Deck 23: Plant Physiology
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/64
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 23: Plant Physiology
1
A florist places a cut white carnation into a glass in which red food coloring has been dissolved in water. The red color travels up the flower into the petals. The color is most likely moving through
A)the phloem.
B)the xylem.
C)the dermal tissue.
D)the ground tissue.
A)the phloem.
B)the xylem.
C)the dermal tissue.
D)the ground tissue.
B
2
A botanist is asked to identify which plant organ is the source of an unknown sample. A cross section shows that the vascular tissue is found in the center of the structure, with the ground tissue outside of the vascular cylinder. Which plant organ is the source of this sample?
A)a bud
B)a leaf
C)a root
D)a stem
A)a bud
B)a leaf
C)a root
D)a stem
C
3
Which of the following statements about the growth patterns of plants and animals is true?
A)Most plants and animals have determinate growth.
B)Most plants and animals have indeterminate growth.
C)Most plants have determinate growth, whereas most animals have indeterminate growth.
D)Most plants have indeterminate growth, whereas most animals have determinate growth.
A)Most plants and animals have determinate growth.
B)Most plants and animals have indeterminate growth.
C)Most plants have determinate growth, whereas most animals have indeterminate growth.
D)Most plants have indeterminate growth, whereas most animals have determinate growth.
D
4
Which of the following is NOT a plant hormone?
A)abscisic acid
B)ethylene
C)gibberellin
D)nicotine
A)abscisic acid
B)ethylene
C)gibberellin
D)nicotine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
After a particularly hot and dry summer, plants are likely to contain elevated levels of
A)auxins.
B)cytokinins.
C)abscisic acid.
D)ethylene.
A)auxins.
B)cytokinins.
C)abscisic acid.
D)ethylene.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
You notice that one of your bean plants has a stem that does not grow in the same direction as all the other bean plants. This plant stem branches often and grows in random directions. This plant most likely lacks which of the following hormones?
A)auxins
B)cytokinins
C)abscisic acid
D)ethylene
A)auxins
B)cytokinins
C)abscisic acid
D)ethylene

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
One of your plants produces more roots and fewer shoots than a healthy plant. This plant most likely has
A)higher-than-normal concentrations of both auxins and cytokinins.
B)lower-than-normal concentrations of both auxins and cytokinins.
C)higher-than-normal concentrations of auxins and lower-than-normal concentrations of cytokinins.
D)lower-than-normal concentrations of auxins and higher-than-normal concentrations of cytokinins.
A)higher-than-normal concentrations of both auxins and cytokinins.
B)lower-than-normal concentrations of both auxins and cytokinins.
C)higher-than-normal concentrations of auxins and lower-than-normal concentrations of cytokinins.
D)lower-than-normal concentrations of auxins and higher-than-normal concentrations of cytokinins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Plant growth aboveground can be accomplished by adding new
A)leaf units.
B)bud units.
C)stem units.
D)bud-stem-leaf units.
A)leaf units.
B)bud units.
C)stem units.
D)bud-stem-leaf units.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Examine the plant in this figure. The plant is most likely a dicot, because of the presence of 
A)a taproot.
B)veins in the leaves.
C)five leaves.
D)both root systems and shoot systems.

A)a taproot.
B)veins in the leaves.
C)five leaves.
D)both root systems and shoot systems.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following is NOT a function of stems?
A)positioning the leaves for photosynthesis
B)supporting the overall shape of the plant
C)water and mineral absorption
D)vertical growth
A)positioning the leaves for photosynthesis
B)supporting the overall shape of the plant
C)water and mineral absorption
D)vertical growth

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Examine this diagram of a root tip. Which letter in the diagram indicates the zone of cell division? 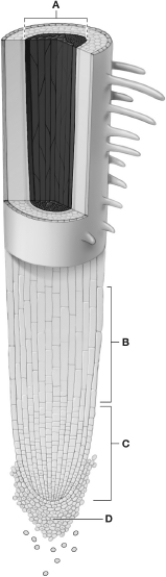
A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D

A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following plant hormones is responsible for fruit ripening?
A)auxins
B)cytokinins
C)abscisic acid
D)ethylene
A)auxins
B)cytokinins
C)abscisic acid
D)ethylene

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A tiny insect known as an aphid obtains nutrition by poking a mouthpart into the stem of a plant. Once the aphid's mouthpart is inserted, fluid from the plant is pushed through the digestive tract of the aphid by pressure. The aphid's mouthpart has most likely penetrated the plant's
A)xylem.
B)phloem.
C)stomata.
D)shoot system.
A)xylem.
B)phloem.
C)stomata.
D)shoot system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following helps a plant deter herbivores, insects, or bacteria?
A)dermal hairs on the roots
B)the production of auxin
C)dermal hairs on the stem and leaves
D)the production of cytokinin
A)dermal hairs on the roots
B)the production of auxin
C)dermal hairs on the stem and leaves
D)the production of cytokinin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The gene-for-gene recognition immune response involves
A)plant alleles that attack matching alleles in pathogens.
B)crossing-over between plant alleles and pathogen alleles.
C)production of antibodies by plants in response to antigens produced by pathogens.
D)production of proteins by plants that protect against pathogens with a particular genetic makeup.
A)plant alleles that attack matching alleles in pathogens.
B)crossing-over between plant alleles and pathogen alleles.
C)production of antibodies by plants in response to antigens produced by pathogens.
D)production of proteins by plants that protect against pathogens with a particular genetic makeup.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following plants is a monocot?
A)a carnation
B)grass
C)an oak tree
D)a rose
A)a carnation
B)grass
C)an oak tree
D)a rose

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which combination of conditions will cause a plant's stomata to open?
A)high moisture and daylight
B)high moisture and darkness
C)dehydration and darkness
D)dehydration and daylight
A)high moisture and daylight
B)high moisture and darkness
C)dehydration and darkness
D)dehydration and daylight

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A plant that is tipped on its side will bend to grow upward again because of the actions of
A)auxins.
B)cytokinins.
C)abscisic acid.
D)ethylene.
A)auxins.
B)cytokinins.
C)abscisic acid.
D)ethylene.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following plant types undergoes secondary growth?
A)both trees and grasses
B)trees but not grasses
C)grasses but not trees
D)neither trees nor grasses
A)both trees and grasses
B)trees but not grasses
C)grasses but not trees
D)neither trees nor grasses

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
A cotyledon is the
A)embryonic root of a seedling.
B)reproductive organ of a plant.
C)food-storing organ found in the seeds of flowering plants.
D)type of ground tissue in mechanical reinforcement of stem structure.
A)embryonic root of a seedling.
B)reproductive organ of a plant.
C)food-storing organ found in the seeds of flowering plants.
D)type of ground tissue in mechanical reinforcement of stem structure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Why is indeterminate growth more beneficial to plants than to animals?
A)Plants are stationary in their habitat, whereas animals can move; indeterminate growth enables plants to respond to changing environmental conditions.
B)Plants are commonly eaten by animals, whereas animals are rarely eaten by plants.
C)Indeterminate growth enables plants to become larger than animals.
D)Indeterminate growth enables plants to avoid reproducing when environmental conditions are unfavorable.
A)Plants are stationary in their habitat, whereas animals can move; indeterminate growth enables plants to respond to changing environmental conditions.
B)Plants are commonly eaten by animals, whereas animals are rarely eaten by plants.
C)Indeterminate growth enables plants to become larger than animals.
D)Indeterminate growth enables plants to avoid reproducing when environmental conditions are unfavorable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The flower is an organ that is found on the ________ of a flowering plant.
A)cotyledon
B)gametophyte
C)sporophyte
D)anther
A)cotyledon
B)gametophyte
C)sporophyte
D)anther

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A typical fertilizer contains no carbon, because carbon is
A)not a plant nutrient.
B)plentiful in all soils.
C)obtained from the atmosphere as carbon dioxide.
D)produced when the plant metabolizes nitrogen.
A)not a plant nutrient.
B)plentiful in all soils.
C)obtained from the atmosphere as carbon dioxide.
D)produced when the plant metabolizes nitrogen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Water and nutrients are taken up from soil by
A)stomata.
B)root hairs.
C)root caps.
D)xylem in taproots.
A)stomata.
B)root hairs.
C)root caps.
D)xylem in taproots.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
After plant gametes fuse, they undergo mitosis to produce the
A)spores.
B)sporophyte.
C)gametophyte.
D)flower.
A)spores.
B)sporophyte.
C)gametophyte.
D)flower.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
In plants, the diploid stage of the life cycle produces ________ by ________.
A)spores; meiosis
B)spores; mitosis
C)gametes; meiosis
D)gametes; mitosis
A)spores; meiosis
B)spores; mitosis
C)gametes; meiosis
D)gametes; mitosis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Fertilizers generally have three numbers on the label (for example, 20:10:20). These numbers refer to the three most essential plant nutrients, which are
A)nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium.
B)nitrogen, calcium, and magnesium.
C)oxygen, hydrogen, and calcium.
D)potassium, phosphorus, and iron.
A)nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium.
B)nitrogen, calcium, and magnesium.
C)oxygen, hydrogen, and calcium.
D)potassium, phosphorus, and iron.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
At what point in the plant life cycle does cell division convert diploid cells into haploid cells?
A)when the gametophyte produces gametes
B)when the sporophyte produces spores
C)when the egg and the sperm fuse to form a zygote
D)when the germinating spore grows to become the gametophyte
A)when the gametophyte produces gametes
B)when the sporophyte produces spores
C)when the egg and the sperm fuse to form a zygote
D)when the germinating spore grows to become the gametophyte

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
During pollination, pollen is moved from
A)endosperm to ovary.
B)anther to ovary.
C)ovary to anther.
D)endosperm to anther.
A)endosperm to ovary.
B)anther to ovary.
C)ovary to anther.
D)endosperm to anther.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Worldwide, more than 80 percent of the calories consumed by humans come from
A)angiosperms.
B)conifers.
C)ferns.
D)mosses.
A)angiosperms.
B)conifers.
C)ferns.
D)mosses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Like other organisms, plants are composed of proteins, lipids, carbohydrates, and nucleic acids. Based on this information, which of the following would be a macronutrient?
A)zinc
B)iron
C)copper
D)carbon
A)zinc
B)iron
C)copper
D)carbon

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Fertilizers, which contain a variety of nutrients, are likely to
A)have higher concentrations of macronutrients than micronutrients.
B)have lower concentrations of macronutrients than micronutrients.
C)have equal concentrations of macronutrients and micronutrients.
D)contain micronutrients but not macronutrients.
A)have higher concentrations of macronutrients than micronutrients.
B)have lower concentrations of macronutrients than micronutrients.
C)have equal concentrations of macronutrients and micronutrients.
D)contain micronutrients but not macronutrients.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Pollen is produced in the
A)ovules.
B)anthers.
C)endosperm.
D)cotyledon.
A)ovules.
B)anthers.
C)endosperm.
D)cotyledon.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Why are anthers typically attached to filaments and elevated within the flower?
A)to improve the transfer of pollen to a pollinator
B)to improve the transfer of pollen to the adjacent ovary
C)to prevent pollen from becoming stuck in the nectar
D)to prevent pollen from being blown away from the flower
A)to improve the transfer of pollen to a pollinator
B)to improve the transfer of pollen to the adjacent ovary
C)to prevent pollen from becoming stuck in the nectar
D)to prevent pollen from being blown away from the flower

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which of the following crops is likely to require the LEAST addition of fertilizers?
A)apples
B)carrots
C)tomatoes
D)wheat
A)apples
B)carrots
C)tomatoes
D)wheat

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Most plants have indeterminate growth. This means that
A)they are perennials.
B)they may complete their life cycles in one, two, or three years.
C)they reach maturity at variable times based on external signals.
D)the final form of the plant is not entirely predictable.
A)they are perennials.
B)they may complete their life cycles in one, two, or three years.
C)they reach maturity at variable times based on external signals.
D)the final form of the plant is not entirely predictable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Because its cells are diploid, the ovule is a part of the
A)gametophyte.
B)sporophyte.
C)carpel.
D)anther.
A)gametophyte.
B)sporophyte.
C)carpel.
D)anther.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Plants get most of their micronutrients from
A)air.
B)soil.
C)photosynthesis.
D)respiration.
A)air.
B)soil.
C)photosynthesis.
D)respiration.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
While walking in the forest, you come across a plant that has a flower with three petals and leaves with parallel veins. You would classify this plant as a
A)cotyledon.
B)dicot.
C)monocot.
D)tricot.
A)cotyledon.
B)dicot.
C)monocot.
D)tricot.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Copper is an example of
A)a toxin produced by plants.
B)a hormone produced by plants.
C)a macronutrient needed by plants.
D)a micronutrient needed by plants.
A)a toxin produced by plants.
B)a hormone produced by plants.
C)a macronutrient needed by plants.
D)a micronutrient needed by plants.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Plants generally require having approximately the same size root system as the size of the shoot system. The hormones auxin and cytokinin work together to balance the root-to-shoot ratio in plants. Identify where each of these hormones is produced (in the root or in the shoot) and how they function to maintain this balance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Spores undergo mitosis to form the haploid ________, one of the two stages in the life cycle of plants.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
What is the purpose of brightly colored flower petals?
A)They are aesthetically pleasing.
B)They help animals identify edible seeds.
C)They are the location of spore production.
D)They help pollinators find similar flowers.
A)They are aesthetically pleasing.
B)They help animals identify edible seeds.
C)They are the location of spore production.
D)They help pollinators find similar flowers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Flowers, like the ones in this figure, display spectacular colors, shapes, and odors, in combination with food rewards such as nectar, to convince pollinating animals to visit several flowers of the same species and transfer pollen for reproduction. How might a flower be specialized to attract hummingbird pollinators (right) and discourage insect pollinators (left)? 
A)by having brightly colored petals
B)by producing sugary nectar
C)by hanging downward from the branch tips
D)by organizing its petals into a flat landing surface

A)by having brightly colored petals
B)by producing sugary nectar
C)by hanging downward from the branch tips
D)by organizing its petals into a flat landing surface

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Plants are protected from herbivores by ________ tissue, which also controls gas exchange.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
In a leaf, why is having the ground tissue - rather than the vascular tissue - directly under the dermal tissue a better strategy?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
What are the advantages and disadvantages of animal pollination versus wind pollination?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Horticulturists often remove the anthers from flowers. The purpose of this technique is to
A)promote branching.
B)prevent self-fertilization.
C)increase egg production.
D)attract pollinators.
A)promote branching.
B)prevent self-fertilization.
C)increase egg production.
D)attract pollinators.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
A plant whose seeds are dispersed by animals most likely produces
A)small, soft seeds.
B)small, light seeds.
C)large, dense seeds.
D)large, sugary seeds.
A)small, soft seeds.
B)small, light seeds.
C)large, dense seeds.
D)large, sugary seeds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Contrast how the growth patterns of plants and animals help each type of organism respond to predators.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
What is the mechanism of seed dispersal for the dandelion?
A)wind
B)water
C)animals
D)humans
A)wind
B)water
C)animals
D)humans

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
A plant's physiological response to day length is called ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Compare and contrast the products of meiosis in plants and in animals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Increases in length as a result of cell divisions at apical meristems are called ________ growth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The hormone ________ is a gas produced by ripening fruit, and it can induce other fruits nearby to ripen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The transfer of the male gametophyte from one flower to another is called ________________..

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Which of the following animals is LEAST likely to be a pollinator?
A)a butterfly
B)a bat
C)a rattlesnake
D)a human
A)a butterfly
B)a bat
C)a rattlesnake
D)a human

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The plant hormone auxin causes cells in the shoot to elongate (grow longer). Auxin is involved in the phototropic response because it moves from one side of the plant to the other in response to light. Discuss the direction in which auxin moves (toward light or away from light) and how this helps the phototropic response.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Match each plant structure to the function that the structure performs.
a.This structure transports water.
b.This structure transports sugars.
c.This structure controls gas exchange.
d.This structure is a protective outer covering.
e.This structure conducts photosynthesis.
dermal tissue
a.This structure transports water.
b.This structure transports sugars.
c.This structure controls gas exchange.
d.This structure is a protective outer covering.
e.This structure conducts photosynthesis.
dermal tissue

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
How might a flower be specialized to attract bat pollinators and discourage insect pollinators?
A)by opening at night
B)by producing a sweet scent
C)by having a flat overall shape
D)by having variegated petal colors
A)by opening at night
B)by producing a sweet scent
C)by having a flat overall shape
D)by having variegated petal colors

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Match each plant structure to the function that the structure performs.
a.This structure transports water.
b.This structure transports sugars.
c.This structure controls gas exchange.
d.This structure is a protective outer covering.
e.This structure conducts photosynthesis.
xylem
a.This structure transports water.
b.This structure transports sugars.
c.This structure controls gas exchange.
d.This structure is a protective outer covering.
e.This structure conducts photosynthesis.
xylem

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Match each plant structure to the function that the structure performs.
a.This structure transports water.
b.This structure transports sugars.
c.This structure controls gas exchange.
d.This structure is a protective outer covering.
e.This structure conducts photosynthesis.
phloem
a.This structure transports water.
b.This structure transports sugars.
c.This structure controls gas exchange.
d.This structure is a protective outer covering.
e.This structure conducts photosynthesis.
phloem

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Match each plant structure to the function that the structure performs.
a.This structure transports water.
b.This structure transports sugars.
c.This structure controls gas exchange.
d.This structure is a protective outer covering.
e.This structure conducts photosynthesis.
ground tissue
a.This structure transports water.
b.This structure transports sugars.
c.This structure controls gas exchange.
d.This structure is a protective outer covering.
e.This structure conducts photosynthesis.
ground tissue

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Match each plant structure to the function that the structure performs.
a.This structure transports water.
b.This structure transports sugars.
c.This structure controls gas exchange.
d.This structure is a protective outer covering.
e.This structure conducts photosynthesis.
stomata
a.This structure transports water.
b.This structure transports sugars.
c.This structure controls gas exchange.
d.This structure is a protective outer covering.
e.This structure conducts photosynthesis.
stomata

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



