Deck 8: Special Senses
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/128
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 8: Special Senses
1
Loss of the same side of the visual field of both eyes from damage to the visual cortex on one side only is called ________.
A) hemianopia
B) emmetropia
C) myopia
D) presbyopia
A) hemianopia
B) emmetropia
C) myopia
D) presbyopia
A
2
The overlapping of the two visual fields that provides for depth perception (3-D vision) results in ________.
A) accommodation
B) convergence
C) binocular vision
D) refraction
A) accommodation
B) convergence
C) binocular vision
D) refraction
C
3
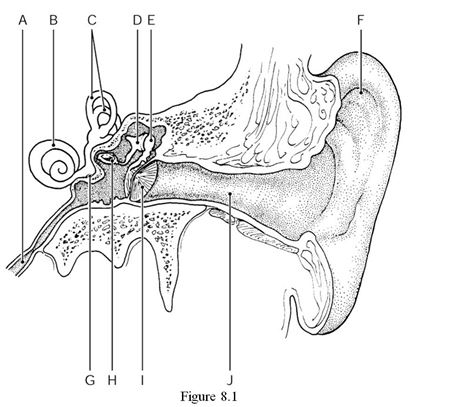
Using Figure 8.1, identify the following:
The tympanic membrane is indicated by ________.
A) Label F
B) Label D
C) Label H
D) Label I
E) Label J
D
4

Using Figure 8.1, identify the following:
The stapes (stirrup) is indicated by ________.
A) Label E
B) Label I
C) Label A
D) Label H
E) Label F

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The region of the optic nerve lacking photoreceptor cells is known as the ________.
A) retina
B) optic disc (blind spot)
C) choroid
D) iris
A) retina
B) optic disc (blind spot)
C) choroid
D) iris

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6

Using Figure 8.1, identify the following:
The pharyngotympanic (auditory) tube is indicated by ________.
A) Label J
B) Label A
C) Label I
D) Label F
E) Label D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7

Using Figure 8.1, identify the following:
The auricle (pinna) is indicated by ________.
A) Label F
B) Label E
C) Label J
D) Label A
E) Label B

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8

Using Figure 8.1, identify the following:
The malleus (hammer) is indicated by ________.
A) Label F
B) Label E
C) Label A
D) Label C
E) Label J

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The external acoustic meatus (auditory canal) is a narrow chamber situated in the ________ bone.
A) frontal
B) sphenoid
C) temporal
D) occipital
A) frontal
B) sphenoid
C) temporal
D) occipital

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The ability of the eye to focus on close objects is known as ________.
A) accommodation
B) refraction
C) binocular vision
D) inversion
A) accommodation
B) refraction
C) binocular vision
D) inversion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11

Using Figure 8.1, identify the following:
The cochlea is indicated by ________.
A) Label I
B) Label G
C) Label E
D) Label A
E) Label B

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The biconvex structure that focuses light on the retina is the ________.
A) cornea
B) pupil
C) lens
D) iris
A) cornea
B) pupil
C) lens
D) iris

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The gel-like substance housed in the posterior segment of the eye is the ________.
A) aqueous humor
B) lens
C) vitreous humor (body)
D) cornea
A) aqueous humor
B) lens
C) vitreous humor (body)
D) cornea

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The innermost sensory layer of the eye that contains bipolar cells and ganglion cells is the ________.
A) choroid
B) retina
C) sclera
D) cornea
A) choroid
B) retina
C) sclera
D) cornea

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The membrane that covers the outer surface of the eye and lines the eyelids is the ________.
A) choroid
B) sclera
C) conjunctiva
D) retina
A) choroid
B) sclera
C) conjunctiva
D) retina

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16

Using Figure 8.1, identify the following:
The semicircular canals are indicated by ________.
A) Label C
B) Label E
C) Label J
D) Label B
E) Label A

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The ________ gland is located above the lateral end of each eye and releases tears.
A) tarsal
B) ceruminous
C) lacrimal
D) ciliary
A) tarsal
B) ceruminous
C) lacrimal
D) ciliary

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Fibers from the medial side of each eye cross over to the opposite side of the brain at the ________.
A) convergence
B) optic radiation
C) optic tracts
D) optic chiasma
A) convergence
B) optic radiation
C) optic tracts
D) optic chiasma

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The fibrous covering of the eye consists of the white outer layer, known as the ________, and a transparent portion known as the ________.
A) sclera; cornea
B) conjunctiva; sclera
C) iris; pupil
D) pupil; cornea
A) sclera; cornea
B) conjunctiva; sclera
C) iris; pupil
D) pupil; cornea

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The structure that divides the outer ear from the middle ear is a membrane known as the ________.
A) tympanic membrane (ear drum)
B) auricle (pinna)
C) vestibule
D) cochlea
A) tympanic membrane (ear drum)
B) auricle (pinna)
C) vestibule
D) cochlea

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The five taste sensations are ________.
A) sweet, sour, bitter, salty, umami
B) sweet, sour, bitter, pasty, gritty
C) sweet, sour, chewy, gritty, greasy
D) sweet, salty, spicy, bitter, gritty
A) sweet, sour, bitter, salty, umami
B) sweet, sour, bitter, pasty, gritty
C) sweet, sour, chewy, gritty, greasy
D) sweet, salty, spicy, bitter, gritty

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which layer of the eye contains rods and cones?
A) sclera
B) retina
C) choroid
D) iris
E) optic nerve
A) sclera
B) retina
C) choroid
D) iris
E) optic nerve

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Tiny stones made of calcium salts that roll in response to changes in gravitational pull are called ________.
A) cupulae
B) otoliths
C) maculae
D) ossicles
A) cupulae
B) otoliths
C) maculae
D) ossicles

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The cochlear nerve transmits impulses to the auditory cortex located in the ________.
A) frontal lobe
B) parietal lobe
C) occipital lobe
D) temporal lobe
A) frontal lobe
B) parietal lobe
C) occipital lobe
D) temporal lobe

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
"Crossed eyes" resulting from unequal control of the external eye muscles is called ________.
A) anosmia
B) otosclerosis
C) strabismus
D) presbyopia
A) anosmia
B) otosclerosis
C) strabismus
D) presbyopia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The greatest visual acuity is housed in the ________.
A) optic disc
B) blind spot
C) ciliary body
D) vitreous humor
E) fovea centralis
A) optic disc
B) blind spot
C) ciliary body
D) vitreous humor
E) fovea centralis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The three cranial nerves that carry taste sensations to the brain are ________.
A) facial, glossopharyngeal, vagus
B) hypoglossal, glossopharyngeal, facial
C) abducens, trochlear, oculomotor
D) hypoglossal, vagus, trigeminal
A) facial, glossopharyngeal, vagus
B) hypoglossal, glossopharyngeal, facial
C) abducens, trochlear, oculomotor
D) hypoglossal, vagus, trigeminal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The rounded opening of the iris through which light enters the eye is called the ________.
A) choroid
B) cornea
C) conjunctiva
D) pupil
E) retina
A) choroid
B) cornea
C) conjunctiva
D) pupil
E) retina

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The function of the choroid layer of the eye is to ________.
A) release tears onto the anterior surface of the eye
B) refract light and focus it on the retina
C) regulate the amount of light entering the eye
D) produce gross eye movements
E) prevent light from scattering inside the eye
A) release tears onto the anterior surface of the eye
B) refract light and focus it on the retina
C) regulate the amount of light entering the eye
D) produce gross eye movements
E) prevent light from scattering inside the eye

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The transparent portion of the fibrous layer of the eye is the ________.
A) choroid
B) conjunctiva
C) cornea
D) retina
E) sclera
A) choroid
B) conjunctiva
C) cornea
D) retina
E) sclera

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
________ deafness arises when there is damage or degeneration of receptor cells in the spiral organ of Corti, cochlear nerve, or neurons in the auditory cortex of the brain.
A) Meniere's
B) Conduction
C) Sensorineural
D) Otosclerosis
A) Meniere's
B) Conduction
C) Sensorineural
D) Otosclerosis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Dynamic equilibrium receptors that detect information about angular or rotational movements of the head are housed in the ________.
A) cochlea
B) vestibule
C) semicircular canals
D) oval window
A) cochlea
B) vestibule
C) semicircular canals
D) oval window

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The pupil is an opening within the ________.
A) retina
B) iris
C) choroid
D) lens
E) sclera
A) retina
B) iris
C) choroid
D) lens
E) sclera

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Select the pathway along which images received by the retina of the eye will travel into the brain ________.
A) optic nerve, optic chiasma, optic tracts, thalamus, optic radiation, occipital lobe
B) cochlear nerve, optic disc, optic tracts, thalamus, temporal lobe
C) optic tracts, optic chiasma, optic nerve, thalamus, optic radiation, occipital lobe
D) optic nerve, optic radiation, optic tracts, hypothalamus, temporal lobe
E) vestibular nerve, optic disc, optic chiasma, optic tracts, thalamus, parietal lobe
A) optic nerve, optic chiasma, optic tracts, thalamus, optic radiation, occipital lobe
B) cochlear nerve, optic disc, optic tracts, thalamus, temporal lobe
C) optic tracts, optic chiasma, optic nerve, thalamus, optic radiation, occipital lobe
D) optic nerve, optic radiation, optic tracts, hypothalamus, temporal lobe
E) vestibular nerve, optic disc, optic chiasma, optic tracts, thalamus, parietal lobe

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which of the external eye muscles is controlled by cranial nerve VI (abducens)?
A) superior rectus
B) inferior rectus
C) lateral rectus
D) medial rectus
E) inferior oblique
A) superior rectus
B) inferior rectus
C) lateral rectus
D) medial rectus
E) inferior oblique

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The type of chemoreceptor responsible for our sense of smell is called a(n) ________.
A) static equilibrium receptor
B) olfactory receptor
C) dynamic equilibrium receptor
D) photoreceptor
A) static equilibrium receptor
B) olfactory receptor
C) dynamic equilibrium receptor
D) photoreceptor

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The small, peglike projections of the tongue's surface are called ________.
A) maculae
B) papillae
C) otoliths
D) basal cells
A) maculae
B) papillae
C) otoliths
D) basal cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
What gland releases tears onto the anterior surface of the eyeball?
A) ceruminous
B) sweat
C) mammary
D) lacrimal
E) tarsal
A) ceruminous
B) sweat
C) mammary
D) lacrimal
E) tarsal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The vibration of sound waves cause the tympanic membrane, or eardrum, to move against an ossicle known as ________.
A) malleus or hammer
B) incus or anvil
C) stapes or stirrup
D) otolith
A) malleus or hammer
B) incus or anvil
C) stapes or stirrup
D) otolith

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Vitamin A deficiency can lead to ________.
A) night blindness
B) presbyopia
C) cataracts
D) glaucoma
E) color blindness
A) night blindness
B) presbyopia
C) cataracts
D) glaucoma
E) color blindness

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The inability to see distant objects is termed "nearsighted" or ________.
A) emmetropia
B) hyperopia
C) myopia
D) astigmatism
E) presbyopia
A) emmetropia
B) hyperopia
C) myopia
D) astigmatism
E) presbyopia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Which one of the following correctly lists the order of the parts through which light passes as it enters the eye?
A) cornea, aqueous humor, lens, vitreous humor
B) aqueous humor, cornea, lens, vitreous humor
C) vitreous humor, lens, aqueous humor, cornea
D) cornea, lens, aqueous humor, vitreous humor
E) lens, aqueous humor, cornea, vitreous humor
A) cornea, aqueous humor, lens, vitreous humor
B) aqueous humor, cornea, lens, vitreous humor
C) vitreous humor, lens, aqueous humor, cornea
D) cornea, lens, aqueous humor, vitreous humor
E) lens, aqueous humor, cornea, vitreous humor

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The pigmented portion of the eye that has a rounded opening through which light passes is the ________.
A) iris
B) lens
C) cornea
D) sclera
E) retina
A) iris
B) lens
C) cornea
D) sclera
E) retina

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The aqueous humor of the eye is reabsorbed into venous blood through the ________.
A) inferior lacrimal canal
B) nasolacrimal duct
C) scleral venous sinus (canal of Schlemm)
D) ciliary body
E) pupil
A) inferior lacrimal canal
B) nasolacrimal duct
C) scleral venous sinus (canal of Schlemm)
D) ciliary body
E) pupil

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The gel-like substance that reinforces the eyeball and prevents it from collapsing inward is the ________.
A) aqueous humor
B) ciliary body
C) choroid
D) vitreous humor (vitreous body)
E) scleral venous sinus (canal of Schlemm)
A) aqueous humor
B) ciliary body
C) choroid
D) vitreous humor (vitreous body)
E) scleral venous sinus (canal of Schlemm)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Hair cells that function as hearing receptors are located within the ________.
A) auditory tube
B) spiral organ of Corti
C) oval window
D) auricle
E) ossicles
A) auditory tube
B) spiral organ of Corti
C) oval window
D) auricle
E) ossicles

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
An ear infection following an illness such as a cold can pass from the throat through the auditory (pharyngotympanic) tube to the ________.
A) eardrum
B) semicircular canals
C) inner ear
D) middle ear
E) outer ear
A) eardrum
B) semicircular canals
C) inner ear
D) middle ear
E) outer ear

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Which of the following is associated with the external (outer) ear?
A) auricle (pinna)
B) vestibule
C) semicircular canals
D) malleus
E) round window
A) auricle (pinna)
B) vestibule
C) semicircular canals
D) malleus
E) round window

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Hearing receptors within the spiral organ of Corti are called ________.
A) hair cells
B) rod cells
C) cone cells
D) Corti cells
E) ceruminous cells
A) hair cells
B) rod cells
C) cone cells
D) Corti cells
E) ceruminous cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Our sense of static equilibrium is created by the ________.
A) vibration of the tympanic membrane
B) movement of otoliths along hair cells
C) transmission of light through the lens
D) sound waves traveling through the cochlea
E) stimulation of hair cells in the spiral organ of Corti
A) vibration of the tympanic membrane
B) movement of otoliths along hair cells
C) transmission of light through the lens
D) sound waves traveling through the cochlea
E) stimulation of hair cells in the spiral organ of Corti

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Sound waves entering the external auditory canal hit the eardrum, also known as the ________.
A) tympanic membrane
B) pinna
C) auricle
D) oval window
E) ossicles
A) tympanic membrane
B) pinna
C) auricle
D) oval window
E) ossicles

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Static equilibrium receptors are located in the ________.
A) semicircular canals
B) auricle (pinna)
C) cochlea
D) tympanic membrane
E) vestibule
A) semicircular canals
B) auricle (pinna)
C) cochlea
D) tympanic membrane
E) vestibule

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The auditory ossicle called the "anvil" is also known as the ________.
A) malleus
B) incus
C) stapes
D) bony labyrinth
E) cochlea
A) malleus
B) incus
C) stapes
D) bony labyrinth
E) cochlea

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Identify the pathway of vibrations as they travel from the tympanic membrane to the ossicles ________.
A) malleus, incus, stapes
B) incus, malleus, stapes
C) stapes, incus, malleus
D) malleus, stapes, incus
E) stapes, malleus, incus
A) malleus, incus, stapes
B) incus, malleus, stapes
C) stapes, incus, malleus
D) malleus, stapes, incus
E) stapes, malleus, incus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Which area of the retina lacks rods and cones and therefore does not detect images?
A) optic disc (blind spot)
B) optic nerve
C) choroid
D) fovea centralis
E) ciliary body
A) optic disc (blind spot)
B) optic nerve
C) choroid
D) fovea centralis
E) ciliary body

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
What structure of the eye focuses light on the retina?
A) iris
B) sclera
C) lens
D) choroid
E) optic chiasma
A) iris
B) sclera
C) lens
D) choroid
E) optic chiasma

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Which of the following is a sex-linked condition that more often affects males?
A) conjunctivitis
B) color blindness
C) night blindness
D) glaucoma
E) cataracts
A) conjunctivitis
B) color blindness
C) night blindness
D) glaucoma
E) cataracts

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Dynamic equilibrium receptors are found in the ________.
A) cochlea
B) semicircular canals
C) malleus
D) oval window
E) vestibule
A) cochlea
B) semicircular canals
C) malleus
D) oval window
E) vestibule

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Eyes suddenly exposed to bright light experience ________.
A) convergence
B) accommodation pupillary reflex
C) photopupillary reflex
D) eyestrain
E) hemianopia
A) convergence
B) accommodation pupillary reflex
C) photopupillary reflex
D) eyestrain
E) hemianopia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The three sets of color receptors within the retina are sensitive to wavelengths of visible light that are ________.
A) red, green, and yellow
B) red, blue, and yellow
C) green, yellow, and purple
D) orange, green, and purple
E) blue, green, and red
A) red, green, and yellow
B) red, blue, and yellow
C) green, yellow, and purple
D) orange, green, and purple
E) blue, green, and red

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The normal resting eye is generally "set" for distant vision.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Which one of the following is NOT a primary taste sensation?
A) sweet
B) salty
C) pungent
D) bitter
E) sour
A) sweet
B) salty
C) pungent
D) bitter
E) sour

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Tarsal glands situated between the eyelashes release an oily secretion that lubricates the eye.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Gustatory hairs are to taste as olfactory hairs are to ________.
A) sight
B) hearing
C) dynamic equilibrium
D) smell
E) both hearing and dynamic equilibrium
A) sight
B) hearing
C) dynamic equilibrium
D) smell
E) both hearing and dynamic equilibrium

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
An astigmatism results from unequal curvatures of the cornea or lens.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The fusion of ear bones is known as ________.
A) hemianopia
B) strabismus
C) otosclerosis
D) presbycusis
E) otitis
A) hemianopia
B) strabismus
C) otosclerosis
D) presbycusis
E) otitis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The visual pathway carries images to the occipital lobe of the brain for visual interpretation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Cones are photoreceptor cells that allow us to see gray tones in dim light.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Which one of the following cranial nerves is NOT involved in either taste or smell?
A) facial nerve (VII)
B) vestibular (VIII)
C) glossopharyngeal (IX)
D) vagus (X)
E) olfactory nerve (I)
A) facial nerve (VII)
B) vestibular (VIII)
C) glossopharyngeal (IX)
D) vagus (X)
E) olfactory nerve (I)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
We cannot see images formed on the optic disc (blind spot).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The ciliary body is a smooth muscle structure to which the lens is attached.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Stimulation of sour receptors occurs in response to ________.
A) lemons
B) mushrooms
C) sugar
D) salt
E) saccharine
A) lemons
B) mushrooms
C) sugar
D) salt
E) saccharine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
The pupil is the circular opening in the iris through which light passes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The age-related condition resulting from decreased lens elasticity is known as ________.
A) hemianopia
B) strabismus
C) presbyopia
D) myopia
E) hyperopia
A) hemianopia
B) strabismus
C) presbyopia
D) myopia
E) hyperopia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Which one of the following nerves serves the anterior tongue?
A) cochlear
B) vestibular
C) glossopharyngeal
D) vagus
E) facial
A) cochlear
B) vestibular
C) glossopharyngeal
D) vagus
E) facial

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
The only special sense that is NOT fully functional at birth is ________.
A) taste
B) smell
C) vision
D) hearing
E) touch
A) taste
B) smell
C) vision
D) hearing
E) touch

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Which cranial nerve transmits hearing and equilibrium information to the brain?
A) abducens (VI)
B) oculomotor (III)
C) vestibulocochlear nerve (VIII)
D) trigeminal (V)
E) trochlear (IV)
A) abducens (VI)
B) oculomotor (III)
C) vestibulocochlear nerve (VIII)
D) trigeminal (V)
E) trochlear (IV)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Eye movements are controlled by the abducens, oculomotor, and trochlear nerves.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
The choroid consists of an outer, pigmented layer and an inner, neural layer which is home to rods and cones.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Sensorineural deafness occurs when there is damage or degeneration of receptor cells of the ________.
A) semicircular canals
B) otoliths
C) ossicles
D) spiral organ of Corti or cochlear nerve
E) round window
A) semicircular canals
B) otoliths
C) ossicles
D) spiral organ of Corti or cochlear nerve
E) round window

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



