Deck 5: Essential Concepts of Metabolism
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/56
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 5: Essential Concepts of Metabolism
1
Chemoautotrophic bacteria obtain the energy they need from:
A)the reactions of photosynthesis
B)sunlight
C)carbon dioxide in the atmosphere
D)chemical reactions in their cytoplasm centered around the use of inorganic substances
A)the reactions of photosynthesis
B)sunlight
C)carbon dioxide in the atmosphere
D)chemical reactions in their cytoplasm centered around the use of inorganic substances
D
2
Substrate-level phosphorylation during glycolysis refers to the transfer of phosphate groups from:
A)ATP to glucose
B)1,3 diphosphoglyceric acid to ADP
C)phosphoenolpyruvic acid to ADP
D)ATP to ADP
A)ATP to glucose
B)1,3 diphosphoglyceric acid to ADP
C)phosphoenolpyruvic acid to ADP
D)ATP to ADP
B
3
Which of the following is not a carrier molecule that carries hydrogen atoms or electrons in oxidative reactions?
A)Cytochrome
B)FAD
C)Niacin
D)NAD⁺
A)Cytochrome
B)FAD
C)Niacin
D)NAD⁺
C
4
Photoautotrophs obtain energy from:
A)light and use carbon dioxide as a carbon source
B)organic molecules and use carbon dioxide as a carbon source
C)inorganic substances and use carbon dioxide as a carbon source
D)light and use organic substances as a carbon source
A)light and use carbon dioxide as a carbon source
B)organic molecules and use carbon dioxide as a carbon source
C)inorganic substances and use carbon dioxide as a carbon source
D)light and use organic substances as a carbon source

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Sulfa drugs bind to the active site of the enzyme which normally converts para-amino benzoic acid (PABA)to folic acid,preventing the production of folic acid and,eventually purine synthesis. In this case,the sulfa drug is acting as a/an:
A)allosteric inhibitor
B)competitive inhibitor
C)noncompetitive inhibitor
D)uncompetitive inhibitor
A)allosteric inhibitor
B)competitive inhibitor
C)noncompetitive inhibitor
D)uncompetitive inhibitor

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
An enzyme-substrate complex forms when substrate binds to an enzyme at the enzyme's ______ site.
A)catalytic
B)allosteric
C)operative
D)active
A)catalytic
B)allosteric
C)operative
D)active

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following statements about enzyme inhibition is true?
A)Most noncompetitive inhibitors bind to several different sites on an enzyme.
B)Enzymes become less efficient as temperatures drop because they begin to denature.
C)Noncompetitive inhibitors bind to a site other than the active site.
D)Most human enzymes have an optimum temperature below normal body temperature.
A)Most noncompetitive inhibitors bind to several different sites on an enzyme.
B)Enzymes become less efficient as temperatures drop because they begin to denature.
C)Noncompetitive inhibitors bind to a site other than the active site.
D)Most human enzymes have an optimum temperature below normal body temperature.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Competitive inhibition of enzymes occurs when the inhibitor:
A)binds to the active site of the enzyme.
B)binds to the allosteric site of the enzyme.
C)changes the shape of the enzyme.
D)is acted upon by the enzyme.
A)binds to the active site of the enzyme.
B)binds to the allosteric site of the enzyme.
C)changes the shape of the enzyme.
D)is acted upon by the enzyme.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
A holoenzyme can consist of:
A)an apoenzyme plus a cofactor
B)an apoenzyme plus a coenzyme
C)a protein and non-protein component
D)all of the above
A)an apoenzyme plus a cofactor
B)an apoenzyme plus a coenzyme
C)a protein and non-protein component
D)all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
In glycolysis,each molecule of glucose eventually produces ________ molecules of pyruvic acid.
A)one
B)two
C)three
D)four
A)one
B)two
C)three
D)four

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Organisms which get their carbon from other organisms are:
A)autotrophs
B)chemotrophs
C)phototrophs
D)heterotrophs
A)autotrophs
B)chemotrophs
C)phototrophs
D)heterotrophs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The synthesis of DNA,in which small nucleotides are joined together to make a single large molecule would be most correctly described as being a/n ________ reaction.
A)metabolic
B)anabolic
C)catabolic
D)cytobolic
A)metabolic
B)anabolic
C)catabolic
D)cytobolic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Degradation reactions where large molecules are broken down into smaller molecule is referred to as:
A)metabolism
B)catabolism
C)biosynthesis
D)anabolism
A)metabolism
B)catabolism
C)biosynthesis
D)anabolism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Animals (humans for example)are:
A)photoautotrophs
B)photheterotrophs
C)chemoautotrophs
D)chemoheterotrophs
A)photoautotrophs
B)photheterotrophs
C)chemoautotrophs
D)chemoheterotrophs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Enzymes work by:
A)lowering the energy of the reactants.
B)raising the energy of the products.
C)decreasing the activation energy of the reaction.
D)increasing the activation energy of the reaction.
A)lowering the energy of the reactants.
B)raising the energy of the products.
C)decreasing the activation energy of the reaction.
D)increasing the activation energy of the reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Oxidation is defined as the ________ while reduction is the ________ .
A)gain of electrons, loss of protons
B)loss of electrons, gain of protons
C)loss of electrons, gain of electrons
D)loss of protons, gain of protons
A)gain of electrons, loss of protons
B)loss of electrons, gain of protons
C)loss of electrons, gain of electrons
D)loss of protons, gain of protons

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
How does concentration affect enzyme-catalyzed reactions?
A)As the concentration of the product goes up the enzyme increases the rate it produces the product.
B)Concentration does not affect enzyme-catalyzed reactions because they are irreversible.
C)At chemical equilibrium, no net change in the concentration of the product or substrate occurs.
D)The quantity of enzyme available usually controls the rate of a metabolic reaction.
A)As the concentration of the product goes up the enzyme increases the rate it produces the product.
B)Concentration does not affect enzyme-catalyzed reactions because they are irreversible.
C)At chemical equilibrium, no net change in the concentration of the product or substrate occurs.
D)The quantity of enzyme available usually controls the rate of a metabolic reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Factors that affect the rate of enzyme catalyzed reactions include:
A)temperature
B)pH
C)concentration of enzyme
D)all of the above
A)temperature
B)pH
C)concentration of enzyme
D)all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which one of the following pairs is mismatched?
A)Alcohol - Fermentation
B)Pyruvate - Glycolysis
C)Carbon dioxide - Glycolysis
D)Oxaloacetic acid - Krebs cycle
A)Alcohol - Fermentation
B)Pyruvate - Glycolysis
C)Carbon dioxide - Glycolysis
D)Oxaloacetic acid - Krebs cycle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which statement is true about enzymes?
A)Enzyme-catalyzed reactions would not go forward without their specific enzymes.
B)Most enzymes catalyze several different reactions.
C)Coenzymes are organic molecules while cofactors are inorganic molecules.
D)A holoenzyme is an apoenzyme that is missing its cofactor.
A)Enzyme-catalyzed reactions would not go forward without their specific enzymes.
B)Most enzymes catalyze several different reactions.
C)Coenzymes are organic molecules while cofactors are inorganic molecules.
D)A holoenzyme is an apoenzyme that is missing its cofactor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
All of the following are electron acceptors for anaerobic respiration,except:
A)carbon dioxide
B)oxygen
C)nitrate ions
D)sulfate ions
A)carbon dioxide
B)oxygen
C)nitrate ions
D)sulfate ions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The prokaryotic aerobic metabolism of glucose produces a total (net)of ________ molecules of ATP.
A)24
B)30
C)34
D)38
A)24
B)30
C)34
D)38

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Electron transport chain:
A)involves transfer of O₂ to electrons in the substrate
B)results in a net consumption of ATP
C)can be thought of as electrons acting as fish increasing in energy as they jump up a waterfall
D)none of the above
A)involves transfer of O₂ to electrons in the substrate
B)results in a net consumption of ATP
C)can be thought of as electrons acting as fish increasing in energy as they jump up a waterfall
D)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Chemiosmosis:
A)forms ATP
B)occurs in the cell membrane of prokaryotes
C)uses a proton gradient to activate ATP synthase
D)all the above
A)forms ATP
B)occurs in the cell membrane of prokaryotes
C)uses a proton gradient to activate ATP synthase
D)all the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
In fermentation reactions occurring in yeast to produce wine,two products of the reaction are __________ and _________.
A)acid; hydrogen gas
B)hydrogen gas; propionic acid
C)ethyl alcohol; methane
D)carbon dioxide; ethyl alcohol
A)acid; hydrogen gas
B)hydrogen gas; propionic acid
C)ethyl alcohol; methane
D)carbon dioxide; ethyl alcohol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
During the metabolism of fats,the product of beta-oxidation enters:
A)glycolysis
B)Krebs cycle
C)oxidative phosphorylation
D)electron transport chain
A)glycolysis
B)Krebs cycle
C)oxidative phosphorylation
D)electron transport chain

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which statement about fermentation is true?
A)All fermentation of pyruvic acid always results in the same end product.
B)All fermentation starts with glucose going through glycolysis.
C)The same fermentation reaction produces both wine and cheese.
D)None of the above
A)All fermentation of pyruvic acid always results in the same end product.
B)All fermentation starts with glucose going through glycolysis.
C)The same fermentation reaction produces both wine and cheese.
D)None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Organisms that can use oxygen for metabolic reactions but can also function in an environment devoid of oxygen are termed _____.
A)aerobes
B)anaerobes
C)aerophiles
D)facultative anaerobes
A)aerobes
B)anaerobes
C)aerophiles
D)facultative anaerobes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The first step in protein metabolism is the breakdown of proteins into:
A)nucleotides
B)fatty acids
C)amino acids
D)coenzymes
A)nucleotides
B)fatty acids
C)amino acids
D)coenzymes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
In aerobic respiration,the final electron acceptor is:
A)water
B)oxygen
C)sulfur
D)coenzyme Q
A)water
B)oxygen
C)sulfur
D)coenzyme Q

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which of the following is true about glycolysis?
A)The net yield of ATP is two ATPs for each molecule of glucose.
B)It provides cells with a relatively large amount of energy.
C)Four molecules of ATP are used in the initial phosphorylation steps.
D)The ATP that is used up during glycolysis is not considered in calculating the net yield of ATP.
A)The net yield of ATP is two ATPs for each molecule of glucose.
B)It provides cells with a relatively large amount of energy.
C)Four molecules of ATP are used in the initial phosphorylation steps.
D)The ATP that is used up during glycolysis is not considered in calculating the net yield of ATP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
How is ATP formed by chemiosmosis?
A)Proton gradient across a membrane provides motive force
B)Nitrates are used as their final electron acceptor
C)The last step involves H₂O to be split into O₂
D)All of the metabolites enter the Krebs cycle
A)Proton gradient across a membrane provides motive force
B)Nitrates are used as their final electron acceptor
C)The last step involves H₂O to be split into O₂
D)All of the metabolites enter the Krebs cycle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which reaction takes place in the mitochondrial membrane?
A)Glycolysis
B)Fermentation
C)Krebs cycle
D)Electron transport chain
A)Glycolysis
B)Fermentation
C)Krebs cycle
D)Electron transport chain

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
In the electron transport chain,the energy to make ATP comes directly from _____.
A)FADH₂
B)NADH
C)both FADH₂ and NADH
D)neither FADH₂ nor NADH
A)FADH₂
B)NADH
C)both FADH₂ and NADH
D)neither FADH₂ nor NADH

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The end product of glycolysis is:
A)fructose-1,6-diphosphate
B)1,3 diphosphoglyceric acid
C)phosphoenolpyruvic acid
D)pyruvic acid
A)fructose-1,6-diphosphate
B)1,3 diphosphoglyceric acid
C)phosphoenolpyruvic acid
D)pyruvic acid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The electrons transferred from acetyl groups in the Krebs cycle are transferred to:
A)NAD⁺ only
B)FAD only
C)neither NAD⁺ and FAD
D)both NAD⁺ and FAD
A)NAD⁺ only
B)FAD only
C)neither NAD⁺ and FAD
D)both NAD⁺ and FAD

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
During glycolysis,electrons are initially transferred to:
A)NAD⁺
B)FAD
C)NADP
D)H₂O
A)NAD⁺
B)FAD
C)NADP
D)H₂O

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Each acetyl-CoA molecule will eventually produce ________ in the Krebs cycle.
A)four pairs of electrons
B)three molecules of NADH
C)one molecule of GTP
D)all of these choices
A)four pairs of electrons
B)three molecules of NADH
C)one molecule of GTP
D)all of these choices

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Pyruvic acid is metabolized in the absence of oxygen during the process of:
A)glycolysis
B)fermentation
C)oxidation
D)dark reactions
A)glycolysis
B)fermentation
C)oxidation
D)dark reactions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The initial substrate molecule for the Krebs cycle is:
A)pyruvic acid
B)acetyl-CoA
C)acetic acid
D)butanediol
A)pyruvic acid
B)acetyl-CoA
C)acetic acid
D)butanediol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
As electrons are passed from carrier to carrier,their energy changes.At which point in the chain would you expect the energy of the electrons to be the highest? 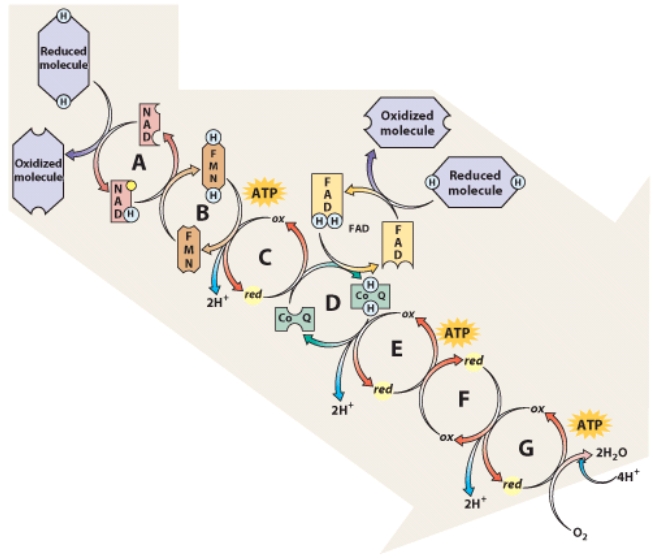
A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
E)E

A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
E)E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Describe the chemical characteristics of enzymes and indicate why they are important in the metabolism of large molecules and how they determine which metabolic pathways occur in a cell.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
In algae,the dark reactions of photosynthesis occur in the:
A)cell membrane
B)matrix of the mitochondria
C)stroma of the chloroplast
D)nucleus
A)cell membrane
B)matrix of the mitochondria
C)stroma of the chloroplast
D)nucleus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
What are chemoheterotrophs and how do they obtain energy? Name and describe two other ways microorganisms obtain energy. Why do you think so many different ways of obtaining energy evolved?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Glucose is to photosynthesis as pyruvate is to:
A)oxidative phosphorylation
B)glycolysis
C)fermentation
D)Krebs cycle
A)oxidative phosphorylation
B)glycolysis
C)fermentation
D)Krebs cycle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The green sulfur and purple sulfur bacteria are capable of:
A)carrying out photosynthesis
B)only obtaining energy from organic molecules
C)bypassing glycolysis for the Krebs cycle
D)metabolizing without enzymes
A)carrying out photosynthesis
B)only obtaining energy from organic molecules
C)bypassing glycolysis for the Krebs cycle
D)metabolizing without enzymes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
At which temperature do enzymes begin to denature? 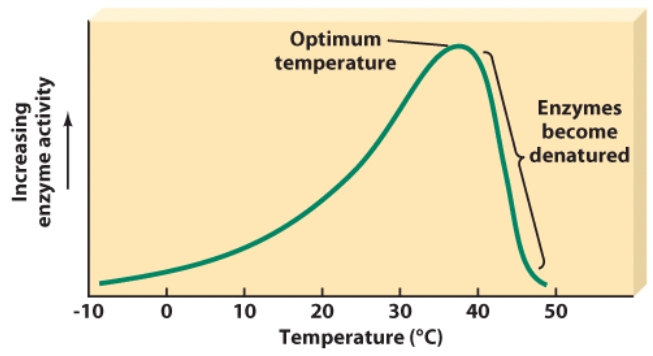
A)20 degrees Celsius
B)30 degrees Celsius
C)40 degrees Celsius
D)50 degrees Celsius

A)20 degrees Celsius
B)30 degrees Celsius
C)40 degrees Celsius
D)50 degrees Celsius

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
A surfactant:
A)lowers the surface tension at the bacterium's posterior end allowing Myxococcus to glide
B)is metabolized to produce phosphoenolpyruvate
C)forms channels through the outer membrane
D)emits light as it returns to its unexcited state
A)lowers the surface tension at the bacterium's posterior end allowing Myxococcus to glide
B)is metabolized to produce phosphoenolpyruvate
C)forms channels through the outer membrane
D)emits light as it returns to its unexcited state

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
In photosynthesis,chemical energy is used to make organic molecules in the:
A)light reaction
B)dark reaction
C)hydrolytic reaction
D)photophosphorylation reaction
A)light reaction
B)dark reaction
C)hydrolytic reaction
D)photophosphorylation reaction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
In photosynthesis,light energy is used to:
A)break down proteins
B)phosphorylate ADP to form ATP
C)synthesize carbohydrates
D)two of these choices
A)break down proteins
B)phosphorylate ADP to form ATP
C)synthesize carbohydrates
D)two of these choices

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The initial breakdown of glucose in a eukaryotic cell takes place in the _____.
A)cytoplasm
B)Golgi
C)nucleus
D)cell membranes
A)cytoplasm
B)Golgi
C)nucleus
D)cell membranes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Compare anaerobic and anaerobic respiration in terms of energy yields and reactants within the pathways. Anaerobic respiration and fermentation are both pathways that may occur in the absence of oxygen. Which confers a greater advantage to the cell? Why is the less advantageous pathway in existence within cells at all?"

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
What is returned to chlorophyll in cyclic photophosphorylation that is not returned in non-cyclic photoreduction?
A)ATP
B)Light
C)Energy
D)Electrons
A)ATP
B)Light
C)Energy
D)Electrons

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
A metabolic pathway that is involved in both breakdown and synthetic reactions is properly termed _____.
A)catabolic
B)amphibolic
C)metabolic
D)anabolic
A)catabolic
B)amphibolic
C)metabolic
D)anabolic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
As electrons are passed from carrier to carrier,their energy changes.At which point in the chain would you expect the energy of the electrons to be the lowest? 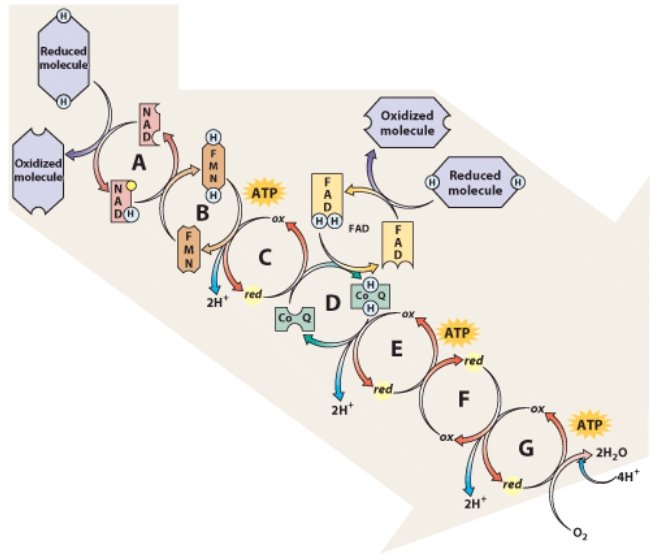
A)A
B)G
C)C
D)F
E)E

A)A
B)G
C)C
D)F
E)E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Bioluminescent microbes:
A)may have evolved because of aerobic metabolism
B)are often beneficiaries of symbiotic relationships with a larger host, producing light in exchange for nutrients
C)often have the enzyme luciferase which catalyzes the oxidation reaction that emits light
D)all of the above
A)may have evolved because of aerobic metabolism
B)are often beneficiaries of symbiotic relationships with a larger host, producing light in exchange for nutrients
C)often have the enzyme luciferase which catalyzes the oxidation reaction that emits light
D)all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



