Deck 14: More About Classes
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/40
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 14: More About Classes
1
Object composition is useful for creating this type of relationship between classes.
A)friend
B)static
C)has a
D)conditional
E)None of these
A)friend
B)static
C)has a
D)conditional
E)None of these
has a
2
A good reason for overloading an operator is to enable it to ________.
A)outperform its C language counterparts
B)work in its usual way, but with programmer-defined data types
C)operate on more operands than in its standard definition
D)operate on no operands
E)None of these
A)outperform its C language counterparts
B)work in its usual way, but with programmer-defined data types
C)operate on more operands than in its standard definition
D)operate on no operands
E)None of these
work in its usual way, but with programmer-defined data types
3
When a class contains an instance of another class, it is known as ________.
A)object overloading
B)operator overloading
C)object composition
D)dynamic composition
E)None of these
A)object overloading
B)operator overloading
C)object composition
D)dynamic composition
E)None of these
object composition
4
It is a good idea to make a copy constructor's parameters ________ by specifying the ________ key word in the parameter list.
A)inline, inline
B)static, static
C)constant, const
D)global, global
E)None of these
A)inline, inline
B)static, static
C)constant, const
D)global, global
E)None of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Each object of a class has its own copy of the class's ________.
A)member functions
B)member variables
C)constructor and destructor functions
D)All of these
E)None of these
A)member functions
B)member variables
C)constructor and destructor functions
D)All of these
E)None of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
This type of function is not a member of a class, but it has access to the private members of the class.
A)static
B)constructor
C)destructor
D)friend
E)None of these
A)static
B)constructor
C)destructor
D)friend
E)None of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A reason to overload the ________ is to write classes that have array-like behaviors.
A)parentheses ( )operator
B)curly braces { } operator
C)square brackets [ ] operator
D)colon : : operator
E)None of these
A)parentheses ( )operator
B)curly braces { } operator
C)square brackets [ ] operator
D)colon : : operator
E)None of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
If a member variable is declared ________, all objects of that class have access to that variable.
A)static
B)dynamic
C)inline
D)default
E)None of these
A)static
B)dynamic
C)inline
D)default
E)None of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
When objects contain pointers, it is a good idea to create an explicit ________ function.
A)destructor
B)copy constructor
C)static constructor
D)inline constructor
E)None of these
A)destructor
B)copy constructor
C)static constructor
D)inline constructor
E)None of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
C++ allows you to redefine the way ________ work when used with class objects.
A)compiler errors
B)preprocessor directives
C)standard operators
D)undefined variables
E)None of these
A)compiler errors
B)preprocessor directives
C)standard operators
D)undefined variables
E)None of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
If you do not furnish one of these a default will be provided for you by the compiler.
A)copy constructor
B)constructor
C)destructor
D)All of these
E)None of these
A)copy constructor
B)constructor
C)destructor
D)All of these
E)None of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
This operator may be used to assign one object to another.
A)=
B)==
C)<>
D)@
E)None of these
A)=
B)==
C)<>
D)@
E)None of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
This type of member variable may be accessed before any objects of the class have been created.
A)private
B)public
C)inline
D)static
E)None of these
A)private
B)public
C)inline
D)static
E)None of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
When you redefine the way a standard operator works when it is used with class objects, you have ________ the operator.
A)reassigned
B)reformatted
C)overloaded
D)overwhelmed
E)None of these
A)reassigned
B)reformatted
C)overloaded
D)overwhelmed
E)None of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
To overload the + operator, you would write a function named ________.
A)overload +
B)operator +
C)function +
D)operator.overload(+)
E)None of these
A)overload +
B)operator +
C)function +
D)operator.overload(+)
E)None of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
If you do not furnish one of these, an automatic memberwise copy will be performed when one object is assigned to another object.
A)overloaded constructor function
B)overloaded assignment operator
C)default constructor function
D)overloaded copy operator
E)None of these
A)overloaded constructor function
B)overloaded assignment operator
C)default constructor function
D)overloaded copy operator
E)None of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
This is a special function that is called whenever a new object is created and initialized with another object's data.
A)destructor
B)static function
C)copy constructor
D)assignment function
E)None of these
A)destructor
B)static function
C)copy constructor
D)assignment function
E)None of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A member function that is declared ________ may not access any non-static data members in the class.
A)private
B)public
C)static
D)inline
E)None of these
A)private
B)public
C)static
D)inline
E)None of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
C++ requires that a copy constructor's parameter be a(n)________.
A)integer data type
B)floating point data type
C)pointer variable
D)reference object
E)None of these
A)integer data type
B)floating point data type
C)pointer variable
D)reference object
E)None of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
This is a special built-in pointer that is available to a class's member functions.
A)overloaded -> operator
B)this pointer
C)&constructor pointer
D)~destructor *ptr
E)None of these
A)overloaded -> operator
B)this pointer
C)&constructor pointer
D)~destructor *ptr
E)None of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
A static member variable can be used when there are no objects of the class in existence.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
When you overload an operator, you cannot change the number of ________ taken by the operator.
A)arguments
B)parameters
C)operations
D)operands
E)None of these
A)arguments
B)parameters
C)operations
D)operands
E)None of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The this pointer is automatically passed to non-static member functions of a class.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
C++ permits you to overload the sizeof operator and the this pointer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
It is possible to declare an entire class as a friend of another class.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
If you overload the prefix ++ operator, the postfix ++ operator is automatically overloaded.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
When you overload the << operator, you must also overload the >> operator.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
By default, when an object is assigned to another, each member of one object is copied to its counterpart in the other object.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
In the following function header: 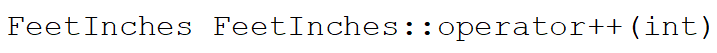
The word (int)is known as a(n):
A)parameterless data type
B)incomplete argument
C)dummy parameter
D)incomplete parameter
E)None of these
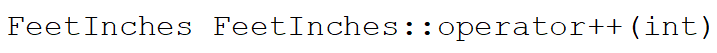
The word (int)is known as a(n):
A)parameterless data type
B)incomplete argument
C)dummy parameter
D)incomplete parameter
E)None of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
A(n)________ informs the compiler that a class will be declared later in the program.
A)static function
B)private data member
C)forward declaration
D)object conversion
E)None of these
A)static function
B)private data member
C)forward declaration
D)object conversion
E)None of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
When a class declares an entire class as its friend, the friendship status is reciprocal. That is, each class's member functions have free access to the other's private members.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
You can overload the conditional operator to make it function as an unconditional operator.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
An ________ operator can work with programmer-defined data types.
A)inline
B)unconditional
C)overloaded
D)undefined
E)None of these
A)inline
B)unconditional
C)overloaded
D)undefined
E)None of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
In C++, if you overload the < operator, you must also overload the > operator.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The this pointer is a special built-in pointer that is automatically passed as a hidden argument to all non-static member functions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
You may overload any C++ operator, and you may use the operator function to define non-standard operators, such as @ and ^.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
When you overload an operator, you can change the operator's original meaning to something entirely different.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
A non-static member function may not access a static member variable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
A public data member may be declared a friend of a private function.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
A static member function does not need to be called by a specific object of the class.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



