Deck 14: Production and Cost
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/266
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 14: Production and Cost
1
The cost that a firm pays in money to hire a resource is referred to as ________ cost.
A)a minimized
B)a maximized
C)an explicit
D)an implicit
E)a total
A)a minimized
B)a maximized
C)an explicit
D)an implicit
E)a total
C
2
Which of the following is an implicit cost?
I∙wages paid to workers
Ii∙the normal profit
Iii∙the electric bill
A)i only
B)ii only
C)i and ii
D)ii and iii
E)Neither i, ii, nor iii
I∙wages paid to workers
Ii∙the normal profit
Iii∙the electric bill
A)i only
B)ii only
C)i and ii
D)ii and iii
E)Neither i, ii, nor iii
B
3
If a business owner decided to expand her business but rather than borrowing money from a bank used her own funds, then
A)she would be unable to earn a normal profit.
B)there is no cost associated with the expansion.
C)she would forego the opportunity to earn interest on the money.
D)the amount of her funds she used is an explicit cost.
E)the amount of her funds she used is part of her normal profit.
A)she would be unable to earn a normal profit.
B)there is no cost associated with the expansion.
C)she would forego the opportunity to earn interest on the money.
D)the amount of her funds she used is an explicit cost.
E)the amount of her funds she used is part of her normal profit.
C
4
John fishes for a living.Last year, he sold $100,000 of fish.Bait, nets and other fishing supplies cost John $10,000 and he paid $40,000 in salaries to his helpers.Depreciation on his boat and other equipment, as calculated using IRS rules, was $15,000.What was John's profit as would be calculated by an accountant?
A)$165,000
B)$100,000
C)$65,000
D)$35,000
E)None of the above answers is correct.
A)$165,000
B)$100,000
C)$65,000
D)$35,000
E)None of the above answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Accountants calculate
A)economic depreciation as part of the firm's cost.
B)depreciation using Internal Revenue Service rules.
C)the opportunity cost of all the resources the firm uses.
D)all the firm's implicit costs but only a few of its explicit costs.
E)All of the above answers are correct.
A)economic depreciation as part of the firm's cost.
B)depreciation using Internal Revenue Service rules.
C)the opportunity cost of all the resources the firm uses.
D)all the firm's implicit costs but only a few of its explicit costs.
E)All of the above answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Darryl runs a ranch in Jackson, Wyoming.The interest on the debt he incurred to buy his ranch totals $3,000 per year.For Darryl, the interest is
A)an implicit cost.
B)an explicit cost.
C)his normal cost.
D)his normal profit.
E)part of his economic profit.
A)an implicit cost.
B)an explicit cost.
C)his normal cost.
D)his normal profit.
E)part of his economic profit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
From a firm's viewpoint, opportunity cost is the
A)best alternative use customers can find for the firm's output.
B)cost the firm must pay for the factors of production it employs to attract them from their best alternative use.
C)accounting cost of resources.
D)price a firm can charge for its output.
E)cost of acquiring the opportunity to sell to its customers.
A)best alternative use customers can find for the firm's output.
B)cost the firm must pay for the factors of production it employs to attract them from their best alternative use.
C)accounting cost of resources.
D)price a firm can charge for its output.
E)cost of acquiring the opportunity to sell to its customers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following is an explicit cost in Jim's business venture?
A)the salary Jim could have earned at another job
B)the interest Jim does not earn because he invested his savings in his business
C)the wages Jim pays his workers
D)Jim's normal profit
E)Answers A, B, and D are correct.
A)the salary Jim could have earned at another job
B)the interest Jim does not earn because he invested his savings in his business
C)the wages Jim pays his workers
D)Jim's normal profit
E)Answers A, B, and D are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
A cost paid in money is
A)not an opportunity cost.
B)an implicit cost and an opportunity cost.
C)an explicit cost and an opportunity cost.
D)not an accounting cost.
E)an explicit cost but not an opportunity cost.
A)not an opportunity cost.
B)an implicit cost and an opportunity cost.
C)an explicit cost and an opportunity cost.
D)not an accounting cost.
E)an explicit cost but not an opportunity cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
A firm's fundamental goal is
A)different for each firm.
B)to make a quality product.
C)to maximize profit.
D)to gain market share.
E)to decrease its employment of workers in order to cut its costs.
A)different for each firm.
B)to make a quality product.
C)to maximize profit.
D)to gain market share.
E)to decrease its employment of workers in order to cut its costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
When an economist uses the term "cost" referring to a firm, the economist refers to the
A)price of the good to the consumer.
B)explicit cost of producing a good or service but not the implicit cost of producing a good or service.
C)implicit cost of producing a good or service but not the explicit cost of producing a good or service..
D)opportunity cost of producing a good or service, which includes both implicit and explicit cost.
E)cost that can be actually verified and measured.
A)price of the good to the consumer.
B)explicit cost of producing a good or service but not the implicit cost of producing a good or service.
C)implicit cost of producing a good or service but not the explicit cost of producing a good or service..
D)opportunity cost of producing a good or service, which includes both implicit and explicit cost.
E)cost that can be actually verified and measured.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Lauren runs a chili restaurant in San Francisco.Her total revenue last year was $110,000.The rent on her restaurant was $48,000, her labor costs were $42,000, and her materials, food and other variable costs were $20,000.Lauren could have worked as a biologist and earned $50,000 per year.An economist calculates her implicit costs as
A)$150,000.
B)$63,000.
C)$50,000.
D)$110,000.
E)$0 because Lauren did not work as a biologist.
A)$150,000.
B)$63,000.
C)$50,000.
D)$110,000.
E)$0 because Lauren did not work as a biologist.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
________ cost is defined as a cost of production that does not entail a direct money payment.
A)An explicit
B)An implicit
C)A total
D)A fixed
E)A marginal
A)An explicit
B)An implicit
C)A total
D)A fixed
E)A marginal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The primary goal of a business firm is to
A)promote fairness.
B)make a quality product.
C)promote workforce job satisfaction.
D)maximize profit.
E)increase its production.
A)promote fairness.
B)make a quality product.
C)promote workforce job satisfaction.
D)maximize profit.
E)increase its production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following is an implicit cost in Jim's business venture?
I∙the salary Jim could have earned at another job
Ii∙the interest Jim must pay on the loan he incurred to help open his business
Iii∙the interest Jim lost when he used his savings to help open his business
A)i only
B)ii only
C)iii only
D)i and iii
E)ii and iii
I∙the salary Jim could have earned at another job
Ii∙the interest Jim must pay on the loan he incurred to help open his business
Iii∙the interest Jim lost when he used his savings to help open his business
A)i only
B)ii only
C)iii only
D)i and iii
E)ii and iii

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
When Ford hires Ernst and Young Consulting to help Ford redesign its marketing, Ford's payment to Ernst and Young is classified as
A)an explicit cost.
B)depreciation.
C)an implicit cost.
D)normal profit.
E)economic profit.
A)an explicit cost.
B)depreciation.
C)an implicit cost.
D)normal profit.
E)economic profit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following is an explicit cost of production?
A)wages paid to workers
B)the electric bill
C)purchases of raw material
D)Only answers A and B are explicit costs because the purchases of raw material is only an opportunity cost.
E)Answers A, B, and C are all correct.
A)wages paid to workers
B)the electric bill
C)purchases of raw material
D)Only answers A and B are explicit costs because the purchases of raw material is only an opportunity cost.
E)Answers A, B, and C are all correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A cost incurred in the production of a good or service and for which the firm does not need to make a direct monetary payment, is referred to as ________ cost.
A)a minimized
B)a maximized
C)an explicit
D)an implicit
E)an invisible
A)a minimized
B)a maximized
C)an explicit
D)an implicit
E)an invisible

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following is an example of an implicit cost?
A)rent on a building
B)the cost of fertilizer for a farmer
C)the economic depreciation of capital equipment the business owns
D)the cost of fuel and materials.
E)wages paid to workers
A)rent on a building
B)the cost of fertilizer for a farmer
C)the economic depreciation of capital equipment the business owns
D)the cost of fuel and materials.
E)wages paid to workers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Lauren runs a chili restaurant in San Francisco.Her total revenue last year equaled $111,000.The rent on her restaurant totaled $48,000.Her labor costs totaled $43,000.Her materials, food and other variable costs totaled $19,000.To Lauren's accountant, Lauren
A)incurred a loss of $1,000.
B)earned a profit of $1,000.
C)incurred a loss of $111,000.
D)earned a profit of $111,000.
E)had a total cost equal to $91,000.
A)incurred a loss of $1,000.
B)earned a profit of $1,000.
C)incurred a loss of $111,000.
D)earned a profit of $111,000.
E)had a total cost equal to $91,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Suppose Billy owns a hair salon in Dallas.He has one large hair dryer for which he paid $1,000.If he can sell the dryer one year later for $800, his total economic depreciation equals
A)$1,000.
B)$200.
C)$800.
D)$1,800.
E)None of the above answers are correct.
A)$1,000.
B)$200.
C)$800.
D)$1,800.
E)None of the above answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Normal profit is
A)part of the firm's opportunity costs.
B)the same as economic profits.
C)part of the firm's explicit costs.
D)Answers A and B are correct.
E)Answers A and C are correct.
A)part of the firm's opportunity costs.
B)the same as economic profits.
C)part of the firm's explicit costs.
D)Answers A and B are correct.
E)Answers A and C are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The opportunity cost of owning and using a firm's capital is defined as the capital's
A)variable cost.
B)fixed cost.
C)economic depreciation.
D)nonpayment depreciation.
E)explicit cost.
A)variable cost.
B)fixed cost.
C)economic depreciation.
D)nonpayment depreciation.
E)explicit cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
A firm's total revenue minus its total opportunity cost is called its
A)accounting profit.
B)normal profit.
C)economic profit.
D)abnormal profit.
E)entrepreneur's profit.
A)accounting profit.
B)normal profit.
C)economic profit.
D)abnormal profit.
E)entrepreneur's profit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Dr.Khan starts his own dental practice after quitting his $150,000 job at The Mall Dental Clinic.His revenues for the first year are $500,000.He paid $90,000 in rent for the dental office, $60,000 for his office manager's salary, $24,000 for the dental hygienist, $150,000 for insurance, and $6,000 for other miscellaneous costs.The normal profit from running his business is $20,000.
A)His explicit costs are $330,000.
B)His implicit costs are $170,000.
C)His economic profit is zero.
D)Only answers A and C are correct.
E)Answers A, B, and C are correct.
A)His explicit costs are $330,000.
B)His implicit costs are $170,000.
C)His economic profit is zero.
D)Only answers A and C are correct.
E)Answers A, B, and C are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Economic profit equals total revenue minus total
A)explicit costs.
B)opportunity costs.
C)implicit costs.
D)accounting costs.
E)entrepreneur's costs.
A)explicit costs.
B)opportunity costs.
C)implicit costs.
D)accounting costs.
E)entrepreneur's costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Suppose that a firm earned $500,000 in total revenue.At the same time, it incurred labor costs of $200,000; economic depreciation of $50,000; normal profit of $75,000; interest paid to the bank of $25,000; and used other factors of production that cost $100,000.The economic profit earned by the firm equals
A)$275,000.
B)$175,000.
C)$50,000.
D)$200,000.
E)$500,000.
A)$275,000.
B)$175,000.
C)$50,000.
D)$200,000.
E)$500,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which of the following are correct statements about implicit and explicit costs?
I∙Normal profit is an implicit cost.
Ii∙Economic depreciation is an explicit cost.
Iii∙Wages are an explicit cost.
A)ii and iii
B)i and iii
C)iii only
D)i, ii, and iii
E)i only
I∙Normal profit is an implicit cost.
Ii∙Economic depreciation is an explicit cost.
Iii∙Wages are an explicit cost.
A)ii and iii
B)i and iii
C)iii only
D)i, ii, and iii
E)i only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
A firm pays $50,000 for a machine that is used in production for one year, after which it is sold for $40,000 to another firm.The $10,000 difference is
A)an explicit cost of production.
B)economic depreciation, an implicit cost of production.
C)normal profit.
D)not counted as an economic cost of production.
E)not an opportunity cost because it is not actually paid.
A)an explicit cost of production.
B)economic depreciation, an implicit cost of production.
C)normal profit.
D)not counted as an economic cost of production.
E)not an opportunity cost because it is not actually paid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Dr.Khan starts his own dental practice after quitting his $150,000 job at The Mall Dental Clinic.His revenues for the first year are $500,000.He paid $90,000 in rent for the dental office, $60,000 for his office manager's salary, $24,000 for the dental hygienist, $150,000 for insurance, and $6,000 for other miscellaneous costs.The normal profit from running his business is $20,000.
A)His accounting profit is $350,000.
B)His economic profit is $150,000.
C)His economic profit is zero.
D)His accounting profit is zero.
E)None of the above answers are correct.
A)His accounting profit is $350,000.
B)His economic profit is $150,000.
C)His economic profit is zero.
D)His accounting profit is zero.
E)None of the above answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
April quit her job as an accountant at Ernst and Young, where she was paid $45,000 per year.She started her own landscaping business.She rents machines and tools for $50,000 and pays $10,000 as wages to her help.These are her only costs.April earned total revenue of $100,000.
A)Her accountant calculates her profit as $40,000.
B)She has an economic loss.
C)Her explicit cost is $105,000.
D)Both answers A and B are correct.
E)Both answers A and C are correct.
A)Her accountant calculates her profit as $40,000.
B)She has an economic loss.
C)Her explicit cost is $105,000.
D)Both answers A and B are correct.
E)Both answers A and C are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
A normal profit is defined as
A)total revenue minus explicit costs.
B)the same thing as accounting profit.
C)the return to entrepreneurship.
D)total revenue minus implicit costs.
E)the economic profit minus the implicit costs.
A)total revenue minus explicit costs.
B)the same thing as accounting profit.
C)the return to entrepreneurship.
D)total revenue minus implicit costs.
E)the economic profit minus the implicit costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Economic depreciation is the
A)fall in value of the firm's capital, calculating using IRS rules.
B)opportunity cost of owning and using the firm's capital, measured as the change in market value.
C)decrease in the value of finished goods and services that are held in inventories prior to being sold.
D)term given to a fall in a company's stock price.
E)name given to how accountants calculate the depreciation of the company's capital.
A)fall in value of the firm's capital, calculating using IRS rules.
B)opportunity cost of owning and using the firm's capital, measured as the change in market value.
C)decrease in the value of finished goods and services that are held in inventories prior to being sold.
D)term given to a fall in a company's stock price.
E)name given to how accountants calculate the depreciation of the company's capital.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
In economics, a "normal profit" is the return to
A)labor.
B)capital.
C)land.
D)entrepreneurship.
E)Answers B and D are correct.
A)labor.
B)capital.
C)land.
D)entrepreneurship.
E)Answers B and D are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The return to entrepreneurship is known as
A)economic profit.
B)normal profit.
C)opportunity revenue.
D)normal revenue.
E)explicit profit.
A)economic profit.
B)normal profit.
C)opportunity revenue.
D)normal revenue.
E)explicit profit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Suppose a firm's total revenue is $1,000,000.The firm has incurred explicit costs of $750,000.There is also $50,000 of forgone wages by the owner, $10,000 of forgone interest by the owner, $3,000 worth of economic depreciation, and $20,000 worth of normal profit.What is the firm's economic profit?
A)$250,000
B)$200,000
C)$190,000
D)$167,000
E)$180,000
A)$250,000
B)$200,000
C)$190,000
D)$167,000
E)$180,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which of the following is true?
A)Profit as calculated by accountants and economic profit are not necessarily equal.
B)Profit as calculated by accountants is always smaller than economic profit.
C)Economic profit ignores implicit costs.
D)The Internal Revenue Service taxes the firm's economic profit but not its normal profit.
E)The Internal Revenue Service taxes the firm's normal profit but not its economic profit.
A)Profit as calculated by accountants and economic profit are not necessarily equal.
B)Profit as calculated by accountants is always smaller than economic profit.
C)Economic profit ignores implicit costs.
D)The Internal Revenue Service taxes the firm's economic profit but not its normal profit.
E)The Internal Revenue Service taxes the firm's normal profit but not its economic profit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Jennifer owns a pig farm near Salina, Kansas.Last year she earned $39,000 in total revenue while incurring $38,000 in explicit costs.She could have earned $27,000 as a teacher in Salina.These are all her revenue and costs.Therefore Jennifer earned an
A)accounting profit of $1,000 but incurred an economic loss of $26,000.
B)accounting profit of $1,000 but incurred an economic loss of $65,000.
C)accounting profit of $1,000 but incurred an economic loss of $38,000.
D)economic profit of $1,000.
E)None of the above answers is correct.
A)accounting profit of $1,000 but incurred an economic loss of $26,000.
B)accounting profit of $1,000 but incurred an economic loss of $65,000.
C)accounting profit of $1,000 but incurred an economic loss of $38,000.
D)economic profit of $1,000.
E)None of the above answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
A normal profit is
A)part of a firm's opportunity cost.
B)equal to total revenue minus total opportunity cost.
C)the same as economic profit.
D)the same as accounting profit.
E)almost always zero if the company is run efficiently.
A)part of a firm's opportunity cost.
B)equal to total revenue minus total opportunity cost.
C)the same as economic profit.
D)the same as accounting profit.
E)almost always zero if the company is run efficiently.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Bill is an economics professor who earns $40,000 teaching but decides to leave and fulfill his dream of catering barbecues.During his first year of barbecuing he earned total revenue of $60,000.He spent $30,000 on food and supplies.He also paid his wife $10,000 to help serve food.The normal profit for an entrepreneur running a barbecue business is $3,000.He also rented an industrial grill/fry truck for $12,000.An accountant would conclude that Bill's profit was
A)$30,000.
B)$20,000.
C)$8,000.
D)-$2,000.
E)$40,000.
A)$30,000.
B)$20,000.
C)$8,000.
D)-$2,000.
E)$40,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The long run is a time period that is
A)five years or longer.
B)long enough to change the amount of labor employed.
C)long enough to change the size of the firm's plant and all other inputs.
D)long enough to change the amount of labor employed but not to change the size of the plant.
E)None of the above answers describes the long run.
A)five years or longer.
B)long enough to change the amount of labor employed.
C)long enough to change the size of the firm's plant and all other inputs.
D)long enough to change the amount of labor employed but not to change the size of the plant.
E)None of the above answers describes the long run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Which of the following is an example of an implicit cost?
A)wages paid to employees
B)interest paid to a bank on a building loan
C)the cost of using capital an owner donates to the business
D)dollars paid to a supplier for materials used in production
E)liability insurance payments made only once a year
A)wages paid to employees
B)interest paid to a bank on a building loan
C)the cost of using capital an owner donates to the business
D)dollars paid to a supplier for materials used in production
E)liability insurance payments made only once a year

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The short run is the time frame
A)during which the quantities of all resources are fixed.
B)that is less than a year.
C)during which the quantities of some resources are fixed.
D)during which the quantities of all resources are variable.
E)during which all costs are implicit costs.
A)during which the quantities of all resources are fixed.
B)that is less than a year.
C)during which the quantities of some resources are fixed.
D)during which the quantities of all resources are variable.
E)during which all costs are implicit costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The short run is
A)less than one year.
B)the time frame in which all resources are fixed.
C)the time frame in which some resources are fixed.
D)the time frame in which output is fixed.
E)a time frame short enough so that some costs are explicit costs.
A)less than one year.
B)the time frame in which all resources are fixed.
C)the time frame in which some resources are fixed.
D)the time frame in which output is fixed.
E)a time frame short enough so that some costs are explicit costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Moving along the total product curve, which of the following is held constant?
A)Quantity of labor
B)Total product
C)Technology
D)Total cost
E)None of the above answers is correct.
A)Quantity of labor
B)Total product
C)Technology
D)Total cost
E)None of the above answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
In the long run,
A)some resources are fixed.
B)all resources are variable.
C)output cannot be varied.
D)all resources are fixed.
E)Both answers B and C are correct.
A)some resources are fixed.
B)all resources are variable.
C)output cannot be varied.
D)all resources are fixed.
E)Both answers B and C are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The short run is a time period that is
A)equal to a day.
B)too short to change the amount of labor hired.
C)too short to change the size of the firm's plant.
D)long enough to change the size of the firm's plant.
E)too short to change the amount of any resource the firm employs.
A)equal to a day.
B)too short to change the amount of labor hired.
C)too short to change the size of the firm's plant.
D)long enough to change the size of the firm's plant.
E)too short to change the amount of any resource the firm employs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
In the long run, the firm ________ change the number of workers it employs and ________ change the size of its plant.
A)can; can
B)can; cannot
C)cannot; can
D)cannot; cannot
E)In order to answer the question more information is needed about how long is the long run.
A)can; can
B)can; cannot
C)cannot; can
D)cannot; cannot
E)In order to answer the question more information is needed about how long is the long run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
For a business, opportunity cost measures
A)only the cost of labor and materials.
B)only the implicit costs of the business.
C)the cost of all the factors of production the firm employs.
D)only the explicit costs the firm must pay.
E)all of the firm's costs including its normal profit and its economic profit.
A)only the cost of labor and materials.
B)only the implicit costs of the business.
C)the cost of all the factors of production the firm employs.
D)only the explicit costs the firm must pay.
E)all of the firm's costs including its normal profit and its economic profit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Which of the following is a list of fixed inputs for a hospital?
A)bandages, casts, and other materials
B)antibiotics, pain medication, and other prescription drugs
C)the emergency room, intensive care unit, and other facilities
D)the nurses, receptionists, and other employees
E)the lobby, the doctors, and the electricity it uses
A)bandages, casts, and other materials
B)antibiotics, pain medication, and other prescription drugs
C)the emergency room, intensive care unit, and other facilities
D)the nurses, receptionists, and other employees
E)the lobby, the doctors, and the electricity it uses

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The total product curve shows the relationship between total product and
A)cost.
B)the quantity of labor.
C)the average product.
D)the marginal product.
E)the marginal cost.
A)cost.
B)the quantity of labor.
C)the average product.
D)the marginal product.
E)the marginal cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Costs paid in money to hire a resource is
A)normal profit.
B)an implicit cost.
C)an explicit cost.
D)an alternative-use cost.
E)economic profit.
A)normal profit.
B)an implicit cost.
C)an explicit cost.
D)an alternative-use cost.
E)economic profit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Which of the following statements correctly describes a total product curve?
A)Points above the total produce curve are efficient.
B)The curve shows that output always increases as labor employed increases.
C)The curve separates attainable outputs from unattainable outputs.
D)The curve shows minimum levels of output.
E)The curve first falls, reaches a minimum, and then rises.
A)Points above the total produce curve are efficient.
B)The curve shows that output always increases as labor employed increases.
C)The curve separates attainable outputs from unattainable outputs.
D)The curve shows minimum levels of output.
E)The curve first falls, reaches a minimum, and then rises.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The long run is defined as
A)any time after six months.
B)any time after one year.
C)the period of time when all resources are fixed.
D)the period of time when most (more than 50 percent)resources are variable.
E)the period of time when all resources are variable.
A)any time after six months.
B)any time after one year.
C)the period of time when all resources are fixed.
D)the period of time when most (more than 50 percent)resources are variable.
E)the period of time when all resources are variable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The long run is a time period in which
A)some of the firm's resources are fixed.
B)all of the firm's resources are fixed.
C)all of the firm's resources are variable.
D)the firm cannot increase its output.
E)all costs become explicit costs.
A)some of the firm's resources are fixed.
B)all of the firm's resources are fixed.
C)all of the firm's resources are variable.
D)the firm cannot increase its output.
E)all costs become explicit costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The paramount goal of a firm is to
A)maximize profit.
B)maximize sales.
C)maximize total revenue.
D)minimize costs.
E)force its competitors into bankruptcy.
A)maximize profit.
B)maximize sales.
C)maximize total revenue.
D)minimize costs.
E)force its competitors into bankruptcy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Bill is an economics professor who earns $37,000 teaching but decides to leave and fulfill his dream of catering barbecues.During his year of barbecuing he earned total revenue of $60,000.He spent $30,000 on food and supplies.He also paid his wife $10,000 to help serve food.The normal profit for an entrepreneur running a barbecue business is $3,000.Bill also rented an industrial grill/fry truck for $12,000.Bill had an economic
A)profit of $20,000.
B)loss of -$32,000.
C)loss of -$42,000.
D)profit of $28,000.
E)profit of zero.
A)profit of $20,000.
B)loss of -$32,000.
C)loss of -$42,000.
D)profit of $28,000.
E)profit of zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The opportunity cost of a firm using its own capital is
A)economic depreciation.
B)self ownership depreciation.
C)economic loss.
D)normal loss.
E)capital loss.
A)economic depreciation.
B)self ownership depreciation.
C)economic loss.
D)normal loss.
E)capital loss.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The difference between a firm's total revenue and its total cost is its ________ profit.
A)explicit
B)normal
C)economic
D)accounting
E)excess
A)explicit
B)normal
C)economic
D)accounting
E)excess

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
To produce more output in the short run, a firm must employ more of
A)all its resources.
B)its fixed resources.
C)its variable resources.
D)the least costly resources regardless of whether they are fixed or variable.
E)Firms cannot produce more output in the short run.
A)all its resources.
B)its fixed resources.
C)its variable resources.
D)the least costly resources regardless of whether they are fixed or variable.
E)Firms cannot produce more output in the short run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The law of decreasing returns states that as a firm uses more of a
A)fixed input, with a given quantity of variable inputs, the marginal product of the fixed input eventually decreases.
B)variable input, total output will increase indefinitely.
C)variable input, with a given quantity of fixed inputs, the marginal product of the variable input eventually decreases.
D)variable input, output will begin to fall immediately.
E)fixed input and a variable input, the marginal product of the fixed input and the marginal product of the variable input both decrease.
A)fixed input, with a given quantity of variable inputs, the marginal product of the fixed input eventually decreases.
B)variable input, total output will increase indefinitely.
C)variable input, with a given quantity of fixed inputs, the marginal product of the variable input eventually decreases.
D)variable input, output will begin to fall immediately.
E)fixed input and a variable input, the marginal product of the fixed input and the marginal product of the variable input both decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
When the slope of the total product curve is steep, the marginal product is
A)zero.
B)negative.
C)high.
D)low.
E)not defined.
A)zero.
B)negative.
C)high.
D)low.
E)not defined.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Increasing marginal returns to labor
A)occur when a particularly efficient worker is employed.
B)describe the portion of a total product curve where the marginal product is negative.
C)mean that two workers produce less than twice the output of one worker.
D)are the result of specialization and division of labor in the production process.
E)occur only when there are increasing marginal returns to capital.
A)occur when a particularly efficient worker is employed.
B)describe the portion of a total product curve where the marginal product is negative.
C)mean that two workers produce less than twice the output of one worker.
D)are the result of specialization and division of labor in the production process.
E)occur only when there are increasing marginal returns to capital.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
The marginal product of labor is the change in
A)total cost from employing one more worker.
B)total revenue from employing one more worker.
C)average product from employing one more worker.
D)total output from employing one more worker.
E)total output divided by the change in cost from employing one more worker.
A)total cost from employing one more worker.
B)total revenue from employing one more worker.
C)average product from employing one more worker.
D)total output from employing one more worker.
E)total output divided by the change in cost from employing one more worker.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
The marginal product of labor is
A)total product divided by labor.
B)the change in total product divided by the increase in labor.
C)a measure of labor.
D)output that does not meet quality specifications.
E)total product minus the quantity of labor.
A)total product divided by labor.
B)the change in total product divided by the increase in labor.
C)a measure of labor.
D)output that does not meet quality specifications.
E)total product minus the quantity of labor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
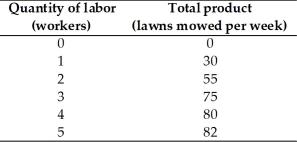
Kenya owns a lawn mowing company.His total product schedule is in the above table.The marginal product of the fourth worker is ________ lawns mowed per week.
A)80
B)25
C)20
D)5
E)320

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
If 9 workers can produce 1,550 units of output and 10 workers can produce 1,700 units of output, then the average product of 10 workers is
A)1,700 units.
B)1,550 units.
C)170 units.
D)150 units.
E)155 units.
A)1,700 units.
B)1,550 units.
C)170 units.
D)150 units.
E)155 units.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Jill runs a factory that makes lie detectors in Little Rock, Arkansas.This month, Jill's 34 workers produced 690 machines.Suppose Jill adds one more worker and, as a result, her factory's output increases to 700.Jill's marginal product of labor from the last worker hired equals ________.
A)10
B)20
C)690
D)700
E)None of the above answers is correct.
A)10
B)20
C)690
D)700
E)None of the above answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
When the marginal product of an additional worker is less than the marginal product of the previous worker, there are ________ returns to labor.
A)increasing total
B)decreasing total
C)increasing marginal
D)decreasing marginal
E)constant average
A)increasing total
B)decreasing total
C)increasing marginal
D)decreasing marginal
E)constant average

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Decreasing marginal returns
A)can be avoided if a firm watches costs.
B)affect all firms, but at different production levels.
C)affect all firms at the same level of production.
D)disappear when the firm produces a large enough level of output.
E)mean that the average product of labor starts as a negative number and then becomes positive.
A)can be avoided if a firm watches costs.
B)affect all firms, but at different production levels.
C)affect all firms at the same level of production.
D)disappear when the firm produces a large enough level of output.
E)mean that the average product of labor starts as a negative number and then becomes positive.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Decreasing marginal returns occur in the short run as more labor is hired to work in a fixed sized plant because
A)less efficient and less productive workers are hired.
B)adding more workers exhausts the possible gains from specialization.
C)the entrepreneur does not know how to manage more workers.
D)each worker will produce more than the worker previously hired.
E)the plant becomes less specialized.
A)less efficient and less productive workers are hired.
B)adding more workers exhausts the possible gains from specialization.
C)the entrepreneur does not know how to manage more workers.
D)each worker will produce more than the worker previously hired.
E)the plant becomes less specialized.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
The marginal product of labor equals the change in ________ from a one-unit increase in the quantity of labor.
A)total product
B)average product
C)total cost
D)the slope of the average product curve
E)the wage rate
A)total product
B)average product
C)total cost
D)the slope of the average product curve
E)the wage rate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73

Kenya owns a lawn mowing company.His total product schedule is in the above table.When 4 workers are employed, the average product is ________ lawns mowed per week.
A)80
B)25
C)20
D)5
E)320

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Increasing marginal returns always occurs when the
A)marginal product of an additional worker exceeds the marginal product of the previous worker.
B)average product of an additional worker exceeds the average product of the previous worker.
C)marginal product of an additional worker is less than the marginal product of the previous worker.
D)average product of an additional worker is less than the average product of the previous worker.
E)marginal product of an additional worker exceeds the average product of the previous worker.
A)marginal product of an additional worker exceeds the marginal product of the previous worker.
B)average product of an additional worker exceeds the average product of the previous worker.
C)marginal product of an additional worker is less than the marginal product of the previous worker.
D)average product of an additional worker is less than the average product of the previous worker.
E)marginal product of an additional worker exceeds the average product of the previous worker.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Jeremiah runs a bullfrog farm in Frogville, Oklahoma.Jeremiah notices that each additional worker he employs adds more to the total output than does the previous worker.Jeremiah must be
A)experiencing increasing marginal returns to labor.
B)producing at a point where the average product of labor decreases as more workers are employed.
C)producing at a point below his total product curve.
D)mistaken because the law of decreasing returns points out that it cannot be the case that the marginal product increases as more workers are employed.
E)producing at a point where the average product of labor exceeds the marginal product of labor.
A)experiencing increasing marginal returns to labor.
B)producing at a point where the average product of labor decreases as more workers are employed.
C)producing at a point below his total product curve.
D)mistaken because the law of decreasing returns points out that it cannot be the case that the marginal product increases as more workers are employed.
E)producing at a point where the average product of labor exceeds the marginal product of labor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
If 9 workers can produce 1,550 units of output and 10 workers can produce 1,700 units of output, then the marginal product of the 10th worker is
A)1,700 units.
B)1,550 units.
C)150 units.
D)170 units.
E)155 units.
A)1,700 units.
B)1,550 units.
C)150 units.
D)170 units.
E)155 units.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Average product is equal to
A)marginal product + total product.
B)total product ÷ marginal product.
C)total product ÷ quantity of labor.
D)total product × quantity of labor.
E)marginal product × quantity of labor.
A)marginal product + total product.
B)total product ÷ marginal product.
C)total product ÷ quantity of labor.
D)total product × quantity of labor.
E)marginal product × quantity of labor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
At the Punjab Bakery, two workers can decorate 14 cakes in an hour and three workers can decorate 18 cakes in an hour.The marginal product of the third worker is
A)18 cakes and the average product for three workers is 6 cakes.
B)9 cakes and is equal to the average product.
C)4 cakes and the average product for three workers is 6 cakes.
D)32 cakes and the average product for three workers is 9 cakes.
E)6 cakes and the average product for three workers is also 6 cakes.
A)18 cakes and the average product for three workers is 6 cakes.
B)9 cakes and is equal to the average product.
C)4 cakes and the average product for three workers is 6 cakes.
D)32 cakes and the average product for three workers is 9 cakes.
E)6 cakes and the average product for three workers is also 6 cakes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Jill runs a factory that makes lie detectors in Little Rock, Arkansas.This month, Jill's 34 workers produced 680 machines.Jill's average product of labor equaled ________ lie detectors per worker.
A)680
B)34
C)23
D)20
E)None of the above answers is correct.
A)680
B)34
C)23
D)20
E)None of the above answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Denise owns a plant that produces watch parts in Ohio.Denise noticed that when she hired the last worker, that worker's marginal product exceeded the marginal product of the previous worker.As a result, when the last worker was hired, Denise's average product of labor
A)decreased.
B)increased.
C)did not change.
D)perhaps changed, but there is not enough information to determine whether or not it did change.
E)equals the marginal product of labor.
A)decreased.
B)increased.
C)did not change.
D)perhaps changed, but there is not enough information to determine whether or not it did change.
E)equals the marginal product of labor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



