Deck 16: Climate Changes: Past and Future
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/117
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 16: Climate Changes: Past and Future
1
What are proxy indicators?
Scientists gain insight into past climates based on information left in the geological and biological records through what are called proxy indicators.
2
The term ________ refers to the climate of the past.
paleoclimate
3
An example of a climatic boundary condition change would be
A)New York city increased by several million people.
B)if the output of the Sun were to increase or decrease.
C)the rain forests of Brazil were all cut or burned.
D)putting more dams on the major rivers of the world.
A)New York city increased by several million people.
B)if the output of the Sun were to increase or decrease.
C)the rain forests of Brazil were all cut or burned.
D)putting more dams on the major rivers of the world.
B
4
All of the following statements about coral reefs are true,except
A)they grow to just below the ocean surface.
B)they require warm water.
C)their composition is independent of water temperature.
D)their shells are composed primarily of calcium.
A)they grow to just below the ocean surface.
B)they require warm water.
C)their composition is independent of water temperature.
D)their shells are composed primarily of calcium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
This isotope of oxygen is the least common: ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Explain why we should not blame climate change for every unusual weather event.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
This is an example of a 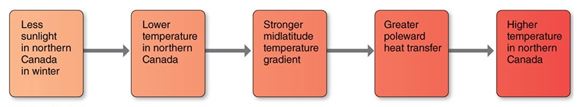
A)positive feedback.
B)negative feedback.
C)boundary condition.
D)proxy indicator.

A)positive feedback.
B)negative feedback.
C)boundary condition.
D)proxy indicator.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
This is NOT a climate boundary condition.
A)composition of the atmosphere
B)amount of sunlight reaching the top of Earth's atmosphere
C)arrangement and size of the oceans
D)the value of the heat capacity of water
A)composition of the atmosphere
B)amount of sunlight reaching the top of Earth's atmosphere
C)arrangement and size of the oceans
D)the value of the heat capacity of water

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
This is an example of a 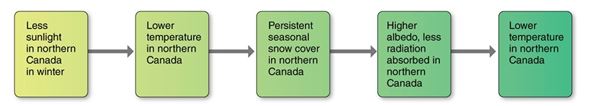
A)positive feedback.
B)negative feedback.
C)boundary condition.
D)proxy indicator.

A)positive feedback.
B)negative feedback.
C)boundary condition.
D)proxy indicator.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Describe three methods used to study past climates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
What are some of the important problems involved in defining climate change?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A system that regulates itself depends on
A)negative feedback.
B)positive feedback.
C)feedback filtered by related variables.
D)inputs from surrounding systems only.
A)negative feedback.
B)positive feedback.
C)feedback filtered by related variables.
D)inputs from surrounding systems only.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Glaciers do all of the following,except
A)move large boulders long distances.
B)leave scratch marks on rock.
C)polish rock.
D)create v-shaped valleys.
A)move large boulders long distances.
B)leave scratch marks on rock.
C)polish rock.
D)create v-shaped valleys.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Climate change is defined as
A)a shift in the upper level flow.
B)a change in how observations are made.
C)noting changes in meteorological statistical values over time.
D)measuring the change in sea level.
A)a shift in the upper level flow.
B)a change in how observations are made.
C)noting changes in meteorological statistical values over time.
D)measuring the change in sea level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The smallest time periods on the geologic column are the ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Oxygen-18
A)is the more common isotope of oxygen.
B)is more prevalent in oceans when glaciers are expanding.
C)has not been a useful tool in ice-core analysis.
D)is useful to scientists because it emits alpha rays.
A)is the more common isotope of oxygen.
B)is more prevalent in oceans when glaciers are expanding.
C)has not been a useful tool in ice-core analysis.
D)is useful to scientists because it emits alpha rays.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
A ________ can transform a v-shaped valley into a u-shaped valley.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
________ is the term for the fact that a single set of boundary values can yield more than one climate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
In the context of climate change,what is a forcing agent?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
This data record from ice cores shows 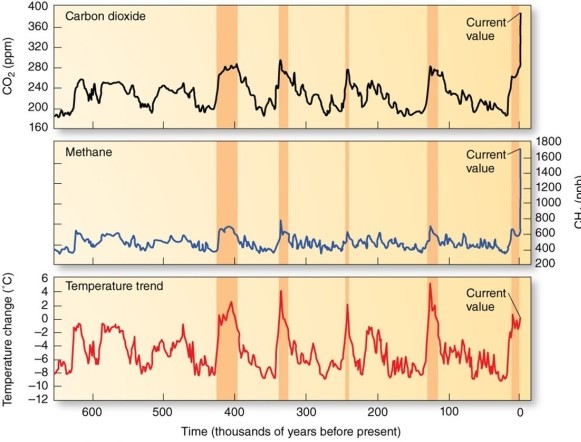
A)increased temperatures have frequently been associated with elevated methane and carbon dioxide concentrations.
B)lower temperatures have frequently been associated with elevated methane and carbon dioxide concentrations.
C)increased temperatures have frequently been associated with reduced methane and carbon dioxide concentrations.

A)increased temperatures have frequently been associated with elevated methane and carbon dioxide concentrations.
B)lower temperatures have frequently been associated with elevated methane and carbon dioxide concentrations.
C)increased temperatures have frequently been associated with reduced methane and carbon dioxide concentrations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
During the mid-Cretaceous period
A)corals grew substantially closer to the poles than they do now.
B)dinosaurs were confined to areas within 10 degrees of the equator.
C)global temperature was 2-4 degrees Celsius higher than now.
D)sea level was lower than now.
A)corals grew substantially closer to the poles than they do now.
B)dinosaurs were confined to areas within 10 degrees of the equator.
C)global temperature was 2-4 degrees Celsius higher than now.
D)sea level was lower than now.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The current ice age
A)began around 38-55MYA.
B)began during the Pleistocene.
C)came about rapidly.
D)had a uniform drop in temperature.
A)began around 38-55MYA.
B)began during the Pleistocene.
C)came about rapidly.
D)had a uniform drop in temperature.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following coincided with the Viking settlement of Greenland?
A)Younger Dryas
B)African Humid Period
C)Little Ice age
D)Medieval Climate Anomaly
A)Younger Dryas
B)African Humid Period
C)Little Ice age
D)Medieval Climate Anomaly

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
During the mid-Cretaceous period,dinosaurs lived as far north as ________ degrees latitude.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
We are currently living in the
A)Mesozoic era.
B)Tertiary period.
C)Holocene epoch.
D)midst of Earth's sixth major ice age.
A)Mesozoic era.
B)Tertiary period.
C)Holocene epoch.
D)midst of Earth's sixth major ice age.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Large-scale human impacts on the climate may have started how long ago?
A)only 200 years ago
B)2,000 years ago
C)8,000 years ago
D)100,000 years ago
A)only 200 years ago
B)2,000 years ago
C)8,000 years ago
D)100,000 years ago

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
During the last 750,000 years
A)Earth has had at least two ice ages.
B)ice volume changes have been highest in the Southern Hemisphere.
C)there has been a pattern of roughly 100,000-year cycles in climate change.
D)there has been little change in climate.
A)Earth has had at least two ice ages.
B)ice volume changes have been highest in the Southern Hemisphere.
C)there has been a pattern of roughly 100,000-year cycles in climate change.
D)there has been little change in climate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
During ice ages,the ice sheets were thickest and most wide spread in
A)the southern hemisphere.
B)the northern hemisphere.
C)Europe, and especially Russia.
D)the south pole.
A)the southern hemisphere.
B)the northern hemisphere.
C)Europe, and especially Russia.
D)the south pole.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
During the last glacial maximum
A)most ice was stored in Eurasia and North America first.
B)sheets of ice did not exceed about 800 meters in thickness.
C)there was a land bridge between Siberia and Alaska.
D)the main sector of glaciation did not extend more than 100 kilometers south of the present U.S.-Canadian border.
A)most ice was stored in Eurasia and North America first.
B)sheets of ice did not exceed about 800 meters in thickness.
C)there was a land bridge between Siberia and Alaska.
D)the main sector of glaciation did not extend more than 100 kilometers south of the present U.S.-Canadian border.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
During the last glacial maximum
A)there were four main pulses of glaciation.
B)Scandinavia was relatively ice-free.
C)sea level was about 20 feet lower than now.
D)higher latitude regions were drier than they are now.
A)there were four main pulses of glaciation.
B)Scandinavia was relatively ice-free.
C)sea level was about 20 feet lower than now.
D)higher latitude regions were drier than they are now.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The time scale of climate change
A)is well defined and immutable.
B)is difficult to pin down for a wide variety of reasons.
C)can be measured and tracked with satellite data.
D)is easy to follow because climate changes little in spatial variation.
A)is well defined and immutable.
B)is difficult to pin down for a wide variety of reasons.
C)can be measured and tracked with satellite data.
D)is easy to follow because climate changes little in spatial variation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
In the United States,how far south did the last major glaciation get?
A)St. Louis
B)San Francisco
C)Oklahoma City
D)Atlanta
A)St. Louis
B)San Francisco
C)Oklahoma City
D)Atlanta

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The Holocene
A)saw a gradual warming trend at its beginning.
B)saw only one period of cooling.
C)saw sea levels rise during its early times.
D)was a transfer from an interglacial period to a glacial period.
A)saw a gradual warming trend at its beginning.
B)saw only one period of cooling.
C)saw sea levels rise during its early times.
D)was a transfer from an interglacial period to a glacial period.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC)is primarily mandated to
A)assess the present state of knowledge concerning climate change.
B)report on the human and environmental impacts of climate change.
C)offer mitigation strategies to deal with climate change.
D)All of these are correct.
A)assess the present state of knowledge concerning climate change.
B)report on the human and environmental impacts of climate change.
C)offer mitigation strategies to deal with climate change.
D)All of these are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
How is it possible to reconstruct past climates when no records were available?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The shape of millennial oscillations is
A)peaked.
B)sinusoidal.
C)indeterminate.
D)square-like.
A)peaked.
B)sinusoidal.
C)indeterminate.
D)square-like.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Explain how caves are used to analyze past climates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The Cretaceous period was in this era
A)Cenozoic.
B)Mesozoic.
C)Paleozoic.
D)Precambrian.
A)Cenozoic.
B)Mesozoic.
C)Paleozoic.
D)Precambrian.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Of the past 2.5 billion years,what % have been ice ages?
A)60-70%
B)10-20%
C)40-50%
D)70-80%
A)60-70%
B)10-20%
C)40-50%
D)70-80%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The geologic column
A)was constructed by looking at evidence of major climate change.
B)is a hierarchical system dividing time into five categories.
C)is based in part on fossil evidence.
D)assigns equal time values to each era.
A)was constructed by looking at evidence of major climate change.
B)is a hierarchical system dividing time into five categories.
C)is based in part on fossil evidence.
D)assigns equal time values to each era.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
How long ago was the last major peak of glaciation?
A)5,000 years
B)20,000 years
C)75,000 years
D)115,000 years
A)5,000 years
B)20,000 years
C)75,000 years
D)115,000 years

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC)report outlines several observed changes in the Earth's climate that are consistent with global warming.List two of these items.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
How many ice ages occurred in the first 2 billion years of Earth's history?
A)0
B)1
C)2
D)5
A)0
B)1
C)2
D)5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
What was significant about African Humid Period?
A)Northern Africa was almost completely vegetated.
B)The Sahara Desert was greatly expanded.
C)Savanna landscapes were minimal.
D)South Africa was heavily glaciated.
A)Northern Africa was almost completely vegetated.
B)The Sahara Desert was greatly expanded.
C)Savanna landscapes were minimal.
D)South Africa was heavily glaciated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
During the last glaciations,what were the moisture conditions like?
A)very wet
B)the same as today
C)a little drier
D)more than 50% drier in the northern latitudes
A)very wet
B)the same as today
C)a little drier
D)more than 50% drier in the northern latitudes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Should Earth be considered a "warm" planet or a "cold" planet? Explain your response.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
During the current geologic period,ice volume changes have been largest in
A)the Southern Hemisphere.
B)Asia.
C)Europe.
D)the Northern Hemisphere.
A)the Southern Hemisphere.
B)Asia.
C)Europe.
D)the Northern Hemisphere.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Carbon dioxide
A)is a noble gas.
B)is a solid that contributes very little to atmospheric and climatic change.
C)is a greenhouse gas that may hold the key to important climatic changes.
D)has become so thick that certain insects can no longer fly but are forced to crawl.
A)is a noble gas.
B)is a solid that contributes very little to atmospheric and climatic change.
C)is a greenhouse gas that may hold the key to important climatic changes.
D)has become so thick that certain insects can no longer fly but are forced to crawl.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Millennial-scale oscillations
A)typically begin with a slow increase in temperature.
B)take 500 or so years for a complete cycle.
C)indicate the earth flips back and forth between warmer states and colder states.
D)have little impact on precipitation patterns.
A)typically begin with a slow increase in temperature.
B)take 500 or so years for a complete cycle.
C)indicate the earth flips back and forth between warmer states and colder states.
D)have little impact on precipitation patterns.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
One of the chief issues with climate change is that
A)climate can change on more than one scale.
B)there is not enough data available to build a reliable climate.
C)climate change is spatially consistent.
D)data are too sparse to develop climatic trends.
A)climate can change on more than one scale.
B)there is not enough data available to build a reliable climate.
C)climate change is spatially consistent.
D)data are too sparse to develop climatic trends.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Describe the characteristics of millennial-scale oscillations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Which regions of North America experienced the greatest temperature differences from current values during the last glacial episode of the Pleistocene?
A)Pacific Northwest
B)Southern Florida
C)Tennessee and South Carolina
D)little difference across North America
A)Pacific Northwest
B)Southern Florida
C)Tennessee and South Carolina
D)little difference across North America

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The Medieval Warm Period
A)began after the end of the Little Ice Age.
B)allowed Vikings to colonize Greenland.
C)was a significant global event.
D)saw glaciers advance in the Rockies of North America.
A)began after the end of the Little Ice Age.
B)allowed Vikings to colonize Greenland.
C)was a significant global event.
D)saw glaciers advance in the Rockies of North America.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Most of Earth history has been characterized by conditions that are
A)about the same as today.
B)colder than today.
C)warmer than today.
D)none of these
A)about the same as today.
B)colder than today.
C)warmer than today.
D)none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The eccentricity of Earth's orbit
A)has been increasing.
B)changes cyclically on several scales.
C)is currently zero, meaning Earth has a circular orbit.
D)varies between 3 and 8 percent.
A)has been increasing.
B)changes cyclically on several scales.
C)is currently zero, meaning Earth has a circular orbit.
D)varies between 3 and 8 percent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The ________ led to decreases in agricultural productivity in Renaissance Europe.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Trace the major changes in temperature during the Holocene,with a special emphasis on the last 1,000 or so years.Also discuss evidence for the temperature changes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Milankovitch cycles include all of the following,except
A)changes in the eccentricity of the earth's orbit.
B)changes in the distance between the earth and the Moon.
C)changes in the earth's obliquity.
D)precession.
A)changes in the eccentricity of the earth's orbit.
B)changes in the distance between the earth and the Moon.
C)changes in the earth's obliquity.
D)precession.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Describe important characteristics of the last glacial maximum,including ice extent and thickness,crustal deformation,and changes in air temperature and sea level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The "Little Ice Age"
A)caused the least impact to humans in Northern Europe.
B)was the reason the Jamestown colony failed.
C)began in about 1600.
D)was a global event.
A)caused the least impact to humans in Northern Europe.
B)was the reason the Jamestown colony failed.
C)began in about 1600.
D)was a global event.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
________ involves long-distance flows of ocean water at deep depths and is driven by both temperature differences and salinity differences.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Precession
A)leads to changes in which star is the pole star.
B)has a 100,000-year cycle.
C)does not have a significant impact on the amount of incoming radiation.
D)was not considered by Milankovitch.
A)leads to changes in which star is the pole star.
B)has a 100,000-year cycle.
C)does not have a significant impact on the amount of incoming radiation.
D)was not considered by Milankovitch.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Large volcanic eruptions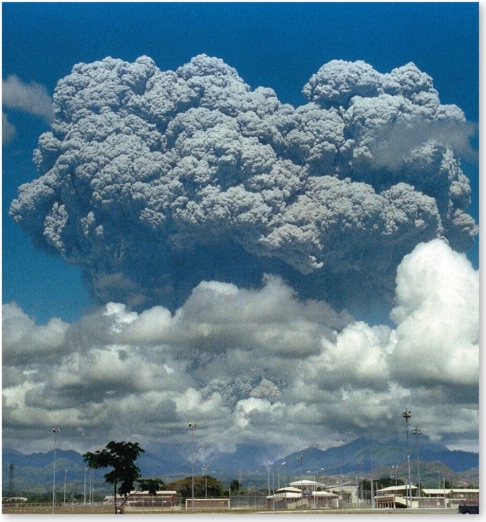 
A)increase global temperatures due to the increased albedo of volcanic aerosols.
B)decrease global temperatures due to the increased albedo of volcanic aerosols.
C)have no effect on global temperatures despite the increased albedo of volcanic aerosols.
D)have little effect on the atmosphere unless only a small amount of sulfuric gases are released.

A)increase global temperatures due to the increased albedo of volcanic aerosols.
B)decrease global temperatures due to the increased albedo of volcanic aerosols.
C)have no effect on global temperatures despite the increased albedo of volcanic aerosols.
D)have little effect on the atmosphere unless only a small amount of sulfuric gases are released.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
If the earth's orbit around the Sun were absolutely spherical
A)the southern hemisphere would be warmer.
B)the northern hemisphere would be cooler.
C)there would be no change because the Sun's energy is constant.
D)the southern hemisphere would be cooler and the northern hemisphere would be warmer.
A)the southern hemisphere would be warmer.
B)the northern hemisphere would be cooler.
C)there would be no change because the Sun's energy is constant.
D)the southern hemisphere would be cooler and the northern hemisphere would be warmer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Tropospheric aerosols
A)have residence time of at least several centuries.
B)have the net effect of reducing global temperatures.
C)form a positive feedback loop with increasing atmospheric carbon dioxide.
D)are rarely anthropogenic in origin.
A)have residence time of at least several centuries.
B)have the net effect of reducing global temperatures.
C)form a positive feedback loop with increasing atmospheric carbon dioxide.
D)are rarely anthropogenic in origin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
If the earth's orbit around the Sun were more elliptical than now with the same inclination angle
A)the northern hemisphere would be warmer.
B)the southern hemisphere would be about the same in yearly temperature.
C)storms in both hemispheres would be stronger.
D)there would be no change because the Sun's energy is constant.
A)the northern hemisphere would be warmer.
B)the southern hemisphere would be about the same in yearly temperature.
C)storms in both hemispheres would be stronger.
D)there would be no change because the Sun's energy is constant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Describe the thermohaline circulation and how it is associated with climate change.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Aerosols
A)typically enter the atmosphere as solid particles.
B)come entirely from nonbiological sources.
C)do not absorb incoming sunlight to a significant extent.
D)can lead to higher nighttime temperatures.
A)typically enter the atmosphere as solid particles.
B)come entirely from nonbiological sources.
C)do not absorb incoming sunlight to a significant extent.
D)can lead to higher nighttime temperatures.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Changes in the output from the Sun
A)are significant and account for varying climatic cycles.
B)are totally insignificant.
C)do effect the earth-atmospheric temperature but the total impact is not fully understood.
D)account for the periods of drought and wetness over North America.
A)are significant and account for varying climatic cycles.
B)are totally insignificant.
C)do effect the earth-atmospheric temperature but the total impact is not fully understood.
D)account for the periods of drought and wetness over North America.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Continental drift
A)is now considered the primary cause of most long-term climate change.
B)occurs very slowly.
C)has been correlated with Milankovitch cycles.
D)did not affect mountain building processes on continents.
A)is now considered the primary cause of most long-term climate change.
B)occurs very slowly.
C)has been correlated with Milankovitch cycles.
D)did not affect mountain building processes on continents.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
A period of minimal sunspot activity between 1645 and 1715 is known as
A)the quasi-biennial oscillation.
B)the Maunder Minimum.
C)eccentricity.
D)a millennial-scale oscillation.
A)the quasi-biennial oscillation.
B)the Maunder Minimum.
C)eccentricity.
D)a millennial-scale oscillation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Explain how aerosols in the troposphere and stratosphere affect global temperature.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Sulfuric gases from volcanic eruptions often rise high to become ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
If a new range of high mountains arose in western Europe along the coast of Spain through France and on to Denmark
A)the climate of England would change drastically.
B)Germany and central Russia would be much drier and colder.
C)Italy would become much warmer.
D)there would be no climate change because the general circulation would compensate for this change in topography.
A)the climate of England would change drastically.
B)Germany and central Russia would be much drier and colder.
C)Italy would become much warmer.
D)there would be no climate change because the general circulation would compensate for this change in topography.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Milankovitch cycles
A)explain little of the Pleistocene climate variation.
B)explain ancient climate change better than more recent climate change.
C)have not yet been tested due to inadequate amounts of data.
D)have difficulty in accounting for effects caused by changes in Earth's eccentricity.
A)explain little of the Pleistocene climate variation.
B)explain ancient climate change better than more recent climate change.
C)have not yet been tested due to inadequate amounts of data.
D)have difficulty in accounting for effects caused by changes in Earth's eccentricity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
The input of anthropogenic carbon dioxide into the atmosphere
A)comes primarily through deforestation.
B)does not affect the rate at which the ocean absorbs carbon dioxide.
C)comes primarily from the Northern Hemisphere.
D)has been significant from a climate standpoint since the late sixteenth century.
A)comes primarily through deforestation.
B)does not affect the rate at which the ocean absorbs carbon dioxide.
C)comes primarily from the Northern Hemisphere.
D)has been significant from a climate standpoint since the late sixteenth century.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Deforestation does all of the following,except
A)increase evapotranspiration.
B)increase temperatures near the surface.
C)decrease precipitation.
D)increase atmospheric carbon dioxide.
A)increase evapotranspiration.
B)increase temperatures near the surface.
C)decrease precipitation.
D)increase atmospheric carbon dioxide.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Which of he following are factors involved in climatic change?
A)variations in Solar Output
B)changes in the Earth's Orbit
C)changes in Atmospheric Turbidity
D)all of these
A)variations in Solar Output
B)changes in the Earth's Orbit
C)changes in Atmospheric Turbidity
D)all of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
How can ice-albedo feedback affect climate?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
The Milankovitch cycles deal with these changing characteristics of Earth: ________,________,and ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



