Deck 11: Public Goods and Common Resources
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/177
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 11: Public Goods and Common Resources
1
A private good is defined as a good or service
A)that is something tangible.
B)that is rival and excludable.
C)that is rival and nonexcludable.
D)produced by a single country.
E)that is nonrival and nonexcludable.
A)that is something tangible.
B)that is rival and excludable.
C)that is rival and nonexcludable.
D)produced by a single country.
E)that is nonrival and nonexcludable.
B
2
An office in the Empire State Building is
A)a private good.
B)nonexcludable, because it is possible to restrict access to it.
C)a common resource.
D)a public good because many people can be in the Empire State Building.
E)excludable and nonrival.
A)a private good.
B)nonexcludable, because it is possible to restrict access to it.
C)a common resource.
D)a public good because many people can be in the Empire State Building.
E)excludable and nonrival.
A
3
If you can prevent someone from consuming a good, that good is called
A)rival.
B)nonrival.
C)excludable.
D)nonexcludable.
E)a public good.
A)rival.
B)nonrival.
C)excludable.
D)nonexcludable.
E)a public good.
C
4
A good or resource is excludable if
A)only the government can produce them.
B)nobody can be excluded from enjoying the benefits of the good or resource.
C)when you pay for the good or resource, you are guaranteed to be the sole consumer.
D)when you consume a unit, that means there is one less for someone else.
E)it is a common resource.
A)only the government can produce them.
B)nobody can be excluded from enjoying the benefits of the good or resource.
C)when you pay for the good or resource, you are guaranteed to be the sole consumer.
D)when you consume a unit, that means there is one less for someone else.
E)it is a common resource.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 177 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A good that is both rival and excludable is
A)a good that is impossible to produce.
B)a private good.
C)a common resource.
D)a public good.
E)nonexistent because no good can be both rival and excludable.
A)a good that is impossible to produce.
B)a private good.
C)a common resource.
D)a public good.
E)nonexistent because no good can be both rival and excludable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 177 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A good is a private good if
A)people who do not pay for the good can enjoy it without paying for it.
B)it is not a common resource.
C)the good is nonrival.
D)the good is excludable and rival.
E)it is both nonexcludable and nonrival.
A)people who do not pay for the good can enjoy it without paying for it.
B)it is not a common resource.
C)the good is nonrival.
D)the good is excludable and rival.
E)it is both nonexcludable and nonrival.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 177 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A good is nonrival if
A)only the government can produce it.
B)nobody can be excluded from enjoying the benefits of the good.
C)when you pay for the good, you are guaranteed to be the sole consumer.
D)when you consume a unit, you have not decreased the amount left for consumption by other people.
E)anybody can be excluded from enjoying the benefits of the good.
A)only the government can produce it.
B)nobody can be excluded from enjoying the benefits of the good.
C)when you pay for the good, you are guaranteed to be the sole consumer.
D)when you consume a unit, you have not decreased the amount left for consumption by other people.
E)anybody can be excluded from enjoying the benefits of the good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 177 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
A basketball game aired as a pay-per-view show by your local cable network and to which you can invite your friends to watch is a ________ good.
A)rival
B)nonrival
C)nonexcludable
D)rival and nonexcludable
E)quasi public/quasi private
A)rival
B)nonrival
C)nonexcludable
D)rival and nonexcludable
E)quasi public/quasi private

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 177 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following goods is best described as nonexcludable?
A)flood-control levees
B)pay-per-view television
C)a restaurant meal
D)a college education
E)a cow grazing in a pasture
A)flood-control levees
B)pay-per-view television
C)a restaurant meal
D)a college education
E)a cow grazing in a pasture

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 177 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The fact that technology prevents Sam in Nevada from using the email account of Samantha in Virginia means that email is an example of
A)a good that is nonexcludable.
B)a good that is excludable.
C)a public good.
D)the free-rider problem.
E)the tragedy of the commons.
A)a good that is nonexcludable.
B)a good that is excludable.
C)a public good.
D)the free-rider problem.
E)the tragedy of the commons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 177 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A good is nonexcludable if
A)only the government can produce it.
B)nobody can be excluded from enjoying the benefits of the good.
C)when you pay for the good, you are guaranteed to be the sole consumer.
D)when you consume a unit, that means there is no less for someone else.
E)it is also nonrival.
A)only the government can produce it.
B)nobody can be excluded from enjoying the benefits of the good.
C)when you pay for the good, you are guaranteed to be the sole consumer.
D)when you consume a unit, that means there is no less for someone else.
E)it is also nonrival.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 177 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A private good is
A)nonexcludable and nonrival.
B)excludable and rival.
C)excludable and nonrival.
D)nonrival and excludable.
E)subject to the free-riding problem.
A)nonexcludable and nonrival.
B)excludable and rival.
C)excludable and nonrival.
D)nonrival and excludable.
E)subject to the free-riding problem.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 177 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A good is rival if
A)it has substitutes.
B)it can be consumed by many people simultaneously.
C)it is excludable.
D)consumption by one person decreases the quantity available for another person.
E)it has no complements.
A)it has substitutes.
B)it can be consumed by many people simultaneously.
C)it is excludable.
D)consumption by one person decreases the quantity available for another person.
E)it has no complements.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 177 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The fact that Florida's consumption of national defense does not preclude North Dakota from consuming the same national defense is an example of
A)a private good.
B)a common resource.
C)the rival nature of consumption.
D)excludable goods.
E)a good that is nonrival in consumption.
A)a private good.
B)a common resource.
C)the rival nature of consumption.
D)excludable goods.
E)a good that is nonrival in consumption.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 177 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A good that is ________ and ________ is a ________.
A)rival; excludable; private good
B)rival; excludable; public good
C)nonrival; excludable; public good
D)rival; nonexcludable; private good
E)nonrival; nonexcludable; private good
A)rival; excludable; private good
B)rival; excludable; public good
C)nonrival; excludable; public good
D)rival; nonexcludable; private good
E)nonrival; nonexcludable; private good

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 177 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A professional football game played in a completely full stadium is NOT a public good because it is
A)nonexcludable and nonrival.
B)excludable and nonrival.
C)excludable and rival.
D)nonexcludable and rival.
E)not supplied by the government.
A)nonexcludable and nonrival.
B)excludable and nonrival.
C)excludable and rival.
D)nonexcludable and rival.
E)not supplied by the government.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 177 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
One important feature that distinguishes a private good from a public good is that
A)only the government can produce private goods.
B)nobody can be excluded from enjoying the benefits of a private good.
C)a private good is excludable and a public good is nonexcludable.
D)if you consume a unit of a private, that means there is no less for someone else.
E)a private good is nonrival and a public good is rival.
A)only the government can produce private goods.
B)nobody can be excluded from enjoying the benefits of a private good.
C)a private good is excludable and a public good is nonexcludable.
D)if you consume a unit of a private, that means there is no less for someone else.
E)a private good is nonrival and a public good is rival.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 177 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
One important feature that distinguishes a public good from a private good is that
A)only the government can produce public goods.
B)it is impossible to prevent a person from enjoying the benefits from a public good.
C)if you pay for a unit of a public good, you are guaranteed to be the sole consumer.
D)if you consume a unit of a public good, there is one unit less for someone else.
E)Both answers C and D are correct.
A)only the government can produce public goods.
B)it is impossible to prevent a person from enjoying the benefits from a public good.
C)if you pay for a unit of a public good, you are guaranteed to be the sole consumer.
D)if you consume a unit of a public good, there is one unit less for someone else.
E)Both answers C and D are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 177 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following is an example of a pure private good?
A)national defense
B)the Florida State Turnpike, a non-congested toll freeway
C)Lake Erie
D)the Metropolitan Museum of Art in New York City
E)the new heat pump your neighbor bought for her house
A)national defense
B)the Florida State Turnpike, a non-congested toll freeway
C)Lake Erie
D)the Metropolitan Museum of Art in New York City
E)the new heat pump your neighbor bought for her house

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 177 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following is the best example of a private good?
A)a can of Diet Pepsi
B)a missile defense system
C)a library in St. Louis
D)a sidewalk in Fargo
E)a cod fish swimming in the middle of the ocean
A)a can of Diet Pepsi
B)a missile defense system
C)a library in St. Louis
D)a sidewalk in Fargo
E)a cod fish swimming in the middle of the ocean

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 177 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
A private good is ________ and ________.
A)rival; excludable
B)rival; nonexcludable
C)nonrival; excludable
D)nonrival; nonexcludable
E)scarce; expensive
A)rival; excludable
B)rival; nonexcludable
C)nonrival; excludable
D)nonrival; nonexcludable
E)scarce; expensive

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 177 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
To hunters, deer in the woods are an example of a
A)public good.
B)private good.
C)common resource.
D)public resource.
E)natural monopoly.
A)public good.
B)private good.
C)common resource.
D)public resource.
E)natural monopoly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 177 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A good or resource from which no one can be excluded and which is nonrival is a
A)government good.
B)private good.
C)common good.
D)public good.
E)common resource.
A)government good.
B)private good.
C)common good.
D)public good.
E)common resource.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 177 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
A common resource is
A)a service rather than a good.
B)nonrival and nonexcludable.
C)rival and excludable.
D)rival and nonexcludable.
E)nonrival and excludable.
A)a service rather than a good.
B)nonrival and nonexcludable.
C)rival and excludable.
D)rival and nonexcludable.
E)nonrival and excludable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 177 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which of the following is the best example of a common resource?
A)national defense
B)a Ford Thunderbird
C)Yosemite National Park
D)a can of Mountain Dew
E)a cable television network
A)national defense
B)a Ford Thunderbird
C)Yosemite National Park
D)a can of Mountain Dew
E)a cable television network

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 177 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
A public good is
A)rival and excludable.
B)rival and nonexcludable.
C)nonrival and excludable.
D)nonrival and nonexcludable.
E)a good that has an infinite number of substitutes.
A)rival and excludable.
B)rival and nonexcludable.
C)nonrival and excludable.
D)nonrival and nonexcludable.
E)a good that has an infinite number of substitutes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 177 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
A public good
A)can only be consumed by one person at a time.
B)can be consumed simultaneously by many people.
C)is any good provided by a company owned by a member of the public.
D)is any good provided by government.
E)is both rival and excludable.
A)can only be consumed by one person at a time.
B)can be consumed simultaneously by many people.
C)is any good provided by a company owned by a member of the public.
D)is any good provided by government.
E)is both rival and excludable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 177 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which of the following is the best example of a public good?
A)national defense
B)a Ford Thunderbird
C)Yosemite National Park
D)a Mountain Dew
E)satellite radio
A)national defense
B)a Ford Thunderbird
C)Yosemite National Park
D)a Mountain Dew
E)satellite radio

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 177 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
A common resource is
A)rival and excludable.
B)rival and nonexcludable.
C)nonrival and excludable.
D)nonrival and nonexcludable.
E)None of the above answers is correct.
A)rival and excludable.
B)rival and nonexcludable.
C)nonrival and excludable.
D)nonrival and nonexcludable.
E)None of the above answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 177 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
An example of a common resource is
A)a bridge.
B)a non-crowded movie theater.
C)a tuna in the ocean.
D)national defense.
E)All of the above answers are correct.
A)a bridge.
B)a non-crowded movie theater.
C)a tuna in the ocean.
D)national defense.
E)All of the above answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 177 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
A good or resource that is both nonrival and nonexcludable is
A)a good that is impossible to produce.
B)a private good.
C)a common resource.
D)a public good.
E)nonexistent because it is impossible for a good or resource to be both nonrival and nonexcludable.
A)a good that is impossible to produce.
B)a private good.
C)a common resource.
D)a public good.
E)nonexistent because it is impossible for a good or resource to be both nonrival and nonexcludable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 177 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The fact that Sha's enjoyment of a sunset on Saint Simon's Island does not preclude Lou from enjoying the sunset is an example of
A)a good that is nonrival.
B)a good that is excludable.
C)a private good.
D)the rival nature of consumption.
E)a common resource.
A)a good that is nonrival.
B)a good that is excludable.
C)a private good.
D)the rival nature of consumption.
E)a common resource.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 177 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
A public good is ________ and ________.
A)rival; excludable
B)rival; nonexcludable
C)nonrival; excludable
D)nonrival; nonexcludable
E)cheap; available
A)rival; excludable
B)rival; nonexcludable
C)nonrival; excludable
D)nonrival; nonexcludable
E)cheap; available

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 177 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which of the following goods is excludable and nonrival?
A)food
B)air
C)the Internet
D)a streetlight
E)a two liter bottle of Mountain Dew
A)food
B)air
C)the Internet
D)a streetlight
E)a two liter bottle of Mountain Dew

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 177 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
When use of a good decreases the quantity available for someone else, the good is
A)rival.
B)nonrival.
C)excludable.
D)nonexcludable.
E)a public good.
A)rival.
B)nonrival.
C)excludable.
D)nonexcludable.
E)a public good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 177 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
If a good or resource is rival, it could be a
A)public good.
B)private good.
C)common resource.
D)Both answers B and C are correct.
E)Both answers A and C are correct.
A)public good.
B)private good.
C)common resource.
D)Both answers B and C are correct.
E)Both answers A and C are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 177 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
A mother notices that when she divides brownies equally between her two children and gives each child her share on a separate plate, the brownies last a long time.But when she gives her children a plate to share, the brownies are gone pretty quickly.The mother concludes from this that brownies given on a single plate are
A)excludable but they might either be rival or nonrival.
B)nonexcludable and nonrival.
C)excludable and rival.
D)excludable and nonrival.
E)nonexcludable and rival.
A)excludable but they might either be rival or nonrival.
B)nonexcludable and nonrival.
C)excludable and rival.
D)excludable and nonrival.
E)nonexcludable and rival.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 177 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
If I order a pizza and invite my neighbors to eat it, the pizza is
A)a private good.
B)a common resource.
C)a public good because many people ate it.
D)either a common resource or a public good depending on whether it is overused.
E)produced by a natural monopoly.
A)a private good.
B)a common resource.
C)a public good because many people ate it.
D)either a common resource or a public good depending on whether it is overused.
E)produced by a natural monopoly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 177 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
A public good
A)only yields benefits to those that decide to buy it.
B)is the same as a common resource.
C)is nonrival and nonexcludable.
D)is rival.
A)only yields benefits to those that decide to buy it.
B)is the same as a common resource.
C)is nonrival and nonexcludable.
D)is rival.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 177 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
If no one can be excluded from receiving the benefits of a good or service and the consumption of the good or service does not decrease the amount available to someone else from consuming it, then the good
A)is a private good.
B)is a common resource.
C)is a public good.
D)is a natural monopoly.
E)Both answers B and C are correct.
A)is a private good.
B)is a common resource.
C)is a public good.
D)is a natural monopoly.
E)Both answers B and C are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 177 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Which of the following represents an efficient quantity of a public good? The quantity at which the
A)marginal cost of production is minimized.
B)number of free riders is maximized.
C)marginal benefit minus marginal cost is minimized.
D)marginal benefit is equal to the marginal cost.
E)marginal benefit exceeds the marginal cost by the maximum amount possible.
A)marginal cost of production is minimized.
B)number of free riders is maximized.
C)marginal benefit minus marginal cost is minimized.
D)marginal benefit is equal to the marginal cost.
E)marginal benefit exceeds the marginal cost by the maximum amount possible.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 177 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
A good that can be consumed even if the consumer does not pay for it
A)is necessarily rival in consumption.
B)completely avoids the free rider problem.
C)does not exist because firms won't produce goods for which consumers won't pay.
D)is nonexcludable.
E)might be nonexcludable but is definitely nonrival.
A)is necessarily rival in consumption.
B)completely avoids the free rider problem.
C)does not exist because firms won't produce goods for which consumers won't pay.
D)is nonexcludable.
E)might be nonexcludable but is definitely nonrival.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 177 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
As more of a public good is produced, the marginal benefit of each additional unit ________ and as more of a private good is produced, the marginal benefit of each additional unit ________.
A)increases; increases
B)increases; decreases
C)decreases; increases
D)decreases; decreases
E)does not change; does not change
A)increases; increases
B)increases; decreases
C)decreases; increases
D)decreases; decreases
E)does not change; does not change

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 177 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Which of the following is an example of the free-rider problem?
A)John attends a lecture on investing in high-tech companies for which he paid $100 to hear.
B)Tom watches Mystery on his local PBS television station but Tom does not contribute anything to PBS.
C)Sarah works overtime while her co-workers opt for a traditional schedule.
D)Jethro buys a skunk-hunting permit that he refuses to share with his sister.
E)Katie catches a swordfish in the ocean.
A)John attends a lecture on investing in high-tech companies for which he paid $100 to hear.
B)Tom watches Mystery on his local PBS television station but Tom does not contribute anything to PBS.
C)Sarah works overtime while her co-workers opt for a traditional schedule.
D)Jethro buys a skunk-hunting permit that he refuses to share with his sister.
E)Katie catches a swordfish in the ocean.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 177 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
To achieve the efficient level of national defense,
A)the government could provide national defense because it is a public good.
B)private firms can provide national defense because it is a private good.
C)the government can provide national defense because it is a private good.
D)the government can provide national defense because it is a common resource.
E)None of the above answers is correct.
A)the government could provide national defense because it is a public good.
B)private firms can provide national defense because it is a private good.
C)the government can provide national defense because it is a private good.
D)the government can provide national defense because it is a common resource.
E)None of the above answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 177 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The efficient quantity of a public good is the quantity at which marginal benefit is
A)greater than marginal cost by any amount.
B)less than marginal cost.
C)equal to marginal cost.
D)zero.
E)greater than marginal cost by the maximum amount.
A)greater than marginal cost by any amount.
B)less than marginal cost.
C)equal to marginal cost.
D)zero.
E)greater than marginal cost by the maximum amount.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 177 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
If we know everyone's individual marginal benefit curve for a public good, then the economy's marginal benefit curve for that public good can be found by
A)finding the average of everyone's marginal benefit.
B)summing horizontally the amount of everyone's marginal benefit.
C)summing vertically the amount of everyone's marginal benefit.
D)averaging either horizontally or vertically the amount of everyone's marginal benefit.
E)none of the above; it is impossible to find this value.
A)finding the average of everyone's marginal benefit.
B)summing horizontally the amount of everyone's marginal benefit.
C)summing vertically the amount of everyone's marginal benefit.
D)averaging either horizontally or vertically the amount of everyone's marginal benefit.
E)none of the above; it is impossible to find this value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 177 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Suppose a public good is provided in an economy with only two consumers, Popeye and Captain Hook.If Popeye values the public good at $4,000 per year, and Captain Hook values it at $3,000 per year, the economy's marginal benefit of the public good per year is
A)$7,000.
B)$4,000.
C)$3,000.
D)$1,000.
E)$12,000.
A)$7,000.
B)$4,000.
C)$3,000.
D)$1,000.
E)$12,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 177 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The free-rider problem is associated with
A)public goods.
B)private goods.
C)common resources.
D)any type of good.
E)natural monopolies.
A)public goods.
B)private goods.
C)common resources.
D)any type of good.
E)natural monopolies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 177 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
To determine the efficient quantity of a public good to supply,
A)the private firms that will produce the good each produce the exact same quantity.
B)marginal benefit and marginal cost are equated, the same as is done to determine the efficient quantity of a private good.
C)total benefit is equated to total cost, the same as is done to determine the efficient quantity of a private good.
D)politicians use the principle of maximum differentiation.
E)marginal benefit must exceed marginal cost by as much as possible.
A)the private firms that will produce the good each produce the exact same quantity.
B)marginal benefit and marginal cost are equated, the same as is done to determine the efficient quantity of a private good.
C)total benefit is equated to total cost, the same as is done to determine the efficient quantity of a private good.
D)politicians use the principle of maximum differentiation.
E)marginal benefit must exceed marginal cost by as much as possible.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 177 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The marginal benefit of a public good ________ as more of the good is produced.
A)increases
B)decreases
C)stays the same
D)None of the above is correct because the marginal benefit could increase, decrease, or not change depending on whether the marginal cost increases, decreases, or does not change as more is produced.
E)None of the above is correct because the marginal benefit could increase, decrease, or not change depending on whether more, fewer, or the same number of people consume the good as more is produced.
A)increases
B)decreases
C)stays the same
D)None of the above is correct because the marginal benefit could increase, decrease, or not change depending on whether the marginal cost increases, decreases, or does not change as more is produced.
E)None of the above is correct because the marginal benefit could increase, decrease, or not change depending on whether more, fewer, or the same number of people consume the good as more is produced.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 177 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Marginal cost curves for public goods are usually
A)downward sloping.
B)upward sloping.
C)horizontal.
D)vertical.
E)U-shaped.
A)downward sloping.
B)upward sloping.
C)horizontal.
D)vertical.
E)U-shaped.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 177 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
For which type of good is it necessary to sum the marginal benefit curves vertically in order to obtain the economy's marginal benefit curve?
A)public goods
B)mixed goods
C)private goods
D)goods that are subject to the exclusion principle
E)common resources
A)public goods
B)mixed goods
C)private goods
D)goods that are subject to the exclusion principle
E)common resources

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 177 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
A library is a public good.The marginal cost curve for libraries in Lafayette, California
A)has a negative slope.
B)is definitely a horizontal line.
C)has a positive slope.
D)is a vertical line.
E)is identical to the marginal benefit curve because libraries are nonrival.
A)has a negative slope.
B)is definitely a horizontal line.
C)has a positive slope.
D)is a vertical line.
E)is identical to the marginal benefit curve because libraries are nonrival.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 177 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Which of the following is a correct statement?
A)To obtain the economy's marginal benefit for a public good, marginal benefits of all individuals at each quantity have to be added.
B)To obtain the economy's marginal benefit for a public good, the quantity that all individuals are willing to buy at each price must be added.
C)To obtain the economy's marginal benefit curve for a public good, we sum the individual demand curves horizontally.
D)Because public goods are nonexcludable, the economy's marginal benefit curve for a public good is the same as its marginal cost curve.
E)None of the above answers is correct.
A)To obtain the economy's marginal benefit for a public good, marginal benefits of all individuals at each quantity have to be added.
B)To obtain the economy's marginal benefit for a public good, the quantity that all individuals are willing to buy at each price must be added.
C)To obtain the economy's marginal benefit curve for a public good, we sum the individual demand curves horizontally.
D)Because public goods are nonexcludable, the economy's marginal benefit curve for a public good is the same as its marginal cost curve.
E)None of the above answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 177 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The free-rider problem
I) means that people can consume a good without paying for it.
Ii) means that people pay too much for a good in order to consume it.
Iii) applies to a public good.
A)i only
B)iii only
C)i and ii
D)ii and iii
E)i and iii
I) means that people can consume a good without paying for it.
Ii) means that people pay too much for a good in order to consume it.
Iii) applies to a public good.
A)i only
B)iii only
C)i and ii
D)ii and iii
E)i and iii

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 177 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The free-rider problem exists because
A)private goods or services cause some people to want to take them for free.
B)some goods or services are excludable and cause envy for those who don't have them.
C)some goods or services that are rival and leave some people without them.
D)people cannot be excluded from consuming public goods even if they don't pay for them.
E)people must all consume the same public good and so everyone wants to pay for it.
A)private goods or services cause some people to want to take them for free.
B)some goods or services are excludable and cause envy for those who don't have them.
C)some goods or services that are rival and leave some people without them.
D)people cannot be excluded from consuming public goods even if they don't pay for them.
E)people must all consume the same public good and so everyone wants to pay for it.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 177 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
To find the economy's marginal benefit curve of a public good, we
A)sum the marginal benefits of each individual at each quantity.
B)sum the costs of the inputs used to produce the good.
C)sum the quantities demanded at each individual price.
D)sum the prices consumers are willing to pay for different quantities of the good.
E)average the prices consumers are willing to pay for the same quantity of the good.
A)sum the marginal benefits of each individual at each quantity.
B)sum the costs of the inputs used to produce the good.
C)sum the quantities demanded at each individual price.
D)sum the prices consumers are willing to pay for different quantities of the good.
E)average the prices consumers are willing to pay for the same quantity of the good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 177 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
We determine the economy's marginal benefit curve for a public good or service by
A)vertically summing the individual marginal benefit curves of each member of society.
B)horizontally summing the individual marginal benefits curves of each member of society.
C)multiplying the marginal benefits of each member of society.
D)dividing the sum of the marginal benefits of each member of society by the number of people in society.
E)vertically summing the individual firm's marginal cost curves.
A)vertically summing the individual marginal benefit curves of each member of society.
B)horizontally summing the individual marginal benefits curves of each member of society.
C)multiplying the marginal benefits of each member of society.
D)dividing the sum of the marginal benefits of each member of society by the number of people in society.
E)vertically summing the individual firm's marginal cost curves.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 177 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Public goods create a free-rider problem because
A)only people who pay for the good or service can enjoy the good or service.
B)people do not want to consume public goods.
C)the good or service is rival in nature.
D)the good or service is excludable.
E)people can enjoy the good or service no matter whether or not they pay for it.
A)only people who pay for the good or service can enjoy the good or service.
B)people do not want to consume public goods.
C)the good or service is rival in nature.
D)the good or service is excludable.
E)people can enjoy the good or service no matter whether or not they pay for it.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 177 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Why are private firms unable to produce public goods?
A)Because the government outlaws private firms from producing them.
B)The marginal cost of production is too high for private production to be possible.
C)They can produce these goods but they would not earn any revenue because of the free-rider problem.
D)The tragedy of the commons means that private firms produce an inefficient amount of public goods.
E)None of the above answers is correct.
A)Because the government outlaws private firms from producing them.
B)The marginal cost of production is too high for private production to be possible.
C)They can produce these goods but they would not earn any revenue because of the free-rider problem.
D)The tragedy of the commons means that private firms produce an inefficient amount of public goods.
E)None of the above answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 177 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62

Paul and Paula are the only members of society.The table above gives their marginal benefits from missile gunboats, a public good.Determine the marginal benefit to society of the fourth missile gunboat.
A)$8 million
B)$4 million
C)$2 million
D)$1 million
E)$40 million

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 177 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The free-rider problem for a public good means that
A)a private market would provide less than the efficient amount of the good.
B)a private market would provide more than the efficient amount of the good.
C)the good is rival.
D)the good is excludable.
E)a private market would provide the efficient amount of the good.
A)a private market would provide less than the efficient amount of the good.
B)a private market would provide more than the efficient amount of the good.
C)the good is rival.
D)the good is excludable.
E)a private market would provide the efficient amount of the good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 177 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64

Paul and Paula are the only members of society.The table above gives their marginal benefits from missile gunboats, a public good.Suppose the marginal cost of a missile gunboat is $8 million.What is the efficient quantity of missile gunboats?
A)1 boat
B)2 boats
C)3 boats
D)4 boats
E)More information about whether the services provided by missile gunboats are rival or not is needed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 177 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
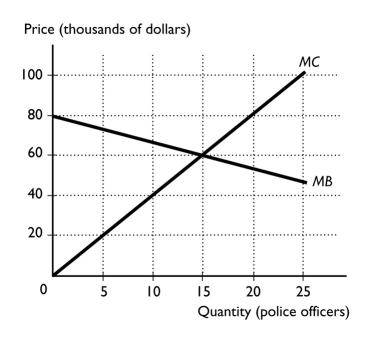
The figure above shows the marginal cost and marginal benefit of police protection in the city of Hugo, Oklahoma.Police protection is a public good.If the city of Hugo hires 25 officers, then
A)marginal cost will exceed marginal benefit, which means that the efficient number of officers is more than 25.
B)marginal cost will exceed marginal benefit, which means that the efficient number of officers is less than 25.
C)marginal benefit will exceed marginal cost, which means that Hugo should reduce the number of officers they hire.
D)marginal benefit equals marginal cost.
E)None of the above answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 177 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
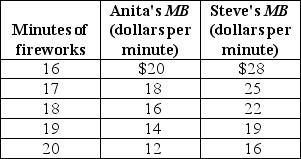
The table above shows Anita and Steve's marginal benefits for the annual 4ᵗʰ of July fireworks show at City Park.If Anita and Steve are the only two people in the economy and the marginal cost to produce one minute of fireworks is $28, what is the efficient quantity of fireworks?
A)16 minutes
B)More than 20 minutes
C)19 minutes
D)Less than 16 minutes
E)20 minutes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 177 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Because national defense is potentially subject to free riding, a private sector market for national defense would lead to
A)the efficient amount of national defense if there is free riding.
B)more than the efficient amount being produced if there is free riding.
C)less than the efficient amount being produced if there is free riding.
D)less than the efficient amount being produced if there is not free riding.
E)None of the above answers is correct.
A)the efficient amount of national defense if there is free riding.
B)more than the efficient amount being produced if there is free riding.
C)less than the efficient amount being produced if there is free riding.
D)less than the efficient amount being produced if there is not free riding.
E)None of the above answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 177 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68

The figure above shows the marginal cost and marginal benefit of police protection in the city of Hugo, Oklahoma.Police protection is a public good.The efficient number of officers that should be hired by the city of Hugo is
A)15.
B)25.
C)10.
D)0.
E)More than 25 because MB > $0 when 25 officers are hired.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 177 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The principle of minimum differentiation describes a tendency of competitors to
A)lower price.
B)offer similar products or policies.
C)decrease the quantity of goods available.
D)offer public goods for sale.
E)free ride.
A)lower price.
B)offer similar products or policies.
C)decrease the quantity of goods available.
D)offer public goods for sale.
E)free ride.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 177 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70

The figure above shows the marginal cost and marginal benefit of police protection in the city of Hugo, Oklahoma.Police protection is a public good.If the city of Hugo hires 5 officers, marginal
A)cost exceeds marginal benefit, so therefore fewer officers should be hired.
B)benefit exceeds marginal cost, so therefore more officers should be hired.
C)benefit equals marginal cost.
D)benefit exceeds marginal cost, so therefore no more officers should be hired.
E)benefit exceeds marginal cost but not by as much as possible, so 5 officers is not the efficient number to be hired.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 177 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Which of the following describes the principle of minimum differentiation?
A)competitors becoming identical to appeal to the largest number of clients or voters
B)minimizing the difference between marginal benefit and marginal cost
C)voters becoming highly informed to elect the best candidate
D)bureaucrats providing the most efficient level of pubic goods provision
E)minimizing the amount of free riding that occurs
A)competitors becoming identical to appeal to the largest number of clients or voters
B)minimizing the difference between marginal benefit and marginal cost
C)voters becoming highly informed to elect the best candidate
D)bureaucrats providing the most efficient level of pubic goods provision
E)minimizing the amount of free riding that occurs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 177 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
A private, competitive market
A)provides the efficient quantity of a public good.
B)allocates too few resources for a public good.
C)allocates too many resources for a public good.
D)can be relied upon to allocate resources efficiently both for private and public goods.
E)will allocate too many resources for a public good only if free riding occurs.
A)provides the efficient quantity of a public good.
B)allocates too few resources for a public good.
C)allocates too many resources for a public good.
D)can be relied upon to allocate resources efficiently both for private and public goods.
E)will allocate too many resources for a public good only if free riding occurs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 177 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73

The table above shows Anita and Steve's marginal benefits for the annual 4ᵗʰ of July fireworks show at City Park.If Anita and Steve are the only two people in the economy, what is the economy's marginal benefit from the 19ᵗʰ minute of fireworks?
A)$38
B)$30
C)$162
D)$129
E)$33

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 177 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The tendency of political parties to propose identical policies which appeal to the maximum number of voters is referred to as the principle of
A)maximum differentiation.
B)minimum differentiation.
C)minimum marginal utility.
D)maximum returns.
E)agreement.
A)maximum differentiation.
B)minimum differentiation.
C)minimum marginal utility.
D)maximum returns.
E)agreement.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 177 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75

Paul and Paula are the only members of society.The table above gives their marginal benefits from missile gunboats, a public good.Determine the marginal benefit to society of the second missile gunboat.
A)$16 million
B)$8 million
C)$12 million
D)$10 million
E)$4 million

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 177 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
For any individual consumer, free-riding is
A)common for private goods.
B)rational.
C)irrational.
D)impossible for public goods.
E)the same as paying a fair price for the good.
A)common for private goods.
B)rational.
C)irrational.
D)impossible for public goods.
E)the same as paying a fair price for the good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 177 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Suppose the marginal cost of the fourth unit of a public good is $20.If Mark and Judy are the only members of society, and they are willing to pay $10 and $11, respectively, for the fourth unit of the good, then the efficient quantity is
A)3 units.
B)4 or more units.
C)0 units.
D)More information is needed about the marginal benefits of the first, second, and third units of the public good.
E)None of the above answers is correct.
A)3 units.
B)4 or more units.
C)0 units.
D)More information is needed about the marginal benefits of the first, second, and third units of the public good.
E)None of the above answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 177 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Suppose the government is producing a public good.If the marginal benefit of the last unit of a public good produced is greater than the marginal cost of that unit, to achieve the efficient amount of production, what should be done?
A)The government should produce more units.
B)The government should cease production.
C)Private firms should take over the production and sale of the good.
D)Nothing because the government is already producing the efficient quantity of the public good.
E)The government should produce fewer units.
A)The government should produce more units.
B)The government should cease production.
C)Private firms should take over the production and sale of the good.
D)Nothing because the government is already producing the efficient quantity of the public good.
E)The government should produce fewer units.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 177 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79

The table above shows Anita and Steve's marginal benefits for the annual 4ᵗʰ of July fireworks show at City Park.If Anita and Steve are the only two people in the economy, what is the economy's marginal benefit from the 18ᵗʰ minute of fireworks?
A)$38
B)$33
C)$30
D)$162
E)$129

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 177 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
In politics, the principle of minimum differentiation is the tendency toward
A)identical policies to appeal to a minimum number of people.
B)different policies to appeal to a maximum number of people.
C)identical policies to appeal to a maximum number of people.
D)different policies to appeal to a minimum number of people.
E)a minimum number of policies in order to appeal to a maximum number of people.
A)identical policies to appeal to a minimum number of people.
B)different policies to appeal to a maximum number of people.
C)identical policies to appeal to a maximum number of people.
D)different policies to appeal to a minimum number of people.
E)a minimum number of policies in order to appeal to a maximum number of people.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 177 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



