C)production efficiency is not achieved.
D)allocative and production efficiency are both achieved.
E)production efficiency is not achieved but allocative efficiency might be achieved.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 352 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The point that each glass of lemonade consumed on a hot day brings lower and lower levels of satisfaction is known as the principle of
A)total benefits.
B)increasing marginal cost.
C)decreasing marginal benefit.
D)increasing opportunity cost.
E)decreasing marginal price.
A)total benefits.
B)increasing marginal cost.
C)decreasing marginal benefit.
D)increasing opportunity cost.
E)decreasing marginal price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 352 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The marginal benefit of a taco is measured by
A)the price of the taco.
B)the amount of another good a person is willing to give up to get one more taco.
C)the amount of another good a person must give up to get one more taco.
D)a point on the PPF.
E)the opportunity cost of producing another taco.
A)the price of the taco.
B)the amount of another good a person is willing to give up to get one more taco.
C)the amount of another good a person must give up to get one more taco.
D)a point on the PPF.
E)the opportunity cost of producing another taco.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 352 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The Ironman Hawaii randomly draws a few hundred slots from thousands of applicants for the race.The method of allocation for the opportunity to participate in the race is __________, and the method of allocation for determining the winner of the race is __________.
A)lottery; contest
B)contest; lottery
C)first-come, first-served; lottery
D)lottery; first-come, first-served
E)contest; command
A)lottery; contest
B)contest; lottery
C)first-come, first-served; lottery
D)lottery; first-come, first-served
E)contest; command

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 352 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
In 2009, tickets to a Presidential Town Hall meeting were distributed to individuals through a random selection of those who registered on a website.The tickets were allocated by which method?
A)lottery
B)majority rule
C)contest
D)first-come, first-served
E)personal characteristics
A)lottery
B)majority rule
C)contest
D)first-come, first-served
E)personal characteristics

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 352 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Marginal benefit curves
A)have positive slopes.
B)have negative slopes.
C)are horizontal lines.
D)are vertical lines.
E)are upside-down U-shaped curves.
A)have positive slopes.
B)have negative slopes.
C)are horizontal lines.
D)are vertical lines.
E)are upside-down U-shaped curves.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 352 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Allocative efficiency refers to
A)producing the goods and services most highly valued.
B)using the least amount of labor to produce output.
C)producing the maximum possible amount of output.
D)obtaining the least output with the most inputs.
E)producing at any point on the PPF.
A)producing the goods and services most highly valued.
B)using the least amount of labor to produce output.
C)producing the maximum possible amount of output.
D)obtaining the least output with the most inputs.
E)producing at any point on the PPF.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 352 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Suppose Jennifer derives $100 in marginal benefits from her first skiing trip and $80 from her third trip.Her marginal benefit from her second trip is likely to be
A)more than $100.
B)between $100 and $80.
C)between $79 and $51.
D)less than $51.
E)some amount that cannot be calculated without additional information.
A)more than $100.
B)between $100 and $80.
C)between $79 and $51.
D)less than $51.
E)some amount that cannot be calculated without additional information.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 352 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
When a society achieves allocative efficiency, it
A)is not achieving production efficiency.
B)is producing that combination of goods and services that society values most highly.
C)might or it might not be producing at a point on society's PPF.
D)is producing a combination of goods and services whose marginal cost exceeds their marginal benefit.
E)is producing the combination of goods and services for which marginal benefit exceeds marginal cost by as much as possible.
A)is not achieving production efficiency.
B)is producing that combination of goods and services that society values most highly.
C)might or it might not be producing at a point on society's PPF.
D)is producing a combination of goods and services whose marginal cost exceeds their marginal benefit.
E)is producing the combination of goods and services for which marginal benefit exceeds marginal cost by as much as possible.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 352 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Marginal benefit is the
A)total benefit we receive from consuming a good or service.
B)additional benefit we receive from consuming one more unit of a good or service.
C)minimum amount of other goods or services we are willing to give up.
D)opportunities given up to get one more unit of a good or service.
E)the benefit we receive from consuming one more unit of a good or service minus the cost of the producing one more unit of the good or service.
A)total benefit we receive from consuming a good or service.
B)additional benefit we receive from consuming one more unit of a good or service.
C)minimum amount of other goods or services we are willing to give up.
D)opportunities given up to get one more unit of a good or service.
E)the benefit we receive from consuming one more unit of a good or service minus the cost of the producing one more unit of the good or service.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 352 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Resource use is allocative efficient
A)when it is not possible to produce more of one good.
B)when we produce goods and services that we value most highly.
C)when most resources are fully employed.
D)at any point on the PPF.
E)at all points either on or within the PPF because all these production points are attainable.
A)when it is not possible to produce more of one good.
B)when we produce goods and services that we value most highly.
C)when most resources are fully employed.
D)at any point on the PPF.
E)at all points either on or within the PPF because all these production points are attainable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 352 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
When allocative efficiency occurs,
A)an economy produces the goods and services most highly valued.
B)marginal benefit exceeds marginal cost by some amount.
C)technology must be increasing.
D)we can simultaneously produce more of all goods.
E)marginal benefit exceeds marginal cost by as much as possible.
A)an economy produces the goods and services most highly valued.
B)marginal benefit exceeds marginal cost by some amount.
C)technology must be increasing.
D)we can simultaneously produce more of all goods.
E)marginal benefit exceeds marginal cost by as much as possible.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 352 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
In general, the marginal benefit curve
A)has a positive slope.
B)has a negative slope.
C)is horizontal.
D)is vertical.
E)is concave.
A)has a positive slope.
B)has a negative slope.
C)is horizontal.
D)is vertical.
E)is concave.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 352 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
If an economy is allocatively efficient, it must be producing
A)beyond its production possibilities frontier.
B)inside its production possibilities frontier.
C)on its production possibilities frontier.
D)the goods and services that are the most expensive.
E)the goods and services that are the least expensive to produce.
A)beyond its production possibilities frontier.
B)inside its production possibilities frontier.
C)on its production possibilities frontier.
D)the goods and services that are the most expensive.
E)the goods and services that are the least expensive to produce.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 352 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The marginal benefit of the first hotdog consumed is ________ the marginal benefit of the fifth hotdog consumed.
A)equal to
B)less than
C)greater than
D)the inverse of
E)equal to 5 times
A)equal to
B)less than
C)greater than
D)the inverse of
E)equal to 5 times

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 352 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
When the marginal cost of producing a bike is greater than the marginal benefit of the bike, for resource use to be allocatively efficient
A)more bikes should be produced.
B)fewer bikes should be produced.
C)no more and no fewer bikes should be produced.
D)it must be determined if the production of bikes can be increased.
E)people must be educated to demand more bikes.
A)more bikes should be produced.
B)fewer bikes should be produced.
C)no more and no fewer bikes should be produced.
D)it must be determined if the production of bikes can be increased.
E)people must be educated to demand more bikes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 352 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Any point on the production possibility frontier is
A)attainable and might be allocatively inefficient.
B)attainable and must be allocatively efficient.
C)less production efficient than a point in the interior of the PPF.
D)always allocatively efficient but might or might not be production efficient.
E)always production efficient and always allocatively efficient.
A)attainable and might be allocatively inefficient.
B)attainable and must be allocatively efficient.
C)less production efficient than a point in the interior of the PPF.
D)always allocatively efficient but might or might not be production efficient.
E)always production efficient and always allocatively efficient.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 352 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
As more of a good is consumed, marginal benefit ________ and as more of a good is produced, marginal cost ________.
A)increases; increases
B)increases; decreases
C)decreases; increases
D)decreases; decreases
E)does not change; does not change
A)increases; increases
B)increases; decreases
C)decreases; increases
D)decreases; decreases
E)does not change; does not change

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 352 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
To achieve allocative efficiency, one must compare the
A)marginal cost of a good to its opportunity cost.
B)opportunity cost to the attainable point on the production possibilities frontier.
C)marginal benefit of a good to its marginal cost.
D)marginal cost to the production efficiency cost.
E)point of production efficiency to the point of allocative efficiency.
A)marginal cost of a good to its opportunity cost.
B)opportunity cost to the attainable point on the production possibilities frontier.
C)marginal benefit of a good to its marginal cost.
D)marginal cost to the production efficiency cost.
E)point of production efficiency to the point of allocative efficiency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 352 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Marginal cost is the opportunity cost of producing
A)every unit possible.
B)zero units.
C)the first unit and only the first unit.
D)one more unit of a good or service.
E)None of the above answers is correct.
A)every unit possible.
B)zero units.
C)the first unit and only the first unit.
D)one more unit of a good or service.
E)None of the above answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 352 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Allocative efficiency occurs
A)anywhere inside or on the production possibilities frontier.
B)when the total cost of production is minimized.
C)at all points on the production possibilities frontier.
D)at only one point on the production possibilities frontier.
E)at the points where the production possibilities frontier crosses the horizontal or vertical axis.
A)anywhere inside or on the production possibilities frontier.
B)when the total cost of production is minimized.
C)at all points on the production possibilities frontier.
D)at only one point on the production possibilities frontier.
E)at the points where the production possibilities frontier crosses the horizontal or vertical axis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 352 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
If the difference between the marginal benefit and the marginal cost of a good is as large as possible,
A)resources are being used with maximum efficiency.
B)resources would create more value producing other goods and hence the production of this good should be decreased.
C)more of the good should be produced.
D)allocative efficiency has been attained.
E)Both answers A and D are correct.
A)resources are being used with maximum efficiency.
B)resources would create more value producing other goods and hence the production of this good should be decreased.
C)more of the good should be produced.
D)allocative efficiency has been attained.
E)Both answers A and D are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 352 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Which of the following is necessary for allocative efficiency to be achieved?
A)Marginal benefit must be maximized.
B)Marginal cost must be minimized.
C)Marginal benefit must equal marginal cost.
D)The difference between marginal benefit and marginal cost must be maximized.
E)Production must be at a point inside the production possibilities frontier.
A)Marginal benefit must be maximized.
B)Marginal cost must be minimized.
C)Marginal benefit must equal marginal cost.
D)The difference between marginal benefit and marginal cost must be maximized.
E)Production must be at a point inside the production possibilities frontier.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 352 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
When the marginal benefit and marginal cost of sodas are equal, then
A)the production of sodas might be allocatively efficient but it is definitely production inefficient.
B)the allocatively inefficient amount of sodas is being produced.
C)more sodas should be produced to reach the allocatively efficient quantity.
D)fewer sodas should be produced to reach the allocatively efficient quantity.
E)the allocatively efficient amount of sodas is being produced.
A)the production of sodas might be allocatively efficient but it is definitely production inefficient.
B)the allocatively inefficient amount of sodas is being produced.
C)more sodas should be produced to reach the allocatively efficient quantity.
D)fewer sodas should be produced to reach the allocatively efficient quantity.
E)the allocatively efficient amount of sodas is being produced.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 352 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
For resource use to be allocatively efficient, when the marginal benefit of a slice of pizza exceeds the marginal cost ________.
A)more slices of pizza should be produced
B)fewer slices of pizza should be produced
C)no more slices of pizza should be produced
D)allocative efficiency is reached only if the marginal benefit exceeds the marginal cost by as much as possible
E)None of the above answers is correct.
A)more slices of pizza should be produced
B)fewer slices of pizza should be produced
C)no more slices of pizza should be produced
D)allocative efficiency is reached only if the marginal benefit exceeds the marginal cost by as much as possible
E)None of the above answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 352 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Which of the following are the rules for finding the point of allocative efficiency?
A)Produce on the PPF and then produce where the marginal benefit and marginal cost are as large as possible.
B)Produce on the PPF and then produce where marginal benefit equals marginal cost.
C)Produce on the PPF and then produce where marginal benefit and marginal cost are constant.
D)Produce on the PPF and then produce where the marginal benefit exceeds marginal cost by as much as possible.
E)Produce anywhere on the PPF.
A)Produce on the PPF and then produce where the marginal benefit and marginal cost are as large as possible.
B)Produce on the PPF and then produce where marginal benefit equals marginal cost.
C)Produce on the PPF and then produce where marginal benefit and marginal cost are constant.
D)Produce on the PPF and then produce where the marginal benefit exceeds marginal cost by as much as possible.
E)Produce anywhere on the PPF.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 352 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The marginal cost curve is
A)downward sloping to reflect the bowed out PPF.
B)downward sloping as marginal benefits increase.
C)upward sloping because marginal cost falls as more of a good or service is produced.
D)upward sloping to reflect the increasing opportunity cost of producing one more unit.
E)U-shaped to reflect the bowed out PPF.
A)downward sloping to reflect the bowed out PPF.
B)downward sloping as marginal benefits increase.
C)upward sloping because marginal cost falls as more of a good or service is produced.
D)upward sloping to reflect the increasing opportunity cost of producing one more unit.
E)U-shaped to reflect the bowed out PPF.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 352 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Moving ________ along the marginal cost curve, the ________.
A)upward; opportunity cost of one more unit increases
B)upward; marginal cost decreases
C)downward; marginal cost increases
D)upward; opportunity cost of one more unit does not change
E)downward; opportunity cost of one more unit does not change
A)upward; opportunity cost of one more unit increases
B)upward; marginal cost decreases
C)downward; marginal cost increases
D)upward; opportunity cost of one more unit does not change
E)downward; opportunity cost of one more unit does not change

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 352 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
All points on the production possibilities frontier
A)are production inefficient.
B)achieve allocative efficiency.
C)are production efficient but only one point achieves allocative efficiency.
D)are allocatively efficient but only one point achieves production efficiency.
E)are allocatively inefficient.
A)are production inefficient.
B)achieve allocative efficiency.
C)are production efficient but only one point achieves allocative efficiency.
D)are allocatively efficient but only one point achieves production efficiency.
E)are allocatively inefficient.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 352 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Marginal cost equals
A)the profitability derived from producing another unit of output.
B)all the opportunity cost of producing the amount of output.
C)or exceeds the marginal benefit.
D)productive efficiency.
E)the opportunity cost of producing one more unit of output.
A)the profitability derived from producing another unit of output.
B)all the opportunity cost of producing the amount of output.
C)or exceeds the marginal benefit.
D)productive efficiency.
E)the opportunity cost of producing one more unit of output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 352 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Allocative efficiency is achieved when the marginal benefit of a good
A)exceeds the marginal cost regardless of how much the difference is.
B)is less than its marginal cost.
C)is equal to its marginal cost.
D)equals zero.
E)exceeds the marginal cost by as much as possible.
A)exceeds the marginal cost regardless of how much the difference is.
B)is less than its marginal cost.
C)is equal to its marginal cost.
D)equals zero.
E)exceeds the marginal cost by as much as possible.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 352 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
We allocate resources efficiently when
A)marginal benefit is equal to marginal cost.
B)marginal benefit is greater than marginal cost by any amount.
C)marginal cost is greater than marginal benefit.
D)total benefit is greater than total cost.
E)marginal benefit is greater than marginal cost by as much as possible.
A)marginal benefit is equal to marginal cost.
B)marginal benefit is greater than marginal cost by any amount.
C)marginal cost is greater than marginal benefit.
D)total benefit is greater than total cost.
E)marginal benefit is greater than marginal cost by as much as possible.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 352 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
In order to efficiently allocate goods and services, we have to compare
A)total cost to total benefit.
B)total cost to price.
C)marginal benefit to price.
D)marginal cost to marginal benefit.
E)price to marginal cost.
A)total cost to total benefit.
B)total cost to price.
C)marginal benefit to price.
D)marginal cost to marginal benefit.
E)price to marginal cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 352 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The marginal cost curves slope upward because of the principle of
A)decreasing marginal benefits.
B)increasing marginal cost.
C)increasing marginal benefits.
D)decreasing marginal cost.
E)decreasing total benefit.
A)decreasing marginal benefits.
B)increasing marginal cost.
C)increasing marginal benefits.
D)decreasing marginal cost.
E)decreasing total benefit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 352 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The marginal cost of a good or service
A)can be calculated from the marginal benefit of that good or service.
B)decreases as more of the good or service is produced.
C)can be derived from the production possibilities frontier.
D)graphs as a positively sloped curve, so it cannot be derived from the production possibilities frontier, which is downward sloping.
E)None of the above answers are correct.
A)can be calculated from the marginal benefit of that good or service.
B)decreases as more of the good or service is produced.
C)can be derived from the production possibilities frontier.
D)graphs as a positively sloped curve, so it cannot be derived from the production possibilities frontier, which is downward sloping.
E)None of the above answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 352 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The phrase "decreasing marginal benefit" means that
A)the more you consume of the product, the less total benefit you derive.
B)the marginal cost will be increasing as you consume more of a good.
C)each additional unit of a good you consume gives you less additional benefit than the previous unit.
D)Both answers A and B are correct.
E)Both answers A and C are correct.
A)the more you consume of the product, the less total benefit you derive.
B)the marginal cost will be increasing as you consume more of a good.
C)each additional unit of a good you consume gives you less additional benefit than the previous unit.
D)Both answers A and B are correct.
E)Both answers A and C are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 352 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The marginal benefit of each additional unit of a good consumed
A)increases as more is consumed.
B)is always equal to its marginal cost.
C)decreases as more is consumed.
D)will maximize consumer surplus.
E)is equal to the deadweight loss if the unit of the good is not produced.
A)increases as more is consumed.
B)is always equal to its marginal cost.
C)decreases as more is consumed.
D)will maximize consumer surplus.
E)is equal to the deadweight loss if the unit of the good is not produced.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 352 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
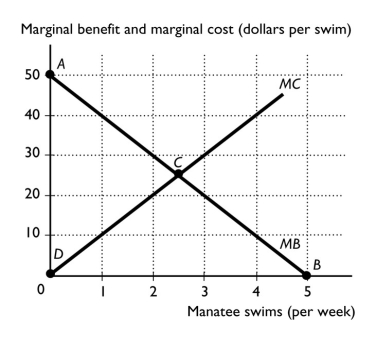
The figure above shows Kaley's marginal benefit from swimming with manatees and Scott's marginal cost of providing manatee swimming tours.If Scott offers two swim tours per week, he incurs a marginal cost of
A)more than $30.
B)$30.
C)$20.
D)$10.
E)$2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 352 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64

The figure above shows Kaley's marginal benefit from swimming with manatees and Scott's marginal cost of providing manatee swimming tours.At 1 manatee swim per week, Kaley's marginal benefit is ________ and Scott's marginal cost is ________.
A)$40; $10
B)$40; $40
C)$90; $50
D)None of the above answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 352 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Value and price can be compared by noting that
A)they are the same thing.
B)value is always greater than price.
C)value is what we must pay while price is what we are willing to pay.
D)price is what we must pay and value is what we are willing to pay.
E)value is what the seller receives when we buy a good and price is what we must pay when we buy a good.
A)they are the same thing.
B)value is always greater than price.
C)value is what we must pay while price is what we are willing to pay.
D)price is what we must pay and value is what we are willing to pay.
E)value is what the seller receives when we buy a good and price is what we must pay when we buy a good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 352 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
When society produces the combination of goods and services on the PPF that it values the most highly, society has
A)achieved only production efficiency and definitely not allocative efficiency.
B)achieved only allocative efficiency definitely not production efficiency.
C)achieved both production efficiency and allocative efficiency.
D)achieved a free lunch.
E)perhaps achieved production efficiency and has perhaps achieved allocative efficiency.
A)achieved only production efficiency and definitely not allocative efficiency.
B)achieved only allocative efficiency definitely not production efficiency.
C)achieved both production efficiency and allocative efficiency.
D)achieved a free lunch.
E)perhaps achieved production efficiency and has perhaps achieved allocative efficiency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 352 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
In general, the marginal cost curve
A)has a positive slope.
B)has a negative slope.
C)is horizontal.
D)is vertical.
E)is U-shaped.
A)has a positive slope.
B)has a negative slope.
C)is horizontal.
D)is vertical.
E)is U-shaped.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 352 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The value of a slice of pizza to a consumer is equal to
A)its marginal benefit.
B)the maximum price the consumer is willing to pay.
C)the consumer surplus.
D)Both answers A and B are correct.
E)Both answers B and C are correct.
A)its marginal benefit.
B)the maximum price the consumer is willing to pay.
C)the consumer surplus.
D)Both answers A and B are correct.
E)Both answers B and C are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 352 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The maximum amount of other goods and services that people are willing to give up in order to get one more unit of a good is defined as the good's
A)marginal benefit.
B)total benefit.
C)marginal cost.
D)total cost.
E)price.
A)marginal benefit.
B)total benefit.
C)marginal cost.
D)total cost.
E)price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 352 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Suppose the nation is producing at a point on its PPF.If the marginal cost of producing one more computer is greater than the marginal benefit, the nation is producing
A)too few computers to be allocatively efficient.
B)too many computers to be allocatively efficient.
C)the correct number of computers to be allocatively efficient.
D)at the point of allocative efficiency.
E)More information is needed to determine if the nation is or is not producing at the allocatively efficient point.
A)too few computers to be allocatively efficient.
B)too many computers to be allocatively efficient.
C)the correct number of computers to be allocatively efficient.
D)at the point of allocative efficiency.
E)More information is needed to determine if the nation is or is not producing at the allocatively efficient point.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 352 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
If a landlord will rent an apartment only to married couples over 30 years old, the landlord is allocating resources using a ________ allocation method.
A)majority rule
B)market price
C)contest
D)personal characteristics
E)command
A)majority rule
B)market price
C)contest
D)personal characteristics
E)command

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 352 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Marginal benefit equals the
A)benefit that a person receives from consuming another unit of a good.
B)additional efficiency from producing another unit of a good.
C)increase in profit from producing another unit of a good.
D)cost of producing another unit of a good.
E)total benefit from consuming all the units of the good or service.
A)benefit that a person receives from consuming another unit of a good.
B)additional efficiency from producing another unit of a good.
C)increase in profit from producing another unit of a good.
D)cost of producing another unit of a good.
E)total benefit from consuming all the units of the good or service.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 352 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
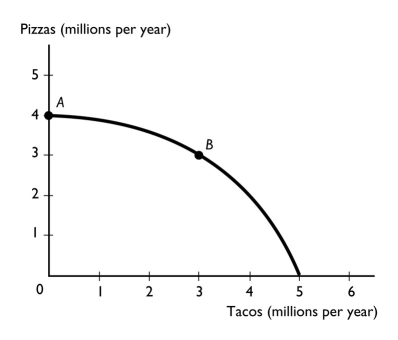
The figure above shows a nation's production possibilities frontier.If the marginal cost equals the marginal benefit at point A when 4 million pizzas are produced,
A)allocative efficiency is achieved but production efficiency is not achieved because there are no tacos being produced.
B)both allocative and production efficiency are achieved.
C)production efficiency is achieved but allocative efficiency is not achieved because there are no tacos being produced.
D)production efficiency is achieved but allocative efficiency is not achieved because the number of tacos produced is at its absolute maximum.
E)neither allocative nor production efficiency has been achieved.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 352 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Allocative efficiency occurs when
A)the most highly valued goods and services are produced.
B)all citizens have equal access to goods and services.
C)the environment is protected at all cost.
D)goods and services are free.
E)production takes place at any point on the PPF.
A)the most highly valued goods and services are produced.
B)all citizens have equal access to goods and services.
C)the environment is protected at all cost.
D)goods and services are free.
E)production takes place at any point on the PPF.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 352 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
To an economist, "value" is the same as
A)marginal cost.
B)consumer surplus.
C)the minimum price that people are willing to pay for another unit of the good.
D)marginal benefit.
E)total surplus.
A)marginal cost.
B)consumer surplus.
C)the minimum price that people are willing to pay for another unit of the good.
D)marginal benefit.
E)total surplus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 352 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Allocative efficiency is achieved when the marginal benefit of a good
A)exceeds the marginal cost by as much as possible.
B)exceeds the marginal cost but not by as much as possible.
C)is less than the marginal cost.
D)equals the marginal cost.
E)equals zero.
A)exceeds the marginal cost by as much as possible.
B)exceeds the marginal cost but not by as much as possible.
C)is less than the marginal cost.
D)equals the marginal cost.
E)equals zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 352 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Which describes the economic meanings of value and price?
A)Value is exchange worth minus marginal benefit and price is the dollars that must be paid.
B)Value is the marginal benefit obtained and price is the dollars that must be paid.
C)Value refers to the gain the producer gets from the good or service and price refers to the gain the consumer gets from the good or service.
D)Value refers to the dollars that must be paid and price refers to the cost of producing the good.
E)They are the same and both mean the dollars that must be paid.
A)Value is exchange worth minus marginal benefit and price is the dollars that must be paid.
B)Value is the marginal benefit obtained and price is the dollars that must be paid.
C)Value refers to the gain the producer gets from the good or service and price refers to the gain the consumer gets from the good or service.
D)Value refers to the dollars that must be paid and price refers to the cost of producing the good.
E)They are the same and both mean the dollars that must be paid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 352 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Which of the following statements is correct?
I∙The demand curve shows the maximum price people are willing to pay for a given quantity of the good.
Ii∙The maximum price a consumer is willing to pay for an additional unit is the marginal benefit of that unit.
Iii∙Value is what a consumer receives and price is what a consumer pays.
A)i only
B)ii only
C)iii only
D)i and iii
E)i, ii, and iii
I∙The demand curve shows the maximum price people are willing to pay for a given quantity of the good.
Ii∙The maximum price a consumer is willing to pay for an additional unit is the marginal benefit of that unit.
Iii∙Value is what a consumer receives and price is what a consumer pays.
A)i only
B)ii only
C)iii only
D)i and iii
E)i, ii, and iii

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 352 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
To determine how much of a good to produce to achieve allocative efficiency, we
A)construct a production possibilities frontier and choose the midpoint.
B)construct a production possibilities frontier and choose any point on it.
C)must produce on the PPF and at the point where the marginal benefit and marginal cost of the good are equal.
D)must produce on the PPF and at the point where the marginal benefit exceeds by any amount the marginal cost of the good.
E)must produce on the PPF and at the point where the marginal benefit exceeds by as much as possible the marginal cost of the good.
A)construct a production possibilities frontier and choose the midpoint.
B)construct a production possibilities frontier and choose any point on it.
C)must produce on the PPF and at the point where the marginal benefit and marginal cost of the good are equal.
D)must produce on the PPF and at the point where the marginal benefit exceeds by any amount the marginal cost of the good.
E)must produce on the PPF and at the point where the marginal benefit exceeds by as much as possible the marginal cost of the good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 352 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80

The figure above shows Kaley's marginal benefit from swimming with manatees and Scott's marginal cost of providing manatee swimming tours.For Kaley and Scott, allocative efficiency is achieved at what point?
A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
E)Either point A or point D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 352 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



