Deck 15: The Urinary System
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/138
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 15: The Urinary System
1
Filtrate contains everything in blood plasma except for ________.
A) water
B) blood proteins
C) solutes
D) electrolytes
A) water
B) blood proteins
C) solutes
D) electrolytes
B
2
The medial indentation where the ureter, blood vessels, and nerves are connected to the kidney is called the ________.
A) renal capsule
B) renal column
C) renal pyramid
D) renal hilum
A) renal capsule
B) renal column
C) renal pyramid
D) renal hilum
D
3
The process that removes ions such as potassium and hydrogen from the blood and places them into the nephron for removal from the body as urine is known as ________.
A) glomerular filtration
B) tubular reabsorption
C) tubular secretion
D) osmosis
A) glomerular filtration
B) tubular reabsorption
C) tubular secretion
D) osmosis
C
4
The blood vessel carrying blood from the aorta into the kidney is the ________.
A) hepatic artery
B) renal artery
C) renal vein
D) glomerulus
A) hepatic artery
B) renal artery
C) renal vein
D) glomerulus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The functional unit of the kidney that filters blood and forms urine is the ________.
A) glomerulus
B) nephron
C) renal pyramid
D) renal pelvis
A) glomerulus
B) nephron
C) renal pyramid
D) renal pelvis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
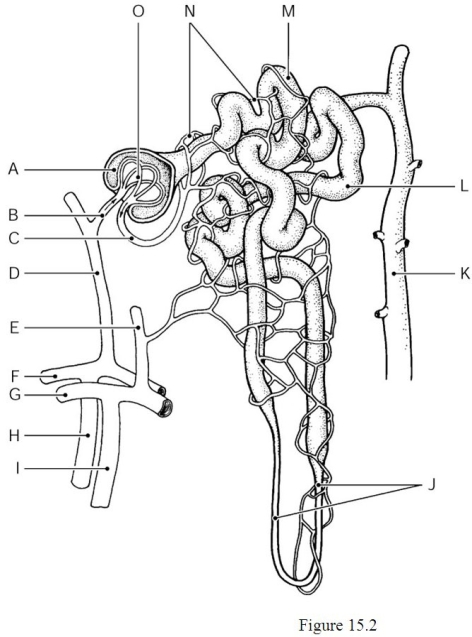
Using Figure 15.2, identify the following:
The nephron loop, or loop of Henle, is indicated by ________.
A) Label I
B) Label J
C) Label K
D) Label M
E) Label O

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7

Using Figure 15.2, identify the following:
The proximal convoluted tubule is indicated by ________.
A) Label M
B) Label N
C) Label O
D) Label I
E) Label F

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8

Using Figure 15.2, identify the following:
The peritubular capillaries are indicated by ________.
A) Label N
B) Label M
C) Label O
D) Label L
E) Label K

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9

Using Figure 15.2, identify the following:
The cortical radiate artery is indicated by ________.
A) Label E
B) Label A
C) Label I
D) Label M
E) Label D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10

Using Figure 15.2, identify the following:
The glomerulus is indicated by ________.
A) Label F
B) Label I
C) Label K
D) Label O
E) Label M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
There are three regions of the kidney; the outermost region is known as the ________.
A) renal medulla
B) renal cortex
C) renal pelvis
D) renal hilum
A) renal medulla
B) renal cortex
C) renal pelvis
D) renal hilum

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
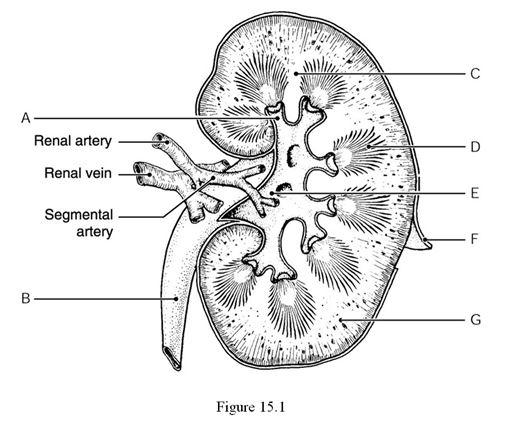
Using Figure 15.1, identify the following:
The renal pelvis is indicated by ________.
A) Label E
B) Label A
C) Label G
D) Label F
E) Label B

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13

Using Figure 15.2, identify the following:
The efferent arteriole is indicated by ________.
A) Label D
B) Label C
C) Label L
D) Label K
E) Label B

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Filtrate formed during glomerular filtration is captured by the ________.
A) renal pyramid
B) renal hilum
C) glomerular (Bowman's) capsule
D) renal column
A) renal pyramid
B) renal hilum
C) glomerular (Bowman's) capsule
D) renal column

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15

Using Figure 15.1, identify the following:
The renal cortex is indicated by ________.
A) Label F
B) Label G
C) Label D
D) Label E
E) Label A

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Renal (medullary) pyramids are separated by extensions of cortex-like tissue called the ________.
A) renal columns
B) renal pelvis
C) renal hilum
D) renal capsule
A) renal columns
B) renal pelvis
C) renal hilum
D) renal capsule

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17

Using Figure 15.1, identify the following:
A calyx is indicated by ________.
A) Label G
B) Label F
C) Label A
D) Label B
E) Label C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The blood vessel directly feeding the glomerulus with blood from the cortical radiate artery is the ________.
A) peritubular capillary
B) efferent arteriole
C) renal vein
D) afferent arteriole
A) peritubular capillary
B) efferent arteriole
C) renal vein
D) afferent arteriole

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19

Using Figure 15.2, identify the following:
The glomerular capsule (Bowman's capsule) is indicated by ________.
A) Label G
B) Label F
C) Label A
D) Label I
E) Label C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20

Using Figure 15.1, identify the following:
The ureter is indicated by ________.
A) Label E
B) Label A
C) Label G
D) Label F
E) Label B

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
A strong acid will dissociate and liberate more ________ ions in water than a weak acid.
A) bicarbonate
B) hydrogen
C) sodium
D) potassium
A) bicarbonate
B) hydrogen
C) sodium
D) potassium

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The inability to voluntarily control the external urethral sphincter is known as ________.
A) incontinence
B) urinary retention
C) urgency
D) hyperplasia
A) incontinence
B) urinary retention
C) urgency
D) hyperplasia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A feeling that it is necessary to void, which is experienced more regularly in the elderly, is known as ________.
A) urgency
B) nocturia
C) frequency
D) urethritis
A) urgency
B) nocturia
C) frequency
D) urethritis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which one of the following is NOT one of the functions of the kidneys?
A) manufacture urine
B) convert vitamin D from its inactive to its active form
C) dispose of metabolic waste products
D) produce hormones that assist in digestion
E) regulate blood volume
A) manufacture urine
B) convert vitamin D from its inactive to its active form
C) dispose of metabolic waste products
D) produce hormones that assist in digestion
E) regulate blood volume

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
About two-thirds of body fluid is found within living cells; this fluid is called the ________.
A) lymph
B) plasma
C) extracellular fluid or ECF
D) intracellular fluid or ICF
A) lymph
B) plasma
C) extracellular fluid or ECF
D) intracellular fluid or ICF

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The smooth triangular region of the urinary bladder base that is outlined by the openings of the two ureters and the urethra is called the ________.
A) trigone
B) calyx
C) pelvis
D) hilum
A) trigone
B) calyx
C) pelvis
D) hilum

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The kidneys can help maintain a rising blood pH by excreting ________ ions and reabsorbing ________ ions by the tubule cells.
A) bicarbonate; hydrogen
B) carbon dioxide; oxygen
C) ammonia; carbonic acid
D) hydrogen; bicarbonate
A) bicarbonate; hydrogen
B) carbon dioxide; oxygen
C) ammonia; carbonic acid
D) hydrogen; bicarbonate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which organ filters blood, regulates blood volume and chemical makeup?
A) kidney
B) ureter
C) liver
D) urinary bladder
E) urethra
A) kidney
B) ureter
C) liver
D) urinary bladder
E) urethra

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The process of emptying the urinary bladder is known as voiding or ________.
A) urgency
B) incontinence
C) micturition
D) nocturia
A) urgency
B) incontinence
C) micturition
D) nocturia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The involuntary sphincter that keeps the urethra closed when urine is not being passed is called the ________.
A) external urethral sphincter
B) internal anal sphincter
C) internal urethral sphincter
D) ileocecal sphincter
A) external urethral sphincter
B) internal anal sphincter
C) internal urethral sphincter
D) ileocecal sphincter

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The abnormal condition that results from the lack of ADH release, causing huge amounts of very dilute urine to be voided, is called ________.
A) diabetes insipidus
B) glomerulonephritis
C) diabetes mellitus
D) urethritis
A) diabetes insipidus
B) glomerulonephritis
C) diabetes mellitus
D) urethritis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Inflammation of the urethra is called ________.
A) pyelonephritis
B) urethritis
C) cystitis
D) glomerulonephritis
A) pyelonephritis
B) urethritis
C) cystitis
D) glomerulonephritis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The tube connecting each kidney to the urinary bladder is the ________.
A) urethra
B) calyx
C) ureter
D) ductus (vas) deferens
A) urethra
B) calyx
C) ureter
D) ductus (vas) deferens

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Highly sensitive cells within the hypothalamus that react to changes in blood composition and cause the release of antidiuretic hormone (ADH) when appropriate are called ________.
A) thermoreceptors
B) baroreceptors
C) mechanoreceptors
D) osmoreceptors
A) thermoreceptors
B) baroreceptors
C) mechanoreceptors
D) osmoreceptors

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Specific gravity is the term used to compare how much heavier urine is than ________.
A) distilled water
B) milk
C) saliva
D) blood
A) distilled water
B) milk
C) saliva
D) blood

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Arterial blood pH above 7.45 is considered to be ________.
A) acidosis
B) normal
C) alkalosis
D) physiological acidosis
A) acidosis
B) normal
C) alkalosis
D) physiological acidosis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The hormone released by the posterior pituitary to prevent excessive water loss in the urine is ________.
A) aldosterone
B) cortisol
C) antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
D) insulin
A) aldosterone
B) cortisol
C) antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
D) insulin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The need to urinate frequently at night, which plagues over 50% of the elderly, is called ________.
A) nocturia
B) incontinence
C) urgency
D) cystitis
A) nocturia
B) incontinence
C) urgency
D) cystitis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Untreated streptococcal infections in childhood that can lead to the kidney infection characterized by antigen-antibody complexes clogging the glomerular filters is known as ________.
A) cystitis
B) hypospadias
C) urethritis
D) glomerulonephritis
A) cystitis
B) hypospadias
C) urethritis
D) glomerulonephritis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The driving force for water intake is ________.
A) metabolism
B) the thirst mechanism
C) the renin-angiotensin mechanism
D) glomerular filtration
A) metabolism
B) the thirst mechanism
C) the renin-angiotensin mechanism
D) glomerular filtration

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Renal calculi can lead to ________.
A) hematuria
B) diabetes mellitus
C) bilirubinuria
D) ketonuria
E) hepatitis
A) hematuria
B) diabetes mellitus
C) bilirubinuria
D) ketonuria
E) hepatitis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The capillary bed surrounding the renal tubule is the ________.
A) afferent arteriole
B) segmental arteries
C) peritubular capillaries
D) cortical radiate arteries
E) glomerular capillaries
A) afferent arteriole
B) segmental arteries
C) peritubular capillaries
D) cortical radiate arteries
E) glomerular capillaries

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Which one of the following terms describes the location of the kidneys?
A) suprarenal
B) retroperineal
C) adrenal
D) intraperitoneal
E) retroperitoneal
A) suprarenal
B) retroperineal
C) adrenal
D) intraperitoneal
E) retroperitoneal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Most nephrons are located within the renal ________.
A) pelvis
B) calyces
C) medulla
D) pyramids
E) cortex
A) pelvis
B) calyces
C) medulla
D) pyramids
E) cortex

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The percentage of filtrate eventually reabsorbed into the bloodstream is closest to ________.
A) 10%
B) 25%
C) 50%
D) 80%
E) 99%
A) 10%
B) 25%
C) 50%
D) 80%
E) 99%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Items in the blood that are NOT filtered will travel from the glomerulus to the ________.
A) glomerular (Bowman's) capsule
B) afferent arteriole
C) efferent arteriole
D) proximal convoluted tubule
E) nephron loop (loop of Henle)
A) glomerular (Bowman's) capsule
B) afferent arteriole
C) efferent arteriole
D) proximal convoluted tubule
E) nephron loop (loop of Henle)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The nonselective, passive process performed by the glomerulus that forms blood plasma without blood proteins is called ________.
A) micturition
B) tubular secretion
C) glomerular filtration
D) tubular reabsorption
E) glomerular reabsorption
A) micturition
B) tubular secretion
C) glomerular filtration
D) tubular reabsorption
E) glomerular reabsorption

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Which one of the following substances is normally found in urine?
A) blood proteins
B) red blood cells
C) hemoglobin
D) white blood cells
E) creatinine
A) blood proteins
B) red blood cells
C) hemoglobin
D) white blood cells
E) creatinine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The triangular regions of the kidneys that are striped in appearance and separated by the renal columns are the ________.
A) renal cortex
B) renal fascia
C) renal (medullary) pyramids
D) renal pelvis
E) calyces
A) renal cortex
B) renal fascia
C) renal (medullary) pyramids
D) renal pelvis
E) calyces

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Dilute urine would have a specific gravity closest to ________.
A) 0.005
B) 1.001
C) 1.010
D) 1.020
E) 1.030
A) 0.005
B) 1.001
C) 1.010
D) 1.020
E) 1.030

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Determine the possible cause of bile pigments in the urine ________.
A) diabetes mellitus
B) kidney infection
C) hypertension
D) kidney stones
E) liver disease
A) diabetes mellitus
B) kidney infection
C) hypertension
D) kidney stones
E) liver disease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Which one of the following is NOT a substance typically reabsorbed by the tubules under normal healthy conditions?
A) glucose
B) urea
C) amino acids
D) sodium
E) water
A) glucose
B) urea
C) amino acids
D) sodium
E) water

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The portion of the renal tubule closest to the glomerulus is the ________.
A) collecting duct
B) proximal convoluted tubule (PCT)
C) glomerular (Bowman's) capsule
D) distal convoluted tubule (DCT)
E) nephron loop (loop of Henle)
A) collecting duct
B) proximal convoluted tubule (PCT)
C) glomerular (Bowman's) capsule
D) distal convoluted tubule (DCT)
E) nephron loop (loop of Henle)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
What region of the kidney is deep to the renal cortex?
A) renal fascia
B) renal medulla
C) renal column
D) calyx
E) renal hilum
A) renal fascia
B) renal medulla
C) renal column
D) calyx
E) renal hilum

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Nitrogenous waste products, such as urea and uric acid, are ________.
A) filtered and usually reabsorbed
B) filtered but poorly reabsorbed
C) not filtered
D) not filtered but often reabsorbed
E) only secreted
A) filtered and usually reabsorbed
B) filtered but poorly reabsorbed
C) not filtered
D) not filtered but often reabsorbed
E) only secreted

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
As venous blood is drained from the kidney, which path does it follow ________.
A) cortical radiate veins, arcuate veins, interlobar veins, renal vein
B) renal vein, interlobar veins, segmental veins, arcuate veins
C) arcuate veins, cortical radiate veins, interlobar veins, renal vein
D) renal vein, segmental veins, interlobar veins, arcuate veins, cortical radiate veins
E) cortical radiate veins, arcuate veins, interlobar veins, segmental veins, renal vein
A) cortical radiate veins, arcuate veins, interlobar veins, renal vein
B) renal vein, interlobar veins, segmental veins, arcuate veins
C) arcuate veins, cortical radiate veins, interlobar veins, renal vein
D) renal vein, segmental veins, interlobar veins, arcuate veins, cortical radiate veins
E) cortical radiate veins, arcuate veins, interlobar veins, segmental veins, renal vein

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Filtrate typically does NOT contain ________.
A) water
B) blood proteins
C) glucose
D) ions
E) amino acids
A) water
B) blood proteins
C) glucose
D) ions
E) amino acids

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Starting from the glomerular capsule, the correct order of the renal tubule regions is ________.
A) proximal convoluted tubule, distal convoluted tubule, nephron loop (loop of Henle)
B) distal convoluted tubule, nephron loop (loop of Henle), proximal convoluted tubule
C) nephron loop (loop of Henle), proximal convoluted tubule, distal convoluted tubule
D) proximal convoluted tubule, nephron loop (loop of Henle), distal convoluted tubule
E) distal convoluted tubule, proximal convoluted tubule, nephron loop (loop of Henle)
A) proximal convoluted tubule, distal convoluted tubule, nephron loop (loop of Henle)
B) distal convoluted tubule, nephron loop (loop of Henle), proximal convoluted tubule
C) nephron loop (loop of Henle), proximal convoluted tubule, distal convoluted tubule
D) proximal convoluted tubule, nephron loop (loop of Henle), distal convoluted tubule
E) distal convoluted tubule, proximal convoluted tubule, nephron loop (loop of Henle)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Of the capillary beds associated with each nephron, the one that is both fed and drained by arterioles is the ________.
A) peritubular capillaries
B) pyramidal capillaries
C) glomerulus
D) Henle capillaries
E) Bowman's capillaries
A) peritubular capillaries
B) pyramidal capillaries
C) glomerulus
D) Henle capillaries
E) Bowman's capillaries

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
In a 24-hour period, a typical volume of urine production is ________.
A) 0.5 L
B) 0.9 L
C) 1.4 L
D) 2.0 L
E) 3.4 L
A) 0.5 L
B) 0.9 L
C) 1.4 L
D) 2.0 L
E) 3.4 L

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Which of the following is the major stimulus for the thirst mechanism?
A) hunger
B) decreased urination
C) increased osmolarity of blood plasma
D) defecation
E) increased saliva production
A) hunger
B) decreased urination
C) increased osmolarity of blood plasma
D) defecation
E) increased saliva production

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Which one of the following is NOT one of the major roles of the kidneys in normal healthy adults?
A) excretion of nitrogen-containing wastes
B) maintenance of water balance of the blood
C) maintenance of electrolyte balance of the blood
D) conversion of ammonia to bicarbonate ion
E) ensuring proper blood pH
A) excretion of nitrogen-containing wastes
B) maintenance of water balance of the blood
C) maintenance of electrolyte balance of the blood
D) conversion of ammonia to bicarbonate ion
E) ensuring proper blood pH

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The voluntarily controlled sphincter fashioned by skeletal muscle at the point where the urethra passes through the pelvic floor is called the ________.
A) internal urethral sphincter
B) internal anal sphincter
C) external urethral sphincter
D) trigone
E) detrusor sphincter
A) internal urethral sphincter
B) internal anal sphincter
C) external urethral sphincter
D) trigone
E) detrusor sphincter

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
The main hormone that acts on the kidneys to regulate sodium ion concentration of the extracellullar fluid (ECF) is ________.
A) ADH
B) renin
C) secretin
D) aldosterone
E) epinephrine
A) ADH
B) renin
C) secretin
D) aldosterone
E) epinephrine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Why is the trigone of the urinary bladder clinically important?
A) The trigone is longer in males than in females.
B) Infections tend to persist in the trigone.
C) Females have a trigone but males lack the trigone.
D) The prostate gland is present in males in the trigone.
E) Both sperm and urine pass through the trigone in males.
A) The trigone is longer in males than in females.
B) Infections tend to persist in the trigone.
C) Females have a trigone but males lack the trigone.
D) The prostate gland is present in males in the trigone.
E) Both sperm and urine pass through the trigone in males.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
In males, the urethra is part of both the urinary system and ________.
A) endocrine system
B) digestive system
C) immune system
D) respiratory system
E) reproductive system
A) endocrine system
B) digestive system
C) immune system
D) respiratory system
E) reproductive system

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The urinary bladder is able to expand as urine accumulates within it due to the presence of ________.
A) simple squamous epithelium
B) transitional epithelium
C) stratified squamous epithelium
D) pseudostratified epithelium
E) sphincters
A) simple squamous epithelium
B) transitional epithelium
C) stratified squamous epithelium
D) pseudostratified epithelium
E) sphincters

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
In one 24-hour period, the kidneys of an average-sized healthy adult filter approximately ________ through their glomeruli into the tubules.
A) 10-15 liters of blood plasma
B) 50-75 liters of blood plasma
C) 100-125 liters of blood plasma
D) 150-180 liters of blood plasma
E) 200-240 liters of blood plasma
A) 10-15 liters of blood plasma
B) 50-75 liters of blood plasma
C) 100-125 liters of blood plasma
D) 150-180 liters of blood plasma
E) 200-240 liters of blood plasma

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Urine is transported from the urinary bladder to the outside of the body by the ________.
A) ureter
B) trigone
C) prostate gland
D) urethra
E) collecting duct
A) ureter
B) trigone
C) prostate gland
D) urethra
E) collecting duct

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
The average adult urinary bladder is moderately full with ________ of urine within it.
A) 100 mL
B) 500 mL
C) 1 liter
D) 2 liters
E) 1 gallon
A) 100 mL
B) 500 mL
C) 1 liter
D) 2 liters
E) 1 gallon

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
What role does angiotensin II play in restoring blood pressure to normal?
A) Angiotension II promotes tubular reabsorption of sodium from the filtrate.
B) Angiotensin II promotes tubular reabsorption of both sodium and water from the filtrate.
C) Angiotensin II causes blood vessels to vasoconstrict.
D) Angiotensin II promotes tubular reabsorption of water from the filtrate.
E) Angiotensin II causes blood vessels to vasodilate.
A) Angiotension II promotes tubular reabsorption of sodium from the filtrate.
B) Angiotensin II promotes tubular reabsorption of both sodium and water from the filtrate.
C) Angiotensin II causes blood vessels to vasoconstrict.
D) Angiotensin II promotes tubular reabsorption of water from the filtrate.
E) Angiotensin II causes blood vessels to vasodilate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Antidiuretic hormone prevents excessive water loss by promoting water reabsorption in the ________.
A) glomerulus
B) proximal convoluted tubule
C) distal convoluted tubule
D) collecting duct
E) urinary bladder
A) glomerulus
B) proximal convoluted tubule
C) distal convoluted tubule
D) collecting duct
E) urinary bladder

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Extracellular fluid is found everywhere in the body EXCEPT ________.
A) within living cells
B) blood plasma
C) interstitial fluid
D) cerebrospinal fluid
E) humors of the eye and lymph
A) within living cells
B) blood plasma
C) interstitial fluid
D) cerebrospinal fluid
E) humors of the eye and lymph

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The chemical buffer system that includes carbonic acid and its salt, which ties up the H⁺ released by strong acids, is called the ________.
A) phosphate buffer system
B) protein buffer system
C) ionic buffer system
D) bicarbonate buffer system
E) carbonic buffer system
A) phosphate buffer system
B) protein buffer system
C) ionic buffer system
D) bicarbonate buffer system
E) carbonic buffer system

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Which of these chemicals dissociates completely and liberates all the hydrogen ions when dissolved in water?
A) strong acids
B) weak acids
C) neutral substances
D) weak bases
E) strong bases
A) strong acids
B) weak acids
C) neutral substances
D) weak bases
E) strong bases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Who has the highest percentage of water in the body?
A) adult male
B) adult female
C) infant
D) elderly female
E) elderly male
A) adult male
B) adult female
C) infant
D) elderly female
E) elderly male

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
What stimulates the release of renin from the juxtaglomerular (JG) apparatus?
A) high blood pressure
B) high blood sodium levels
C) low blood pressure
D) low blood potassium levels
E) high blood volume
A) high blood pressure
B) high blood sodium levels
C) low blood pressure
D) low blood potassium levels
E) high blood volume

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Aldosterone does NOT directly or indirectly regulate ________.
A) sodium
B) chlorine
C) magnesium
D) potassium
E) glucose
A) sodium
B) chlorine
C) magnesium
D) potassium
E) glucose

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
The process of emptying the urinary bladder is referred to as voiding or ________.
A) nocturia
B) filtration
C) urethritis
D) incontinence
E) micturition
A) nocturia
B) filtration
C) urethritis
D) incontinence
E) micturition

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
The micturition reflex forces urine into the upper part of the ________.
A) urethra
B) ureter
C) urinary bladder
D) kidney
E) rectum
A) urethra
B) ureter
C) urinary bladder
D) kidney
E) rectum

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



