Deck 11: Lightning, thunder, and Tornadoes
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/116
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 11: Lightning, thunder, and Tornadoes
1
The stepped-leader 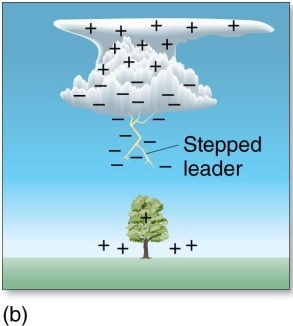
A)moves downward in one continuous movement.
B)occurs after the formation of the return stroke.
C)creates the pathway for the flow of electrons.
D)has no similarities to a dart leader.

A)moves downward in one continuous movement.
B)occurs after the formation of the return stroke.
C)creates the pathway for the flow of electrons.
D)has no similarities to a dart leader.
C
2
________ lightning is extremely dangerous since it can occur from a relatively cloud-free sky.
A)Sheet
B)Heat
C)Anvil
D)Cloud-to-cloud
A)Sheet
B)Heat
C)Anvil
D)Cloud-to-cloud
C
3
Lightning is
A)when warm and cold air collide.
B)an indication of a high salt content in the air.
C)an indication that the atmosphere is virtually dust free.
D)a discharge of static electricity.
A)when warm and cold air collide.
B)an indication of a high salt content in the air.
C)an indication that the atmosphere is virtually dust free.
D)a discharge of static electricity.
D
4
Between the earth's surface and the ionosphere,
A)a large voltage difference occurs only when thunderstorms are present.
B)a large voltage difference always exists.
C)a very small voltage difference usually exists.
D)a very small voltage difference occurs only when thunderstorms are present.
A)a large voltage difference occurs only when thunderstorms are present.
B)a large voltage difference always exists.
C)a very small voltage difference usually exists.
D)a very small voltage difference occurs only when thunderstorms are present.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
During a lightning event
A)a large quantity of electrons is transferred.
B)there is typically only one stroke.
C)the negative charge near the bottom of the cloud increases.
D)the air around the conducting channel is heated to temperatures up to 30,000 K.
A)a large quantity of electrons is transferred.
B)there is typically only one stroke.
C)the negative charge near the bottom of the cloud increases.
D)the air around the conducting channel is heated to temperatures up to 30,000 K.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Cloud-to-cloud lightning makes up what % of all lightning?
A)20%
B)40%
C)60%
D)80%
A)20%
B)40%
C)60%
D)80%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Lightning
A)never strikes twice at the same place.
B)strikes anywhere conductivity can be established.
C)never strikes water.
D)always strikes cedar trees.
A)never strikes twice at the same place.
B)strikes anywhere conductivity can be established.
C)never strikes water.
D)always strikes cedar trees.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Most lightning discharges
A)originate in a cloud and travel toward the ground.
B)originate at the ground and travel toward a cloud.
C)occur within clouds.
D)originate within the ionosphere and travel to the ground.
A)originate in a cloud and travel toward the ground.
B)originate at the ground and travel toward a cloud.
C)occur within clouds.
D)originate within the ionosphere and travel to the ground.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Worldwide,lightning results in how many deaths per year?
A)100
B)400
C)600
D)1000
A)100
B)400
C)600
D)1000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Thunder
A)moves at the speed of light.
B)always appears to the listener as a sharp clap.
C)is the cause of heat lightning.
D)results from the explosive expansion of air.
A)moves at the speed of light.
B)always appears to the listener as a sharp clap.
C)is the cause of heat lightning.
D)results from the explosive expansion of air.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The fair-weather electric field
A)results in only a small voltage difference between the ionosphere and the surface.
B)is maintained in large part through lightning.
C)distributes much electricity to the ground because air is a good conductor.
D)has its negative portion in the ionosphere.
A)results in only a small voltage difference between the ionosphere and the surface.
B)is maintained in large part through lightning.
C)distributes much electricity to the ground because air is a good conductor.
D)has its negative portion in the ionosphere.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
When a large number of runaway electrons accumulates in a small volume,the energy is released in a process called a
A)electron conveyer.
B)positive discharge.
C)runaway breakdown.
D)volumetric discharge.
A)electron conveyer.
B)positive discharge.
C)runaway breakdown.
D)volumetric discharge.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Sheet lightning
A)does not require a separation of charge.
B)is visible as sharp streaks of lightning arcing through the sky.
C)occurs when the electrical resistance in the air overcomes the voltage gradient within a cloud or between clouds.
D)accounts for the majority of all lightning events.
A)does not require a separation of charge.
B)is visible as sharp streaks of lightning arcing through the sky.
C)occurs when the electrical resistance in the air overcomes the voltage gradient within a cloud or between clouds.
D)accounts for the majority of all lightning events.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Lightning can strike
A)below a thunderstorm cloud.
B)out of the anvil of a thunderstorm cloud.
C)from the side of the cloud.
D)all of these
A)below a thunderstorm cloud.
B)out of the anvil of a thunderstorm cloud.
C)from the side of the cloud.
D)all of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The thermoelectric-effect explanation for lightning
A)depends on the transfer of negative charge to hailstones.
B)cannot occur in a cloud that extends above the freezing level.
C)is dependent upon a magnetic field to induce charge separation in ice pellets.
D)depends upon ice crystals moving to the bottom of the cloud.
A)depends on the transfer of negative charge to hailstones.
B)cannot occur in a cloud that extends above the freezing level.
C)is dependent upon a magnetic field to induce charge separation in ice pellets.
D)depends upon ice crystals moving to the bottom of the cloud.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Charge separation
A)results in the top of the cloud having a negative charge.
B)most often occurs in clouds that are not precipitating.
C)results in lightning only if the cloud extends above the freezing level.
D)is not explained by the thermoelectric effect.
A)results in the top of the cloud having a negative charge.
B)most often occurs in clouds that are not precipitating.
C)results in lightning only if the cloud extends above the freezing level.
D)is not explained by the thermoelectric effect.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
A typical cloud-to-ground lightning event consists of
A)a single electrical discharge.
B)a massive release of latent heat.
C)a combination of ionospheric discharge and wind shear.
D)several distinct steps that look to the human eye like a single lightning strike.
A)a single electrical discharge.
B)a massive release of latent heat.
C)a combination of ionospheric discharge and wind shear.
D)several distinct steps that look to the human eye like a single lightning strike.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
This type of lightning extends up to 95 kilometers above the top of a thunderstorm,and it resembles a jellyfish:
A)sprite.
B)St. Elmo's fire.
C)ball lightning.
D)sheet lightning.
A)sprite.
B)St. Elmo's fire.
C)ball lightning.
D)sheet lightning.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Lightning that seems to occur without thunder is called
A)heat lightning.
B)silent lightning.
C)sheet lightning.
D)northern lightning.
A)heat lightning.
B)silent lightning.
C)sheet lightning.
D)northern lightning.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The sound of thunder caused by a lightning strike reaches your ears ________ the light from the lightning flash reaches your eyes.
A)before
B)at the same time as
C)after
A)before
B)at the same time as
C)after

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Give two reasons why lightning kills fewer people now than in the past.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The induction explanation for lightning
A)is criticized by some scientists for not allowing enough time for the transfer of charge from ice crystals to hailstones.
B)assumes that the upper atmosphere has a positive charge.
C)assumes the transfer of electrons from ice pellets to ice crystals.
D)is criticized by some scientists for not taking into account that the electrical field is too strong.
A)is criticized by some scientists for not allowing enough time for the transfer of charge from ice crystals to hailstones.
B)assumes that the upper atmosphere has a positive charge.
C)assumes the transfer of electrons from ice pellets to ice crystals.
D)is criticized by some scientists for not taking into account that the electrical field is too strong.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Thunder exhibiting a prolonged,rumbling sound
A)is likely originating from multiple lightning bolts.
B)is likely originating from different regions of a single lightning stroke.
C)indicates a reduced intensity of the associated lightning strike.
D)indicates a higher-temperature thunderstorm.
A)is likely originating from multiple lightning bolts.
B)is likely originating from different regions of a single lightning stroke.
C)indicates a reduced intensity of the associated lightning strike.
D)indicates a higher-temperature thunderstorm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Explain how the aviation industry safeguards modern aircraft against lightning.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
First describe the two main theories that describe charge separation.Then describe the formation and movement of a stepped-leader,return strokes,and dart leaders.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Give two lightning safety rules.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Explain why non-convertible automobiles are well protected against lightning.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Cloud-to-ground lightning makes up what % of all lightning?
A)10%
B)20%
C)25%
D)50%
A)10%
B)20%
C)25%
D)50%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Describe the four less-common types of lightning.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
In order to determine how far lightning is from your observation point
A)count the seconds from flash-to-bang and divide by ten.
B)count the seconds from flash-to-bang and divide by five to get miles.
C)listen to your AM radio and count the seconds from loud static to hearing the thunder and divide by ten.
D)count the seconds from flash-to-bang and divide by 30.
A)count the seconds from flash-to-bang and divide by ten.
B)count the seconds from flash-to-bang and divide by five to get miles.
C)listen to your AM radio and count the seconds from loud static to hearing the thunder and divide by ten.
D)count the seconds from flash-to-bang and divide by 30.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which of the following is NOT a part of the Earth's electric field?
A)positive charge in the upper atmosphere
B)negative charge on the surface
C)recharged by thunderstorm lightning
D)negative charge in the upper atmosphere
A)positive charge in the upper atmosphere
B)negative charge on the surface
C)recharged by thunderstorm lightning
D)negative charge in the upper atmosphere

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
This process of charge separation relies on the earth's electric field: ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which portion of the lightning process is the most visible?
A)charge separation
B)stepped leader
C)return stroke
D)dart leader
A)charge separation
B)stepped leader
C)return stroke
D)dart leader

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The sound of thunder travels how many miles every 10 seconds?
A)1/2-mile
B)1 mile
C)2 miles
D)10 miles
A)1/2-mile
B)1 mile
C)2 miles
D)10 miles

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Cloud-to-cloud lightning is called ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
What % of the moisture that condenses within an air mass thunderstorm actually falls as precipitation?
A)5%
B)10%
C)20%
D)33%
A)5%
B)10%
C)20%
D)33%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The Earth's electric field carries about ________ times the current of a North American home.
A)2
B)10
C)100
D)1,000
A)2
B)10
C)100
D)1,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Airplanes are struck by lightning
A)frequently.
B)only during clear-sky flights.
C)only during high altitude flights.
D)only during takeoff and landing.
A)frequently.
B)only during clear-sky flights.
C)only during high altitude flights.
D)only during takeoff and landing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
If you are outside in the presence of lightning and cannot take cover indoors,which of the following would be the safest course of action?
A)go to a low-lying area, crouch down and minimize your contact with the ground
B)lie face down in a ditch
C)seek shelter beneath a large tree
D)climb into the open back of a pickup truck
A)go to a low-lying area, crouch down and minimize your contact with the ground
B)lie face down in a ditch
C)seek shelter beneath a large tree
D)climb into the open back of a pickup truck

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The death toll from lightning in the United States has ________ since the 1920s.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Supercell storms
A)are not readily visible on Doppler radar.
B)account for a majority of tornadoes.
C)do not exhibit any rotational aspects.
D)are larger than mesoscale convective complexes.
A)are not readily visible on Doppler radar.
B)account for a majority of tornadoes.
C)do not exhibit any rotational aspects.
D)are larger than mesoscale convective complexes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Severe thunderstorms
A)have, by definition, wind speeds in excess of 90 miles per hour.
B)often appear in groups.
C)typically take place on the microscale.
D)rarely last more than an hour.
A)have, by definition, wind speeds in excess of 90 miles per hour.
B)often appear in groups.
C)typically take place on the microscale.
D)rarely last more than an hour.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Derecho winds are strongest when
A)upper-level winds are strong, because it spreads out the downdrafts.
B)upper-level winds are strong, because their momentum is carried to the surface.
C)upper-level winds are weak, because more wind shear is created.
D)upper-level winds are weak, because less wind shear is created.
A)upper-level winds are strong, because it spreads out the downdrafts.
B)upper-level winds are strong, because their momentum is carried to the surface.
C)upper-level winds are weak, because more wind shear is created.
D)upper-level winds are weak, because less wind shear is created.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
This image,showing storm radial velocity (the air motions taking place within a cloud)is especially useful in studying supercell storms: ________.
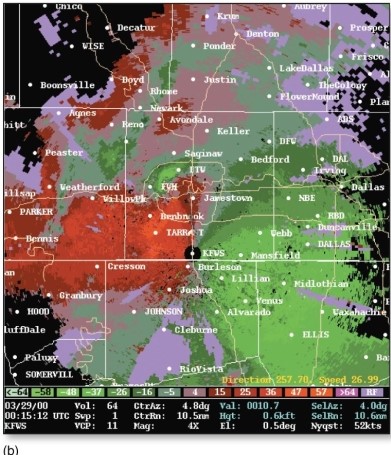


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Downdrafts that occupy the entire base of the cloud spell the end of this type of storm: ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Doppler radar
A)measures the sound waves emitted by thunderstorms.
B)is used more extensively in Canada than in the United States.
C)uses ultraviolet light.
D)measures shifts in wavelengths of reflected electromagnetic radiation.
A)measures the sound waves emitted by thunderstorms.
B)is used more extensively in Canada than in the United States.
C)uses ultraviolet light.
D)measures shifts in wavelengths of reflected electromagnetic radiation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Describe the physical properties and other important characteristics of a supercell storm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
A common Doppler radar signature associated with a supercell tornado is the 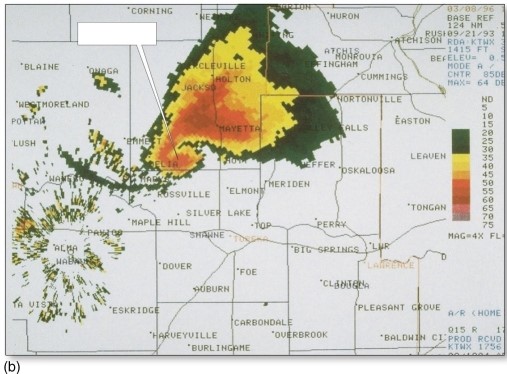
A)gust front.
B)hook echo.
C)shelf cloud.
D)roll cloud.

A)gust front.
B)hook echo.
C)shelf cloud.
D)roll cloud.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
A circular cluster of strong thunderstorms is a ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Doppler radar helps the meteorologist to
A)hear storm noises much more clearly.
B)infer the movement of air within a storm.
C)see through hills and mountains.
D)interrogate much larger sectors of the atmosphere than was possible with conventional radar.
A)hear storm noises much more clearly.
B)infer the movement of air within a storm.
C)see through hills and mountains.
D)interrogate much larger sectors of the atmosphere than was possible with conventional radar.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The mature stage of air-mass thunderstorms
A)is marked by an absence of significant downdrafts.
B)occurs before the anvil shape at the top of the cloud has formed.
C)sees the end of additional water vapor entering the cloud.
D)is marked by the heaviest precipitation.
A)is marked by an absence of significant downdrafts.
B)occurs before the anvil shape at the top of the cloud has formed.
C)sees the end of additional water vapor entering the cloud.
D)is marked by the heaviest precipitation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Describe the characteristics of these successive stages of air mass thunderstorm formation and dissipation.
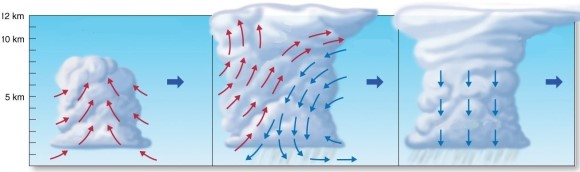


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The cumulus stage of air-mass thunderstorm development
A)is marked by strong updrafts throughout the cloud.
B)is when much of the storm's precipitation occurs.
C)begins when unstable air begins to rise.
D)occurs before the Bergeron process starts.
A)is marked by strong updrafts throughout the cloud.
B)is when much of the storm's precipitation occurs.
C)begins when unstable air begins to rise.
D)occurs before the Bergeron process starts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The only requirement for a thunderstorm is
A)sinking air.
B)still air.
C)rising air.
D)upper level convergence.
A)sinking air.
B)still air.
C)rising air.
D)upper level convergence.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Mesoscale convective complexes are self-sustaining because
A)wind shear is typically absent.
B)downdrafts from individual cells become warmer as the precipitation evaporates.
C)downdrafts from individual cells rise over the outflow boundary.
D)downdrafts from individual cells combine with surface winds to create updrafts and wind shear.
A)wind shear is typically absent.
B)downdrafts from individual cells become warmer as the precipitation evaporates.
C)downdrafts from individual cells rise over the outflow boundary.
D)downdrafts from individual cells combine with surface winds to create updrafts and wind shear.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
This phenomenon 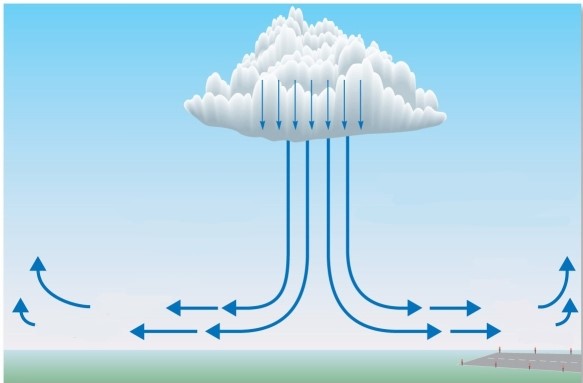
A)is a type of updraft associated with severe thunderstorms.
B)typically flows in only one direction.
C)causes little damage at the surface.
D)is a major potential hazard at airports.

A)is a type of updraft associated with severe thunderstorms.
B)typically flows in only one direction.
C)causes little damage at the surface.
D)is a major potential hazard at airports.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
A Mesoscale Convective Complex (MCC)is
A)a small group of air mass thunderstorms.
B)usually a line of severe weather.
C)totally disorganized and random in nature.
D)a group of self-propagating thunderstorm cells that can last for hours.
A)a small group of air mass thunderstorms.
B)usually a line of severe weather.
C)totally disorganized and random in nature.
D)a group of self-propagating thunderstorm cells that can last for hours.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The three stages of the air mass thunderstorm are
A)cumulus, mature, dissipating.
B)cumulus, dissipating, mature.
C)initial, mature, degenerating.
D)initial, middle, dissipating.
A)cumulus, mature, dissipating.
B)cumulus, dissipating, mature.
C)initial, mature, degenerating.
D)initial, middle, dissipating.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which of these can be characteristics of severe thunderstorms?
A)wind speeds in excess of 58 mph
B)hailstones one inch or larger in diameter
C)tornadoes
D)all of these
A)wind speeds in excess of 58 mph
B)hailstones one inch or larger in diameter
C)tornadoes
D)all of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
An outflow boundary is
A)the leading edge of cold air from a thunderstorm downdraft.
B)a favorable place for future severe storm development, especially if two intersect.
C)can be clearly seen on radar images.
D)all of these
A)the leading edge of cold air from a thunderstorm downdraft.
B)a favorable place for future severe storm development, especially if two intersect.
C)can be clearly seen on radar images.
D)all of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The glaciated part of a thunderstorm is usually found at
A)the top of the storm.
B)the middle of the storm.
C)the bottom of the storm.
D)throughout the entire storm.
A)the top of the storm.
B)the middle of the storm.
C)the bottom of the storm.
D)throughout the entire storm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Mesoscale convective complexes
A)are a common cause of severe weather in Canada.
B)are typically linear.
C)are not able to propagate new cells.
D)require potential stability in the atmosphere.
A)are a common cause of severe weather in Canada.
B)are typically linear.
C)are not able to propagate new cells.
D)require potential stability in the atmosphere.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Describe the size,duration,potential destruction,and physical characteristics of the various types of thunderstorms and thunderstorm complexes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Mesoscale convective systems
A)are individual thunderstorms called supercells.
B)do not last more than 12 to 24 hours.
C)typically have low water-vapor content.
D)require wind shear and substantial uplift.
A)are individual thunderstorms called supercells.
B)do not last more than 12 to 24 hours.
C)typically have low water-vapor content.
D)require wind shear and substantial uplift.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Which of the following stages of thunderstorm development is characterized by the dominance of downdrafts and entrainment of the storm?
A)cumulus
B)mature
C)dissipating
D)none of these
A)cumulus
B)mature
C)dissipating
D)none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The principle hazard of microbursts to aircraft in the process of taking off or landing is
A)windblown sand and dust damaging jet engines.
B)sudden changes in lift and tailwinds.
C)Doppler radar.
D)lightning.
A)windblown sand and dust damaging jet engines.
B)sudden changes in lift and tailwinds.
C)Doppler radar.
D)lightning.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
For a cumulus cloud grows that taller over time but never develops a downdraft,
A)precipitation will not occur.
B)precipitation will be in the form of rain.
C)all lightning will be cloud-to-ground.
D)the thunder will have a weak, rumbling sound.
A)precipitation will not occur.
B)precipitation will be in the form of rain.
C)all lightning will be cloud-to-ground.
D)the thunder will have a weak, rumbling sound.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
In the United States,thunderstorms are most common in
A)central Florida.
B)Kansas.
C)Oklahoma.
D)Louisiana.
A)central Florida.
B)Kansas.
C)Oklahoma.
D)Louisiana.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Squall line thunderstorms
A)can have lengths of up to 100 kilometers.
B)are most common in late winter.
C)have downdrafts that create a gust front.
D)usually consist of five or fewer cells.
A)can have lengths of up to 100 kilometers.
B)are most common in late winter.
C)have downdrafts that create a gust front.
D)usually consist of five or fewer cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
The ability to detect mesocyclones using Doppler radar
A)reduces the risk of damage of stepped leaders.
B)allows meteorologists to predict where and when cumulonimbus clouds may form.
C)gives meteorologists the opportunity to change the direction of the rotation.
D)allows meteorologists to issue tornado warnings before tornados form.
A)reduces the risk of damage of stepped leaders.
B)allows meteorologists to predict where and when cumulonimbus clouds may form.
C)gives meteorologists the opportunity to change the direction of the rotation.
D)allows meteorologists to issue tornado warnings before tornados form.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
One of the most detrimental events that can occur to a developing thunderstorm is
A)entrainment.
B)lightning.
C)hail.
D)release of latent heat.
A)entrainment.
B)lightning.
C)hail.
D)release of latent heat.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Thunderstorms occur about how many times a day?
A)5,000
B)10,000
C)40,000
D)75,000
A)5,000
B)10,000
C)40,000
D)75,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Air mass thunderstorms
A)extinguish themselves through the formation of extensive downdrafts.
B)often last for several hours.
C)are associated with severe weather.
D)usually form at the borders of air masses.
A)extinguish themselves through the formation of extensive downdrafts.
B)often last for several hours.
C)are associated with severe weather.
D)usually form at the borders of air masses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Explain how downdrafts create the strong precipitation within air mass thunderstorms,yet also cause the storm to die out.
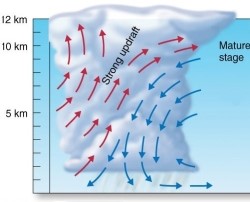


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Globally,air mass thunderstorms are most common in the ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
In which stage of the air mass thunderstorm are there up- and down-drafts?
A)initial
B)middle
C)dissipating
D)mature
A)initial
B)middle
C)dissipating
D)mature

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Explain why strong vertical wind shear is a necessary ingredient of all intense thunderstorms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
A thunderstorm becomes severe because
A)inflow equals outflow.
B)outflow equals inflow.
C)the updraft and downdraft become quasi-steady state.
D)entrainment enhances convection.
A)inflow equals outflow.
B)outflow equals inflow.
C)the updraft and downdraft become quasi-steady state.
D)entrainment enhances convection.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Describe the Doppler effect and how it is applied with Doppler radar to study thunderstorms and severe storms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
According to data from lightning detection networks,the average thunderstorm across the continental United States and Canada produces ________ lightning strikes.
A)36
B)100
C)200
D)280
A)36
B)100
C)200
D)280

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



