Deck 18: Financing Trade and the Trade Deficit
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/77
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 18: Financing Trade and the Trade Deficit
1
The United States has the highest ratio of indebtedness to GDP in the world.
False
2
In a fixed exchange rate system, supply and demand determine exchange rates, much like in a flexible exchange rate system.
False
3
Under a flexible exchange rate regime, exchange rates are determined by the forces of demand and supply.
True
4
The U.S. tends to have relatively more capital flowing into the country than out of the country.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The greater a country's ratio of international indebtedness to GDP, the greater the likelihood that the country will have problems repaying this debt.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Suppose the current exchange rate is 3 German Marks for 1 U.S. dollar. If the exchange rate falls, the dollar will have appreciated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
When the U.S. imports goods from Brazil, this is entered as a debit in the current account.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
If U.S. citizens purchase foreign stock, this is a debit in the current account.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
When U.S. companies establish foreign subsidiaries, this is included in the capital account.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Under a fixed exchange rate system, if a exchange rates are allowed to fall, we say the currency has been devalued.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Most of the current account deficit is financed by the intervention of the Federal Reserve in international transactions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The balance of payments is only occasionally out of balance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
If an exchange rate is above the equilibrium rate (and exchange rates are flexible) the exchange rate will tend to fall.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
If the yen depreciates, it now takes fewer yen to purchase a dollar.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
In recent years, the United States has run a deficit in its current account.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The largest debtor nations are less-developed countries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The increase in foreign ownership in the U.S. means that foreigners will receive more income and interest from the U.S. and U.S. citizens will receive less.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A current account deficit is usually the result of exports being greater than imports.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The current account contains imports, exports, and net unilateral transfers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
If GDP in the U.S. rises, the U.S. will buy more from abroad.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which of the following might affect flexible exchange rates between two countries?
A) Inflation in one country relative to the other.
B) Interest rates in one country relative to the other.
C) GDP growth in one country relative to the other.
D) All of the above.
A) Inflation in one country relative to the other.
B) Interest rates in one country relative to the other.
C) GDP growth in one country relative to the other.
D) All of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of the following is not a reason why the U.S. continues to be a large debtor nation?
A) The U.S. is the largest market in the world in which to invest.
B) The U.S. is a safe place to invest.
C) Creditors believe the U.S. is capable of servicing this debt.
D) The U.S. has the highest ratio of indebtedness to GDP in the world.
A) The U.S. is the largest market in the world in which to invest.
B) The U.S. is a safe place to invest.
C) Creditors believe the U.S. is capable of servicing this debt.
D) The U.S. has the highest ratio of indebtedness to GDP in the world.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
When is the balance of payments out of balance?
A) Whenever imports exceed exports.
B) Whenever exports exceed imports.
C) If the balance in the capital account exceeds the balance in the current account.
D) Never.
A) Whenever imports exceed exports.
B) Whenever exports exceed imports.
C) If the balance in the capital account exceeds the balance in the current account.
D) Never.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following would not be included in the current account?
A) net unilateral transfers
B) purchases of foreign currencies
C) exports
D) imports
A) net unilateral transfers
B) purchases of foreign currencies
C) exports
D) imports

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The number of units of one currency exchangeable for one unit of another currency is called:
A) currency revaluation.
B) a quota.
C) an exchange rate.
D) a balance of payment.
A) currency revaluation.
B) a quota.
C) an exchange rate.
D) a balance of payment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The balance of payments refers to:
A) the value of country's exports less the value of its imports during a given time period.
B) a summary of all economic transactions between one country and all other countries during a given time period.
C) the capital inflows into a country less the capital outflows during a given time period.
D) a country's gross domestic product less the value of its imports during a given time period.
A) the value of country's exports less the value of its imports during a given time period.
B) a summary of all economic transactions between one country and all other countries during a given time period.
C) the capital inflows into a country less the capital outflows during a given time period.
D) a country's gross domestic product less the value of its imports during a given time period.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
In recent years, the U.S. has run a deficit in which of the following?
A) balance of payments
B) capital account
C) current account
D) b and c only
A) balance of payments
B) capital account
C) current account
D) b and c only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
A summary of all economic transactions between the residents of one country and those of all other countries during a given time period is called:
A) the balance of payments
B) the current account
C) a net unilateral transfer
D) the capital account
A) the balance of payments
B) the current account
C) a net unilateral transfer
D) the capital account

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
In the United States, much of the deficit balance in the current account has been financed by:
A) selling U.S. Treasury securities.
B) foreign investment in the United States.
C) selling U.S. savings bonds.
D) increasing the size of the federal deficit.
A) selling U.S. Treasury securities.
B) foreign investment in the United States.
C) selling U.S. savings bonds.
D) increasing the size of the federal deficit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The depreciation of the Mexican peso had which of the following effects?
A) Mexican goods became cheaper to Americans.
B) American goods became more expensive to Mexicans.
C) The U.S. went from having a trade surplus with Mexico to having a trade deficit.
D) All of the above.
A) Mexican goods became cheaper to Americans.
B) American goods became more expensive to Mexicans.
C) The U.S. went from having a trade surplus with Mexico to having a trade deficit.
D) All of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Under a flexible exchange rate system, if a country's exchange rate increases, then the currency has:
A) devalued.
B) revalued.
C) depreciated.
D) appreciated.
A) devalued.
B) revalued.
C) depreciated.
D) appreciated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which of the following is not an argument in favor of flexible exchange rates?
A) Flexible exchange rates result in greater economic stability.
B) Flexible exchange rates provide a discipline for central banks in their practice of monetary policy.
C) Flexible rates allow central banks the freedom to pursue the whatever policies are necessary for full employment.
D) Destabilizing speculation is less likely to occur when exchange rates adjust continuously.
A) Flexible exchange rates result in greater economic stability.
B) Flexible exchange rates provide a discipline for central banks in their practice of monetary policy.
C) Flexible rates allow central banks the freedom to pursue the whatever policies are necessary for full employment.
D) Destabilizing speculation is less likely to occur when exchange rates adjust continuously.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Financing a deficit balance in the current account by increasing foreign investment:
A) increases the income of domestic citizens.
B) increases the interest payments domestic citizens receive from foreign investors.
C) causes more domestic assets to be owned by foreigners.
D) decreases the size of the current account deficit.
A) increases the income of domestic citizens.
B) increases the interest payments domestic citizens receive from foreign investors.
C) causes more domestic assets to be owned by foreigners.
D) decreases the size of the current account deficit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
An exchange rate is:
A) the price consumers pay for goods in the market place.
B) the rate at which consumers are willing to exchange one good for another.
C) the rate at which producers can transform inputs into outputs.
D) the rate at which the units of one currency can be exchanged for units of another.
A) the price consumers pay for goods in the market place.
B) the rate at which consumers are willing to exchange one good for another.
C) the rate at which producers can transform inputs into outputs.
D) the rate at which the units of one currency can be exchanged for units of another.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which nation owes more to foreign creditors than any other nation in the world?
A) The United States
B) Mexico
C) Russia
D) Australia
A) The United States
B) Mexico
C) Russia
D) Australia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The ____ the ratio of international debt to GDP, the ____ the likelihood that the country will have trouble repaying the debt.
A) greater; greater
B) smaller; greater
C) greater; smaller
D) None of the above are true.
A) greater; greater
B) smaller; greater
C) greater; smaller
D) None of the above are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
If a country that maintains fixed exchange rates decides to let their exchange rate fall, the currency has:
A) devalued
B) revalued
C) appreciated
D) depreciated
A) devalued
B) revalued
C) appreciated
D) depreciated

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Under a system of flexible exchange rates, rates are determined by:
A) the forces of demand and supply.
B) the central bank in the economy.
C) an international monetary board.
D) the federal government.
A) the forces of demand and supply.
B) the central bank in the economy.
C) an international monetary board.
D) the federal government.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Why did the European Economic and Monetary Union (EMU) introduce the euro in 1999?
A) To lower the transaction costs of trade between member nations.
B) To eliminate member nations' ability to use monetary policy.
C) To reduce unemployment in European labor markets.
D) All of the above were factors.
A) To lower the transaction costs of trade between member nations.
B) To eliminate member nations' ability to use monetary policy.
C) To reduce unemployment in European labor markets.
D) All of the above were factors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following would not be included in the capital account?
A) purchases of U.S. securities by foreigners
B) establishment of foreign subsidiaries by U.S. companies
C) purchases of foreign securities
D) net unilateral transfers
A) purchases of U.S. securities by foreigners
B) establishment of foreign subsidiaries by U.S. companies
C) purchases of foreign securities
D) net unilateral transfers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Suppose the current exchange rate of Euro per dollars is 0.75 while the equilibrium exchange rate is 0.70. This implies that:
A) the quantity of dollars demanded by Italy exceeds the quantity of dollars supplied.
B) the quantity of dollars supplied exceeds the quantity of dollars demanded by Italy.
C) the exchange rate will tend to increase.
D) the exchange rate is in equilibrium.
A) the quantity of dollars demanded by Italy exceeds the quantity of dollars supplied.
B) the quantity of dollars supplied exceeds the quantity of dollars demanded by Italy.
C) the exchange rate will tend to increase.
D) the exchange rate is in equilibrium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
If a country has a positive balance in its current account we know that:
A) the balance in its capital account must be negative.
B) the balance in its capital account must be positive.
C) the balance in its capital account must be zero.
D) the balance in its capital account cannot be determined without further information.
A) the balance in its capital account must be negative.
B) the balance in its capital account must be positive.
C) the balance in its capital account must be zero.
D) the balance in its capital account cannot be determined without further information.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Use the following diagram to answer the following questions.
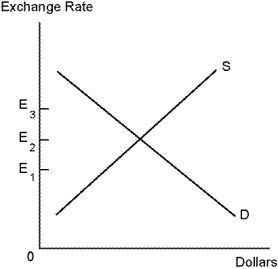
Refer to Exchange Rate. Suppose the exchange rate is currently E₃. In this case, there is:
A) an excess demand for dollars and the exchange rate will fall.
B) an excess demand for dollars and the exchange rate will increase.
C) an excess supply of dollars and the exchange rate will fall.
D) an excess supply of dollars and the exchange rate will increase.

Refer to Exchange Rate. Suppose the exchange rate is currently E₃. In this case, there is:
A) an excess demand for dollars and the exchange rate will fall.
B) an excess demand for dollars and the exchange rate will increase.
C) an excess supply of dollars and the exchange rate will fall.
D) an excess supply of dollars and the exchange rate will increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Use the following diagram to answer the following questions.
Suppose that Toon Land enters an expansionary period and GDP rises by 4.8 percent. If we were examining Toon dollars per U.S. dollar, the increase in GDP would result in:
A) an appreciation of the U.S. dollar.
B) a depreciation of the U.S. dollar.
C) no change in exchange rates.
D) a decrease in Toon Land's imports from the United States.

Suppose that Toon Land enters an expansionary period and GDP rises by 4.8 percent. If we were examining Toon dollars per U.S. dollar, the increase in GDP would result in:
A) an appreciation of the U.S. dollar.
B) a depreciation of the U.S. dollar.
C) no change in exchange rates.
D) a decrease in Toon Land's imports from the United States.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Use the following diagram to answer the following questions.

Refer to Exchange Rate. If the exchange rate is currently E₁, the dollar will:
A) appreciate as the market moves towards equilibrium.
B) depreciate as the market moves towards equilibrium.
C) be less valuable as the market moves towards equilibrium.
D) will remain unchanged in value as the market moves towards equilibrium.

Refer to Exchange Rate. If the exchange rate is currently E₁, the dollar will:
A) appreciate as the market moves towards equilibrium.
B) depreciate as the market moves towards equilibrium.
C) be less valuable as the market moves towards equilibrium.
D) will remain unchanged in value as the market moves towards equilibrium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Use the following diagram to answer the following questions.

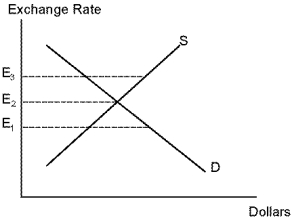
Refer to Euros. Suppose the exchange rate of Euros per dollar is E₃. There will be a tendency for:
A) the price of imports to fall.
B) the price of exports to rise.
C) the price of imports to rise.
D) the relative price of imports and exports to be unchanged.

Refer to Euros. Suppose the exchange rate of Euros per dollar is E₃. There will be a tendency for:
A) the price of imports to fall.
B) the price of exports to rise.
C) the price of imports to rise.
D) the relative price of imports and exports to be unchanged.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
To prevent a ____ of its currency, a country may impose controls to prevent capital ____.
A) devaluation; inflow
B) appreciation; outflow
C) depreciation; outflow
D) none of the above
A) devaluation; inflow
B) appreciation; outflow
C) depreciation; outflow
D) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Suppose the current exchange rate between the United States and Japan is 3.9 yen per dollar while the equilibrium exchange rate is 3.3 yen per dollar. It is likely that:
A) the quantity of imports into the United States will decrease because of an appreciation of the dollar.
B) the quantity of imports into the United States will increase because of a depreciation of the dollar.
C) the quantity of imports into the United States will increase because of an appreciation of the dollar.
D) the quantity of imports into the United States will decrease because of a depreciation of the dollar.
A) the quantity of imports into the United States will decrease because of an appreciation of the dollar.
B) the quantity of imports into the United States will increase because of a depreciation of the dollar.
C) the quantity of imports into the United States will increase because of an appreciation of the dollar.
D) the quantity of imports into the United States will decrease because of a depreciation of the dollar.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Suppose a country has $500 million in exports, $600 million in imports, and $50 million in net unilateral transfers. The balance in its capital account must be:
A) -$100 million.
B) +$100 million.
C) -$50 million.
D) +$50 million.
A) -$100 million.
B) +$100 million.
C) -$50 million.
D) +$50 million.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Suppose a country has a balance of -$25 billion in its current account. It must have what balance in its capital account?
A) -$25 billion.
B) $25 billion.
C) $10 billion.
D) $0.
A) -$25 billion.
B) $25 billion.
C) $10 billion.
D) $0.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Use the following diagram to answer the following questions.

Refer to Exchange Rate. Suppose the exchange rate is currently E₁. In this case, there is:
A) an excess demand for dollars and the exchange rate will fall.
B) an excess demand for dollars and the exchange rate will increase.
C) an excess supply of dollars and the exchange rate will fall.
D) an excess supply of dollars and the exchange rate will increase.

Refer to Exchange Rate. Suppose the exchange rate is currently E₁. In this case, there is:
A) an excess demand for dollars and the exchange rate will fall.
B) an excess demand for dollars and the exchange rate will increase.
C) an excess supply of dollars and the exchange rate will fall.
D) an excess supply of dollars and the exchange rate will increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Suppose the current exchange rate between the United States and Germany is 3.7 Euro per dollar while the equilibrium exchange rate is 4 Euro per dollar. It is likely that:
A) the quantity of imports into the United States will decrease because of an appreciation of the dollar.
B) the quantity of imports into the United States will increase because of a depreciation of the dollar.
C) the quantity of imports into the United States will increase because of an appreciation of the dollar.
D) the quantity of imports into the United States will decrease because of a depreciation of the dollar.
A) the quantity of imports into the United States will decrease because of an appreciation of the dollar.
B) the quantity of imports into the United States will increase because of a depreciation of the dollar.
C) the quantity of imports into the United States will increase because of an appreciation of the dollar.
D) the quantity of imports into the United States will decrease because of a depreciation of the dollar.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Suppose that in 1995 Narnia exported $350 thousand worth of goods and services, imported $275 thousand worth of goods and services, had net unilateral transfers of -$15 thousand, and had a net capital outflow of $30 thousand. The balance on its current account would be:
A) $75 thousand.
B) $60 thousand.
C) -$60 thousand.
D) -$75 thousand.
A) $75 thousand.
B) $60 thousand.
C) -$60 thousand.
D) -$75 thousand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Use the following diagram to answer the following questions.

Refer to Exchange Rate. Given the demand for and supply of dollars, the equilibrium exchange rate is:
A) E1.
B) E2.
C) E3.
D) between E1 and E2.

Refer to Exchange Rate. Given the demand for and supply of dollars, the equilibrium exchange rate is:
A) E1.
B) E2.
C) E3.
D) between E1 and E2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Use the following diagram to answer the following questions.
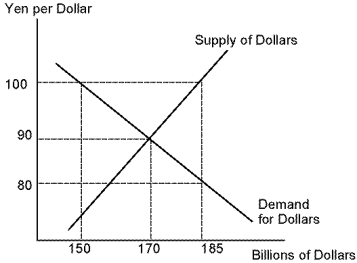
Refer to Yen. Assume that exchange rates have been fixed at 90 yen per dollar, what should the United States do if it is determined that the current exchange rate is already 90 yen per dollar?
A) The Federal Reserve should sell dollars as a preventative action.
B) The Federal Reserve should buy dollars as a preventative action.
C) No intervention is necessary to maintain the exchange rate.
D) The Federal Reserve should buy yen as a preventative measure.

Refer to Yen. Assume that exchange rates have been fixed at 90 yen per dollar, what should the United States do if it is determined that the current exchange rate is already 90 yen per dollar?
A) The Federal Reserve should sell dollars as a preventative action.
B) The Federal Reserve should buy dollars as a preventative action.
C) No intervention is necessary to maintain the exchange rate.
D) The Federal Reserve should buy yen as a preventative measure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Use the following diagram to answer the following questions.

Refer to Euros. Suppose the exchange rate Euros per dollar is currently E₁. There will be a tendency for:
A) the price of imports to rise.
B) the price of exports to rise.
C) the price of exports to fall.
D) the relative price of imports and exports to be unchanged.

Refer to Euros. Suppose the exchange rate Euros per dollar is currently E₁. There will be a tendency for:
A) the price of imports to rise.
B) the price of exports to rise.
C) the price of exports to fall.
D) the relative price of imports and exports to be unchanged.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Which events triggered the Asian financial crisis?
A) The IMF intervened in the Malaysian economy.
B) Thailand's largest finance company failed.
C) Capital flowed out of the Asian countries and currencies depreciated.
D) Both b and c
A) The IMF intervened in the Malaysian economy.
B) Thailand's largest finance company failed.
C) Capital flowed out of the Asian countries and currencies depreciated.
D) Both b and c

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Suppose the current exchange rate of pounds per dollars is 1.5 while the equilibrium exchange rate of pounds per dollars is 2. This implies that:
A) the quantity of dollars demanded by Great Britain exceeds the quantity of dollars supplied.
B) the quantity of dollars supplied exceeds the quantity of dollars demanded by Great Britain.
C) the exchange rate will tend to decrease.
D) the exchange rate is in equilibrium.
A) the quantity of dollars demanded by Great Britain exceeds the quantity of dollars supplied.
B) the quantity of dollars supplied exceeds the quantity of dollars demanded by Great Britain.
C) the exchange rate will tend to decrease.
D) the exchange rate is in equilibrium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The traditional view of capital flows says that:
A) capital should be free to flow from countries offering low prospective returns to those offering high prospective returns.
B) capital flows should be restricted in order to reduce short-term volatility.
C) capital should be free to flow only from greater developed countries to lesser developed countries.
D) capital controls allow time for countries to initiate new policies and undertake fundamental reforms in their banking systems and financial markets.
A) capital should be free to flow from countries offering low prospective returns to those offering high prospective returns.
B) capital flows should be restricted in order to reduce short-term volatility.
C) capital should be free to flow only from greater developed countries to lesser developed countries.
D) capital controls allow time for countries to initiate new policies and undertake fundamental reforms in their banking systems and financial markets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Use the following diagram to answer the following questions.

Refer to Exchange Rate. If the exchange rate is currently E₃, the dollar will:
A) appreciate as the market moves towards equilibrium.
B) depreciate as the market moves towards equilibrium.
C) be more valuable as the market moves towards equilibrium.
D) will remain unchanged in value as the market moves towards equilibrium.

Refer to Exchange Rate. If the exchange rate is currently E₃, the dollar will:
A) appreciate as the market moves towards equilibrium.
B) depreciate as the market moves towards equilibrium.
C) be more valuable as the market moves towards equilibrium.
D) will remain unchanged in value as the market moves towards equilibrium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Suppose the exchange rate is $0.01 per ¥ 1. A SONY television selling for ¥ 30,000 in Tokyo would be sell for ____ in New York.
A) $100.
B) $300.
C) $350.
D) $400.
A) $100.
B) $300.
C) $350.
D) $400.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
A decrease in the interest rate in the United States relative to the rest of the world would:
A) increase foreign investment in the United States.
B) decrease foreign investment in the United States.
C) decrease U.S. investment in other countries.
D) increase the demand for U.S. dollars.
A) increase foreign investment in the United States.
B) decrease foreign investment in the United States.
C) decrease U.S. investment in other countries.
D) increase the demand for U.S. dollars.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Suppose the exchange rate is $1 per ¥ 100. A SONY television selling for ¥ 30,000 in Tokyo would be sell for ____ in New York.
A) $100.
B) $300.
C) $350.
D) $400.
A) $100.
B) $300.
C) $350.
D) $400.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Suppose the exchange rate is $1 per ¥ 100. An IBM computer selling for $1500 in New York would be sell for ____ in Tokyo.
A) ¥100,000.
B) ¥150.
C) ¥150,000.
D) ¥1,500.
A) ¥100,000.
B) ¥150.
C) ¥150,000.
D) ¥1,500.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
"Changes in exchange rates alter the international price of goods and service." Explain this statement.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
If 1 dollar can be traded for 5 francs, how many dollars will 1 franc buy?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
If the U.S. Federal Reserve were to purchase yen using dollars, what would be the result?
A) The dollar would not change in value against the yen.
B) The dollar would appreciate against the yen.
C) The supply of dollars to Japan would decrease.
D) The supply of dollars to Japan would increase.
A) The dollar would not change in value against the yen.
B) The dollar would appreciate against the yen.
C) The supply of dollars to Japan would decrease.
D) The supply of dollars to Japan would increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Evaluate the following statement, "Only countries with fixed exchange rates will be interested in restricting capital flows."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Suppose the U.S. balance of payments in 2000 was equal to the following.

a.What is the balance on the current account?
b.What is the balance on the capital account?
c.What is the balance of payments?

a.What is the balance on the current account?
b.What is the balance on the capital account?
c.What is the balance of payments?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Use the following diagram to answer the following questions.

Refer to Yen. If the United States fixes the exchange rate at 100, what action will be necessary to maintain this rate?
A) The Federal Reserve may use any foreign currency holdings to purchase dollars.
B) The Federal Reserve may purchase any foreign currency using its holdings of dollars.
C) The Federal Reserve must use yen to buy dollars.
D) The Federal Reserve must use dollars to buy yen.

Refer to Yen. If the United States fixes the exchange rate at 100, what action will be necessary to maintain this rate?
A) The Federal Reserve may use any foreign currency holdings to purchase dollars.
B) The Federal Reserve may purchase any foreign currency using its holdings of dollars.
C) The Federal Reserve must use yen to buy dollars.
D) The Federal Reserve must use dollars to buy yen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Suppose GDP in the United States increases as the economy enters an expansion. How will this change in GDP affect trade between the United States and other countries?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Evaluate the following statement, "Economists agree that a system of flexible exchange rates is the most appropriate for all countries."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Suppose the exchange rate is $0.01 per ¥ 1. An IBM computer selling for $1500 in New York would be sell for ____ in Tokyo.
A) ¥100,000.
B) ¥150,000.
C) ¥150.
D) ¥1,500.
A) ¥100,000.
B) ¥150,000.
C) ¥150.
D) ¥1,500.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Your trip to Mexico cost you 9,000 pesos. The exchange rate is 3 pesos per dollar. How much did the trip cost you in American dollars? How much would you pay in American dollars if the exchange rate was 5 pesos per dollar?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Use the following diagram to answer the following questions.
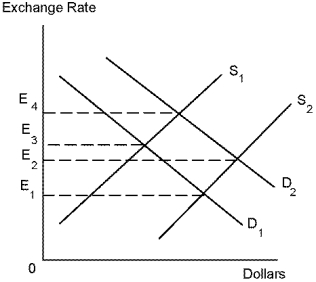
Refer to Diagram 18-1. Suppose that the demand for and supply of dollars is initially D₂ and S₂, respectively. If real GDP in the U.S. were to decrease, the effect would be to:
A) decrease the supply of dollars to S₁ and increase the exchange rate to E4.
B) decrease the demand for dollars to D₁ and decrease the exchange rate to E1.
C) decrease the supply of dollars to S₁ and increase the exchange rate to E3.
D) decrease the supply of dollars to S₁, decrease the demand for dollars to D₁, and increase the exchange rate to E3.

Refer to Diagram 18-1. Suppose that the demand for and supply of dollars is initially D₂ and S₂, respectively. If real GDP in the U.S. were to decrease, the effect would be to:
A) decrease the supply of dollars to S₁ and increase the exchange rate to E4.
B) decrease the demand for dollars to D₁ and decrease the exchange rate to E1.
C) decrease the supply of dollars to S₁ and increase the exchange rate to E3.
D) decrease the supply of dollars to S₁, decrease the demand for dollars to D₁, and increase the exchange rate to E3.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Use the following diagram to answer the following questions.

Refer to Diagram 18-1. Suppose that the demand for dollars is initially represented by D₁ and the supply of dollars is represented by S₂. If the inflation rate were to decrease, the effect would:
A) decrease the supply of dollars to S₁, thereby increasing the exchange rate to E3.
B) decrease the supply of dollars to S₁ and increase the demand for dollars to D₂, thereby increasing the exchange rate to E4.
C) increase the demand for dollars to D₂, thereby increasing the exchange rate to E2.
D) increase the supply of dollars and decrease the demand for dollars, thereby raising the exchange rate.

Refer to Diagram 18-1. Suppose that the demand for dollars is initially represented by D₁ and the supply of dollars is represented by S₂. If the inflation rate were to decrease, the effect would:
A) decrease the supply of dollars to S₁, thereby increasing the exchange rate to E3.
B) decrease the supply of dollars to S₁ and increase the demand for dollars to D₂, thereby increasing the exchange rate to E4.
C) increase the demand for dollars to D₂, thereby increasing the exchange rate to E2.
D) increase the supply of dollars and decrease the demand for dollars, thereby raising the exchange rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Use the following diagram to answer the following questions.

Refer to Yen. If the United States fixes the exchange rate at 100, there will be a(n):
A) U.S. balance of payments deficit.
B) U.S. balance of payments surplus.
C) excess demand for dollars.
D) Mismatch in trade between the U.S. and Japan.

Refer to Yen. If the United States fixes the exchange rate at 100, there will be a(n):
A) U.S. balance of payments deficit.
B) U.S. balance of payments surplus.
C) excess demand for dollars.
D) Mismatch in trade between the U.S. and Japan.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



