Deck 13: Antimicrobial Therapy
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/56
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 13: Antimicrobial Therapy
1
Destruction or inactivation of antimicrobial agents is an example of what kind of bacterial resistance mechanism?
A)target alteration
B)membrane permeability alteration
C)enzyme development
D)enzyme alteration
A)target alteration
B)membrane permeability alteration
C)enzyme development
D)enzyme alteration
C
2
Because the tetracyclines are effective against a large variety of different organisms,they are considered to:
A)be narrow-spectrum drugs
B)have a therapeutic dosage level
C)be bacteriocidal
D)be broad-spectrum drugs
A)be narrow-spectrum drugs
B)have a therapeutic dosage level
C)be bacteriocidal
D)be broad-spectrum drugs
D
3
Mechanisms of bacterial resistance to antimicrobial agents include all of the following except:
A)alteration of ribosomes
B)alteration of an enzyme
C)development of enzymes
D)alteration of normal microflora
A)alteration of ribosomes
B)alteration of an enzyme
C)development of enzymes
D)alteration of normal microflora
D
4
The mode of action of an antimicrobial agent refers to _____.
A)killing of all microorganisms.
B)inhibition of growth of bacteria.
C)how it exerts its effects upon microorganisms.
D)the broad spectrum of activity of the antimicrobial agent.
A)killing of all microorganisms.
B)inhibition of growth of bacteria.
C)how it exerts its effects upon microorganisms.
D)the broad spectrum of activity of the antimicrobial agent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Rifampin:
A)inhibits RNA synthesis
B)inhibits all nucleic acid synthesis
C)disrupts of cell membrane function
D)acts as an antimetabolite
A)inhibits RNA synthesis
B)inhibits all nucleic acid synthesis
C)disrupts of cell membrane function
D)acts as an antimetabolite

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Side effects due to antimicrobial agents may involve all of the following except:
A)allergic reactions
B)anaphylactic shock
C)disruption of microbial flora
D)increased antibiotic susceptibility of replacement microflora
A)allergic reactions
B)anaphylactic shock
C)disruption of microbial flora
D)increased antibiotic susceptibility of replacement microflora

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Mutation of DNA that produces an altered ribosome is an example of what type of bacterial resistance mechanism?
A)Alteration of a metabolic pathway
B)Alteration of an enzyme
C)Development of enzymes
D)Alteration of target
A)Alteration of a metabolic pathway
B)Alteration of an enzyme
C)Development of enzymes
D)Alteration of target

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Penicillin was discovered by ____________ and was isolated by ________ .
A)Gerhard Domagk; Alexander Fleming
B)Selman Walksman; Ernest Fourneau and Paul Ehrlich
C)Ernst Chain and Howard Florey; Paul Ehrlich
D)Alexander Fleming; Ernst Chain and Howard Florey
A)Gerhard Domagk; Alexander Fleming
B)Selman Walksman; Ernest Fourneau and Paul Ehrlich
C)Ernst Chain and Howard Florey; Paul Ehrlich
D)Alexander Fleming; Ernst Chain and Howard Florey

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Antibiotics inhibit bacterial protein synthesis:
A)by disrupting cell membrane integrity
B)by binding to 80S ribosomal subunits
C)by interfering with the accurate reading of the mRNA message
D)by binding to a 60S ribosomal subunit
A)by disrupting cell membrane integrity
B)by binding to 80S ribosomal subunits
C)by interfering with the accurate reading of the mRNA message
D)by binding to a 60S ribosomal subunit

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following is not considered a mode of action by antimicrobial agents?
A)Inhibition of protein synthesis.
B)Inhibition of cell wall synthesis.
C)Inhibition of membrane permeability.
D)Disruption of selective toxicity.
A)Inhibition of protein synthesis.
B)Inhibition of cell wall synthesis.
C)Inhibition of membrane permeability.
D)Disruption of selective toxicity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A special group of chemical substances that are used to treat diseases caused by microbes are called _____.
A)antibiotics
B)synthetic drugs
C)semi-synthetic drugs
D)antimicrobial agents
A)antibiotics
B)synthetic drugs
C)semi-synthetic drugs
D)antimicrobial agents

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Polypeptide antibiotics that act as detergents and distort bacterial cellular membranes do so by:
A)acting as antimetabolites
B)inhibition of cell wall synthesis
C)disruption of cell membrane integrity
D)inhibition of nucleic acid synthesis
A)acting as antimetabolites
B)inhibition of cell wall synthesis
C)disruption of cell membrane integrity
D)inhibition of nucleic acid synthesis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Any chemical substance used in medical practice is known as a/an:
A)antibiotic
B)antimicrobial agent
C)semi-synthetic drug
D)chemotherapeutic agent
A)antibiotic
B)antimicrobial agent
C)semi-synthetic drug
D)chemotherapeutic agent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following directly pertain to inhibition of cellular protein synthesis by antimicrobial agents?
A)cellular cytoplasm is lost
B)binding and inhibition of RNA polymerase
C)imitation or molecular mimicry of normal molecules
D)interferes with accurate translation of mRNA message
A)cellular cytoplasm is lost
B)binding and inhibition of RNA polymerase
C)imitation or molecular mimicry of normal molecules
D)interferes with accurate translation of mRNA message

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A microorganism that can use ready-made folic acid from its environment and no longer needs to synthesize it from the PABA precursor demonstrates an example of what type of antimicrobial resistance mechanism?
A)Alteration of an enzyme
B)Alteration of targets
C)Development of enzymes
D)Alteration of a metabolic pathway
A)Alteration of an enzyme
B)Alteration of targets
C)Development of enzymes
D)Alteration of a metabolic pathway

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Antibiotics that bind to RNA polymerase_____.
A)act as base analogs
B)inhibit of cell wall synthesis
C)disrupt of cell membrane function
D)inhibit transcription
A)act as base analogs
B)inhibit of cell wall synthesis
C)disrupt of cell membrane function
D)inhibit transcription

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of following is not a way to limit the ability of microorganisms to acquire drug resistance?
A)High levels of antimicrobial agent in the patient
B)Inhibiting growth of invading microbes so immune defenses can kill them
C)Taking antibiotics until the patient feels better
D)Taking two antibiotics synergistically
A)High levels of antimicrobial agent in the patient
B)Inhibiting growth of invading microbes so immune defenses can kill them
C)Taking antibiotics until the patient feels better
D)Taking two antibiotics synergistically

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Selective toxicity:
A)harms the microbes without significantly harming the host.
B)causes host damage without causing significant damage to the microbe.
C)is the maximum tolerable dose of a drug per kilogram of body weight.
D)is the same as the spectrum of activity for any given drug.
A)harms the microbes without significantly harming the host.
B)causes host damage without causing significant damage to the microbe.
C)is the maximum tolerable dose of a drug per kilogram of body weight.
D)is the same as the spectrum of activity for any given drug.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Paul Ehrlich:
A)coined the term chemotherapy
B)discovered salvarsan in 1910
C)discovered the antibiotic streptomycin
D)accomplished two of the above.
A)coined the term chemotherapy
B)discovered salvarsan in 1910
C)discovered the antibiotic streptomycin
D)accomplished two of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Purine or pyrimidine analogs:
A)act as antimetabolites
B)inhibit ribosome function
C)disrupt cell membrane function
D)inhibit nucleic acid synthesis
A)act as antimetabolites
B)inhibit ribosome function
C)disrupt cell membrane function
D)inhibit nucleic acid synthesis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which does not involve testing microbial sensitivity to antimicrobials?
A)Disk diffusion method
B)Dilution method
C)Minimum inhibitory concentration
D)Toxic dosage level
A)Disk diffusion method
B)Dilution method
C)Minimum inhibitory concentration
D)Toxic dosage level

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
What antibiotic kills bacteria by disrupting their cell membranes?
A)Erythromycin
B)Rifampin
C)Tetracycline
D)Polymyxin B
A)Erythromycin
B)Rifampin
C)Tetracycline
D)Polymyxin B

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Characteristics of an ideal antimicrobial agent include all of the following except:
A)resistance by microorganisms
B)reasonable cost
C)long shelf life
D)toxicity not easily altered
A)resistance by microorganisms
B)reasonable cost
C)long shelf life
D)toxicity not easily altered

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Antibiotics that contain a beta-lactam ring:
A)interfere with peptidoglycan synthesis
B)act as an antimetabolite
C)bind to a bacterial RNA polymerase
D)are erroneously incorporated into nucleic acids
A)interfere with peptidoglycan synthesis
B)act as an antimetabolite
C)bind to a bacterial RNA polymerase
D)are erroneously incorporated into nucleic acids

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Clear area on agar that surrounds a filter paper disk on the disk diffusion tests and represents inhibited growth of a test microorganism is called:
A)minimum inhibitory concentration
B)minimum bactericidal concentration
C)zone of inhibition
D)serum killing power
A)minimum inhibitory concentration
B)minimum bactericidal concentration
C)zone of inhibition
D)serum killing power

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Imidazoles and triazoles are antimicrobial agents that are effective:
A)bacteriostatic agents
B)bactericidal agents
C)antifungal agents
D)antiviral agents
A)bacteriostatic agents
B)bactericidal agents
C)antifungal agents
D)antiviral agents

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The mode of action of the penicillin is:
A)inhibition of cell wall synthesis
B)disruption of cell membranes
C)inhibition of protein synthesis
D)inhibition of nucleic acid synthesis
A)inhibition of cell wall synthesis
B)disruption of cell membranes
C)inhibition of protein synthesis
D)inhibition of nucleic acid synthesis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Chloramphenicol,a bacteriostatic antimicrobial agent,is an inhibitor of:
A)nucleic acid synthesis
B)cell wall synthesis
C)cell membrane function
D)protein synthesis
A)nucleic acid synthesis
B)cell wall synthesis
C)cell membrane function
D)protein synthesis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
A test to determine the effectiveness of an antimicrobial agent that uses growth of a test microorganism in patients' blood serum is the:
A)disk dilution method
B)dilution method
C)disk diffusion method
D)serum killing power method
A)disk dilution method
B)dilution method
C)disk diffusion method
D)serum killing power method

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The lowest concentration of drug that yields no growth during a second inoculation into fresh medium is called:
A)minimum bactericidal concentration
B)minimum inhibitory concentration
C)mutant prevention concentration
D)serum killing power
A)minimum bactericidal concentration
B)minimum inhibitory concentration
C)mutant prevention concentration
D)serum killing power

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which of the characteristics apply to an ideal antimicrobial agent?
A)Allergenic
B)Instability
C)Short shelf life
D)Selective toxicity
A)Allergenic
B)Instability
C)Short shelf life
D)Selective toxicity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The development of second-line and third-line antimicrobial agents demonstrates:
A)cross-resistance
B)the effectiveness of first-line drugs
C)an effective method to limit drug resistance
D)the increasingly difficultly of treating drug resistant bacteria
A)cross-resistance
B)the effectiveness of first-line drugs
C)an effective method to limit drug resistance
D)the increasingly difficultly of treating drug resistant bacteria

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The ideal antimicrobial agent:
A)should be soluble in body fluids
B)have an unpredictable toxicity
C)should have interactions with other drugs or foods
D)criteria are met by most antimicrobial agents
A)should be soluble in body fluids
B)have an unpredictable toxicity
C)should have interactions with other drugs or foods
D)criteria are met by most antimicrobial agents

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which of the following antibiotics is an inhibitor of DNA gyrase?
A)Ethambutol
B)Ciprofloxacin
C)Tobramycin
D)Neomycin
A)Ethambutol
B)Ciprofloxacin
C)Tobramycin
D)Neomycin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which of the antibiotics inhibit protein synthesis in susceptible bacteria?
A)Amikacin
B)Tyrothricin
C)Vancomycin
D)Cephalexin
A)Amikacin
B)Tyrothricin
C)Vancomycin
D)Cephalexin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Antimetabolites include all of the following except:
A)trimethoprin
B)isoniazid
C)nitrofurantoin
D)sulfanilamide
A)trimethoprin
B)isoniazid
C)nitrofurantoin
D)sulfanilamide

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Determining microbial sensitivity to an antimicrobial agent by using a filter paper soaked with the drug on a bacterial lawn on an agar plate is called:
A)the dilution method
B)the disk diffusion method
C)automated testing
D)phage typing
A)the dilution method
B)the disk diffusion method
C)automated testing
D)phage typing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
A decreased efficacy of an antimicrobial agent during combination therapy is called:
A)antagonism
B)cross-resistance
C)synergism
D)second-line
A)antagonism
B)cross-resistance
C)synergism
D)second-line

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Resistance of a microorganism to an antibiotic:
A)means that the microorganism is susceptible to the antibiotic
B)can be acquired by genetic changes
C)leads to a disruption of cell membrane function
D)leads to a disruption of normal microflora
A)means that the microorganism is susceptible to the antibiotic
B)can be acquired by genetic changes
C)leads to a disruption of cell membrane function
D)leads to a disruption of normal microflora

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which one of the following antimicrobial agents is an inhibitor of cell wall synthesis?
A)Tetracycline
B)Carbapenems
C)Chloramphenicol
D)Erythromycin
A)Tetracycline
B)Carbapenems
C)Chloramphenicol
D)Erythromycin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Cephalosporins are not _____.
A)wide spectrum antibiotics
B)antibiotics with few side effects
C)disruptors of cell membrane function
D)used prophylactically in patients undergoing surgery
A)wide spectrum antibiotics
B)antibiotics with few side effects
C)disruptors of cell membrane function
D)used prophylactically in patients undergoing surgery

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The sulfonamide antibiotics kill bacteria by _____.
A)interfering with cell wall synthesis
B)disrupting folic acid metabolism
C)reacting with bacterial cell membranes
D)inhibiting bacterial motility
A)interfering with cell wall synthesis
B)disrupting folic acid metabolism
C)reacting with bacterial cell membranes
D)inhibiting bacterial motility

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
How many zones of inhibition are depicted in this image?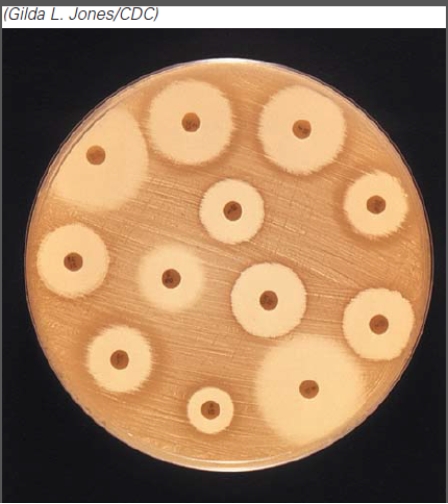 
A)None
B)Five
C)Ten
D)Twelve

A)None
B)Five
C)Ten
D)Twelve

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
A Candida albicans infection of the intestine,vagina or oral cavity is commonly treated with _____.
A)cefotaxime
B)rifampin
C)streptomycin
D)nystatin
A)cefotaxime
B)rifampin
C)streptomycin
D)nystatin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
A patient comes to you from a nursing home with a high fever. Is it better to start the patient on a broad spectrum drug or a narrow spectrum drug? Is it better to start the patient on one antibiotic or multiple antibiotics? Defend your decision.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Describe the targets or action for three of the following: antifungal agents,antiviral agents,antiprotozoan agents and antihelminthic agents.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
What is happening in this image? 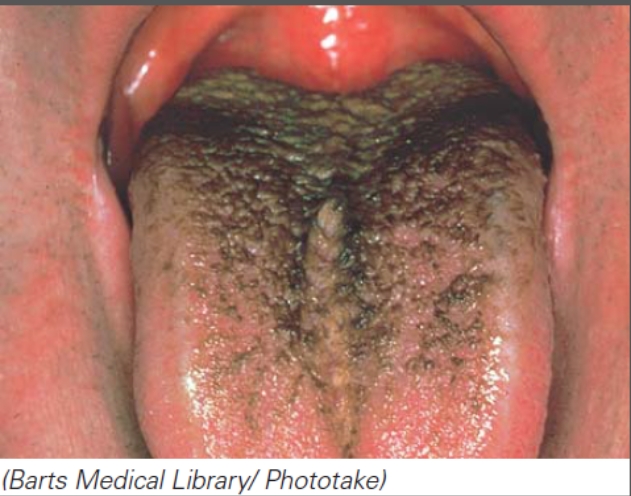
A)The individual is experiencing a side effect from taking an antifungal agent.
B)The individual is experiencing a side effect from taking an antibiotic.
C)The individual is experiencing a side effect from taking an antiviral agent.
D)The individual is experiencing a side effect from taking an antiprotozoan agent.
E)The individual is experiencing a side effect from taking an antihelminthic agent.

A)The individual is experiencing a side effect from taking an antifungal agent.
B)The individual is experiencing a side effect from taking an antibiotic.
C)The individual is experiencing a side effect from taking an antiviral agent.
D)The individual is experiencing a side effect from taking an antiprotozoan agent.
E)The individual is experiencing a side effect from taking an antihelminthic agent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Select the incorrect statement. 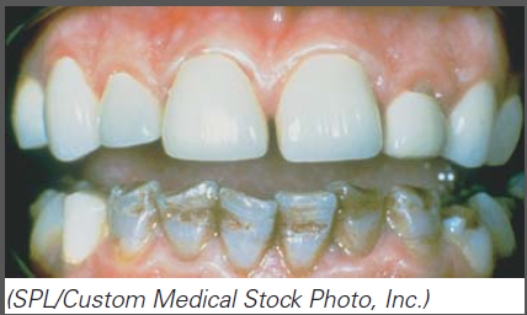
A)Chloramphenicol is responsible for the staining of these teeth.
B)One can expect the baby teeth and adult teeth to be affected by the antibiotic taken by this individual if consumed by their pregnant mother during the last trimester.
C)Tetracycline leads to abnormal bone formation as observed in this image.
D)All of these statements are correct.

A)Chloramphenicol is responsible for the staining of these teeth.
B)One can expect the baby teeth and adult teeth to be affected by the antibiotic taken by this individual if consumed by their pregnant mother during the last trimester.
C)Tetracycline leads to abnormal bone formation as observed in this image.
D)All of these statements are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Metronidazole:
A)is effective against viruses
B)has no side effects
C)prevents overgrowth of Candida yeast infections
D)is useful in the treatment of amoebas and Giardia
A)is effective against viruses
B)has no side effects
C)prevents overgrowth of Candida yeast infections
D)is useful in the treatment of amoebas and Giardia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Rimantadine is an effective antimicrobial agent against:
A)viruses
B)protozoa
C)bacteria
D)fungi
A)viruses
B)protozoa
C)bacteria
D)fungi

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Tetracyclines interfere with _____.
A)the effectiveness of birth control pills
B)transcription
C)patients with heart defects
D)metabolic reactions
A)the effectiveness of birth control pills
B)transcription
C)patients with heart defects
D)metabolic reactions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Describe three mechanisms for antibiotic resistance.If exposure to antibiotics does not induce drug-resistant mutations to occur,why do we see so many more drug-resistant strains today?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Examples of antiviral agents include all of the following agents except:
A)acyclovir
B)ribavirin
C)quinine
D)zidovudine (AZT)
A)acyclovir
B)ribavirin
C)quinine
D)zidovudine (AZT)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Why are resistant organisms found often in hospitalized patients?
A)Stringent efforts maintain sanitary conditions.
B)Many infections in patients are being treated with different antibiotics.
C)Doctors are treating outpatients with multiple antibiotics.
D)Two of the above
A)Stringent efforts maintain sanitary conditions.
B)Many infections in patients are being treated with different antibiotics.
C)Doctors are treating outpatients with multiple antibiotics.
D)Two of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Which one of the following pairs is incorrectly matched with antibiotic and its target?
A)penicillin; Gram-positive bacteria
B)nystatin; fungi
C)tetracycline; viruses
D)griseofulvin; fungi
A)penicillin; Gram-positive bacteria
B)nystatin; fungi
C)tetracycline; viruses
D)griseofulvin; fungi

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Interferons and immunoenhancers:
A)are widely used to treat viruses
B)cause no side effects
C)include levamisole and inosiplex
D)have been thoroughly researched
A)are widely used to treat viruses
B)cause no side effects
C)include levamisole and inosiplex
D)have been thoroughly researched

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



