Deck 16: The Reproductive System
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/169
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 16: The Reproductive System
1
The gonads, or primary sex organs, produce sex cells, also known as ________.
A) zygotes
B) interstitial cells
C) gametes
D) spermatids
A) zygotes
B) interstitial cells
C) gametes
D) spermatids
C
2
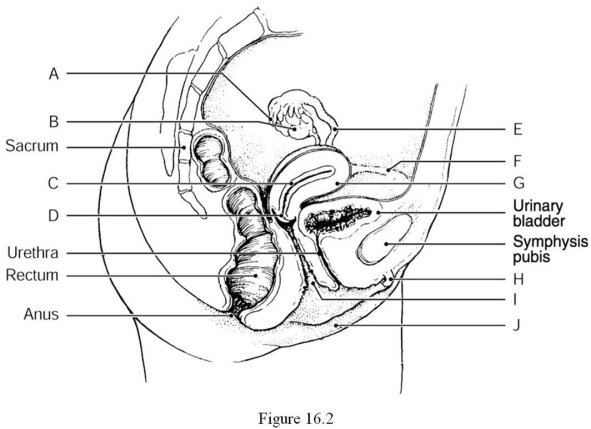
Using Figure 16.2, identify the following:
The ovary is indicated by ________.
A) Label J
B) Label H
C) Label I
D) Label A
E) Label B
E
3

Using Figure 16.2, identify the following:
The uterine (fallopian) tube is indicated by ________.
A) Label B
B) Label D
C) Label H
D) Label E
E) Label J
D
4

Using Figure 16.2, identify the following:
The myometrium of the uterus is indicated by ________.
A) Label C
B) Label I
C) Label H
D) Label G
E) Label F

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The female reproductive organs, known as ________, produce both eggs (ova) and hormones such as estrogen and progesterone.
A) follicles
B) uterine (fallopian) tubes
C) testes
D) ovaries
A) follicles
B) uterine (fallopian) tubes
C) testes
D) ovaries

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
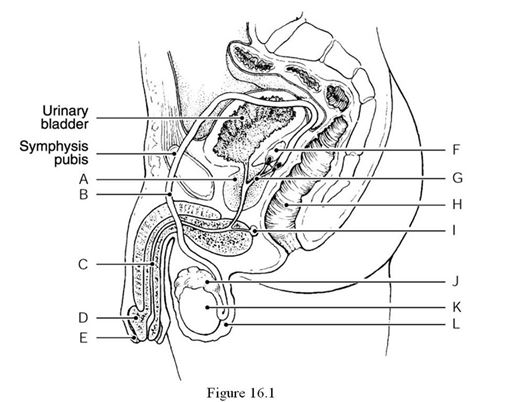
Using Figure 16.1, identify the following:
The epididymis is indicated by ________.
A) Label J
B) Label K
C) Label L
D) Label A
E) Label B

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following is suitable for the fertilization of an egg?
A) sperm
B) spermatid
C) primary spermatocyte
D) spermatogonium
A) sperm
B) spermatid
C) primary spermatocyte
D) spermatogonium

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8

Using Figure 16.1, identify the following:
The urethra is indicated by ________.
A) Label C
B) Label D
C) Label B
D) Label A
E) Label F

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Sperm are formed in tightly coiled tubes called seminiferous tubules that are found within each ________.
A) spermatic cord
B) testis
C) ductus deferens
D) epididymis
A) spermatic cord
B) testis
C) ductus deferens
D) epididymis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which gland surrounds the upper portion of the urethra just below the junction with the urinary bladder?
A) ejaculatory
B) seminal vesicles
C) bulbourethral
D) prostate
A) ejaculatory
B) seminal vesicles
C) bulbourethral
D) prostate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following is NOT a role of semen?
A) Semen dilutes sperm.
B) The acidity of semen helps neutralize the pH environment of a female's vagina.
C) Semen contains enzymes that enhance sperm motility.
D) Semen contains antibiotic chemicals that destroy bacteria.
A) Semen dilutes sperm.
B) The acidity of semen helps neutralize the pH environment of a female's vagina.
C) Semen contains enzymes that enhance sperm motility.
D) Semen contains antibiotic chemicals that destroy bacteria.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12

Using Figure 16.1, identify the following:
The testis is indicated by ________.
A) Label L
B) Label J
C) Label I
D) Label K
E) Label C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
What is the enlarged tip of the penis called?
A) glans penis
B) shaft
C) scrotum
D) prepuce (foreskin)
A) glans penis
B) shaft
C) scrotum
D) prepuce (foreskin)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14

Using Figure 16.1, identify the following:
The prostate gland is indicated by ________.
A) Label E
B) Label D
C) Label A
D) Label B
E) Label G

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which glands produce a thick, yellowish secretion which nourishes and activates sperm?
A) bulbourethral glands
B) prostate
C) seminal vesicles
D) ejaculatory duct
A) bulbourethral glands
B) prostate
C) seminal vesicles
D) ejaculatory duct

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The helmet-like region of the sperm that is similar to a large lysosome and assists penetration of the egg is called the ________.
A) flagellum
B) midpiece
C) spermatid
D) acrosome
A) flagellum
B) midpiece
C) spermatid
D) acrosome

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which process streamlines spermatids into sperm?
A) mitosis
B) spermiogenesis
C) oogenesis
D) spermatogenesis
A) mitosis
B) spermiogenesis
C) oogenesis
D) spermatogenesis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18

Using Figure 16.2, identify the following:
The vaginal orifice is indicated by ________.
A) Label I
B) Label J
C) Label G
D) Label F
E) Label D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19

Using Figure 16.1, identify the following:
The ejaculatory duct is indicated by ________.
A) Label L
B) Label F
C) Label H
D) Label C
E) Label G

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20

Using Figure 16.2, identify the following:
The clitoris is indicated by ________.
A) Label C
B) Label I
C) Label G
D) Label F
E) Label H

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Ovulation occurs in response to the release of an anterior pituitary hormone known as ________ hormone.
A) antidiuretic
B) thyroid-stimulating
C) luteinizing
D) follicle-stimulating
A) antidiuretic
B) thyroid-stimulating
C) luteinizing
D) follicle-stimulating

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
What is the rounded region of the uterus that is superior to the entrance of the uterine tubes?
A) infundibulum
B) cervix
C) fundus
D) body
A) infundibulum
B) cervix
C) fundus
D) body

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A fertilized egg, which represents the first cell of a new individual, is called a(n) ________.
A) blastocyst
B) zygote
C) fetus
D) embryo
A) blastocyst
B) zygote
C) fetus
D) embryo

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
What is the fatty, rounded area overlying the pubic symphysis of a female?
A) vestibule
B) perineum
C) mons pubis
D) vulva
A) vestibule
B) perineum
C) mons pubis
D) vulva

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
What is the process by which the acrosome membranes of sperm break down and release enzymes that digest holes in the surrounding oocyte membrane?
A) the acrosomal reaction
B) cleavage
C) ovulation
D) implantation
A) the acrosomal reaction
B) cleavage
C) ovulation
D) implantation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The external genitalia of a female are also known as the ________.
A) clitoris
B) vestibule
C) vulva
D) perineum
A) clitoris
B) vestibule
C) vulva
D) perineum

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The ducts or tubes responsible for receiving the ovulated oocyte and providing the site for fertilization are the ________.
A) uterine (fallopian) tubes
B) vagina
C) ductus deferens
D) uterus
A) uterine (fallopian) tubes
B) vagina
C) ductus deferens
D) uterus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Upon fertilization, an oocyte completes its second meiotic division and produces ________.
A) the corona radiata and a polar body
B) the morula and blastocyst
C) the ovum and another polar body
D) the primary oocyte and secondary oocyte
A) the corona radiata and a polar body
B) the morula and blastocyst
C) the ovum and another polar body
D) the primary oocyte and secondary oocyte

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
A mature ovarian follicle that is ready to be ejected from an ovary is called a(n) ________.
A) primary oocyte
B) vesicular (Graafian) follicle
C) ovum
D) corpus luteum
A) primary oocyte
B) vesicular (Graafian) follicle
C) ovum
D) corpus luteum

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Burrowing of the fertilized egg into the endometrium lining of the uterus is called ________.
A) ovulation
B) implantation
C) cleavage
D) fertilization
A) ovulation
B) implantation
C) cleavage
D) fertilization

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
An oocyte is viable up to ________ hours after ovulation.
A) 2
B) 24
C) 48
D) 104
A) 2
B) 24
C) 48
D) 104

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The process of creating female gametes is called ________.
A) spermatogenesis
B) oogenesis
C) spermiogenesis
D) cleavage
A) spermatogenesis
B) oogenesis
C) spermiogenesis
D) cleavage

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which hormone promotes a small number of primary follicles within the ovary to grow and mature each month?
A) luteinizing hormone (LH)
B) estrogen
C) follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)
D) testosterone
A) luteinizing hormone (LH)
B) estrogen
C) follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)
D) testosterone

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which hormone is produced by the corpus luteum that helps maintain pregnancy?
A) estrogen
B) testosterone
C) progesterone
D) relaxin
A) estrogen
B) testosterone
C) progesterone
D) relaxin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The pigmented area of a female's breast that surrounds the nipple is the ________.
A) areola
B) lactiferous sinus
C) lactiferous duct
D) lobule
A) areola
B) lactiferous sinus
C) lactiferous duct
D) lobule

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which ligament anchors the anterior portion of the uterus?
A) suspensory ligament
B) ovarian ligament
C) broad ligament
D) round ligament
A) suspensory ligament
B) ovarian ligament
C) broad ligament
D) round ligament

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Of the two functional areas of the blastocyst, which one gives rise to the three primary germ layers?
A) amnion
B) morula
C) inner cell mass
D) trophoblast
A) amnion
B) morula
C) inner cell mass
D) trophoblast

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which layer of the uterus is constructed of smooth muscle?
A) endometrium
B) perimetrium
C) myometrium
D) epimetrium
A) endometrium
B) perimetrium
C) myometrium
D) epimetrium

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Days 6-14 of the uterine (menstrual) cycle are known as the ________ phase. This phase concludes with ovulation.
A) secretory
B) luteal
C) proliferative
D) menstrual
A) secretory
B) luteal
C) proliferative
D) menstrual

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
What is the early stage of embryonic development during which rapid mitotic cell divisions occur as the zygote travels down the uterine (fallopian) tube?
A) the acrosomal reaction
B) cleavage
C) fertilization
D) implantation
A) the acrosomal reaction
B) cleavage
C) fertilization
D) implantation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
In what specific part of the male reproductive system do maturing sperm gain increased motility and their ability to swim?
A) seminiferous tubules
B) epididymis
C) ductus deferens
D) ejaculatory duct
E) urethra
A) seminiferous tubules
B) epididymis
C) ductus deferens
D) ejaculatory duct
E) urethra

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The male gonads have both sperm-producing and testosterone-producing functions and are called ________.
A) testes
B) sperm
C) ovaries
D) ovum
E) gametes
A) testes
B) sperm
C) ovaries
D) ovum
E) gametes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
What is removed during male circumcision?
A) glans penis
B) shaft of the penis
C) scrotum
D) prepuce
E) ductus deferens
A) glans penis
B) shaft of the penis
C) scrotum
D) prepuce
E) ductus deferens

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The placenta and its attached fetal membranes, expelled from the uterus during the placental stage of labor, are collectively referred to as ________.
A) the vertex position
B) the afterbirth
C) dystocia
D) parturition
A) the vertex position
B) the afterbirth
C) dystocia
D) parturition

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Which rare condition results in individuals who possess both ovarian and testicular tissues?
A) phimosis
B) cryptorchidism
C) hermaphroditism
D) orchiditis
A) phimosis
B) cryptorchidism
C) hermaphroditism
D) orchiditis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Trace the pathway of sperm through the duct system during ejaculation.
A) epididymis, ductus deferens, ejaculatory duct, urethra
B) epididymis, ductus deferens, seminiferous tubules, ejaculatory duct
C) seminiferous tubule, ductus deferens, epididymis, ejaculatory duct, urethra
D) epididymis, seminal vesicles, ductus deferens, ejaculatory duct, urethra
E) ductus deferens, epididymis, seminiferous tubule, urethra, seminal vesicles
A) epididymis, ductus deferens, ejaculatory duct, urethra
B) epididymis, ductus deferens, seminiferous tubules, ejaculatory duct
C) seminiferous tubule, ductus deferens, epididymis, ejaculatory duct, urethra
D) epididymis, seminal vesicles, ductus deferens, ejaculatory duct, urethra
E) ductus deferens, epididymis, seminiferous tubule, urethra, seminal vesicles

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Peristaltic waves squeeze sperm from the epididymis along to the outside of the male's body during ________.
A) vasectomy
B) circumcision
C) spermatogenesis
D) ejaculation
E) erection
A) vasectomy
B) circumcision
C) spermatogenesis
D) ejaculation
E) erection

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Which hormone causes pelvic ligaments and the pubic symphysis to relax, widen, and become more flexible during pregnancy?
A) estrogen
B) progesterone
C) relaxin
D) luteinizing hormone (LH)
A) estrogen
B) progesterone
C) relaxin
D) luteinizing hormone (LH)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Which gland produces thick, clear mucus that cleanses the penile urethra of acidic urine?
A) testes
B) seminal vesicles
C) prostate
D) bulbo-urethral glands
E) epididymis
A) testes
B) seminal vesicles
C) prostate
D) bulbo-urethral glands
E) epididymis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Which of the following is the exocrine function of the testes?
A) testosterone production
B) ovum fertilization
C) sperm production
D) embryo nutrition
E) estrogen production
A) testosterone production
B) ovum fertilization
C) sperm production
D) embryo nutrition
E) estrogen production

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The spongy tissue of the penis fills with blood during sexual excitement and causes the penis to enlarge and become rigid during ________.
A) erection
B) circumcision
C) ejaculation
D) emission
E) parturition
A) erection
B) circumcision
C) ejaculation
D) emission
E) parturition

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Which of the following connects the ampulla of the ductus deferens with the urethra?
A) ureter
B) ejaculatory duct
C) rete testis
D) epididymis
E) seminal vesicles
A) ureter
B) ejaculatory duct
C) rete testis
D) epididymis
E) seminal vesicles

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Where are androgens, such as testosterone, produced?
A) seminiferous tubules of the testis
B) interstitial cells of the testis
C) epididymis
D) bulbourethral glands
E) prostate
A) seminiferous tubules of the testis
B) interstitial cells of the testis
C) epididymis
D) bulbourethral glands
E) prostate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The series of events that expel the infant from the uterus are referred to collectively as ________.
A) labor
B) menarche
C) menstruation
D) menopause
A) labor
B) menarche
C) menstruation
D) menopause

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Where are sperm produced within a male's testis?
A) seminiferous tubules
B) ejaculatory duct
C) interstitial cells
D) rete testis
E) lobules
A) seminiferous tubules
B) ejaculatory duct
C) interstitial cells
D) rete testis
E) lobules

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
What is the distal portion of the male urethra that runs the length of the penis?
A) prostatic urethra
B) membranous urethra
C) spongy urethra
D) intermediate urethra
E) bulbourethra
A) prostatic urethra
B) membranous urethra
C) spongy urethra
D) intermediate urethra
E) bulbourethra

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
During which stage of labor does the cervix soften, efface, and dilate?
A) dilation stage
B) parturition stage
C) placental stage
D) expulsion stage
A) dilation stage
B) parturition stage
C) placental stage
D) expulsion stage

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The period of life between 10 and 15 years of age is known as ________. It is during this time that the reproductive organs grow to their adult size and become functional under the influence of hormones.
A) adulthood
B) menarche
C) puberty
D) menopause
A) adulthood
B) menarche
C) puberty
D) menopause

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
What is the function of the milky-colored fluids secreted from the prostate?
A) enable sperm to swim
B) activate sperm
C) cleanse the urethra
D) neutralize urine
E) begin spermatogenesis
A) enable sperm to swim
B) activate sperm
C) cleanse the urethra
D) neutralize urine
E) begin spermatogenesis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Which one of the following is NOT a component of semen?
A) sperm
B) seminal fluid
C) prostatic fluid
D) bulbourethral fluid
E) epididymal fluid
A) sperm
B) seminal fluid
C) prostatic fluid
D) bulbourethral fluid
E) epididymal fluid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The entire process of spermatogenesis takes approximately ________.
A) 25-50 days
B) 64-72 days
C) 120 days
D) 1 year
E) 15 years
A) 25-50 days
B) 64-72 days
C) 120 days
D) 1 year
E) 15 years

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Which of the following cells could be fertilized?
A) polar body
B) primary oocyte
C) secondary oocyte
D) oogonium
E) corpus luteum
A) polar body
B) primary oocyte
C) secondary oocyte
D) oogonium
E) corpus luteum

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
During oogenesis, an oogonium directly gives rise to ________.
A) an ovum
B) a primary oocyte
C) a secondary oocyte
D) a first polar body
E) a second polar body
A) an ovum
B) a primary oocyte
C) a secondary oocyte
D) a first polar body
E) a second polar body

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
What results from spermiogenesis?
A) four spermatogonia
B) four spermatids
C) two sperm
D) two spermatids
E) four sperm
A) four spermatogonia
B) four spermatids
C) two sperm
D) two spermatids
E) four sperm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Which of the following does NOT occur during puberty in a female?
A) increased fat deposits beneath the skin
B) onset of menopause
C) widening and lightening of the pelvis
D) development of the breasts
E) appearance of axillary and pubic hair
A) increased fat deposits beneath the skin
B) onset of menopause
C) widening and lightening of the pelvis
D) development of the breasts
E) appearance of axillary and pubic hair

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The inner mucosal layer of the uterus that is sloughed off approximately every 28 days is called the ________.
A) endometrium
B) myometrium
C) perimetrium
D) epimetrium
E) hypometrium
A) endometrium
B) myometrium
C) perimetrium
D) epimetrium
E) hypometrium

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
How many chromosomes do each sperm and each ovum have?
A) 23 pairs of chromosomes
B) 23 chromosomes
C) 46 pairs of chromosomes
D) 46 chromosomes
E) 2n chromosomes
A) 23 pairs of chromosomes
B) 23 chromosomes
C) 46 pairs of chromosomes
D) 46 chromosomes
E) 2n chromosomes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Which one of the following is NOT one of the secondary sex characteristics typical of males?
A) deepening voice
B) increased growth of body hair
C) enlargement of skeletal muscle mass
D) development of breast tissue
E) thickening of bones
A) deepening voice
B) increased growth of body hair
C) enlargement of skeletal muscle mass
D) development of breast tissue
E) thickening of bones

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
What effect does luteinizing hormone (LH) have on a female?
A) LH promotes enlargement of the female's breasts.
B) LH has no effect on a female.
C) LH causes secondary sex characteristics to develop in a female.
D) LH stimulates primary follicles in a female's ovary to grow each month.
E) LH triggers ovulation in a female.
A) LH promotes enlargement of the female's breasts.
B) LH has no effect on a female.
C) LH causes secondary sex characteristics to develop in a female.
D) LH stimulates primary follicles in a female's ovary to grow each month.
E) LH triggers ovulation in a female.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Which layer of the uterus serves as the site of implantation?
A) fundus
B) cervix
C) myometrium
D) endometrium
E) perimetrium
A) fundus
B) cervix
C) myometrium
D) endometrium
E) perimetrium

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The process by which a mature egg is ejected from the ovary is called ________.
A) emission
B) menses
C) fertilization
D) ovulation
E) parturition
A) emission
B) menses
C) fertilization
D) ovulation
E) parturition

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Which of the following cells undergoes meiosis to produce four sperm?
A) spermatids
B) spermatogonium
C) primary spermatocyte
D) ovum
E) zygote
A) spermatids
B) spermatogonium
C) primary spermatocyte
D) ovum
E) zygote

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Which portion of the sperm houses the nucleus and its DNA?
A) midpiece
B) flagellum
C) head
D) tail
E) acrosome
A) midpiece
B) flagellum
C) head
D) tail
E) acrosome

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Which of the following is responsible for secondary sex characteristics in females?
A) estrogens
B) progesterone
C) follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)
D) human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG)
E) testosterone
A) estrogens
B) progesterone
C) follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)
D) human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG)
E) testosterone

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
What is NOT a True statement concerning the vagina?
A) The vagina serves as the birth canal.
B) The distal end of the vagina is partially enclosed by the hymen.
C) The vagina is the female organ of copulation.
D) The innermost lining of the vagina sloughs off periodically.
E) The vagina is situated between the rectum and urinary bladder.
A) The vagina serves as the birth canal.
B) The distal end of the vagina is partially enclosed by the hymen.
C) The vagina is the female organ of copulation.
D) The innermost lining of the vagina sloughs off periodically.
E) The vagina is situated between the rectum and urinary bladder.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
How long are the typical ovarian and uterine (menstrual) cycles in a female?
A) 7 days
B) 14 days
C) 28 days
D) 40 days
E) 60 days
A) 7 days
B) 14 days
C) 28 days
D) 40 days
E) 60 days

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
On which day of the female's uterine (menstrual) cycle does ovulation typically occur?
A) day 7
B) day 14
C) day 21
D) day 24
E) day 28
A) day 7
B) day 14
C) day 21
D) day 24
E) day 28

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
What effect does follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) have on males?
A) Male testes are not influenced by FSH.
B) FSH functions solely in females.
C) FSH stimulates sperm production in males.
D) FSH causes the testes to enlarge in size.
E) FSH stimulates estrogen production in males.
A) Male testes are not influenced by FSH.
B) FSH functions solely in females.
C) FSH stimulates sperm production in males.
D) FSH causes the testes to enlarge in size.
E) FSH stimulates estrogen production in males.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Where does fertilization usually occur?
A) ovary
B) vesicular (Graafian) follicle
C) uterine (fallopian) tubes
D) uterus
E) vagina
A) ovary
B) vesicular (Graafian) follicle
C) uterine (fallopian) tubes
D) uterus
E) vagina

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
The primitive stem cell of spermatogenesis, which is found on the periphery of each seminiferous tubule, is called a ________.
A) spermatogonium
B) spermatid
C) primary spermatocyte
D) secondary spermatocyte
E) sperm
A) spermatogonium
B) spermatid
C) primary spermatocyte
D) secondary spermatocyte
E) sperm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



