Deck 17: Atmospheric Optics Online Only in Masteringmeteorology
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/62
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 17: Atmospheric Optics Online Only in Masteringmeteorology
1
Being able to see the Sun before it rises or just after it sets is due to
A)refraction.
B)reflection.
C)scattering.
D)absorption.
A)refraction.
B)reflection.
C)scattering.
D)absorption.
A
2
The study of the effects of the atmosphere on the path of visible radiation passing through it is called ________.
Atmospheric Optics
3
Mirages are caused by
A)apparent horizontal displacements of objects by refraction.
B)apparent upward or downward displacements of objects by reflection.
C)apparent upward or downward displacements of objects by refraction.
D)apparent horizontal displacements of objects by reflection.
A)apparent horizontal displacements of objects by refraction.
B)apparent upward or downward displacements of objects by reflection.
C)apparent upward or downward displacements of objects by refraction.
D)apparent horizontal displacements of objects by reflection.
C
4
Refraction occurs because radiation speed varies with 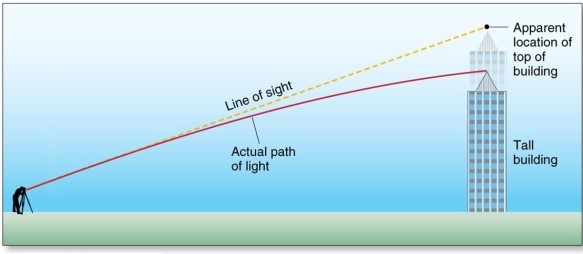
A)moisture.
B)density.
C)sunlight.
D)temperature.

A)moisture.
B)density.
C)sunlight.
D)temperature.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Mirages are caused by
A)refraction.
B)reflection.
C)scattering.
D)absorption.
A)refraction.
B)reflection.
C)scattering.
D)absorption.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
An inferior mirage
A)is made of a single degraded image.
B)is made of 2 images, both imaginary.
C)is made of 2 images, one a true image and one an inverted one.
D)is made of 3 images, one a true image and the two others are degraded replicas of the original.
A)is made of a single degraded image.
B)is made of 2 images, both imaginary.
C)is made of 2 images, one a true image and one an inverted one.
D)is made of 3 images, one a true image and the two others are degraded replicas of the original.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A superior image
A)forms when images are displaced upward.
B)forms when there is one largest image in a group of images.
C)forms when one image is an exact replica of a true feature.
D)all of these
A)forms when images are displaced upward.
B)forms when there is one largest image in a group of images.
C)forms when one image is an exact replica of a true feature.
D)all of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Near the earth's surface,vertical changes of air density with height are caused primarily by
A)vertical moisture gradients.
B)horizontal moisture gradients.
C)horizontal temperature gradients.
D)vertical temperature gradients.
A)vertical moisture gradients.
B)horizontal moisture gradients.
C)horizontal temperature gradients.
D)vertical temperature gradients.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
A refraction pattern in which rays are bent concave upward can be caused by
A)increased moisture.
B)strong winds.
C)a steady, steep drop in temperature with height.
D)low clouds.
A)increased moisture.
B)strong winds.
C)a steady, steep drop in temperature with height.
D)low clouds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The figure depicts 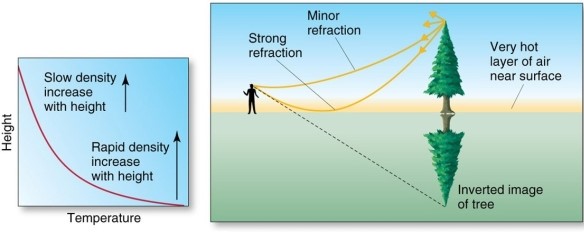
A)a superior mirage.
B)an inferior mirage.
C)a green flash.
D)a twilight mirage.

A)a superior mirage.
B)an inferior mirage.
C)a green flash.
D)a twilight mirage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Because the index of refraction varies slightly with wavelength,
A)white light refracts much less than black light.
B)white light refracts much more than black light.
C)the amount and direction of refraction is exactly the same for all colors of light.
D)the amount and direction of refraction is slightly different for different colors of light.
A)white light refracts much less than black light.
B)white light refracts much more than black light.
C)the amount and direction of refraction is exactly the same for all colors of light.
D)the amount and direction of refraction is slightly different for different colors of light.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
In a superior mirage,the false image occurs
A)below the actual image.
B)above the actual image.
C)both above and below the actual image.
A)below the actual image.
B)above the actual image.
C)both above and below the actual image.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Why does refraction occur?
A)Some wavelengths are more absorbed than other.
B)because radiation speed varies with density of the atmosphere
C)because the denser the atmosphere is the higher the speed that light is transmitted
D)none of these
A)Some wavelengths are more absorbed than other.
B)because radiation speed varies with density of the atmosphere
C)because the denser the atmosphere is the higher the speed that light is transmitted
D)none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
When is refraction of incoming solar radiation greatest?
A)at sunrise
B)at sunset
C)at mid-day
D)both A and B
A)at sunrise
B)at sunset
C)at mid-day
D)both A and B

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The bright green spot that momentarily appears over a setting sun is called a
A)halo.
B)sundog.
C)superior mirage.
D)green flash.
A)halo.
B)sundog.
C)superior mirage.
D)green flash.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The figure demonstrates 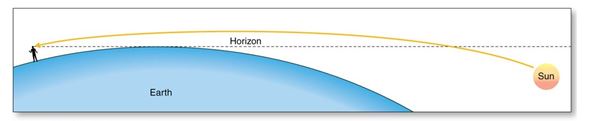
A)reflection.
B)refraction.
C)diffraction.
D)scattering.

A)reflection.
B)refraction.
C)diffraction.
D)scattering.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Twilight is caused by
A)negative albedo.
B)scattering.
C)diffuse radiation.
D)absorption.
A)negative albedo.
B)scattering.
C)diffuse radiation.
D)absorption.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A difference in air density can cause
A)refraction.
B)reflection.
C)scattering.
D)absorption.
A)refraction.
B)reflection.
C)scattering.
D)absorption.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following is defined as the bending of light rays as they pass through the atmosphere?
A)reflection
B)refraction
C)absorption
D)scattering
A)reflection
B)refraction
C)absorption
D)scattering

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
In its path from the top of the atmosphere to the surface of the earth,radiation undergoes which of the following?
A)refraction
B)reflection
C)scattering
D)all of these
A)refraction
B)reflection
C)scattering
D)all of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Where are rainbows located?
A)always just above the horizon
B)always in the center of the sky
C)always in the same part of the sky as the sun
D)always in the part of the sky opposite from the sun
A)always just above the horizon
B)always in the center of the sky
C)always in the same part of the sky as the sun
D)always in the part of the sky opposite from the sun

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
A mirage that forms with warm air above a cool water surface is
A)an inferior mirage.
B)a superior mirage.
C)a desert mirage.
D)a twilight mirage.
A)an inferior mirage.
B)a superior mirage.
C)a desert mirage.
D)a twilight mirage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Under most circumstances the density ________ with increasing altitude.
A)decreases
B)increases
C)remains constant
A)decreases
B)increases
C)remains constant

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The optics of rainbow formation involve 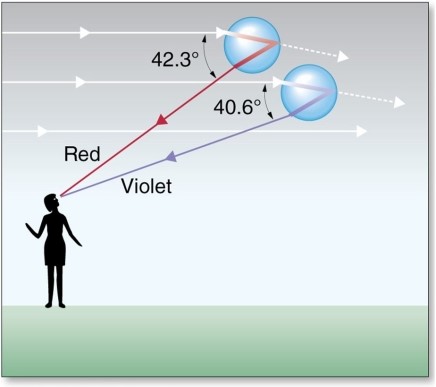
A)reflection only.
B)refraction only.
C)both reflection and refraction.
D)neither reflection nor refraction.

A)reflection only.
B)refraction only.
C)both reflection and refraction.
D)neither reflection nor refraction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
How does the length of twilight vary from summer to winter?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
When the Sun is positioned slightly below the horizon,its direct rays cannot be seen at the surface,but diffuse radiation can illuminate the sky to create ________ conditions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Explain how,where,and when the green flash occurs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which of the following is NOT associated with a superior mirage?
A)diffraction occurring in cirrus clouds
B)decreasing density with height in the atmosphere
C)warm air moves over cooler water surfaces
D)images are displaced upward
A)diffraction occurring in cirrus clouds
B)decreasing density with height in the atmosphere
C)warm air moves over cooler water surfaces
D)images are displaced upward

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
How many degrees of arc does a primary rainbow extend?
A)30 degrees
B)45 degrees
C)85 degrees
D)110 degrees
A)30 degrees
B)45 degrees
C)85 degrees
D)110 degrees

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The brightest and most common rainbows are
A)primary rainbows.
B)secondary rainbows.
C)moonbows.
D)glories.
A)primary rainbows.
B)secondary rainbows.
C)moonbows.
D)glories.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Characterize the conditions of the atmosphere that are favorable for the formation of an inferior mirage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which of the following is NOT associated with an inferior mirage?
A)steep temperature differences near the surface
B)the "puddle" of water on the road
C)increasing density with height in the atmosphere
D)reflection and refraction of raindrops
A)steep temperature differences near the surface
B)the "puddle" of water on the road
C)increasing density with height in the atmosphere
D)reflection and refraction of raindrops

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Sundogs form when platelike ice crystals
A)tumble while falling.
B)orient themselves vertically.
C)orient themselves horizontally.
D)melt while falling.
A)tumble while falling.
B)orient themselves vertically.
C)orient themselves horizontally.
D)melt while falling.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Describe the atmospheric conditions under which a superior mirage would form.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
________ are formed by the interaction of light with ice crystals.
A)Primary rainbows
B)Secondary rainbows
C)Haloes
D)Glories
A)Primary rainbows
B)Secondary rainbows
C)Haloes
D)Glories

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Explain the presence of red and orange at sunrise and sunset.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
What types of clouds help produce halo when the sun shines through them?
A)cumulonimbus
B)cirrostratus
C)altocumulus
D)stratus
A)cumulonimbus
B)cirrostratus
C)altocumulus
D)stratus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
A secondary rainbow requires
A)a single reflection within a raindrop.
B)two reflections within a raindrop.
C)three reflections within a raindrop.
D)no reflection within a raindrop.
A)a single reflection within a raindrop.
B)two reflections within a raindrop.
C)three reflections within a raindrop.
D)no reflection within a raindrop.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
If the density of the atmosphere decreases with height,than a distant building would appear ________ than it really is.
A)taller
B)shorter
C)wider
D)thinner
A)taller
B)shorter
C)wider
D)thinner

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The figure depicts the formation of a 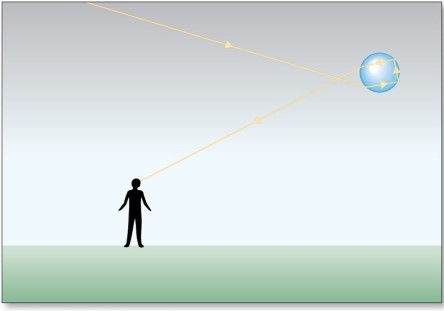
A)primary rainbow.
B)secondary rainbow.
C)green flash.
D)glories.

A)primary rainbow.
B)secondary rainbow.
C)green flash.
D)glories.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The ________ is a circular illumination of the sky immediately surrounding the Moon,or in rarer instances,the Sun.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
What is a sundog and how is it formed?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Halos are associated with
A)stratus clouds.
B)thunderstorms.
C)cumulus clouds.
D)cirrostratus clouds.
A)stratus clouds.
B)thunderstorms.
C)cumulus clouds.
D)cirrostratus clouds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Platelike crystals between a low Sun and an observer can also ________ sunlight off their tops and bottoms to produce ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Are halos frequently associated with stratus clouds? Explain your answer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Explain how a secondary rainbow is formed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Sun pillars form when ________-oriented platelike ice crystals ________ light. 
A)vertically; reflect
B)vertically; refract
C)horizontally; reflect
D)horizontally; refract

A)vertically; reflect
B)vertically; refract
C)horizontally; reflect
D)horizontally; refract

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
A ________ requires diffraction along the edge of a cloud droplet as the sunlight exits the droplet.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The occurrence of a sundog tells you that
A)the ice crystals are columnar in shape and are horizontally-oriented as they fall.
B)the ice crystals are platelike in shape and are horizontally-oriented as they fall.
C)the ice crystals are columnar in shape and are tumbling while they fall.
D)the ice crystals are platelike in shape and are tumbling while they fall.
A)the ice crystals are columnar in shape and are horizontally-oriented as they fall.
B)the ice crystals are platelike in shape and are horizontally-oriented as they fall.
C)the ice crystals are columnar in shape and are tumbling while they fall.
D)the ice crystals are platelike in shape and are tumbling while they fall.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Which of the following are necessary for rainbows to appear?
A)rain falling at some distance away
B)clear sky above the viewer
C)clear sky behind the viewer
D)all of these
A)rain falling at some distance away
B)clear sky above the viewer
C)clear sky behind the viewer
D)all of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The bending of light as it passes around water droplets is known as ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
What is a sun pillar and how is it formed?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Sundogs
A)are formed by refraction caused by water droplets.
B)are formed by refraction caused by ice crystals.
C)occur only at low levels in the atmosphere.
D)occur only in latitudes close to the poles.
A)are formed by refraction caused by water droplets.
B)are formed by refraction caused by ice crystals.
C)occur only at low levels in the atmosphere.
D)occur only in latitudes close to the poles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The optical effect in the figure is 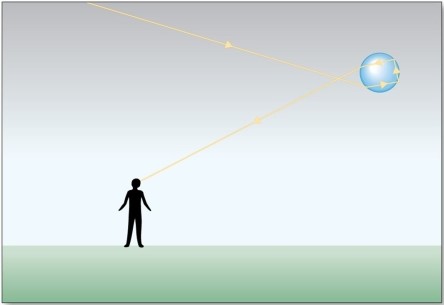
A)a halo.
B)a sundog.
C)a glory.
D)a corona.

A)a halo.
B)a sundog.
C)a glory.
D)a corona.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The occurrence of a halo tells you that
A)the ice crystals are columnar in shape and are horizontally-oriented as they fall.
B)the ice crystals are platelike in shape and are horizontally-oriented as they fall.
C)the ice crystals are columnar in shape and are tumbling while they fall.
D)the ice crystals are platelike in shape and are tumbling while they fall.
A)the ice crystals are columnar in shape and are horizontally-oriented as they fall.
B)the ice crystals are platelike in shape and are horizontally-oriented as they fall.
C)the ice crystals are columnar in shape and are tumbling while they fall.
D)the ice crystals are platelike in shape and are tumbling while they fall.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The optical effect in the figure is 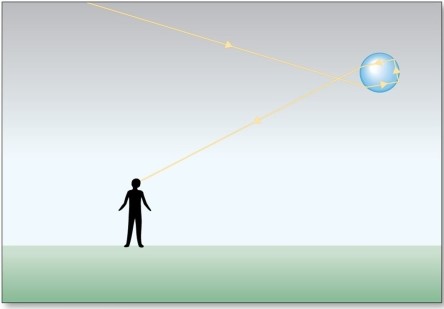
A)a halo.
B)a sundog.
C)a glory.
D)a corona.

A)a halo.
B)a sundog.
C)a glory.
D)a corona.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The optical effect in the figure is 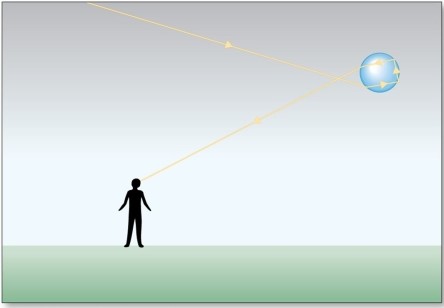
A)a halo.
B)a sundog.
C)a glory.
D)a green flash.

A)a halo.
B)a sundog.
C)a glory.
D)a green flash.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Halos exhibit radii of refraction of ________ degrees and ________ degrees.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The brightest and most common rainbows are ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Can falling ice crystals produce a rainbow? Explain your answer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Explain how a primary rainbow is formed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Which of the colors of the primary rainbow is refracted at the greatest angle? Explain your answer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



