Deck 12: Markets With Private Information
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/101
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 12: Markets With Private Information
1
Of the following, the best example of private information is when
A)Michael knows the price of a gallon of milk at the minimart but Michelle doesn't know.
B)you are selling a used car and you know your used car's defects but a potential buyer cannot find out about them until after buying.
C)you are selling a used car and you do not know your used car's defects
D)you don't know the quality of a used car and must hire a trained mechanic who tells you all its defects.
E)you pay the owner of a used car a little extra and she lets you know all of the car's defects.
A)Michael knows the price of a gallon of milk at the minimart but Michelle doesn't know.
B)you are selling a used car and you know your used car's defects but a potential buyer cannot find out about them until after buying.
C)you are selling a used car and you do not know your used car's defects
D)you don't know the quality of a used car and must hire a trained mechanic who tells you all its defects.
E)you pay the owner of a used car a little extra and she lets you know all of the car's defects.
B
2
In the used car market without warranties, adverse selection results in
A)sellers of "lemons" claiming that their car is a lemon.
B)only lemons being available for sale.
C)the market price of used cars equal to that of good used cars.
D)an efficient pooling equilibrium.
E)all of the above
A)sellers of "lemons" claiming that their car is a lemon.
B)only lemons being available for sale.
C)the market price of used cars equal to that of good used cars.
D)an efficient pooling equilibrium.
E)all of the above
B
3
Used car buyers believe a car is good quality when the seller signals the car's quality by offering a warranty because
A)car sellers would never lie.
B)car buyers are gullible.
C)signals lead to efficient pooling equilibriums.
D)the signal cannot be false.
E)a false signal can be costly to the seller.
A)car sellers would never lie.
B)car buyers are gullible.
C)signals lead to efficient pooling equilibriums.
D)the signal cannot be false.
E)a false signal can be costly to the seller.
E
4
Adverse selection is the tendency for people who accept contracts to be those who
A)buy goods and then regret it later.
B)buy goods for more than their own reservation price.
C)want to avoid the lemons problem.
D)plan to use private information to the disadvantage of the less well-informed party.
E)engage in a number of searches larger than that specified in the contract.
A)buy goods and then regret it later.
B)buy goods for more than their own reservation price.
C)want to avoid the lemons problem.
D)plan to use private information to the disadvantage of the less well-informed party.
E)engage in a number of searches larger than that specified in the contract.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Private information is a situation in which
A)two parties to an exchange have information that is available to outsiders if they ask.
B)one party to an exchange has information that is not available to the other.
C)the marginal cost of a person's obtaining additional information is zero.
D)the marginal cost of making information available to one more person is zero.
E)outsiders have relevant information that is not available to the people in the market.
A)two parties to an exchange have information that is available to outsiders if they ask.
B)one party to an exchange has information that is not available to the other.
C)the marginal cost of a person's obtaining additional information is zero.
D)the marginal cost of making information available to one more person is zero.
E)outsiders have relevant information that is not available to the people in the market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Suppose that there are only two types of used cars, peaches and lemons.Peaches are worth $10,000 and lemons are worth $4,000.Without effective signals such as warranties, the owners of peaches cannot sell their cars for $10,000 because the
A)owners of peaches cannot convince buyers that their cars are worth $10,000.
B)buyers cannot convince owners of peaches to sell their cars for $10,000.
C)owners of lemons cannot convince buyers that their cars are worth more than $4,000.
D)buyers cannot convince owners of lemons to sell their cars for more than $4,000.
E)buyers cannot convince owners of lemons to sell their cars for $4,000.
A)owners of peaches cannot convince buyers that their cars are worth $10,000.
B)buyers cannot convince owners of peaches to sell their cars for $10,000.
C)owners of lemons cannot convince buyers that their cars are worth more than $4,000.
D)buyers cannot convince owners of lemons to sell their cars for more than $4,000.
E)buyers cannot convince owners of lemons to sell their cars for $4,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Signals are believable when the cost of sending a ________ is known to be ________.
A)false signal; low
B)false signal; high
C)true signal; low
D)true or false signal; low
E)true signal; high
A)false signal; low
B)false signal; high
C)true signal; low
D)true or false signal; low
E)true signal; high

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
In the used car market, adverse selection is a problem primarily when
A)sellers cannot judge buyers' creditworthiness.
B)buyers cannot signal their willingness to buy.
C)buyers cannot determine the quality of a used car.
D)sellers offer warranties on all used cars.
E)sellers and buyers both agree that a particular used car is a lemon.
A)sellers cannot judge buyers' creditworthiness.
B)buyers cannot signal their willingness to buy.
C)buyers cannot determine the quality of a used car.
D)sellers offer warranties on all used cars.
E)sellers and buyers both agree that a particular used car is a lemon.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Used car buyers believe a car is good quality when the seller signals the car's quality by offering a warranty because
A)a warranty on a lemon is costly to the seller.
B)warranties are only offered on lemons.
C)the signal cannot be false.
D)adverse selection means that warranties will not be used as a signal.
E)a false signal has no effect on the seller.
A)a warranty on a lemon is costly to the seller.
B)warranties are only offered on lemons.
C)the signal cannot be false.
D)adverse selection means that warranties will not be used as a signal.
E)a false signal has no effect on the seller.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Your grade point average acts as ________ to potential employers.
A)a signal
B)private information
C)a reservation price
D)a guarantee
E)insurance
A)a signal
B)private information
C)a reservation price
D)a guarantee
E)insurance

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Suppose there are only two kind of cars in the market for used cars: lemons and good cars.A lemon is worth $1,000 both to its current owner and to anyone who buys it.A good car is worth $8,000 to its current and potential owners.Buyers can't tell whether a car is a lemon until after they have bought the car, and there is no warranty.What is the equilibrium price of a used car?
A)$8,000
B)$1,000
C)$4,500
D)$9,000
E)The equilibrium price depends on how many lemons and how many good cars are traded.
A)$8,000
B)$1,000
C)$4,500
D)$9,000
E)The equilibrium price depends on how many lemons and how many good cars are traded.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Adverse selection is created by
A)incentives to change behavior after two parties have reached an agreement.
B)risk.
C)signaling.
D)taxes.
E)private information.
A)incentives to change behavior after two parties have reached an agreement.
B)risk.
C)signaling.
D)taxes.
E)private information.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The tendency for people to enter into agreements in which they can use their private information to their own advantage and to the disadvantage of the less informed party is known as
A)adverse selection.
B)a pooling selection.
C)moral hazard.
D)the market for oranges.
E)a signal.
A)adverse selection.
B)a pooling selection.
C)moral hazard.
D)the market for oranges.
E)a signal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
In the used car market with no warranties, the market for lemons (poor quality used cars)is ________ and the market for good cars is ________.
A)efficient; efficient
B)inefficient because of over-supply; inefficient because of under-supply
C)inefficient because of over-supply; inefficient because of over-supply
D)efficient; inefficient because of under-supply
E)inefficient because of over-supply; efficient
A)efficient; efficient
B)inefficient because of over-supply; inefficient because of under-supply
C)inefficient because of over-supply; inefficient because of over-supply
D)efficient; inefficient because of under-supply
E)inefficient because of over-supply; efficient

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Without warranties, used car buyers can assume that all used cars are "lemons" because of
A)moral hazard.
B)false signals.
C)moral dilemma.
D)adverse selection.
E)adverse reaction.
A)moral hazard.
B)false signals.
C)moral dilemma.
D)adverse selection.
E)adverse reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Suppose that there are only two types of used cars, peaches and lemons.Peaches are worth $10,000, and lemons are worth $6,000.Three fourths of all used cars are peaches, and one fourth are lemons.In a market with no signals, for instance, a market without warranties, the average value of cars actually sold will be
A)$6,000.
B)$7,000.
C)$7,500.
D)$9,000.
E)$10,000.
A)$6,000.
B)$7,000.
C)$7,500.
D)$9,000.
E)$10,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Warranties in the used car market ________ the problem of private information thereby causing the price of good and bad used cars to ________.
A)reduce; be the same
B)reduce; differ
C)magnify; be the same
D)magnify; differ
E)None of the above answers is correct because warranties have nothing to do with private information.
A)reduce; be the same
B)reduce; differ
C)magnify; be the same
D)magnify; differ
E)None of the above answers is correct because warranties have nothing to do with private information.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Adverse selection can occur when
A)all parties have full information.
B)one party has information not available to the other party.
C)information is not full but both parties have the same information.
D)incentives result in one party not reaching an agreement with the other party.
E)nobody has any information.
A)all parties have full information.
B)one party has information not available to the other party.
C)information is not full but both parties have the same information.
D)incentives result in one party not reaching an agreement with the other party.
E)nobody has any information.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The used car market without warranties suffers from
A)perfect competition.
B)a separating equilibrium.
C)oligopoly.
D)adverse selection and moral hazard.
E)excessive signaling.
A)perfect competition.
B)a separating equilibrium.
C)oligopoly.
D)adverse selection and moral hazard.
E)excessive signaling.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
One of the ways the market for used cars copes with the problems associated with private information is through the offering of
A)leases.
B)warranties.
C)low interest rates.
D)high prices for high-quality used cars.
E)low prices.
A)leases.
B)warranties.
C)low interest rates.
D)high prices for high-quality used cars.
E)low prices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
In the used car market with no warranties, the equilibrium is a ________ and there is ________.
A)pooling equilibrium; inefficiency, partly because of over-supply of good cars
B)pooling equilibrium; inefficiency, partly because of over-supply of lemons
C)separating equilibrium; no inefficiency
D)separating equilibrium; inefficiency, partly because of over-supply of lemons
E)pooling equilibrium; no inefficiency
A)pooling equilibrium; inefficiency, partly because of over-supply of good cars
B)pooling equilibrium; inefficiency, partly because of over-supply of lemons
C)separating equilibrium; no inefficiency
D)separating equilibrium; inefficiency, partly because of over-supply of lemons
E)pooling equilibrium; no inefficiency

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
In the used car market with warranties, the equilibrium is a ________ and the lemons problem is ________.
A)pooling equilibrium; solved
B)pooling equilibrium; unresolved
C)separating equilibrium; unresolved
D)separating equilibrium; solved
E)pooling equilibrium; possibly solved and possibly unresolved, depending on whether good used cars sell for a higher price than do lemons
A)pooling equilibrium; solved
B)pooling equilibrium; unresolved
C)separating equilibrium; unresolved
D)separating equilibrium; solved
E)pooling equilibrium; possibly solved and possibly unresolved, depending on whether good used cars sell for a higher price than do lemons

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
If Sally drives less carefully after buying auto insurance, she illustrates
A)adverse selection.
B)negative selection.
C)screening risk.
D)moral hazard.
E)lemon hazard.
A)adverse selection.
B)negative selection.
C)screening risk.
D)moral hazard.
E)lemon hazard.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Moral hazard is
A)the tendency for people to enter into agreements in which they can use their private information to their own advantage and to the disadvantage of the less informed party.
B)when one of the parties to an agreement has an incentive after the agreement is made to act in a manner that brings additional benefits to himself or herself at the expense of the other party.
C)a situation in which only bad quality items are bought and sold.
D)absent after a person who dislikes risk buys insurance against the risk.
E)an action taken outside a market that conveys information that can be used by that market.
A)the tendency for people to enter into agreements in which they can use their private information to their own advantage and to the disadvantage of the less informed party.
B)when one of the parties to an agreement has an incentive after the agreement is made to act in a manner that brings additional benefits to himself or herself at the expense of the other party.
C)a situation in which only bad quality items are bought and sold.
D)absent after a person who dislikes risk buys insurance against the risk.
E)an action taken outside a market that conveys information that can be used by that market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Asymmetric information means that
A)the buyer must have information that the seller does not have.
B)the seller must have information that the buyer does not have.
C)the buyer and seller have the same information.
D)either the buyer has information that the seller does not have or the seller has information that the buyer does not have.
E)None of the above answers are correct.
A)the buyer must have information that the seller does not have.
B)the seller must have information that the buyer does not have.
C)the buyer and seller have the same information.
D)either the buyer has information that the seller does not have or the seller has information that the buyer does not have.
E)None of the above answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Because Don has health insurance, he is more likely to see the doctor when he has a cold.This is an example of
A)adverse selection.
B)moral hazard.
C)the lemons problem.
D)both moral hazard and adverse selection.
E)private information.
A)adverse selection.
B)moral hazard.
C)the lemons problem.
D)both moral hazard and adverse selection.
E)private information.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
In the insurance market, private information
A)creates moral hazard but eliminates adverse selection.
B)creates adverse selection but eliminates moral hazard.
C)creates both moral hazard and adverse selection.
D)eliminates both moral hazard and adverse selection.
E)means that screening is unnecessary.
A)creates moral hazard but eliminates adverse selection.
B)creates adverse selection but eliminates moral hazard.
C)creates both moral hazard and adverse selection.
D)eliminates both moral hazard and adverse selection.
E)means that screening is unnecessary.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
In the insurance market, moral hazard and adverse selection are the result of
A)poorly functioning markets.
B)government intervention.
C)private information.
D)treachery.
E)a separating equilibrium.
A)poorly functioning markets.
B)government intervention.
C)private information.
D)treachery.
E)a separating equilibrium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
In the used car market with warranties, the equilibrium is a ________ and there is ________.
A)pooling equilibrium; inefficiency, partly because of over-supply of good cars
B)pooling equilibrium; inefficiency, partly because of over-supply of lemons (poor quality used cars)
C)separating equilibrium; no inefficiency
D)separating equilibrium; inefficiency, partly because of over-supply of lemons (poor quality used cars)
E)pooling equilibrium; no inefficiency
A)pooling equilibrium; inefficiency, partly because of over-supply of good cars
B)pooling equilibrium; inefficiency, partly because of over-supply of lemons (poor quality used cars)
C)separating equilibrium; no inefficiency
D)separating equilibrium; inefficiency, partly because of over-supply of lemons (poor quality used cars)
E)pooling equilibrium; no inefficiency

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
JCPenney guarantees to refund a customer's money if the customer returns poorly made clothing.This guarantee is an example of
A)the adverse selection. problem.
B)the moral hazard problem.
C)the cost of risk.
D)signaling.
E)a lemon problem.
A)the adverse selection. problem.
B)the moral hazard problem.
C)the cost of risk.
D)signaling.
E)a lemon problem.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
In the auto insurance market, who is most likely to have private information that leads to adverse selection?
A)the government agency that regulates insurance companies
B)the insurance company
C)the drivers
D)the insurance company and the drivers
E)the government regulating agency and the insurance company
A)the government agency that regulates insurance companies
B)the insurance company
C)the drivers
D)the insurance company and the drivers
E)the government regulating agency and the insurance company

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The idea of an insurance company "pooling" the risk means that
A)the risk is completely eliminated from society.
B)the insurance company requires buyers to pay a large deductible.
C)the risk is spread over a large population.
D)the insurance company insists on a pooling equilibrium.
E)moral hazard and adverse selection are eliminated.
A)the risk is completely eliminated from society.
B)the insurance company requires buyers to pay a large deductible.
C)the risk is spread over a large population.
D)the insurance company insists on a pooling equilibrium.
E)moral hazard and adverse selection are eliminated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The fact that people who know they are risky drivers are more likely to buy auto insurance reflects
A)adverse selection..
B)moral hazard.
C)a separating equilibrium.
D)signaling.
E)the lemons problem.
A)adverse selection..
B)moral hazard.
C)a separating equilibrium.
D)signaling.
E)the lemons problem.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
If buyers cannot assess the quality of used cars and there are no warranties,
A)only lemons are sold.
B)only good used cars are sold.
C)good cars are sold at a higher price than bad cars.
D)there is no adverse selection problem.
E)lemons and good cars sell for the same price.
A)only lemons are sold.
B)only good used cars are sold.
C)good cars are sold at a higher price than bad cars.
D)there is no adverse selection problem.
E)lemons and good cars sell for the same price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
In the used car market with warranties, the market for lemons (poor quality used cars)is ________ and the market for good cars is ________.
A)efficient; efficient
B)inefficient because of over-supply; inefficient because of under-supply
C)inefficient because of over-supply; inefficient because of over-supply
D)efficient; inefficient because of under-supply
E)inefficient because of over-supply; efficient
A)efficient; efficient
B)inefficient because of over-supply; inefficient because of under-supply
C)inefficient because of over-supply; inefficient because of over-supply
D)efficient; inefficient because of under-supply
E)inefficient because of over-supply; efficient

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
In the used car market, with a pooling equilibrium the price of a lemon is ________ the price of a good used car and with a separating equilibrium the price of a lemon is ________ the price of a good used car.
A)less than; equal to
B)equal to; less than
C)equal to; more than
D)more than; more than
E)equal to; equal to
A)less than; equal to
B)equal to; less than
C)equal to; more than
D)more than; more than
E)equal to; equal to

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
In an insurance market, moral hazard exists chiefly because of
A)economies of scale.
B)adverse selection.
C)diseconomies of scale.
D)private information.
E)public information.
A)economies of scale.
B)adverse selection.
C)diseconomies of scale.
D)private information.
E)public information.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Dan, age 19, may have trouble buying auto insurance at a low price because insurance companies
A)have private information that he is a risky driver.
B)have private information that his signals are valid.
C)fear that he has private information that his deductible is too high.
D)fear that he has private information that he is a risky driver.
E)operate in markets in which screening is inefficient.
A)have private information that he is a risky driver.
B)have private information that his signals are valid.
C)fear that he has private information that his deductible is too high.
D)fear that he has private information that he is a risky driver.
E)operate in markets in which screening is inefficient.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The lemons problem in the used car market is that
A)the price of a lemon is too high.
B)the price of a lemon is too low.
C)no lemons are bought and sold.
D)only lemons are bought and sold.
E)Both answers A and D are correct.
A)the price of a lemon is too high.
B)the price of a lemon is too low.
C)no lemons are bought and sold.
D)only lemons are bought and sold.
E)Both answers A and D are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
In the market for automobile insurance, moral hazard implies that
A)those who are insured might take greater risks.
B)those who are uninsured might take greater risks.
C)insured and uninsured alike will take greater risks.
D)screening will have no effect in the market.
E)drivers with greater risks are more likely to buy insurance.
A)those who are insured might take greater risks.
B)those who are uninsured might take greater risks.
C)insured and uninsured alike will take greater risks.
D)screening will have no effect in the market.
E)drivers with greater risks are more likely to buy insurance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Insurance companies
A)pool risk and enable everyone to share the costs of bad outcomes.
B)never can earn a profit because they accept risk.
C)eliminate the risk of a bad outcome.
D)know who will have a bad outcome.
E)are risk averse.
A)pool risk and enable everyone to share the costs of bad outcomes.
B)never can earn a profit because they accept risk.
C)eliminate the risk of a bad outcome.
D)know who will have a bad outcome.
E)are risk averse.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
In the United States, of all types of insurance, people spend the most on ________ insurance.
A)health
B)hurricane
C)auto
D)life
E)property and casualty
A)health
B)hurricane
C)auto
D)life
E)property and casualty

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
In the market for automobile insurance, adverse selection implies that
A)drivers with greater risks want to buy a policy without deductibles.
B)drivers with greater risks want to buy a policy with large deductibles.
C)uninsured drivers will drive recklessly.
D)insured drivers will drive recklessly.
E)moral hazard does not exist in this market.
A)drivers with greater risks want to buy a policy without deductibles.
B)drivers with greater risks want to buy a policy with large deductibles.
C)uninsured drivers will drive recklessly.
D)insured drivers will drive recklessly.
E)moral hazard does not exist in this market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
If a health insurance company offers coverage regardless of age, health status, or smoking history, it is likely to suffer
A)moral hazard problems.
B)adverse selection problems.
C)lower costs.
D)low demand for its product.
E)a screening equilibrium.
A)moral hazard problems.
B)adverse selection problems.
C)lower costs.
D)low demand for its product.
E)a screening equilibrium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Ben is an aggressive driver so he is more likely to buy auto insurance.This situation illustrates the idea of
A)moral hazard.
B)adverse selection.
C)the lemon problem.
D)inefficiency.
E)a pooling equilibrium.
A)moral hazard.
B)adverse selection.
C)the lemon problem.
D)inefficiency.
E)a pooling equilibrium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
One way of screening in the automobile insurance market is for companies to
A)offer policies with different deductibles and different premiums.
B)insure only careful drivers.
C)insure only risky drivers.
D)eliminate policies with no-claim bonuses because these policies are usually not profitable.
E)offer warranties.
A)offer policies with different deductibles and different premiums.
B)insure only careful drivers.
C)insure only risky drivers.
D)eliminate policies with no-claim bonuses because these policies are usually not profitable.
E)offer warranties.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
In the health insurance market, adverse selection occurs when
A)chronically ill people buy health insurance.
B)insured people go to the doctor unnecessarily.
C)patients sue their doctor.
D)people with health insurance tend to behave more recklessly.
E)chronically ill people are unable to buy health insurance.
A)chronically ill people buy health insurance.
B)insured people go to the doctor unnecessarily.
C)patients sue their doctor.
D)people with health insurance tend to behave more recklessly.
E)chronically ill people are unable to buy health insurance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
When an auto insurance company is screening, it is
A)ignoring the possibility of moral hazard in order to minimize adverse selection.
B)attempting to keep its private information private.
C)trying to determine if a driver is an aggressive driver or a safe driver.
D)making its private information public.
E)marketing its policies to customers.
A)ignoring the possibility of moral hazard in order to minimize adverse selection.
B)attempting to keep its private information private.
C)trying to determine if a driver is an aggressive driver or a safe driver.
D)making its private information public.
E)marketing its policies to customers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
If you have private information that you are a riskier driver than your record indicates, you are likely to buy an insurance policy that has a ________ deductible and a ________ premium.
A)high; high
B)high; low
C)low; high
D)low; low
E)None of the above answers are correct because private information has no effect in the market for auto insurance.
A)high; high
B)high; low
C)low; high
D)low; low
E)None of the above answers are correct because private information has no effect in the market for auto insurance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
In the market for auto insurance, with a pooling equilibrium ________ and with a separating equilibrium ________.
A)aggressive drivers pay a higher premium than do safer drivers; aggressive drivers pay a higher premium than do safer drivers
B)no one can buy auto insurance; aggressive drivers pay a higher premium than do safer drivers
C)aggressive and safe drivers pay the same premium; aggressive and safe drivers pay the same premium
D)aggressive and safe drivers pay the same premium; aggressive drivers pay a higher premium than do safer drivers
E)aggressive drivers pay a higher premium than do safer drivers; aggressive and safe drivers pay the same premium
A)aggressive drivers pay a higher premium than do safer drivers; aggressive drivers pay a higher premium than do safer drivers
B)no one can buy auto insurance; aggressive drivers pay a higher premium than do safer drivers
C)aggressive and safe drivers pay the same premium; aggressive and safe drivers pay the same premium
D)aggressive and safe drivers pay the same premium; aggressive drivers pay a higher premium than do safer drivers
E)aggressive drivers pay a higher premium than do safer drivers; aggressive and safe drivers pay the same premium

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Screening
A)leads to a pooling equilibrium in the insurance market.
B)means an uninformed person passes knowledge to an informed person.
C)makes no-claim bonuses unnecessary.
D)explains why insurance companies offer low-premium, high-deductible policies and high-premium, low-deductible policies.
E)makes the insurance market inefficient.
A)leads to a pooling equilibrium in the insurance market.
B)means an uninformed person passes knowledge to an informed person.
C)makes no-claim bonuses unnecessary.
D)explains why insurance companies offer low-premium, high-deductible policies and high-premium, low-deductible policies.
E)makes the insurance market inefficient.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Life insurance companies often give applicants a physical examination to prevent
A)moral hazard.
B)screening.
C)adverse selection.
D)signaling.
E)warranties.
A)moral hazard.
B)screening.
C)adverse selection.
D)signaling.
E)warranties.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Bill purchases property insurance for his office building, which includes coverage for fire damage.The policy offers premium discounts for smoke detectors, fire alarms, fire extinguishers and sprinkler systems.This is an incentive system to help avoid
A)adverse selection.
B)adverse signals.
C)moral hazard.
D)screening.
E)None of the above answers are correct.
A)adverse selection.
B)adverse signals.
C)moral hazard.
D)screening.
E)None of the above answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Auto insurance companies charge a lower premium to drivers who carry a higher deductible because
A)insurance companies are not profit maximizers.
B)a driver's riskiness increases as the driver's deductible increases.
C)a high deductible signals a high risk.
D)insurance companies prefer that drivers carry no deductible.
E)a high deductible reveals that driver is a careful driver.
A)insurance companies are not profit maximizers.
B)a driver's riskiness increases as the driver's deductible increases.
C)a high deductible signals a high risk.
D)insurance companies prefer that drivers carry no deductible.
E)a high deductible reveals that driver is a careful driver.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
"Screening" means that an auto insurance company is
A)enforcing a pooling equilibrium.
B)ignoring all private information.
C)creating an incentive to eliminate moral hazard even though it reinforces the possibility of adverse selection.
D)creating an incentive to eliminate adverse selection even though it reinforces the possibility of moral hazard.
E)creating an incentive for a risky driver to reveal that he or she is risky.
A)enforcing a pooling equilibrium.
B)ignoring all private information.
C)creating an incentive to eliminate moral hazard even though it reinforces the possibility of adverse selection.
D)creating an incentive to eliminate adverse selection even though it reinforces the possibility of moral hazard.
E)creating an incentive for a risky driver to reveal that he or she is risky.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
In the market for auto insurance, in a separating equilibrium,
A)risky and safe drivers pay the same premium for insurance.
B)risky drivers pay a larger premium than do safe drivers for insurance.
C)risky drivers pay a smaller premium than do safe drivers for insurance.
D)risky drivers cannot obtain insurance.
E)safe drivers cannot obtain insurance.
A)risky and safe drivers pay the same premium for insurance.
B)risky drivers pay a larger premium than do safe drivers for insurance.
C)risky drivers pay a smaller premium than do safe drivers for insurance.
D)risky drivers cannot obtain insurance.
E)safe drivers cannot obtain insurance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
When Sam makes an agreement and then behaves after the agreement in a way to increase his benefits and harm then other party to the agreement, Sam is illustrating
A)moral hazard.
B)adverse selection.
C)signaling.
D)the cost of contracting.
E)a pooling equilibrium.
A)moral hazard.
B)adverse selection.
C)signaling.
D)the cost of contracting.
E)a pooling equilibrium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
In the market for auto insurance, in a pooling equilibrium,
A)risky and safe drivers pay the same premium for insurance.
B)risky drivers pay a larger premium than do safe drivers for insurance.
C)risky drivers pay a smaller premium than do safe drivers for insurance.
D)risky drivers cannot obtain insurance.
E)safe drivers cannot obtain insurance.
A)risky and safe drivers pay the same premium for insurance.
B)risky drivers pay a larger premium than do safe drivers for insurance.
C)risky drivers pay a smaller premium than do safe drivers for insurance.
D)risky drivers cannot obtain insurance.
E)safe drivers cannot obtain insurance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
A safe drive is likely to prefer an auto insurance policy that has a ________ deductible and a ________ premium.
A)high; high
B)high; low
C)low; high
D)low; low
E)None of the above answers are correct because private information has no effect in the market for auto insurance.
A)high; high
B)high; low
C)low; high
D)low; low
E)None of the above answers are correct because private information has no effect in the market for auto insurance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
In the market for automobile insurance, adverse selection implies that
A)those who are insured might take greater risks.
B)those who are uninsured might take greater risks.
C)private information cannot be successfully screened.
D)insured and uninsured alike will take greater risks.
E)drivers with greater risks are more likely to buy insurance.
A)those who are insured might take greater risks.
B)those who are uninsured might take greater risks.
C)private information cannot be successfully screened.
D)insured and uninsured alike will take greater risks.
E)drivers with greater risks are more likely to buy insurance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Which of the following has a positive externality and hence can be under provided?
A)chronically ill people are not allowed to buy insurance.
B)health insurance purchased through an employer
C)vaccination
D)Health Maintenance Organizations
E)None of the above have a positive externality.
A)chronically ill people are not allowed to buy insurance.
B)health insurance purchased through an employer
C)vaccination
D)Health Maintenance Organizations
E)None of the above have a positive externality.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Which of the following statements about health-care systems is correct?
A)Most major nations do not have extensive government-funded insurance programs.
B)U.S. expenditure per person on health care is near the middle of the range of expenditures made in major nations.
C)Unlike other major nations, private health insurance is available only in the United States.
D)In the United States, Medicare and Medicaid account for slightly less than 90 percent of total expenditures on health care.
E)Every major country except the United States has a comprehensive national health-care system.
A)Most major nations do not have extensive government-funded insurance programs.
B)U.S. expenditure per person on health care is near the middle of the range of expenditures made in major nations.
C)Unlike other major nations, private health insurance is available only in the United States.
D)In the United States, Medicare and Medicaid account for slightly less than 90 percent of total expenditures on health care.
E)Every major country except the United States has a comprehensive national health-care system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
In a pooling equilibrium, there is ________ of insurance in the market for safe drivers and there is ________ of insurance in the market for aggressive drivers.
A)overprovision; underprovision
B)overprovision; overprovision
C)underprovision; underprovision
D)underprovision; overprovision
E)underprovision; an efficient quantity
A)overprovision; underprovision
B)overprovision; overprovision
C)underprovision; underprovision
D)underprovision; overprovision
E)underprovision; an efficient quantity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Which of the following is not a problem in health-care markets?
A)hospitals are not trying to maximize their profit.
B)asymmetric information.
C)public-health externalities.
D)a missing insurance market.
E)None of the above answers are correct; that is, all the answers are problems in health-care markets.
A)hospitals are not trying to maximize their profit.
B)asymmetric information.
C)public-health externalities.
D)a missing insurance market.
E)None of the above answers are correct; that is, all the answers are problems in health-care markets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
In the health insurance market, moral hazard occurs when
A)chronically ill people buy insurance.
B)chronically ill people cannot buy insurance.
C)insured people adopt an unhealthy lifestyle.
D)patients sue their doctor.
E)chronically ill people refuse appropriate medical treatment.
A)chronically ill people buy insurance.
B)chronically ill people cannot buy insurance.
C)insured people adopt an unhealthy lifestyle.
D)patients sue their doctor.
E)chronically ill people refuse appropriate medical treatment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
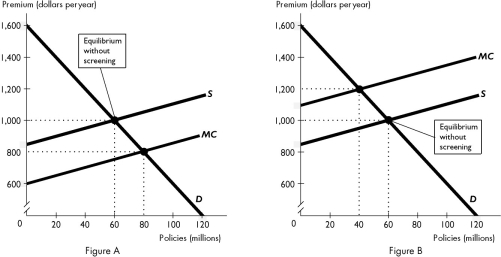
The market for aggressive drivers is illustrated in ________ and the market for safe drivers is illustrated in ________.
A)Figure A; Figure A also
B)Figure B; Figure A
C)Figure A; Figure B
D)Figure B; Figure B also
E)More information is needed to answer the question.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Moral hazard in the market for health-care services leads
A)patients to adopt healthy life styles.
B)a separating equilibrium.
C)to all people buying health insurance.
D)to healthy people not buying health insurance.
E)to providers over treating patients..
A)patients to adopt healthy life styles.
B)a separating equilibrium.
C)to all people buying health insurance.
D)to healthy people not buying health insurance.
E)to providers over treating patients..

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Most observers suggest that health care in the United States faces two major problems:
A)too many people have health insurance, and health care costs too much.
B)a significant shortage of doctors and health care costs too much.
C)a vast oversupply of hospital rooms and a significant shortage of doctors.
D)Health Maintenance Organizations are too common, and too many people do not have health insurance.
E)too many people do not have health insurance, and health care costs too much.
A)too many people have health insurance, and health care costs too much.
B)a significant shortage of doctors and health care costs too much.
C)a vast oversupply of hospital rooms and a significant shortage of doctors.
D)Health Maintenance Organizations are too common, and too many people do not have health insurance.
E)too many people do not have health insurance, and health care costs too much.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Compared to other major nations, the United States spends ________ on health care and achieves ________ efficiency.
A)less; greater
B)more; about the same
C)less; less
D)more; less
E)about the same; less
A)less; greater
B)more; about the same
C)less; less
D)more; less
E)about the same; less

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
In a pooling equilibrium, there ________ a deadweight loss in the market for safe drivers and there ________ a deadweight loss in the market for aggressive drivers.
A)is; is
B)is; is not
C)is not; is
D)is not; is not
E)might be; might be
A)is; is
B)is; is not
C)is not; is
D)is not; is not
E)might be; might be

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
In a separating equilibrium, aggressive drivers pay a premium of ________ and safe drivers pay a premium of ________.
A)$1,000; $1,000
B)$800; $1,200
C)$1,200; $800
D)$1,000; $800
E)$1,200; $1,000
A)$1,000; $1,000
B)$800; $1,200
C)$1,200; $800
D)$1,000; $800
E)$1,200; $1,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Vaccination against infectious diseases ________ so private markets will provide ________ efficient quantity of vaccination.
A)is a public good; less than
B)is a public good; the
C)leads to adverse selection; less than
D)has a positive externality; less than
E)has a positive externality; the
A)is a public good; less than
B)is a public good; the
C)leads to adverse selection; less than
D)has a positive externality; less than
E)has a positive externality; the

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
The missing insurance market in health care is the insurance market for
A)young healthy people.
B)infectious diseases.
C)people who have pre-existing health problems.
D)people in Health Maintenance Organizations.
E)vaccinations.
A)young healthy people.
B)infectious diseases.
C)people who have pre-existing health problems.
D)people in Health Maintenance Organizations.
E)vaccinations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
In a separating equilibrium, there is ________ of insurance in the market for safe drivers and there is ________ of insurance in the market for aggressive drivers.
A)overprovision; underprovision
B)overprovision; overprovision
C)underprovision; underprovision
D)underprovision; overprovision
E)an efficient quantity; an efficient quantity
A)overprovision; underprovision
B)overprovision; overprovision
C)underprovision; underprovision
D)underprovision; overprovision
E)an efficient quantity; an efficient quantity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
In the market for health care services, Health Maintenance Organizations
A)exist to insure people with pre-existing medical conditions.
B)overprovide medical care and thereby result in increased costs.
C)help overcome adverse selection by enrolling only healthy clients.
D)help overcome moral hazard by monitoring the quality of the service.
E)None of the above answers are correct.
A)exist to insure people with pre-existing medical conditions.
B)overprovide medical care and thereby result in increased costs.
C)help overcome adverse selection by enrolling only healthy clients.
D)help overcome moral hazard by monitoring the quality of the service.
E)None of the above answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
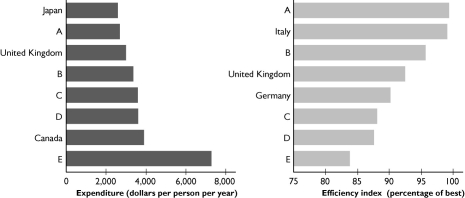
The figures show the expenditures per person on health care and the efficiency of the health care system in 8 different nations.The United States is bar ________ in expenditures per person and is bar ________ in efficiency index.
A)A; A
B)B; A
C)A; D
D)E; E
E)D; B

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
In a pooling equilibrium, aggressive drivers pay a premium of ________ and safe drivers pay a premium of ________.
A)$1,000; $1,000
B)$800; $1,200
C)$1,200; $800
D)$1,000; $800
E)$1,200; $1,000
A)$1,000; $1,000
B)$800; $1,200
C)$1,200; $800
D)$1,000; $800
E)$1,200; $1,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78

Moral hazard typically occurs because
A)people are dishonest.
B)agreements sometimes create incentives that are costly to monitor so people can act in their self interest.
C)workers possess diminishing marginal productivity.
D)screening leads to informed people revealing their relevant private information.
E)workers possess adverse selection.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Which of the following has a positive externality and hence can be under provided?
A)chronically ill people are not allowed to buy insurance.
B)health insurance purchased through an employer
C)vaccination
D)Health Maintenance Organizations
E)None of the above have a positive externality.
A)chronically ill people are not allowed to buy insurance.
B)health insurance purchased through an employer
C)vaccination
D)Health Maintenance Organizations
E)None of the above have a positive externality.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Health-care vouchers have been proposed.These vouchers would
A)cap total expenditure on health care but do nothing to solve the problem of uninsurance.
B)limit choice and would create long waiting times for health care service.
C)solve the problem of the doctor shortage but would not affect the problem of over spending on health care.
D)ensure universal coverage for health care and would cap total expenditure on health care.
E)None of the above answers are correct.
A)cap total expenditure on health care but do nothing to solve the problem of uninsurance.
B)limit choice and would create long waiting times for health care service.
C)solve the problem of the doctor shortage but would not affect the problem of over spending on health care.
D)ensure universal coverage for health care and would cap total expenditure on health care.
E)None of the above answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



