Deck 13: The Brain and Cranial Nerves
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/261
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 13: The Brain and Cranial Nerves
1
The cerebellum and pons develop from the
A) telencephalon.
B) diencephalon.
C) mesencephalon.
D) metencephalon.
E) myelencephalon.
A) telencephalon.
B) diencephalon.
C) mesencephalon.
D) metencephalon.
E) myelencephalon.
D
2
During embryonic development, which of the following secondary brain vesicles will form the cerebrum?
A) telencephalon
B) diencephalon
C) midbrain
D) metencephalon
E) myelencephalon
A) telencephalon
B) diencephalon
C) midbrain
D) metencephalon
E) myelencephalon
A
3
The floor of the diencephalon is formed by the
A) hypothalamus.
B) thalamus.
C) brainstem.
D) midbrain.
E) myelencephalon.
A) hypothalamus.
B) thalamus.
C) brainstem.
D) midbrain.
E) myelencephalon.
A
4
Cerebrospinal fluid
A) is secreted by ependymal cells.
B) is formed by a passive process.
C) is normally produced twice as fast as it is removed.
D) has almost the same composition as blood plasma.
E) is formed by a passive process and has almost the same composition as blood plasma.
A) is secreted by ependymal cells.
B) is formed by a passive process.
C) is normally produced twice as fast as it is removed.
D) has almost the same composition as blood plasma.
E) is formed by a passive process and has almost the same composition as blood plasma.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The dural fold that projects into the longitudinal fissure between cerebral hemispheres is called the
A) dural sinus.
B) falx cerebri.
C) tentorium cerebelli.
D) falx cerebelli.
E) choroid plexus.
A) dural sinus.
B) falx cerebri.
C) tentorium cerebelli.
D) falx cerebelli.
E) choroid plexus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Autonomic centers that control blood pressure, heart rate, and digestion are located in the
A) medulla oblongata.
B) pons.
C) midbrain.
D) diencephalon.
E) cerebellum.
A) medulla oblongata.
B) pons.
C) midbrain.
D) diencephalon.
E) cerebellum.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The ventricle associated with the pons and upper medulla is the
A) first.
B) second.
C) third.
D) fourth.
E) lateral.
A) first.
B) second.
C) third.
D) fourth.
E) lateral.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The adult human brain contains almost ________ of the body's neural tissue.
A) 15 percent
B) 25 percent
C) 68 percent
D) 97 percent
E) none of the above
A) 15 percent
B) 25 percent
C) 68 percent
D) 97 percent
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The third and fourth ventricles are linked by a slender canal designated as the
A) central canal.
B) tentorium cerebelli.
C) aqueduct of midbrain.
D) interventricular foramina.
E) pontine canal.
A) central canal.
B) tentorium cerebelli.
C) aqueduct of midbrain.
D) interventricular foramina.
E) pontine canal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of these is not one of the main divisions of the adult brain?
A) cerebrum
B) diencephalon
C) prosencephalon
D) midbrain
E) pons
A) cerebrum
B) diencephalon
C) prosencephalon
D) midbrain
E) pons

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Sensory information is processed and relayed to the cerebrum by the
A) medulla oblongata.
B) pons.
C) midbrain.
D) thalamus.
E) cerebellum.
A) medulla oblongata.
B) pons.
C) midbrain.
D) thalamus.
E) cerebellum.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The tracts that connect the cerebellum to the brainstem are located in the
A) medulla oblongata.
B) pons.
C) midbrain.
D) diencephalon.
E) thalamus.
A) medulla oblongata.
B) pons.
C) midbrain.
D) diencephalon.
E) thalamus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The dural sinuses are located in the
A) paranasal cavity.
B) arachnoid.
C) pia mater.
D) dural folds.
E) tentorium cerebelli.
A) paranasal cavity.
B) arachnoid.
C) pia mater.
D) dural folds.
E) tentorium cerebelli.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Male brains are typically ________ compared to female brains.
A) larger
B) smaller
C) the same size
D) very smooth
E) more convoluted
A) larger
B) smaller
C) the same size
D) very smooth
E) more convoluted

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following lies between the cerebrum and the brainstem?
A) medulla oblongata
B) pons
C) midbrain
D) diencephalon
E) cerebellum
A) medulla oblongata
B) pons
C) midbrain
D) diencephalon
E) cerebellum

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The cells that cover the outer surfaces of CNS capillaries cells are the
A) blastocytes.
B) astrocytes.
C) monocytes.
D) leukocytes.
E) lymphocytes.
A) blastocytes.
B) astrocytes.
C) monocytes.
D) leukocytes.
E) lymphocytes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
What structure is covered by many blood vessels and adheres tightly to the surface of the brain?
A) pia mater
B) arachnoid
C) dura mater
D) cranial plexus
E) choroid plexus
A) pia mater
B) arachnoid
C) dura mater
D) cranial plexus
E) choroid plexus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The thin partition that separates the first and second ventricles is the
A) falx cerebri.
B) septum pellucidum.
C) septum insula.
D) interventricular foramina.
E) cerebral aqueduct.
A) falx cerebri.
B) septum pellucidum.
C) septum insula.
D) interventricular foramina.
E) cerebral aqueduct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
What contains a spiderweb-like network of cells and fibers through which cerebrospinal fluid flows?
A) subdural space
B) dural sinus
C) falx cerebri
D) subarachnoid space
E) pia mater
A) subdural space
B) dural sinus
C) falx cerebri
D) subarachnoid space
E) pia mater

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Each lateral ventricle communicates with the third ventricle through a(n)
A) aqueduct of Sylvius.
B) cerebral aqueduct.
C) aqueduct of midbrain.
D) interventricular foramen.
E) medulla oblongata.
A) aqueduct of Sylvius.
B) cerebral aqueduct.
C) aqueduct of midbrain.
D) interventricular foramen.
E) medulla oblongata.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
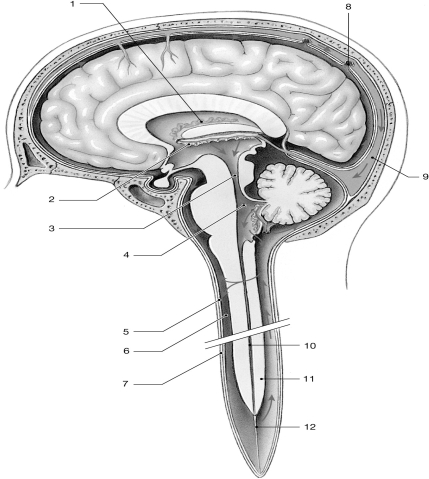
Figure 13-1 The Circulation of Cerebrospinal Fluid
Use Figure 13-1 to answer the following questions:
Identify the structure labeled "7."
A) dura mater
B) lateral ventricle
C) fourth ventricle
D) subarachnoid space
E) filum terminale

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Cerebrospinal fluid enters the subarachnoid space through the
A) interventricular foramina.
B) aqueduct of Sylvius.
C) dural sinus.
D) lateral and median apertures.
E) falx cerebri.
A) interventricular foramina.
B) aqueduct of Sylvius.
C) dural sinus.
D) lateral and median apertures.
E) falx cerebri.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The choroid plexuses produces CSF at a rate of about
A) 500 mL/day.
B) 250 mL/day.
C) 50 mL/day.
D) 1000 mL/day.
E) 150 mL/day.
A) 500 mL/day.
B) 250 mL/day.
C) 50 mL/day.
D) 1000 mL/day.
E) 150 mL/day.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The neural tissue is isolated from the general circulation by the ________.
A) dura mater
B) choroid plexuses
C) arachnoid granulations
D) meninges
E) blood-brain barrier
A) dura mater
B) choroid plexuses
C) arachnoid granulations
D) meninges
E) blood-brain barrier

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which of these dural folds is mismatched with its location?
A) falx cerebri; transverse fissure
B) tentorium cerebelli; between cerebral hemispheres and cerebellum
C) falx cerebelli; between cerebellar hemispheres
D) all are mismatched
E) none are mismatched
A) falx cerebri; transverse fissure
B) tentorium cerebelli; between cerebral hemispheres and cerebellum
C) falx cerebelli; between cerebellar hemispheres
D) all are mismatched
E) none are mismatched

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Cerebrospinal fluid enters the blood circulation at the
A) jugular veins.
B) dural drain.
C) superior sagittal sinus.
D) tentorium cerebelli.
E) frontal sinus.
A) jugular veins.
B) dural drain.
C) superior sagittal sinus.
D) tentorium cerebelli.
E) frontal sinus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which of the following is not a function of cerebrospinal fluid?
A) provides cushioning for delicate neural tissues
B) provides buoyant support for the brain
C) acts as a transport medium for nutrients
D) provides ATP for impulse transmission
E) acts as a transport medium for waste products
A) provides cushioning for delicate neural tissues
B) provides buoyant support for the brain
C) acts as a transport medium for nutrients
D) provides ATP for impulse transmission
E) acts as a transport medium for waste products

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The cardiovascular reflexes are based in the
A) cerebrum.
B) midbrain.
C) cerebellum.
D) medulla oblongata.
E) spinal cord.
A) cerebrum.
B) midbrain.
C) cerebellum.
D) medulla oblongata.
E) spinal cord.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Absorption at the arachnoid granulations returns CSF to the
A) third ventricle.
B) arterial circulation.
C) venous circulation.
D) fourth ventricle.
E) central canal.
A) third ventricle.
B) arterial circulation.
C) venous circulation.
D) fourth ventricle.
E) central canal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30

Figure 13-1 The Circulation of Cerebrospinal Fluid
Use Figure 13-1 to answer the following questions:
Identify the structure labeled "10."
A) arbor vitae
B) central canal
C) corpus callosum
D) pons
E) diencephalon

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31

Figure 13-1 The Circulation of Cerebrospinal Fluid
Use Figure 13-1 to answer the following questions:
Identify the structure labeled "8."
A) pia mater
B) dura mater
C) corpus callosum
D) ventricles
E) arachnoid granulation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The layer of the meninges that closely follows every gyrus and sulcus is the
A) pia mater.
B) dura mater.
C) arachnoid membrane.
D) neural cortex.
E) subarachnoid mater.
A) pia mater.
B) dura mater.
C) arachnoid membrane.
D) neural cortex.
E) subarachnoid mater.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The respiratory rhythmicity center is located in
A) the pons.
B) the cerebrum.
C) the medulla oblongata.
D) the cerebellum.
E) all of the above
A) the pons.
B) the cerebrum.
C) the medulla oblongata.
D) the cerebellum.
E) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34

Figure 13-1 The Circulation of Cerebrospinal Fluid
Use Figure 13-1 to answer the following questions:
What is produced by the structure labeled "2"?
A) cerebrospinal fluid
B) neurotransmitters
C) white matter
D) hormones
E) blood

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The pons contains
A) sensory and motor nuclei for four cranial nerves.
B) nuclei concerned with the control of respiration.
C) tracts that link the cerebellum with the brainstem.
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
A) sensory and motor nuclei for four cranial nerves.
B) nuclei concerned with the control of respiration.
C) tracts that link the cerebellum with the brainstem.
D) all of the above
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The nucleus gracilis and nucleus cuneatus
A) are located in the medulla oblongata.
B) relay somatic sensory information to the thalamus.
C) pass motor information to the cerebellum.
D) are located in the medulla oblongata and relay somatic sensory information to the thalamus.
E) none of the above
A) are located in the medulla oblongata.
B) relay somatic sensory information to the thalamus.
C) pass motor information to the cerebellum.
D) are located in the medulla oblongata and relay somatic sensory information to the thalamus.
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
As CSF circulates, ________ between it and the interstitial fluid of the CNS is unrestricted between and across the ependyma.
A) osmosis
B) perfusion
C) diffusion
D) convection
E) conduction
A) osmosis
B) perfusion
C) diffusion
D) convection
E) conduction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38

Figure 13-1 The Circulation of Cerebrospinal Fluid
Use Figure 13-1 to answer the following questions:
Identify the structure labeled "3."
A) arbor vitae
B) corpora quadrigemina
C) aqueduct of midbrain
D) pons
E) diencephalon

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Specialized ________ cells form the secretory component of the choroid plexus.
A) epididymal
B) ependymal
C) appended
D) epididymal and ependymal
E) ependymal and appended
A) epididymal
B) ependymal
C) appended
D) epididymal and ependymal
E) ependymal and appended

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following help to protect the brain?
A) the blood-brain barrier
B) the bones of the skull
C) the cranial meninges
D) the CSF
E) all of the above
A) the blood-brain barrier
B) the bones of the skull
C) the cranial meninges
D) the CSF
E) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Which of the following is a property of the mamillary bodies?
A) control reflex eating movements
B) responsible for auditory reflexes
C) located the posterior pons
D) connect the hypothalamus to the pituitary gland
E) secrete melatonin
A) control reflex eating movements
B) responsible for auditory reflexes
C) located the posterior pons
D) connect the hypothalamus to the pituitary gland
E) secrete melatonin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Stimulation of the reticular formation results in
A) increased consciousness.
B) sleep.
C) coma.
D) decreased cerebral function.
E) all of the above
A) increased consciousness.
B) sleep.
C) coma.
D) decreased cerebral function.
E) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
A neural cortex is found on the surface of the
A) cerebral hemispheres.
B) pons.
C) cerebellum.
D) cerebellum and cerebral hemispheres.
E) all of the above
A) cerebral hemispheres.
B) pons.
C) cerebellum.
D) cerebellum and cerebral hemispheres.
E) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The control of heart rate and blood pressure is based in the
A) cerebrum.
B) cerebellum.
C) diencephalon.
D) medulla oblongata.
E) heart.
A) cerebrum.
B) cerebellum.
C) diencephalon.
D) medulla oblongata.
E) heart.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Damage to the superior colliculi would interfere with the reflex ability to
A) express rage.
B) voluntarily move the arm.
C) react to a bright light.
D) react to loud noises.
E) maintain proper posture.
A) express rage.
B) voluntarily move the arm.
C) react to a bright light.
D) react to loud noises.
E) maintain proper posture.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The ________ provides the principal link between the nervous and endocrine systems.
A) cerebellum
B) medulla oblongata
C) cerebrum
D) pons
E) hypothalamus
A) cerebellum
B) medulla oblongata
C) cerebrum
D) pons
E) hypothalamus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The regions of the midbrain that issue subconscious motor commands that affect upper limb position and background muscle tone are the
A) tecta.
B) red nuclei.
C) cerebral peduncles.
D) superior colliculi.
E) inferior colliculi.
A) tecta.
B) red nuclei.
C) cerebral peduncles.
D) superior colliculi.
E) inferior colliculi.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The tract that links the cerebellum with the pons is the
A) superior cerebellar peduncle.
B) inferior cerebellar peduncle.
C) middle cerebellar peduncle.
D) longitudinal fibers.
E) obverse fibers.
A) superior cerebellar peduncle.
B) inferior cerebellar peduncle.
C) middle cerebellar peduncle.
D) longitudinal fibers.
E) obverse fibers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Damage to the corpora quadrigemina would interfere with
A) control of autonomic function.
B) regulation of body temperature.
C) visual and auditory reflex movements of the head and neck.
D) conscious control of skeletal muscles.
E) control of breathing.
A) control of autonomic function.
B) regulation of body temperature.
C) visual and auditory reflex movements of the head and neck.
D) conscious control of skeletal muscles.
E) control of breathing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The cerebellar hemispheres are separated by a band of cortex called the
A) flocculonodular lobe.
B) arbor vitae.
C) folia.
D) vermis.
E) pyramid.
A) flocculonodular lobe.
B) arbor vitae.
C) folia.
D) vermis.
E) pyramid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The tectum of the midbrain contains the
A) substantia nigra.
B) red nuclei.
C) superior and inferior colliculi.
D) cerebral peduncles.
E) basal ganglia.
A) substantia nigra.
B) red nuclei.
C) superior and inferior colliculi.
D) cerebral peduncles.
E) basal ganglia.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The cerebellum adjusts motor activity in response to all of the following, except
A) touch sensations.
B) visual information.
C) equilibrium-related sensations.
D) input from the motor cortex.
E) input from proprioceptors.
A) touch sensations.
B) visual information.
C) equilibrium-related sensations.
D) input from the motor cortex.
E) input from proprioceptors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Overseeing the postural muscles of the body and making rapid adjustments to maintain balance and equilibrium are functions of the
A) cerebrum.
B) midbrain.
C) cerebellum.
D) pons.
E) medulla oblongata.
A) cerebrum.
B) midbrain.
C) cerebellum.
D) pons.
E) medulla oblongata.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The reflex movement of the head toward a loud noise is directed by the midbrain. Which nuclei accomplish this?
A) substantia nigra
B) red nuclei
C) tectum
D) superior colliculi
E) inferior colliculi
A) substantia nigra
B) red nuclei
C) tectum
D) superior colliculi
E) inferior colliculi

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The presence of many large, highly-branched Purkinje cells in a sample of brain tissue indicates that it came from the
A) pons.
B) medulla.
C) cerebral cortex.
D) cerebellar cortex.
E) arbor vitae.
A) pons.
B) medulla.
C) cerebral cortex.
D) cerebellar cortex.
E) arbor vitae.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Examination of a tissue sample from the central nervous system reveals many darkly pigmented cells. This tissue probably came from the
A) nucleus gracilis.
B) nucleus cuneatus.
C) motor cortex.
D) substantia nigra.
E) red nucleus.
A) nucleus gracilis.
B) nucleus cuneatus.
C) motor cortex.
D) substantia nigra.
E) red nucleus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Nerve fiber bundles on the ventrolateral surface of the midbrain are the
A) tegmenta.
B) corpora quadrigemina.
C) cerebral peduncles.
D) superior colliculi.
E) inferior colliculi.
A) tegmenta.
B) corpora quadrigemina.
C) cerebral peduncles.
D) superior colliculi.
E) inferior colliculi.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The ________ filters and relays sensory information to the cerebral cortex.
A) cerebrum
B) thalamus
C) pons
D) medulla oblongata
E) cerebellum
A) cerebrum
B) thalamus
C) pons
D) medulla oblongata
E) cerebellum

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The white matter of the cerebellum forms the
A) flocculonodular lobe.
B) arbor vitae.
C) folia.
D) vermis.
E) pyramid.
A) flocculonodular lobe.
B) arbor vitae.
C) folia.
D) vermis.
E) pyramid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The medulla oblongata relays auditory information to the
A) substantia nigra.
B) red nuclei.
C) cerebral peduncles.
D) superior colliculi.
E) inferior colliculi.
A) substantia nigra.
B) red nuclei.
C) cerebral peduncles.
D) superior colliculi.
E) inferior colliculi.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The ventral nuclei of the thalamus
A) relay input from basal ganglia to the motor areas of the cerebral cortex.
B) relay input from cerebellum to the motor areas of the cerebral cortex.
C) relay general sensory input to the primary sensory cortex.
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
A) relay input from basal ganglia to the motor areas of the cerebral cortex.
B) relay input from cerebellum to the motor areas of the cerebral cortex.
C) relay general sensory input to the primary sensory cortex.
D) all of the above
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Terry suffers from dissociation of memories from their emotional content as the result of an automobile accident. What system of the brain is probably damaged?
A) the prefrontal lobe
B) the general interpretive area
C) the limbic system
D) the thalamus
E) the putamen
A) the prefrontal lobe
B) the general interpretive area
C) the limbic system
D) the thalamus
E) the putamen

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The ________ integrate(s) sensory information for projection to the association areas of the cerebral cortex.
A) pulvinar
B) lateral geniculate bodies
C) medial geniculate bodies
D) supraoptic nuclei
E) paraventricular nuclei
A) pulvinar
B) lateral geniculate bodies
C) medial geniculate bodies
D) supraoptic nuclei
E) paraventricular nuclei

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Which of the following is a function of the thalamus?
A) secrete cerebrospinal fluid
B) secrete melatonin
C) process sensory information and relay it to the cerebrum
D) store memories
E) regulate food intake
A) secrete cerebrospinal fluid
B) secrete melatonin
C) process sensory information and relay it to the cerebrum
D) store memories
E) regulate food intake

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Which of the following is not a property of the limbic system?
A) contains cerebral and diencephalic components
B) functions in maintaining homeostasis in cold weather
C) located between the border of the cerebrum and diencephalon
D) links conscious functions of the cerebral cortex with unconscious functions of the brainstem
E) functions in emotions, learning, and memory
A) contains cerebral and diencephalic components
B) functions in maintaining homeostasis in cold weather
C) located between the border of the cerebrum and diencephalon
D) links conscious functions of the cerebral cortex with unconscious functions of the brainstem
E) functions in emotions, learning, and memory

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The anterior nuclei of the thalamus
A) are part of the limbic system.
B) secrete pituitary hormones.
C) secrete melatonin.
D) receive axon collaterals from the optic nerve.
E) all of the above
A) are part of the limbic system.
B) secrete pituitary hormones.
C) secrete melatonin.
D) receive axon collaterals from the optic nerve.
E) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The ________ relay auditory information to the auditory cortex.
A) pulvinar
B) lateral geniculate nucleus
C) medial geniculate nucleus
D) supraoptic nuclei
E) paraventricular nuclei
A) pulvinar
B) lateral geniculate nucleus
C) medial geniculate nucleus
D) supraoptic nuclei
E) paraventricular nuclei

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Which of the following is a function of the hypothalamus?
A) coordinates day-night cycles of activity/inactivity
B) controls autonomic centers
C) regulates body temperature
D) secretes hormones
E) all of the above
A) coordinates day-night cycles of activity/inactivity
B) controls autonomic centers
C) regulates body temperature
D) secretes hormones
E) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The posterior nuclei of the thalamus include the
A) pulvinar.
B) lateral geniculate.
C) medial geniculate.
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
A) pulvinar.
B) lateral geniculate.
C) medial geniculate.
D) all of the above
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
The medial nuclei of the thalamus
A) are part of the limbic system.
B) integrates sensory information for projection to the frontal lobes.
C) produce the hormone oxytocin.
D) process visual information.
E) process olfactory information.
A) are part of the limbic system.
B) integrates sensory information for projection to the frontal lobes.
C) produce the hormone oxytocin.
D) process visual information.
E) process olfactory information.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The ________ is located at the tip of the tail of the caudate nucleus.
A) amygdaloid body
B) claustrum
C) putamen
D) globus pallidus
E) corpus striatum
A) amygdaloid body
B) claustrum
C) putamen
D) globus pallidus
E) corpus striatum

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Damage to the preoptic area of the hypothalamus leads to which problem?
A) an intense thirst
B) an uncontrolled sex drive
C) reduced ability to regulate body temperature
D) an insatiable appetite
E) production of a large volume of urine
A) an intense thirst
B) an uncontrolled sex drive
C) reduced ability to regulate body temperature
D) an insatiable appetite
E) production of a large volume of urine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
The mamillary bodies of the hypothalamus
A) regulate lactation.
B) secrete oxytocin.
C) control feeding reflexes.
D) control heart rate and blood pressure.
E) secrete antidiuretic hormone.
A) regulate lactation.
B) secrete oxytocin.
C) control feeding reflexes.
D) control heart rate and blood pressure.
E) secrete antidiuretic hormone.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The ________ receive visual input from the lateral geniculate bodies.
A) substantia nigra
B) red nuclei
C) cerebral peduncles
D) superior colliculi
E) inferior colliculi
A) substantia nigra
B) red nuclei
C) cerebral peduncles
D) superior colliculi
E) inferior colliculi

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
The ________ is important in storage and recall of new long-term memories.
A) amygdaloid body
B) cingulate gyrus
C) mamillary bodies
D) hippocampus
E) fornix
A) amygdaloid body
B) cingulate gyrus
C) mamillary bodies
D) hippocampus
E) fornix

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
A tract of white matter that connects the hippocampus with the hypothalamus is the
A) amygdaloid body.
B) cingulate gyrus.
C) mamillary bodies.
D) hippocampus.
E) fornix.
A) amygdaloid body.
B) cingulate gyrus.
C) mamillary bodies.
D) hippocampus.
E) fornix.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
The optic tracts carry visual information from the retina to the
A) pulvinar.
B) lateral geniculate nucleus.
C) medial geniculate nucleus.
D) supraoptic nuclei.
E) paraventricular nuclei.
A) pulvinar.
B) lateral geniculate nucleus.
C) medial geniculate nucleus.
D) supraoptic nuclei.
E) paraventricular nuclei.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Which of the following is not one of the basal nuclei?
A) caudate nucleus
B) globus pallidus
C) putamen
D) hippocampus
E) amygdaloid body
A) caudate nucleus
B) globus pallidus
C) putamen
D) hippocampus
E) amygdaloid body

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Joe begins to experience mood swings and disturbed thirst and hunger. Imaging studies indicate that a brain tumor is the likely cause of these disorders. In what part of the brain is the tumor most likely located?
A) prefrontal cortex
B) postcentral gyrus
C) basal nuclei
D) hypothalamus
E) reticular formation
A) prefrontal cortex
B) postcentral gyrus
C) basal nuclei
D) hypothalamus
E) reticular formation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Which of the following is not a component of the limbic system?
A) amygdaloid body
B) cingulate gyrus
C) globus pallidus
D) hippocampus
E) fornix
A) amygdaloid body
B) cingulate gyrus
C) globus pallidus
D) hippocampus
E) fornix

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



