Deck 15: Money, Interest Rates, and Exchange Rates
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/64
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 15: Money, Interest Rates, and Exchange Rates
1
What are the main factors that determine aggregate money demand?
The three main factors are interest rate, the price level and real national income. A rise in the interest rate causes individuals in the economy to reduce their demand for money. If the price level rises, individual households and firms will spend more money than before. When real national income (GNP) rises the demand for money will also rise.
2
Money includes
A) currency.
B) checking deposits held by households and firms.
C) deposits in the foreign exchange markets.
D) currency and checking deposits held by households and firms.
E) futures and deposits in the foreign exchange market.
A) currency.
B) checking deposits held by households and firms.
C) deposits in the foreign exchange markets.
D) currency and checking deposits held by households and firms.
E) futures and deposits in the foreign exchange market.
currency and checking deposits held by households and firms.
3
What are the factors that determine the amount of money an individual desires to hold?
Three main factors: first, the expected return the asset offers compared with the returns offered by other assets; second, the riskiness of the asset's expected return; and third, the asset's liquidity.
4
What are the main functions of money?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The aggregate demand for money can be expressed by
A) Md = P × L(R,Y).
B) Md = L × P(R,Y).
C) Md = P × Y(R, L).
D) Md = R × L(P,Y).
E) Md = R × L(R, P).
A) Md = P × L(R,Y).
B) Md = L × P(R,Y).
C) Md = P × Y(R, L).
D) Md = R × L(P,Y).
E) Md = R × L(R, P).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Individuals base their demand for an asset on
A) the expected return the asset offers compared with the returns offered by other assets.
B) the riskiness of the asset's expected return.
C) the asset's liquidity.
D) the expected return, how risky that expected return is, and the asset's liquidity.
E) the aesthetic qualities of the asset.
A) the expected return the asset offers compared with the returns offered by other assets.
B) the riskiness of the asset's expected return.
C) the asset's liquidity.
D) the expected return, how risky that expected return is, and the asset's liquidity.
E) the aesthetic qualities of the asset.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
An individual's need for liquidity would increase if
A) the average value of transactions carried out by the individual fell.
B) the average value of transactions carried out by the individual rose.
C) the individual got a raise.
D) the individual received a new ATM card.
E) the individual wanted to avoid risks.
A) the average value of transactions carried out by the individual fell.
B) the average value of transactions carried out by the individual rose.
C) the individual got a raise.
D) the individual received a new ATM card.
E) the individual wanted to avoid risks.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which one of the following statements is the MOST accurate?
A) A rise in the average value of transactions carried out by a household or a firm causes its demand for money to fall.
B) A reduction in the average value of transactions carried out by a household or a firm causes its demand for money to rise.
C) A rise in the average value of transactions carried out by a household or a firm causes its demand for money to rise.
D) A rise in the average value of transactions carried out by a household or a firm causes its demand for real money to rise.
E) A decrease in the average value of transactions carried out by a household or a firm causes its demand for real money to rise.
A) A rise in the average value of transactions carried out by a household or a firm causes its demand for money to fall.
B) A reduction in the average value of transactions carried out by a household or a firm causes its demand for money to rise.
C) A rise in the average value of transactions carried out by a household or a firm causes its demand for money to rise.
D) A rise in the average value of transactions carried out by a household or a firm causes its demand for real money to rise.
E) A decrease in the average value of transactions carried out by a household or a firm causes its demand for real money to rise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
In the United States at the end of 2012, the total money supply, M1, amounted to approximately
A) 16 percent of that year's GNP.
B) 20 percent of that year's GNP.
C) 30 percent of that year's GNP.
D) 40 percent of that year's GNP.
E) 50 percent of that year's GNP.
A) 16 percent of that year's GNP.
B) 20 percent of that year's GNP.
C) 30 percent of that year's GNP.
D) 40 percent of that year's GNP.
E) 50 percent of that year's GNP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Explain why one can write the demand for money as the price level times a function of the interest rate and real income as follows:
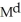 = PxL (R, Y)
= PxL (R, Y)
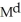 = PxL (R, Y)
= PxL (R, Y)
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
For a given level of
A) nominal GNP, changes in interest rates cause movements along the L(R,Y) schedule.
B) real GNP, changes in interest rates cause a decrease of the L(R,Y) schedule.
C) real GNP, changes in interest rates cause an increase of the L(R,Y) schedule.
D) nominal GNP, changes in interest rates cause an increase in the L(R,Y) schedule.
E) real GNP, changes in interest rates cause movements along the L(R,Y) schedule.
A) nominal GNP, changes in interest rates cause movements along the L(R,Y) schedule.
B) real GNP, changes in interest rates cause a decrease of the L(R,Y) schedule.
C) real GNP, changes in interest rates cause an increase of the L(R,Y) schedule.
D) nominal GNP, changes in interest rates cause an increase in the L(R,Y) schedule.
E) real GNP, changes in interest rates cause movements along the L(R,Y) schedule.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
In a world with money and bonds only
A) it is not risky to hold money.
B) it is risky to hold money.
C) risk is an important factor in the demand for money.
D) there is no relationship between risk and holding money.
E) assets become meaningless.
A) it is not risky to hold money.
B) it is risky to hold money.
C) risk is an important factor in the demand for money.
D) there is no relationship between risk and holding money.
E) assets become meaningless.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The aggregate money demand depends on
A) the interest rate.
B) the price level.
C) real national income.
D) the interest rate, price level, and real national income.
E) the price level and the liquidity of the asset.
A) the interest rate.
B) the price level.
C) real national income.
D) the interest rate, price level, and real national income.
E) the price level and the liquidity of the asset.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Money serves as all of the following EXCEPT
A) a medium of exchange.
B) a unit of account.
C) a store of value.
D) a symbol that is made of or can be redeemed for a fixed amount of precious metal.
E) a highly liquid asset.
A) a medium of exchange.
B) a unit of account.
C) a store of value.
D) a symbol that is made of or can be redeemed for a fixed amount of precious metal.
E) a highly liquid asset.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
If there is initially an
A) excess demand for money, the interest rate will fall, and the supply of money will rise.
B) excess supply of money, the interest rate will fall, and if there is initially an excess demand, it will rise.
C) excess supply of money, the interest rate will rise, and if there is initially an excess demand, it will fall.
D) excess supply of money, the interest rate will fall, and if there is also an excess demand, it will fall rapidly.
E) excess supply of money, the interest rate will rise, and if there is also an excess demand, it will rise rapidly.
A) excess demand for money, the interest rate will fall, and the supply of money will rise.
B) excess supply of money, the interest rate will fall, and if there is initially an excess demand, it will rise.
C) excess supply of money, the interest rate will rise, and if there is initially an excess demand, it will fall.
D) excess supply of money, the interest rate will fall, and if there is also an excess demand, it will fall rapidly.
E) excess supply of money, the interest rate will rise, and if there is also an excess demand, it will rise rapidly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
An increase in
A) nominal output raises the interest rate while a fall in real output lowers the interest rate, given the price level and the money supply.
B) real output decreases the interest rate while a fall in real output increases the interest rate, given the price level.
C) real output raises the interest rate while a fall in real output lowers the interest rate, given the money supply.
D) nominal output raises the interest rate while a fall in real output lowers the interest rate, given the price level.
E) real output increase raises the interest rate while a fall in real output lowers the interest rate, given the price level and the money supply.
A) nominal output raises the interest rate while a fall in real output lowers the interest rate, given the price level and the money supply.
B) real output decreases the interest rate while a fall in real output increases the interest rate, given the price level.
C) real output raises the interest rate while a fall in real output lowers the interest rate, given the money supply.
D) nominal output raises the interest rate while a fall in real output lowers the interest rate, given the price level.
E) real output increase raises the interest rate while a fall in real output lowers the interest rate, given the price level and the money supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The aggregate real money demand schedule L(R,Y)
A) slopes upward because a fall in the interest rate raises the desired real money holdings of each household and firm in the economy.
B) slopes downward because a fall in the interest rate reduces the desired real money holdings of each household and firm in the economy.
C) has a zero slope because a fall in the interest rate keeps constant the desired real money holdings of each household and firm in the economy.
D) slopes downward because a fall in the interest rate raises the desired real money holdings of each household and firm in the economy.
E) slopes downward because a rise in the interest rate makes consumers less focused on the liquidity of their assets.
A) slopes upward because a fall in the interest rate raises the desired real money holdings of each household and firm in the economy.
B) slopes downward because a fall in the interest rate reduces the desired real money holdings of each household and firm in the economy.
C) has a zero slope because a fall in the interest rate keeps constant the desired real money holdings of each household and firm in the economy.
D) slopes downward because a fall in the interest rate raises the desired real money holdings of each household and firm in the economy.
E) slopes downward because a rise in the interest rate makes consumers less focused on the liquidity of their assets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The exchange rate between currencies depends on
A) the interest rate that can be earned on deposits of those currencies.
B) the interest rate that can be earned on deposits of those currencies and the expected future exchange rate.
C) the expected future exchange rate.
D) national output.
E) the interest rate that can be earned on deposits of those countries and the national output.
A) the interest rate that can be earned on deposits of those currencies.
B) the interest rate that can be earned on deposits of those currencies and the expected future exchange rate.
C) the expected future exchange rate.
D) national output.
E) the interest rate that can be earned on deposits of those countries and the national output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
A family's summer house on Cape Cod pays a return in the form of
A) interest rate.
B) capital gains.
C) the pleasure of vacations at the beach.
D) stock options.
E) capital gains and pleasure.
A) interest rate.
B) capital gains.
C) the pleasure of vacations at the beach.
D) stock options.
E) capital gains and pleasure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which one of the following statements is the MOST accurate?
A) A decrease in the money supply lowers the interest rate while an increase in the money supply raises the interest rate, given the price level and output.
B) An increase in the money supply lowers the interest rate while a fall in the money supply raises the interest rate, given the price level.
C) An increase in the money supply lowers the interest rate while a fall in the money supply raises the interest rate, given the output level.
D) An increase in the money supply lowers the interest rate while a fall in the money supply raises the interest rate, given the price level and output.
E) An increase in the money supply does not usually affect the interest rate.
A) A decrease in the money supply lowers the interest rate while an increase in the money supply raises the interest rate, given the price level and output.
B) An increase in the money supply lowers the interest rate while a fall in the money supply raises the interest rate, given the price level.
C) An increase in the money supply lowers the interest rate while a fall in the money supply raises the interest rate, given the output level.
D) An increase in the money supply lowers the interest rate while a fall in the money supply raises the interest rate, given the price level and output.
E) An increase in the money supply does not usually affect the interest rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Combine a graph showing the interest parity condition and one showing money demand and supply to demonstrate simultaneous equilibrium in the money market and the foreign exchange market.
How would an increase in the U.S. money supply affect the dollar/euro exchange rate and the U.S. interest rate?
Illustrate your answer graphically and explain.
How would an increase in the U.S. money supply affect the dollar/euro exchange rate and the U.S. interest rate?
Illustrate your answer graphically and explain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
What will be the effects of an increase in real output on the interest rate?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A permanent increase in a country's money supply
A) causes a more than proportional increase in its price level.
B) causes a less than proportional increase in its price level.
C) causes a proportional increase in its price level.
D) leaves its price level constant in long-run equilibrium.
E) causes an inversely proportional fall in its price level.
A) causes a more than proportional increase in its price level.
B) causes a less than proportional increase in its price level.
C) causes a proportional increase in its price level.
D) leaves its price level constant in long-run equilibrium.
E) causes an inversely proportional fall in its price level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
If there is an excess supply of money
A) the interest rate falls.
B) the interest rate rises.
C) the real money supply shifts left to make an equilibrium.
D) the real money supply shifts right to make an equilibrium.
E) the interest rate stays constant, but consumer confidence falters.
A) the interest rate falls.
B) the interest rate rises.
C) the real money supply shifts left to make an equilibrium.
D) the real money supply shifts right to make an equilibrium.
E) the interest rate stays constant, but consumer confidence falters.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which one of the following statements is the MOST accurate?
A) Given PUS, when the money supply rises, the dollar interest rate declines and the dollar depreciates against the euro.
B) Given YUS, when the money supply rises, the dollar interest rate declines and the dollar depreciates against the euro.
C) Given PUS and YUS, when the money supply decreases, the dollar interest rate declines and the dollar depreciates against the euro.
D) Given PUS and YUS, when the money supply rises, the dollar interest rate declines and the dollar appreciates against the euro.
E) Given PUS and YUS, when the money supply rises, the dollar interest rate declines and the dollar depreciates against the euro.
A) Given PUS, when the money supply rises, the dollar interest rate declines and the dollar depreciates against the euro.
B) Given YUS, when the money supply rises, the dollar interest rate declines and the dollar depreciates against the euro.
C) Given PUS and YUS, when the money supply decreases, the dollar interest rate declines and the dollar depreciates against the euro.
D) Given PUS and YUS, when the money supply rises, the dollar interest rate declines and the dollar appreciates against the euro.
E) Given PUS and YUS, when the money supply rises, the dollar interest rate declines and the dollar depreciates against the euro.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Explain the following figure.
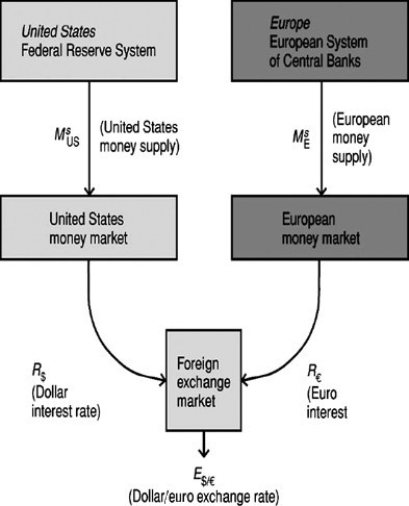


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Using a figure describing both the U.S. money market and the foreign exchange market, analyze the effects of a temporary increase in the European money supply on the dollar/euro exchange rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
What will be the effects of an increase in the money supply on the interest rate?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
An increase in a country's money supply causes
A) its currency to appreciate in the foreign exchange market while a reduction in the money supply causes its currency to depreciate.
B) its currency to depreciate in the foreign exchange market while a reduction in the money supply causes its currency to appreciate.
C) no effect on the values of it currency in international markets.
D) its currency to depreciate in the foreign exchange market while a reduction in the money supply causes its currency to further depreciate.
E) its currency to depreciate in the domestic market and appreciate in the foreign market.
A) its currency to appreciate in the foreign exchange market while a reduction in the money supply causes its currency to depreciate.
B) its currency to depreciate in the foreign exchange market while a reduction in the money supply causes its currency to appreciate.
C) no effect on the values of it currency in international markets.
D) its currency to depreciate in the foreign exchange market while a reduction in the money supply causes its currency to further depreciate.
E) its currency to depreciate in the domestic market and appreciate in the foreign market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Explain how the money markets of two countries are linked through the foreign exchange market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
A change in the level of the supply of money
A) increases the long-run values of the interest rate and real output.
B) decreases the long-run values of the interest rate and real output.
C) has no effect on the long-run values of the interest rate, but may affect real output.
D) has no effect on the long-run values of real output, but may affect the interest rate.
E) has no effect on the long-run values of the interest rate and real output.
A) increases the long-run values of the interest rate and real output.
B) decreases the long-run values of the interest rate and real output.
C) has no effect on the long-run values of the interest rate, but may affect real output.
D) has no effect on the long-run values of real output, but may affect the interest rate.
E) has no effect on the long-run values of the interest rate and real output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
An economy's long-run equilibrium is
A) the equilibrium that would occur if prices were perfectly flexible.
B) the equilibrium that would occur if prices were perfectly flexible and always adjusted immediately.
C) the equilibrium that would occur if prices were perfectly flexible and always adjusted immediately to preserve full employment.
D) the equilibrium that would occur if prices were perfectly fixed to preserve full employment.
E) the equilibrium that would occur if prices were perfectly fixed at the full employment point.
A) the equilibrium that would occur if prices were perfectly flexible.
B) the equilibrium that would occur if prices were perfectly flexible and always adjusted immediately.
C) the equilibrium that would occur if prices were perfectly flexible and always adjusted immediately to preserve full employment.
D) the equilibrium that would occur if prices were perfectly fixed to preserve full employment.
E) the equilibrium that would occur if prices were perfectly fixed at the full employment point.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
If individuals are holding more money than they desire
A) they will attempt to reduce their liquidity by using money to purchase goods.
B) they will attempt to reduce their liquidity by using money to purchase interest-bearing assets.
C) they will attempt to reduce their liquidity by converting real money holdings into nominal money holdings.
D) they will keep their holdings constant.
A) they will attempt to reduce their liquidity by using money to purchase goods.
B) they will attempt to reduce their liquidity by using money to purchase interest-bearing assets.
C) they will attempt to reduce their liquidity by converting real money holdings into nominal money holdings.
D) they will keep their holdings constant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
A reduction in a country's money supply causes
A) its currency to depreciate in the foreign exchange market.
B) its currency to appreciate in the foreign exchange market.
C) does not affect its currency in the foreign market.
D) does affect its currency in the foreign market in an ambiguous manor.
E) affects other countries currency in the foreign market.
A) its currency to depreciate in the foreign exchange market.
B) its currency to appreciate in the foreign exchange market.
C) does not affect its currency in the foreign market.
D) does affect its currency in the foreign market in an ambiguous manor.
E) affects other countries currency in the foreign market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Given PUS and YUS
A) An increase in the European money supply causes the euro to appreciate against the dollar, but it does not disturb the U.S. money market equilibrium.
B) An increase in the European money supply causes the euro to appreciate against the dollar, and it creates excess demand for dollars in the U.S. money market.
C) An increase in the European money supply causes the euro to depreciate against the dollar, and it creates excess demand for dollars in the U.S. money market.
D) An increase in the European money supply causes the euro to depreciate against the dollar, but it does not disturb the U.S. money market equilibrium.
E) An increase in the European money supply causes the euro to depreciate against the dollar, and disturbing the U.S. money market equilibrium.
A) An increase in the European money supply causes the euro to appreciate against the dollar, but it does not disturb the U.S. money market equilibrium.
B) An increase in the European money supply causes the euro to appreciate against the dollar, and it creates excess demand for dollars in the U.S. money market.
C) An increase in the European money supply causes the euro to depreciate against the dollar, and it creates excess demand for dollars in the U.S. money market.
D) An increase in the European money supply causes the euro to depreciate against the dollar, but it does not disturb the U.S. money market equilibrium.
E) An increase in the European money supply causes the euro to depreciate against the dollar, and disturbing the U.S. money market equilibrium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
What would be the effect of an increase in the European money supply in the dollar /euro exchange rate?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Using a figure describing both the U.S. money market and the foreign exchange market, analyze the effects of an increase in the U.S. money supply on the dollar/euro exchange rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Analyze the effects of an increase in the European money supply on the dollar/euro exchange rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The money supply schedule is
A) horizontal because MS is set by the central bank while P is taken as given.
B) horizontal because MS is set by the central bank.
C) vertical because MS is set by the households and firms while P is taken as given.
D) vertical because MS and P are set by the central bank.
E) vertical because MS is set by the central bank while P is taken as given.
A) horizontal because MS is set by the central bank while P is taken as given.
B) horizontal because MS is set by the central bank.
C) vertical because MS is set by the households and firms while P is taken as given.
D) vertical because MS and P are set by the central bank.
E) vertical because MS is set by the central bank while P is taken as given.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Changes in the money supply growth rate
A) are neutral in the short run.
B) need not be neutral in the short run.
C) are neutral in the long run.
D) need not be neutral in the long run.
E) affect the real output of the economy.
A) are neutral in the short run.
B) need not be neutral in the short run.
C) are neutral in the long run.
D) need not be neutral in the long run.
E) affect the real output of the economy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
What term means an explosive and seemingly uncontrollable inflation in which money loses value rapidly and may even go out of use?
A) superinflation
B) stagflation
C) hyperinflation
D) maginflation
E) deflation
A) superinflation
B) stagflation
C) hyperinflation
D) maginflation
E) deflation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
After a permanent increase in the money supply
A) the exchange rate overshoots in the short run.
B) the exchange rate overshoots in the long run.
C) the exchange rate smoothly depreciates in the short run.
D) the exchange rate smoothly appreciates in the short run.
E) the exchange rate remains the same.
A) the exchange rate overshoots in the short run.
B) the exchange rate overshoots in the long run.
C) the exchange rate smoothly depreciates in the short run.
D) the exchange rate smoothly appreciates in the short run.
E) the exchange rate remains the same.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
For main industrial countries such as Japan and the U.S.
A) there is much less month-to-month variability of the exchange rate, suggesting that price levels are relatively sticky in the short run.
B) there is much more month-to-month variability of the exchange rate, suggesting that price levels are relatively sticky in the short run.
C) there is almost the same month-to-month variability of the exchange rate and price levels.
D) it is hard to tell whether month-to-month variability of the exchange rate is similar to changes in price levels.
E) there is much more month-to-month variability of the exchange rate, suggesting that price levels are relatively sticky in the long run.
A) there is much less month-to-month variability of the exchange rate, suggesting that price levels are relatively sticky in the short run.
B) there is much more month-to-month variability of the exchange rate, suggesting that price levels are relatively sticky in the short run.
C) there is almost the same month-to-month variability of the exchange rate and price levels.
D) it is hard to tell whether month-to-month variability of the exchange rate is similar to changes in price levels.
E) there is much more month-to-month variability of the exchange rate, suggesting that price levels are relatively sticky in the long run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Michael Woodford says the following is an advantage of interest-rate instruments for central banks.
A) Conduct monetary policy without inflation.
B) Conduct monetary policy even if checking deposits pay interest at competitive rates.
C) Conduct monetary policy without government approval.
D) Conduct monetary policy with consumers in mind.
E) Conduct monetary policy with workers in mind.
A) Conduct monetary policy without inflation.
B) Conduct monetary policy even if checking deposits pay interest at competitive rates.
C) Conduct monetary policy without government approval.
D) Conduct monetary policy with consumers in mind.
E) Conduct monetary policy with workers in mind.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
In a world where the price level could adjust immediately to its new long-run level after a money supply increase
A) the dollar interest rate would increase because prices would adjust immediately and prevent the money supply from rising.
B) the dollar interest rate would not fall because prices would adjust immediately and prevent the money supply from rising.
C) the dollar interest rate would fall because prices would adjust immediately and prevent the money supply from decreasing.
D) the dollar interest rate would decrease because prices would adjust immediately and prevent the money supply from decreasing.
E) the dollar interest rate would fall because prices would not be able to prevent the money supply from rising.
A) the dollar interest rate would increase because prices would adjust immediately and prevent the money supply from rising.
B) the dollar interest rate would not fall because prices would adjust immediately and prevent the money supply from rising.
C) the dollar interest rate would fall because prices would adjust immediately and prevent the money supply from decreasing.
D) the dollar interest rate would decrease because prices would adjust immediately and prevent the money supply from decreasing.
E) the dollar interest rate would fall because prices would not be able to prevent the money supply from rising.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
In Zimbabwe, the government stopped the country's hyperinflation by
A) reducing domestic monetary growth drastically.
B) returning to a gold/silver currency standard.
C) switching to foreign currencies that are relatively stable.
D) passing a law making price increases illegal.
E) implementing a new currency based on diamonds.
A) reducing domestic monetary growth drastically.
B) returning to a gold/silver currency standard.
C) switching to foreign currencies that are relatively stable.
D) passing a law making price increases illegal.
E) implementing a new currency based on diamonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The long run effects of money supply change has
A) an ambiguous effect on the long-run values of the interest rate or real output, a proportional change in the price level's long-run value in the opposite direction.
B) a proportional effect on the long-run values of the interest rate or real output, a proportional change in the price level's long-run value in the same direction.
C) no effect on the long-run values of the interest rate or real output, a proportional change in the price level's long-run value in the same direction.
D) no effect on the long-run values of the interest rate or real output, no change in the price level's long-run value.
E) an ambiguous effect on the long-run values of the interest rate or real output, a disproportional change in the price level's long-run value in the same direction.
A) an ambiguous effect on the long-run values of the interest rate or real output, a proportional change in the price level's long-run value in the opposite direction.
B) a proportional effect on the long-run values of the interest rate or real output, a proportional change in the price level's long-run value in the same direction.
C) no effect on the long-run values of the interest rate or real output, a proportional change in the price level's long-run value in the same direction.
D) no effect on the long-run values of the interest rate or real output, no change in the price level's long-run value.
E) an ambiguous effect on the long-run values of the interest rate or real output, a disproportional change in the price level's long-run value in the same direction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
During hyperinflation, exploding inflation causes real money demand to
A) fall over time, and this additional monetary change makes money prices rise even more quickly than the money supply itself rises.
B) increase over time, and this additional monetary change makes money prices rise even more quickly than the money supply itself rises.
C) fall over time, and this additional monetary change makes money prices decrease even more quickly than the money supply itself rises.
D) increase over time, and this additional monetary change makes money prices decrease even more quickly than the money supply itself rises.
E) fall over time, and this additional monetary change makes money prices decrease even less quickly than the money supply itself rises.
A) fall over time, and this additional monetary change makes money prices rise even more quickly than the money supply itself rises.
B) increase over time, and this additional monetary change makes money prices rise even more quickly than the money supply itself rises.
C) fall over time, and this additional monetary change makes money prices decrease even more quickly than the money supply itself rises.
D) increase over time, and this additional monetary change makes money prices decrease even more quickly than the money supply itself rises.
E) fall over time, and this additional monetary change makes money prices decrease even less quickly than the money supply itself rises.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Which one of the following statements is the MOST accurate?
A) There is a lively academic debate over the possibility that seemingly sticky wages and prices are in reality quite fixed.
B) There is a lively academic debate over the possibility that seemingly sticky wages and prices are in reality much more sticky than theory assumes.
C) There is a lively academic debate over the possibility that seemingly sticky wages and prices are in reality quite flexible.
D) There is no debate over the possibility that wages and prices are sticky in the long run.
E) There is no debate over the possibility that wages and prices are sticky in the short run.
A) There is a lively academic debate over the possibility that seemingly sticky wages and prices are in reality quite fixed.
B) There is a lively academic debate over the possibility that seemingly sticky wages and prices are in reality much more sticky than theory assumes.
C) There is a lively academic debate over the possibility that seemingly sticky wages and prices are in reality quite flexible.
D) There is no debate over the possibility that wages and prices are sticky in the long run.
E) There is no debate over the possibility that wages and prices are sticky in the short run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Money demand behavior may
A) change as a result of demographic trends or financial innovations such as electronic cash-transfer facilities.
B) change only as a result of demographic trends.
C) change only as a result of financial innovations such as electronic cash-transfer facilities.
D) not change as a result of demographic trends or financial innovations such as electronic cash-transfer facilities.
E) change as a result of demographic trends but not as a result of financial innovations such as electronic cash-transfer facilities.
A) change as a result of demographic trends or financial innovations such as electronic cash-transfer facilities.
B) change only as a result of demographic trends.
C) change only as a result of financial innovations such as electronic cash-transfer facilities.
D) not change as a result of demographic trends or financial innovations such as electronic cash-transfer facilities.
E) change as a result of demographic trends but not as a result of financial innovations such as electronic cash-transfer facilities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
A sustained change in the monetary growth rate will
A) immediately affect equilibrium real money balances by raising the money interest rate.
B) eventually affect equilibrium nominal money balances by raising the money interest rate.
C) eventually affect equilibrium real money balances by reducing the money interest rate.
D) eventually affect equilibrium real money balances by raising the real interest rate.
E) eventually affect equilibrium real money balances by raising the money interest rate.
A) immediately affect equilibrium real money balances by raising the money interest rate.
B) eventually affect equilibrium nominal money balances by raising the money interest rate.
C) eventually affect equilibrium real money balances by reducing the money interest rate.
D) eventually affect equilibrium real money balances by raising the real interest rate.
E) eventually affect equilibrium real money balances by raising the money interest rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
A change in the money supply creates demand and cost pressures that lead to future increases in the price level from which main sources?
I.Excess demand for output and labor
II.Inflationary expectations
III.Raw materials prices
A) I
B) II
C) II and III
D) I and II
E) I, II, and III
I.Excess demand for output and labor
II.Inflationary expectations
III.Raw materials prices
A) I
B) II
C) II and III
D) I and II
E) I, II, and III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
In a classic paper, Columbia University economist Phillip Cagan drew the line between inflation and hyperinflation at an inflation rate of
A) 50 percent per month.
B) 10 percent per month.
C) 20 percent per month.
D) 5 percent per month.
E) 25 percent per month.
A) 50 percent per month.
B) 10 percent per month.
C) 20 percent per month.
D) 5 percent per month.
E) 25 percent per month.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Which one of the following statements is the MOST accurate?
A) A permanent increase in a country's money supply causes a proportional long-run depreciation of its currency against foreign currencies.
B) A temporary increase in a country's money supply causes a proportional long-run depreciation of its currency against foreign currencies.
C) A permanent increase in a country's money supply causes a proportional long-run appreciation of its currency against foreign currencies.
D) A permanent increase in a country's money supply causes a proportional short-run depreciation of its currency against foreign currencies.
E) A permanent increase in a country's money supply causes a proportional short-run appreciation of its currency against foreign currencies.
A) A permanent increase in a country's money supply causes a proportional long-run depreciation of its currency against foreign currencies.
B) A temporary increase in a country's money supply causes a proportional long-run depreciation of its currency against foreign currencies.
C) A permanent increase in a country's money supply causes a proportional long-run appreciation of its currency against foreign currencies.
D) A permanent increase in a country's money supply causes a proportional short-run depreciation of its currency against foreign currencies.
E) A permanent increase in a country's money supply causes a proportional short-run appreciation of its currency against foreign currencies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
In a classic paper, Columbia University economist Phillip Cagan drew the line between inflation and hyperinflation at an inflation rate of
A) more than 120 percent per year.
B) more than 100 percent per year.
C) more than 200 percent per year.
D) more than 12,000 percent per year.
E) more than 1,000 percent per year.
A) more than 120 percent per year.
B) more than 100 percent per year.
C) more than 200 percent per year.
D) more than 12,000 percent per year.
E) more than 1,000 percent per year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Which one of the countries below announces inflation targets?
A) Japan
B) U.S.
C) Canada
D) Mexico
E) Nicaragua
A) Japan
B) U.S.
C) Canada
D) Mexico
E) Nicaragua

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The most extreme inflationary conditions occurred
A) in Zimbabwe in 2008.
B) in Chile in 2012.
C) in Eastern Europe in the 1990s.
D) in Western Europe in the 1980s.
E) in Germany in 2013.
A) in Zimbabwe in 2008.
B) in Chile in 2012.
C) in Eastern Europe in the 1990s.
D) in Western Europe in the 1980s.
E) in Germany in 2013.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Inflation targeting was initiated by which central bank in 1989?
A) U.S.
B) Japan
C) Canada
D) New Zealand
E) U.K.
A) U.S.
B) Japan
C) Canada
D) New Zealand
E) U.K.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which of the following can help to explain why higher inflation may lead to currency appreciations?
A) The interest rate is not the prime target of monetary policy.
B) Most central banks adjust their policy interest rates expressly so as to keep inflation in check.
C) Central banks increase the money supply leading to overshooting of the exchange rate.
D) Inflation will increase the purchasing power of a currency.
E) The world market does not adjust their currency trade to reflect inflation.
A) The interest rate is not the prime target of monetary policy.
B) Most central banks adjust their policy interest rates expressly so as to keep inflation in check.
C) Central banks increase the money supply leading to overshooting of the exchange rate.
D) Inflation will increase the purchasing power of a currency.
E) The world market does not adjust their currency trade to reflect inflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Using year-by-year data from 1987-2007 shows that
A) there is a strong positive relation between average Latin American money-supply growth and inflation.
B) there is a strong negative relation between average Latin American money-supply growth and inflation.
C) there is a strong positive relation between average Latin American money-supply growth and deflation.
D) it is difficult to find a strong positive relation between average Latin American money-supply growth and inflation.
E) there is a weak positive relation between average Latin American money-supply growth and inflation.
A) there is a strong positive relation between average Latin American money-supply growth and inflation.
B) there is a strong negative relation between average Latin American money-supply growth and inflation.
C) there is a strong positive relation between average Latin American money-supply growth and deflation.
D) it is difficult to find a strong positive relation between average Latin American money-supply growth and inflation.
E) there is a weak positive relation between average Latin American money-supply growth and inflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Explain the effects of a permanent increase in the U.S. money supply in the short run and in the long run. Assume that the U.S. real national income is constant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
"Although the price levels appear to display short-run stickiness in many countries, a change in the money supply creates immediate demand and cost pressures that eventually lead to future increase in the price level." Discuss.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Explain the exchange rate over-shooting hypothesis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Using 4 different figures, plot the time paths showing the effects of a permanent increase in the United States money supply on:
(a)U.S. Money supply
(b)The dollar interest rate.
(c)The U.S. price level
(d)The dollar/euro exchange rate
(a)U.S. Money supply
(b)The dollar interest rate.
(c)The U.S. price level
(d)The dollar/euro exchange rate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



