Deck 14: Lower Extremity and Pelvis
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/70
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 14: Lower Extremity and Pelvis
1
Small,flat,oval bones in the region of the first metatarsophalangeal joint are called:
A) phalanges.
B) tarsals.
C) metatarsals.
D) sesamoid bones.
A) phalanges.
B) tarsals.
C) metatarsals.
D) sesamoid bones.
sesamoid bones.
2
The anatomical name for the bone commonly known as the "kneecap" is:
A) fibula.
B) tibia.
C) patella.
D) flabella.
A) fibula.
B) tibia.
C) patella.
D) flabella.
patella.
3
Which bones are located in the lower leg?
A) Tibia and femur
B) Fibula and femur
C) Tibia and fibula
D) Tibula and fibia
A) Tibia and femur
B) Fibula and femur
C) Tibia and fibula
D) Tibula and fibia
Tibia and fibula
4
Which bone of the lower leg is on the medial side?
A) Tibia
B) Fibula
C) Femur
D) Ulna
A) Tibia
B) Fibula
C) Femur
D) Ulna

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
What is the name given to the distal end of the fibula?
A) Talus
B) Medial malleolus
C) Lateral malleolus
D) Astragalus
A) Talus
B) Medial malleolus
C) Lateral malleolus
D) Astragalus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following bones are in the hindfoot portion of the foot?
1) Cuneiforms
2) Calcaneus
3) Talus
A) 1 and 2 only
B) 1 and 3 only
C) 2 and 3 only
D) 1, 2, and 3
1) Cuneiforms
2) Calcaneus
3) Talus
A) 1 and 2 only
B) 1 and 3 only
C) 2 and 3 only
D) 1, 2, and 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
When the ankle is flexed and raises the foot,the movement is termed:
A) plantar flexion.
B) eversion.
C) inversion.
D) dorsiflexion.
A) plantar flexion.
B) eversion.
C) inversion.
D) dorsiflexion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
What is the name of the palpable,bony protuberance on the anterior aspect of the proximal tibia?
A) Tibial spine
B) Intercondylar eminence
C) Greater trochanter
D) Tibial tuberosity
A) Tibial spine
B) Intercondylar eminence
C) Greater trochanter
D) Tibial tuberosity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
What tarsal is commonly referred to as the "heel bone"?
A) Talus
B) Cuneiforms
C) Navicular
D) Calcaneus
A) Talus
B) Cuneiforms
C) Navicular
D) Calcaneus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
A normal variation in which an additional small sesamoid bone is located posterior to the knee is termed:
A) patella.
B) fabella.
C) meniscus.
D) mortise.
A) patella.
B) fabella.
C) meniscus.
D) mortise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The bones of the midfoot are called the:
A) metatarsals.
B) tarsals.
C) phalanges.
D) cuneiforms.
A) metatarsals.
B) tarsals.
C) phalanges.
D) cuneiforms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The bones of the forefoot include the:
A) phalanges and tarsals.
B) tarsals and metatarsals.
C) phalanges and metatarsals.
D) cuneiforms and cuboid.
A) phalanges and tarsals.
B) tarsals and metatarsals.
C) phalanges and metatarsals.
D) cuneiforms and cuboid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
What is a fabella?
A) An additional sesamoid bone that can develop in the posterior portion of the knee
B) The articular cartilage located at the condyle of the femur
C) The large sesamoid bone on the anterior surface of the knee
D) The head of the fibula
A) An additional sesamoid bone that can develop in the posterior portion of the knee
B) The articular cartilage located at the condyle of the femur
C) The large sesamoid bone on the anterior surface of the knee
D) The head of the fibula

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
What name is given to the articular surface of the proximal,superior aspect of the tibia?
A) Intercondylar fossa
B) Intercondylar eminence
C) Tibial spine
D) Tibial plateau
A) Intercondylar fossa
B) Intercondylar eminence
C) Tibial spine
D) Tibial plateau

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which bone of the lower leg is located on the lateral side?
A) Tibia
B) Fibula
C) Femur
D) Ulna
A) Tibia
B) Fibula
C) Femur
D) Ulna

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The palpable portion at the distal end of the tibia is called the:
A) lateral malleolus.
B) medial malleolus.
C) medial condyle.
D) lateral condyle.
A) lateral malleolus.
B) medial malleolus.
C) medial condyle.
D) lateral condyle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
How are the toes identified?
A) The toes are numbered 1 to 5 beginning on the medial side.
B) The toes are numbered 1 to 5 beginning on the lateral side.
C) The toes are referred to as digits without identifying numbers.
D) The toes have individual names.
A) The toes are numbered 1 to 5 beginning on the medial side.
B) The toes are numbered 1 to 5 beginning on the lateral side.
C) The toes are referred to as digits without identifying numbers.
D) The toes have individual names.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following are the bones that articulate to form the ankle mortise?
A) Talus, tibia, and fibula
B) Tibia, fibula, and calcaneus
C) Talus and tibia
D) Calcaneus and tibia
A) Talus, tibia, and fibula
B) Tibia, fibula, and calcaneus
C) Talus and tibia
D) Calcaneus and tibia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The patella is classified as a(n)______ bone.
A) irregular
B) short
C) sesamoid
D) long
A) irregular
B) short
C) sesamoid
D) long

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following are parts of the tibia?
1) Tibial tuberosity
2) Lesser trochanter
3) Medial malleolus
A) 1 and 2 only
B) 1 and 3 only
C) 2 and 3 only
D) 1, 2, and 3
1) Tibial tuberosity
2) Lesser trochanter
3) Medial malleolus
A) 1 and 2 only
B) 1 and 3 only
C) 2 and 3 only
D) 1, 2, and 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The ilium,ischium,and pubis make up a large composite bone called the:
A) acetabulum.
B) ilium.
C) innominate bone.
D) cuboid.
A) acetabulum.
B) ilium.
C) innominate bone.
D) cuboid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
A bony prominence on the anterior aspect of the lateral pelvis above the hip is called the:
A) acetabulum.
B) symphysis pubis.
C) greater trochanter.
D) anterior superior iliac spine.
A) acetabulum.
B) symphysis pubis.
C) greater trochanter.
D) anterior superior iliac spine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which is the largest and heaviest bone in the body?
A) Tibia
B) Femur
C) Humerus
D) Cranium
A) Tibia
B) Femur
C) Humerus
D) Cranium

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Where is the tibial tuberosity located?
A) On the anterior aspect of the proximal tibia
B) On the posterior aspect of the proximal tibia
C) On the anterior aspect of the distal tibia
D) On the posterior aspect of the distal tibia
A) On the anterior aspect of the proximal tibia
B) On the posterior aspect of the proximal tibia
C) On the anterior aspect of the distal tibia
D) On the posterior aspect of the distal tibia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
What anatomy articulates to form the knee joint?
A) The condyles of the femur and the tibial plateaus articulate to form the knee joint.
B) The condyles of the femur and the tibial tuberosities articulate to form the knee joint.
C) The head of the femur and the acetabulum articulate to form the knee joint.
D) The head of the femur and the tibial plateaus articulate to form the knee joint.
A) The condyles of the femur and the tibial plateaus articulate to form the knee joint.
B) The condyles of the femur and the tibial tuberosities articulate to form the knee joint.
C) The head of the femur and the acetabulum articulate to form the knee joint.
D) The head of the femur and the tibial plateaus articulate to form the knee joint.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
When taking an AP axial projection of the foot,the central ray is directed:
A) 10 degrees toward the toes.
B) 10 degrees toward the heel.
C) 25 degrees toward the heel.
D) perpendicular to the IR.
A) 10 degrees toward the toes.
B) 10 degrees toward the heel.
C) 25 degrees toward the heel.
D) perpendicular to the IR.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Where does the CR enter the patient for the AP axial projection of the foot?
A) At the third metatarsophalangeal (MTP) joint
B) At the first MTP joint
C) At the base of the third metatarsal
D) At the head of the third metatarsal
A) At the third metatarsophalangeal (MTP) joint
B) At the first MTP joint
C) At the base of the third metatarsal
D) At the head of the third metatarsal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which foot projection and position demonstrate the metatarsals without superimposition?
A) AP projection with plantar surface of foot in contact with IR
B) AP oblique projection in 30-degree lateral rotation
C) AP oblique projection in 30-degree medial rotation
D) Lateral projection with MTP joints perpendicular to IR
A) AP projection with plantar surface of foot in contact with IR
B) AP oblique projection in 30-degree lateral rotation
C) AP oblique projection in 30-degree medial rotation
D) Lateral projection with MTP joints perpendicular to IR

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which of the following combine to form the hip bone?
1) Ilium
2) Ischium
3) Pubis
A) 1 and 2 only
B) 1 and 3 only
C) 2 and 3 only
D) 1, 2, and 3
1) Ilium
2) Ischium
3) Pubis
A) 1 and 2 only
B) 1 and 3 only
C) 2 and 3 only
D) 1, 2, and 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
What is the name of the large,palpable prominence on the proximal and lateral portion of the femur?
A) Lateral condyle
B) Greater trochanter
C) Greater tuberosity
D) Lesser trochanter
A) Lateral condyle
B) Greater trochanter
C) Greater tuberosity
D) Lesser trochanter

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
What is the name of the socket portion of the hip joint,which is located on the pelvis?
A) Acetabulum
B) Ischial tuberosity
C) Anterior superior iliac spine
D) Obturator foramen
A) Acetabulum
B) Ischial tuberosity
C) Anterior superior iliac spine
D) Obturator foramen

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which surface of the foot should be in contact with the IR for the lateral projection of the foot?
A) Lateral
B) Medial
C) Dorsal
D) Plantar
A) Lateral
B) Medial
C) Dorsal
D) Plantar

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The rounded,superior part of the ilium that is used as a palpable landmark is called the:
A) ala.
B) wing.
C) iliac crest.
D) anterior superior iliac spine.
A) ala.
B) wing.
C) iliac crest.
D) anterior superior iliac spine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
What is the name of the large bone located in the thigh?
A) Femur
B) Humerus
C) Tibia
D) Os calcis
A) Femur
B) Humerus
C) Tibia
D) Os calcis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
How much is the plantar surface of the foot elevated from the IR for the AP oblique projection of the foot?
A) 45 degrees
B) 30 degrees
C) 10 degrees
D) 25 degrees
A) 45 degrees
B) 30 degrees
C) 10 degrees
D) 25 degrees

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Where is the medial malleolus located?
A) On the anterior aspect of the knee joint
B) On the lateral aspect of the knee joint
C) On the anterior aspect of the ankle joint
D) On the medial aspect of the ankle joint
A) On the anterior aspect of the knee joint
B) On the lateral aspect of the knee joint
C) On the anterior aspect of the ankle joint
D) On the medial aspect of the ankle joint

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Where is the tibial spine located?
A) On the anterior aspect of the proximal tibia
B) On the superior aspect of the proximal tibia
C) On the anterior aspect of the distal tibia
D) On the inferior aspect of the distal tibia
A) On the anterior aspect of the proximal tibia
B) On the superior aspect of the proximal tibia
C) On the anterior aspect of the distal tibia
D) On the inferior aspect of the distal tibia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Where is the intercondylar fossa located?
A) On the proximal, anterior aspect of the femur
B) On the distal, anterior aspect of the femur
C) On the distal, posterior aspect of the femur
D) On the proximal, posterior aspect of the tibia
A) On the proximal, anterior aspect of the femur
B) On the distal, anterior aspect of the femur
C) On the distal, posterior aspect of the femur
D) On the proximal, posterior aspect of the tibia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which of the following is true regarding the lateral projection of the foot?
A) The ankle does not have a specific position when performing the lateral projection of the foot.
B) The ankle should be dorsiflexed so that the long axis of the foot forms a 45-degree angle with the tibia.
C) The ankle should be extended so that the plantar surface of the foot forms a 45-degree angle with the IR.
D) The ankle should be dorsiflexed so that the long axis of the foot is perpendicular to the tibia.
A) The ankle does not have a specific position when performing the lateral projection of the foot.
B) The ankle should be dorsiflexed so that the long axis of the foot forms a 45-degree angle with the tibia.
C) The ankle should be extended so that the plantar surface of the foot forms a 45-degree angle with the IR.
D) The ankle should be dorsiflexed so that the long axis of the foot is perpendicular to the tibia.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
What device may help provide an even density on a radiograph of an AP axial projection of the foot?
A) Lead shield
B) Wedge compensating filter
C) Wedge positioning sponge
D) Sandbag
A) Lead shield
B) Wedge compensating filter
C) Wedge positioning sponge
D) Sandbag

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
When taking a lateral projection of the knee,flexion of the knee joint should be limited to 10 degrees when there is suspicion of:
A) loose fragment within the joint.
B) collateral ligament injury.
C) damage to the medial meniscus cartilage.
D) fracture of the patella.
A) loose fragment within the joint.
B) collateral ligament injury.
C) damage to the medial meniscus cartilage.
D) fracture of the patella.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Which of the following radiographic methods is used to demonstrate the patella and the femoropatellar joint space?
A) Holmblad method
B) Camp-Coventry method
C) Settegast method
D) Grashey method
A) Holmblad method
B) Camp-Coventry method
C) Settegast method
D) Grashey method

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Which of the following must be included on an AP projection of the lower leg?
1) Entire tibia and fibula
2) Knee joint
3) Ankle joint
A) 1 and 2 only
B) 1 and 3 only
C) 2 and 3 only
D) 1, 2, and 3
1) Entire tibia and fibula
2) Knee joint
3) Ankle joint
A) 1 and 2 only
B) 1 and 3 only
C) 2 and 3 only
D) 1, 2, and 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Where should the CR enter the patient for the AP projection of the knee?
A)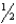 inch below the apex of the patella
inch below the apex of the patella
B) inch below the base of the patella
C) 1 inch distal to the medial epicondyle of the femur
D) 1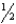 inch proximal to the medial epicondyle of the femur
inch proximal to the medial epicondyle of the femur
A)
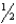 inch below the apex of the patella
inch below the apex of the patellaB) inch below the base of the patella
C) 1 inch distal to the medial epicondyle of the femur
D) 1
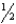 inch proximal to the medial epicondyle of the femur
inch proximal to the medial epicondyle of the femur
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
When the leg is extended in the supine position,the foot is maximally dorsiflexed,and the central ray is directed 40 degrees cephalad through the plantar surface of the foot,the resulting image demonstrates:
A) an axial projection of the calcaneus.
B) a medial oblique position of the tarsals and metatarsals.
C) the ankle mortise, especially the talofibular articulation.
D) the cuboid and the third cuneiform.
A) an axial projection of the calcaneus.
B) a medial oblique position of the tarsals and metatarsals.
C) the ankle mortise, especially the talofibular articulation.
D) the cuboid and the third cuneiform.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
When the patient is prone,the knee is flexed to form an angle of 80 degrees between the femur and the lower leg,and the central ray is directed approximately 15 to 20 degrees cephalad through the inferior margin of the patella,the resulting radiograph demonstrates:
A) the articulation between the proximal tibia and fibula.
B) the intercondylar notch.
C) the tibial eminences.
D) a tangential projection of the patella.
A) the articulation between the proximal tibia and fibula.
B) the intercondylar notch.
C) the tibial eminences.
D) a tangential projection of the patella.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
On a lateral projection of the knee,what anatomy is used to determine if the knee joint is properly positioned?
A) Femoral condyles should be demonstrated superimposed.
B) The tibial tuberosity should be superimposed on the superior tibia.
C) The intercondylar eminence should be centered between the tibial plateaus.
D) The patella is demonstrated superimposed on the distal femur.
A) Femoral condyles should be demonstrated superimposed.
B) The tibial tuberosity should be superimposed on the superior tibia.
C) The intercondylar eminence should be centered between the tibial plateaus.
D) The patella is demonstrated superimposed on the distal femur.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
What is the proper CR angle and direction for the axial projection of the calcaneus when the ankle is dorsiflexed so that the plantar surface of the foot is perpendicular to the IR?
A) 10 degrees cephalad
B) 40 degrees cephalad
C) 10 degrees caudad
D) 40 degrees caudad
A) 10 degrees cephalad
B) 40 degrees cephalad
C) 10 degrees caudad
D) 40 degrees caudad

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
If a knee x-ray is made while the patient is wearing denim jeans,which of the following is likely to occur on the image?
A) Nothing; denim jeans are radiolucent.
B) The jeans will leave an artifact on the image.
C) Nothing; leaving the patient's jeans on helps to protect the patient's modesty.
D) The jeans will totally block out the knee anatomy because x-rays cannot penetrate denim.
A) Nothing; denim jeans are radiolucent.
B) The jeans will leave an artifact on the image.
C) Nothing; leaving the patient's jeans on helps to protect the patient's modesty.
D) The jeans will totally block out the knee anatomy because x-rays cannot penetrate denim.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Which surface of the lower leg is placed in contact with the IR for the lateral projection of the lower leg?
A) Anterior surface
B) Posterior surface
C) Medial surface
D) Lateral surface
A) Anterior surface
B) Posterior surface
C) Medial surface
D) Lateral surface

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Which of the following are true regarding the correct position for an AP projection of the lower leg?
1) The leg should be extended and resting on the IR.
2) The ankle should be dorsiflexed so that the foot forms a 90-degree angle with the lower leg.
3) The sagittal plane of the leg should be placed parallel to the IR.
A) 1 and 2 only
B) 1 and 3 only
C) 2 and 3 only
D) 1, 2, and 3
1) The leg should be extended and resting on the IR.
2) The ankle should be dorsiflexed so that the foot forms a 90-degree angle with the lower leg.
3) The sagittal plane of the leg should be placed parallel to the IR.
A) 1 and 2 only
B) 1 and 3 only
C) 2 and 3 only
D) 1, 2, and 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
When the leg is extended,the ankle is dorsiflexed to form an angle of 90 degrees between foot and leg,the leg is rotated medially approximately 15 degrees,and the CR is perpendicular to the IR through the midpoint between the malleoli,the resulting image demonstrates:
A) an axial projection of the calcaneus.
B) an AP projection of the tarsals and metatarsals.
C) the ankle mortise, especially the talofibular articulation.
D) the cuboid and the third cuneiform.
A) an axial projection of the calcaneus.
B) an AP projection of the tarsals and metatarsals.
C) the ankle mortise, especially the talofibular articulation.
D) the cuboid and the third cuneiform.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Where does the CR enter the patient for the AP projection of the first toe?
A) Base of the third metatarsal
B) Proximal IP joint
C) Metatarsophalangeal joint
D) Distal IP joint
A) Base of the third metatarsal
B) Proximal IP joint
C) Metatarsophalangeal joint
D) Distal IP joint

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Which of the following is true regarding the correct positioning of the ankle for a lateral projection?
A) The medial surface of the ankle joint is in contact with the IR.
B) The sagittal plane of the foot and leg is perpendicular to the IR.
C) The CR enters perpendicular to the medial malleolus.
D) The ankle joint is extended so that the foot is 15 to 20 degrees from the IR.
A) The medial surface of the ankle joint is in contact with the IR.
B) The sagittal plane of the foot and leg is perpendicular to the IR.
C) The CR enters perpendicular to the medial malleolus.
D) The ankle joint is extended so that the foot is 15 to 20 degrees from the IR.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Which of the following radiographic methods are used to demonstrate the intercondylar fossa?
1) Holmblad method
2) Camp-Coventry method
3) Settegast method
A) 1 and 2 only
B) 1 and 3 only
C) 2 and 3 only
D) 1, 2, and 3
1) Holmblad method
2) Camp-Coventry method
3) Settegast method
A) 1 and 2 only
B) 1 and 3 only
C) 2 and 3 only
D) 1, 2, and 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
What is the correct amount of knee flexion for the PA axial projection (Holmblad method)of the intercondylar fossa?
A) 45 degrees
B) 15 to 20 degrees
C) 70 degrees
D) 40 to 50 degrees
A) 45 degrees
B) 15 to 20 degrees
C) 70 degrees
D) 40 to 50 degrees

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Where should the CR enter the patient for the AP projection of the ankle joint?
A) Perpendicular to a point midway between the malleoli
B) Perpendicular to the base of the third metatarsal
C) Angled 10 degrees cephalic to a point midway between the malleoli
D) Angled 10 degrees cephalic to the base of the third metatarsal
A) Perpendicular to a point midway between the malleoli
B) Perpendicular to the base of the third metatarsal
C) Angled 10 degrees cephalic to a point midway between the malleoli
D) Angled 10 degrees cephalic to the base of the third metatarsal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which surface of the knee is in contact with the IR for the lateral projection of the knee?
A) Medial surface
B) Lateral surface
C) Anterior surface
D) Posterior surface
A) Medial surface
B) Lateral surface
C) Anterior surface
D) Posterior surface

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which surface of the ankle is placed in contact with the IR for the lateral projection of the ankle?
A) Medial surface
B) Lateral surface
C) Anterior surface
D) Posterior surface
A) Medial surface
B) Lateral surface
C) Anterior surface
D) Posterior surface

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
A tube angle of 5 degrees cephalic is used when taking a(n):
A) lateral projection of the knee.
B) AP projection of the foot.
C) axial projection of the calcaneus.
D) AP projection of the pelvis.
A) lateral projection of the knee.
B) AP projection of the foot.
C) axial projection of the calcaneus.
D) AP projection of the pelvis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
What is the purpose of internally rotating the lower limbs for the AP projection of the pelvis?
A) Improves visualization of the acetabula
B) Reduces magnification of the pelvis
C) Increases patient comfort
D) Places femoral necks parallel to IR
A) Improves visualization of the acetabula
B) Reduces magnification of the pelvis
C) Increases patient comfort
D) Places femoral necks parallel to IR

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
What is the name of the fracture caused by repeated injuries that would not be caused by a single injury?
A) Bimalleolar fracture
B) Stress fracture
C) Spiral fracture
D) Colles fracture
A) Bimalleolar fracture
B) Stress fracture
C) Spiral fracture
D) Colles fracture

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Which patient population is most likely to suffer a hip fracture?
A) Children
B) Young adults, especially athletes
C) Elderly
D) Males who are long-term smokers
A) Children
B) Young adults, especially athletes
C) Elderly
D) Males who are long-term smokers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Exostosis,also called osteochondroma,is a type of:
A) arthritis.
B) bone infection.
C) malignant tumor.
D) benign tumor.
A) arthritis.
B) bone infection.
C) malignant tumor.
D) benign tumor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
A systemic disorder that increases the uric acid content of the blood and may cause a joint condition that commonly affects the feet (particularly the joints of the great toe)is called:
A) osteoarthritis.
B) gout.
C) rheumatoid arthritis.
D) osteoporosis.
A) osteoarthritis.
B) gout.
C) rheumatoid arthritis.
D) osteoporosis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
In addition to an AP projection,which of the following should be used to image the hip of a patient with a suspected fracture?
A) Lateral projection of the pelvis
B) AP oblique projection of the pelvis (modified Cleaves method)
C) Lateral projection of the hip (frog-leg lateral)
D) Axiolateral projection (Danelius-Miller method)
A) Lateral projection of the pelvis
B) AP oblique projection of the pelvis (modified Cleaves method)
C) Lateral projection of the hip (frog-leg lateral)
D) Axiolateral projection (Danelius-Miller method)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
When a twisting injury occurs in the lower leg,what type of fracture usually occurs?
A) A spiral fracture
B) A comminuted fracture
C) A stress fracture
D) A bimalleolar fracture
A) A spiral fracture
B) A comminuted fracture
C) A stress fracture
D) A bimalleolar fracture

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
When taking an AP projection of the hip,the lower limb is:
A) abducted maximally.
B) flexed at the knee joint.
C) laterally rotated 15 degrees.
D) medially rotated 15 degrees.
A) abducted maximally.
B) flexed at the knee joint.
C) laterally rotated 15 degrees.
D) medially rotated 15 degrees.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
What is the proper position of the lower limbs for an AP projection of the pelvis?
A) 15-degree medial rotation
B) 5-degree medial rotation
C) 5-degree lateral rotation
D) 15-degree lateral rotation
A) 15-degree medial rotation
B) 5-degree medial rotation
C) 5-degree lateral rotation
D) 15-degree lateral rotation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
When taking an AP projection of the proximal femur,the IR should be placed so that the:
A) superior margin is at the level of the greater trochanter.
B) superior margin is at the level of the anterior superior iliac spine.
C) superior margin is at the level of the iliac crest.
D) center is aligned to the midfemur.
A) superior margin is at the level of the greater trochanter.
B) superior margin is at the level of the anterior superior iliac spine.
C) superior margin is at the level of the iliac crest.
D) center is aligned to the midfemur.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



