Deck 10: Aggregate Supply
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/156
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 10: Aggregate Supply
1
Suppose that the real wage remained the same from year 1 to 2, but the nominal wage increased from $20 to $24.How was the price level affected?
A) It rose by 25 percent.
B) It rose by 20 percent.
C) It fell by 20 percent.
D) It fell by 10 percent.
A) It rose by 25 percent.
B) It rose by 20 percent.
C) It fell by 20 percent.
D) It fell by 10 percent.
It rose by 20 percent.
2
What is the key resource underlying aggregate supply?
A) production incentives
B) labour
C) technology
D) natural resources
A) production incentives
B) labour
C) technology
D) natural resources
labour
3
What is the term for wages in dollars as measured by the amount of goods and services that the dollars buy?
A) real wages
B) inflationary wages
C) nominal wages
D) normal wages
A) real wages
B) inflationary wages
C) nominal wages
D) normal wages
real wages
4
What does potential output represent?
A) the amount produced when firms' and workers' expectations about the price level are realized
B) the amount produced when the actual price level is higher than workers expected
C) the amount produced when firms and workers have the same expectations about the price level
D) the amount produced when the actual price level remains constant
A) the amount produced when firms' and workers' expectations about the price level are realized
B) the amount produced when the actual price level is higher than workers expected
C) the amount produced when firms and workers have the same expectations about the price level
D) the amount produced when the actual price level remains constant

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Suppose the price level rises by 5 percent and the nominal wage rises by 3 percent.How is the real wage affected?
A) It falls by 8 percent.
B) It falls by 2 percent.
C) It rises by 8 percent.
D) It rises by 2 percent.
A) It falls by 8 percent.
B) It falls by 2 percent.
C) It rises by 8 percent.
D) It rises by 2 percent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Suppose the economy is at its potential output level.Which of the following best characterizes the unemployment rate?
A) It is at the natural rate.
B) It is greater than its natural rate.
C) It is less than its natural rate.
D) It would include only those people who do NOT have enough work.
A) It is at the natural rate.
B) It is greater than its natural rate.
C) It is less than its natural rate.
D) It would include only those people who do NOT have enough work.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following characterizes the relationship between wages and inflation?
A) During periods of low inflation, real wages are constant and nominal wages decline.
B) During periods of high inflation, real wages increase more than nominal wages.
C) During periods of inflation, real wages will change if nominal wages are constant.
D) During periods with a constant inflation rate, real wages will NOT change unless nominal wages do.
A) During periods of low inflation, real wages are constant and nominal wages decline.
B) During periods of high inflation, real wages increase more than nominal wages.
C) During periods of inflation, real wages will change if nominal wages are constant.
D) During periods with a constant inflation rate, real wages will NOT change unless nominal wages do.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
What does the real wage represent?
A) the quantity of goods and services a worker can purchase in exchange for performing work
B) the dollar value of the goods and services a worker can purchase in exchange for performing work
C) a worker's nominal wage minus taxes paid on wages
D) the actual amount of income a worker receives after deductions for such things as taxes and insurance
A) the quantity of goods and services a worker can purchase in exchange for performing work
B) the dollar value of the goods and services a worker can purchase in exchange for performing work
C) a worker's nominal wage minus taxes paid on wages
D) the actual amount of income a worker receives after deductions for such things as taxes and insurance

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
How is nominal wage measured?
A) in constant dollars
B) in terms of the goods it can buy
C) in terms of the goods and services it can buy
D) in current dollars rather than in constant dollars
A) in constant dollars
B) in terms of the goods it can buy
C) in terms of the goods and services it can buy
D) in current dollars rather than in constant dollars

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
What does the nominal wage represent?
A) the quantity of goods and services a worker can purchase in exchange for performing work
B) the dollar value of the goods and services a worker can purchase in exchange for performing work
C) a worker's real wages minus taxes paid on wages
D) a worker's real wages divided by the price level
A) the quantity of goods and services a worker can purchase in exchange for performing work
B) the dollar value of the goods and services a worker can purchase in exchange for performing work
C) a worker's real wages minus taxes paid on wages
D) a worker's real wages divided by the price level

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Why is the expected price level significant?
A) because it is the equilibrium price level in the short run
B) because it determines the actual price level in the short run
C) because it determines the actual price level in the long run
D) because firms and resource owners make long-term agreements based on the expected price level
A) because it is the equilibrium price level in the short run
B) because it determines the actual price level in the short run
C) because it determines the actual price level in the long run
D) because firms and resource owners make long-term agreements based on the expected price level

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following characterizes the relationship between real wages and nominal wages?
A) The real wage will be constant only if the inflation rate is constant.
B) Changes in the nominal wage will be the same as changes in the real wage only if the price level is constant.
C) The real wage will be constant only if the price level is constant.
D) The real wage will be constant only if the nominal wage is constant.
A) The real wage will be constant only if the inflation rate is constant.
B) Changes in the nominal wage will be the same as changes in the real wage only if the price level is constant.
C) The real wage will be constant only if the price level is constant.
D) The real wage will be constant only if the nominal wage is constant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following characterizes an economy that is at its potential output level?
A) Firms' and workers' expectations about the price level are NOT realized.
B) The nominal wage is NOT a good measure of the expected real wage.
C) The unemployment rate is about 2 percent.
D) The economy is producing its minimum sustainable output.
A) Firms' and workers' expectations about the price level are NOT realized.
B) The nominal wage is NOT a good measure of the expected real wage.
C) The unemployment rate is about 2 percent.
D) The economy is producing its minimum sustainable output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Suppose the economy is at its potential output level.Which of the following best characterizes how the economy is producing?
A) The economy is producing less than it is capable of producing.
B) The economy is producing the maximum it can produce given resource constraints.
C) The economy is producing beyond its productive capacity.
D) The economy is producing at its minimum capacity.
A) The economy is producing less than it is capable of producing.
B) The economy is producing the maximum it can produce given resource constraints.
C) The economy is producing beyond its productive capacity.
D) The economy is producing at its minimum capacity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Other things constant, what relationship is expressed by aggregate supply?
A) the relationship between the price level in the economy and the aggregate output that firms will produce
B) the relationship between the price level and the aggregate amount that people will buy at that price level
C) the relationship between the price level and the potential amount of output
D) the relationship between the quantity of output that will be produced and that which will be sold in a one-year period
A) the relationship between the price level in the economy and the aggregate output that firms will produce
B) the relationship between the price level and the aggregate amount that people will buy at that price level
C) the relationship between the price level and the potential amount of output
D) the relationship between the quantity of output that will be produced and that which will be sold in a one-year period

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
What does the potential output of an economy represent?
A) the level of output produced when the real wage equals the nominal wage
B) the level of output produced when the price level is constant
C) the level of output produced when the expected price level equals the unemployment rate
D) the level of output produced when the expected price level equals the actual price level
A) the level of output produced when the real wage equals the nominal wage
B) the level of output produced when the price level is constant
C) the level of output produced when the expected price level equals the unemployment rate
D) the level of output produced when the expected price level equals the actual price level

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following describes the short-run aggregate supply curve?
A) It shows an inverse relationship between the price level and real GDP.
B) It shows the relationship between the price of labour and the aggregate quantity of labour that workers supply, other things constant.
C) It shows the relationship between the interest rate and the quantity of capital goods that firms supply, other things constant.
D) It shows the relationship between the price level and the quantity of aggregate output that firms supply, other things constant.
A) It shows an inverse relationship between the price level and real GDP.
B) It shows the relationship between the price of labour and the aggregate quantity of labour that workers supply, other things constant.
C) It shows the relationship between the interest rate and the quantity of capital goods that firms supply, other things constant.
D) It shows the relationship between the price level and the quantity of aggregate output that firms supply, other things constant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Suppose that the real wage remained unchanged between year 1 and 2 but the nominal wage was $20 in year 1 and $18 in year 2.How was the price level affected?
A) It rose by 20 percent.
B) It rose by 25 percent.
C) It fell by 10 percent.
D) It fell by 20 percent.
A) It rose by 20 percent.
B) It rose by 25 percent.
C) It fell by 10 percent.
D) It fell by 20 percent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Suppose the price level rises by 4 percent and the nominal wage rises 6 percent.How is the real wage affected?
A) It falls by 2 percent.
B) It falls by 10 percent.
C) It rises by 2 percent.
D) It rises by 10 percent.
A) It falls by 2 percent.
B) It falls by 10 percent.
C) It rises by 2 percent.
D) It rises by 10 percent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Who makes the billions of production decisions reflected in aggregate supply?
A) consumers
B) all households and firms
C) only the largest firms and the largest households
D) resource suppliers and firms
A) consumers
B) all households and firms
C) only the largest firms and the largest households
D) resource suppliers and firms

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which term refers to a wage rate above what is necessary to attract a sufficient number of workers?
A) market-clearing wage
B) efficiency wage
C) marginal productivity wage
D) minimum wage
A) market-clearing wage
B) efficiency wage
C) marginal productivity wage
D) minimum wage

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
In constructing the short-run aggregate supply curve, how would an economist define the short run?
A) a period during which the price level is constant
B) a period during which output is fixed
C) a period during which profit is constant
D) a period during which the costs of some resources are fixed
A) a period during which the price level is constant
B) a period during which output is fixed
C) a period during which profit is constant
D) a period during which the costs of some resources are fixed

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following best characterizes prices in the long run, but NOT in the short run?
A) All prices are flexible.
B) Prices are NOT flexible.
C) Some resource prices are fixed.
D) Only input prices are flexible.
A) All prices are flexible.
B) Prices are NOT flexible.
C) Some resource prices are fixed.
D) Only input prices are flexible.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Suppose the price level is rising faster than expected.Which of the following is among the reasons a firm would find it profitable to expand output in the short run?
A) All the firm's costs are contractually fixed.
B) Prices for the firm's output are rising with the price level.
C) The firm is interested in minimizing cost per unit, but NOT total profits.
D) All of the firm's costs are variable.
A) All the firm's costs are contractually fixed.
B) Prices for the firm's output are rising with the price level.
C) The firm is interested in minimizing cost per unit, but NOT total profits.
D) All of the firm's costs are variable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
What does the long-run equilibrium price level represent?
A) the price level the economy is expected to reach when the economy produces its potential output
B) the price level the economy is expected to reach when interest rates are stabilized
C) the price level the economy is expected to reach when the federal budget is balanced
D) the price level the economy is expected to reach when the discount rate equals the prime rate
A) the price level the economy is expected to reach when the economy produces its potential output
B) the price level the economy is expected to reach when interest rates are stabilized
C) the price level the economy is expected to reach when the federal budget is balanced
D) the price level the economy is expected to reach when the discount rate equals the prime rate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
What do fixed resource prices help explain?
A) why firms increase output in the short run when the price level increases
B) why firms keep production levels constant in the short run when the price level decreases
C) why firms sell output in the short run at fixed prices
D) why firms increase output in the long run when the price level increases
A) why firms increase output in the short run when the price level increases
B) why firms keep production levels constant in the short run when the price level decreases
C) why firms sell output in the short run at fixed prices
D) why firms increase output in the long run when the price level increases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
What types of unemployment can exist in an economy that is at its potential output level?
A) only cyclical unemployment
B) only structural unemployment
C) frictional, cyclical, and seasonal unemployment
D) frictional, seasonal, and structural unemployment
A) only cyclical unemployment
B) only structural unemployment
C) frictional, cyclical, and seasonal unemployment
D) frictional, seasonal, and structural unemployment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Suppose the actual price level exceeds the expected price level reflected in long-term contracts.How will firms respond?
A) Firms will find production more profitable than they had expected, and will increase the quantity of output supplied.
B) Firms will find production less profitable than they had expected, and will decrease the quantity of output supplied.
C) Firms will find production more profitable than they had expected, and will decrease the quantity of output supplied.
D) Firms will find production less profitable than they had expected, and will increase the quantity of output supplied.
A) Firms will find production more profitable than they had expected, and will increase the quantity of output supplied.
B) Firms will find production less profitable than they had expected, and will decrease the quantity of output supplied.
C) Firms will find production more profitable than they had expected, and will decrease the quantity of output supplied.
D) Firms will find production less profitable than they had expected, and will increase the quantity of output supplied.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Suppose the price level turns out to be higher than expected in the short run.Which of the following actions will businesses take?
A) Businesses will increase production.
B) Businesses will decrease production.
C) Initially, the short-run aggregate supply curve will shift rightward, but later an upward movement will occur along that curve.
D) Initially, the short-run aggregate supply curve will shift rightward, but later a downward movement will occur along that curve.
A) Businesses will increase production.
B) Businesses will decrease production.
C) Initially, the short-run aggregate supply curve will shift rightward, but later an upward movement will occur along that curve.
D) Initially, the short-run aggregate supply curve will shift rightward, but later a downward movement will occur along that curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
In theory what kind of unemployment can exist in the short run, but NOT in the long run?
A) seasonal unemployment
B) cyclical unemployment
C) structural unemployment
D) frictional unemployment
A) seasonal unemployment
B) cyclical unemployment
C) structural unemployment
D) frictional unemployment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
What is the definition of the short run?
A) a period of time when there is an expansionary gap and firms run their plants only for short periods
B) a period of up to one year long
C) a period of time when resource buyers and sellers can adjust fully to changes in the price level
D) a period of time during which resource buyers and sellers CANNOT adjust fully to changes in the price level
A) a period of time when there is an expansionary gap and firms run their plants only for short periods
B) a period of up to one year long
C) a period of time when resource buyers and sellers can adjust fully to changes in the price level
D) a period of time during which resource buyers and sellers CANNOT adjust fully to changes in the price level

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which of the following is NOT a factor in determining potential output?
A) the supply of labour
B) labour productivity
C) the technology in current use
D) the number of consumers in the market
A) the supply of labour
B) labour productivity
C) the technology in current use
D) the number of consumers in the market

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Suppose the economy is at its potential output level.Which of the following best describes the price level?
A) The actual price level is less than the expected price level.
B) The actual price level is greater than the expected price level.
C) The actual price level is the same as the expected price level.
D) The actual price level is NOT the same as its expected price level.
A) The actual price level is less than the expected price level.
B) The actual price level is greater than the expected price level.
C) The actual price level is the same as the expected price level.
D) The actual price level is NOT the same as its expected price level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Why might a rising price level in the short run create an incentive for firms to increase production?
A) because costs of production will increase
B) because total sales revenue will decrease
C) because profits will increase
D) because costs of production will increase faster than total revenue
A) because costs of production will increase
B) because total sales revenue will decrease
C) because profits will increase
D) because costs of production will increase faster than total revenue

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which of the following will cause potential output to decrease?
A) if the price level increases
B) if the price level decreases
C) if technological change increases labour productivity
D) if workers choose shorter work schedules in order to enjoy more leisure time
A) if the price level increases
B) if the price level decreases
C) if technological change increases labour productivity
D) if workers choose shorter work schedules in order to enjoy more leisure time

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Suppose the economy is producing below its potential output level.Which of the following characterizes the unemployment situation?
A) The actual unemployment rate would equal the natural rate.
B) No cyclical unemployment would occur.
C) Structural unemployment would be equal to zero.
D) Some cyclical unemployment would occur.
A) The actual unemployment rate would equal the natural rate.
B) No cyclical unemployment would occur.
C) Structural unemployment would be equal to zero.
D) Some cyclical unemployment would occur.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Some resource prices are assumed to be constant in the short run.How does this affect the shape of the short-run aggregate supply curve?
A) The aggregate supply curve is horizontal in the short run.
B) The aggregate supply curve is vertical in the short run.
C) The aggregate supply curve slopes upward in the short run.
D) The aggregate supply curve slopes downward in the short run.
A) The aggregate supply curve is horizontal in the short run.
B) The aggregate supply curve is vertical in the short run.
C) The aggregate supply curve slopes upward in the short run.
D) The aggregate supply curve slopes downward in the short run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Suppose the economy is producing beyond its potential output level.Which of the following best describes the state of the economy?
A) The economy is producing beyond the natural rate of unemployment.
B) The economy is producing at its maximum capacity.
C) The economy is producing less than its productive capacity.
D) The economy is producing at less than its natural rate of unemployment.
A) The economy is producing beyond the natural rate of unemployment.
B) The economy is producing at its maximum capacity.
C) The economy is producing less than its productive capacity.
D) The economy is producing at less than its natural rate of unemployment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Suppose workers are willing to work more hours when the nominal wage increases.Which of the following characterizes the economic rationality of their decision?
A) The decision is NOT economically rational, because it should be based on the real wage only.
B) The decision could be rational if workers thought that the inflation rate would fall in the future.
C) The decision could be rational if workers thought that the real wage had fallen.
D) The decision could be rational if workers thought that the nominal wage and the real wage were equal.
A) The decision is NOT economically rational, because it should be based on the real wage only.
B) The decision could be rational if workers thought that the inflation rate would fall in the future.
C) The decision could be rational if workers thought that the real wage had fallen.
D) The decision could be rational if workers thought that the nominal wage and the real wage were equal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
In constructing a short-run aggregate supply curve, what would an economist assume is the goal of business?
A) to maximize sales revenue
B) to maximize profit
C) to maximize growth in sales
D) to minimize cost
A) to maximize sales revenue
B) to maximize profit
C) to maximize growth in sales
D) to minimize cost

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
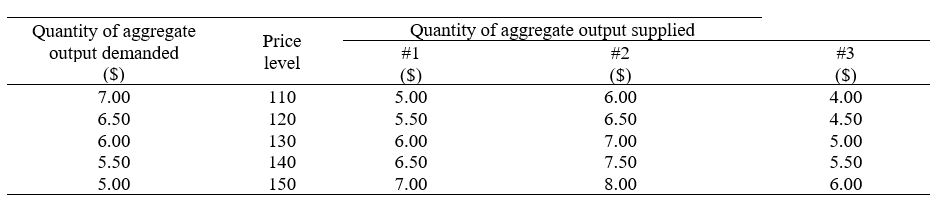
Refer to the table in the exhibit.Consider the aggregate demand and aggregate supply schedule #1.What is the equilibrium price level?
A) 110
B) 120
C) 130
D) 140

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Suppose nominal wage rates increase by 5 percent per year and the price level increases by 3 percent per year.How will real wages be affected?
A) Real wages will increase by 2 percent per year.
B) Real wages will increase by 3 percent per year.
C) Real wages will decrease by 2 percent per year.
D) Real wages will decrease by 3 percent per year.
A) Real wages will increase by 2 percent per year.
B) Real wages will increase by 3 percent per year.
C) Real wages will decrease by 2 percent per year.
D) Real wages will decrease by 3 percent per year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
On what does the steepness of the short-run aggregate supply curve primarily depend?
A) on the length of time for which resource prices are fixed
B) on the length of time for which output prices are fixed
C) on the difference between the expected price level and the actual price level
D) on how quickly production costs increase as output expands
A) on the length of time for which resource prices are fixed
B) on the length of time for which output prices are fixed
C) on the difference between the expected price level and the actual price level
D) on how quickly production costs increase as output expands

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44

Refer to the table in the exhibit.Consider the aggregate demand and aggregate supply schedule #1.What is the equilibrium level of output?
A) $5.00
B) $5.50
C) $6.00
D) $6.50

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
For the purpose of aggregate supply analysis, what is the definition of the long run?
A) the period of time during which aggregate supply adjusts to equal aggregate demand
B) the period of time during which excess aggregate demand is fulfilled
C) the period of time during which real wages are constant
D) the period of time during which all resource prices can be varied
A) the period of time during which aggregate supply adjusts to equal aggregate demand
B) the period of time during which excess aggregate demand is fulfilled
C) the period of time during which real wages are constant
D) the period of time during which all resource prices can be varied

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Suppose the actual price level exceeds the expected price level reflected in long-term contracts.How will unemployment be affected?
A) Unemployment will increase.
B) Unemployment will decrease.
C) Unemployment will stay the same.
D) Unemployment will become underemployment.
A) Unemployment will increase.
B) Unemployment will decrease.
C) Unemployment will stay the same.
D) Unemployment will become underemployment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Suppose the actual price level is less than the expected price level reflected in long-term contracts.How will profits and output be affected, all things equal?
A) Firms will find production more profitable than they had expected, and will increase the quantity of output supplied.
B) Firms will find production less profitable than they had expected, and will decrease the quantity of output supplied.
C) Firms, because they are making less profit than they had expected, will increase the quantity of output supplied.
D) Resource owners, because they are making a lower profit than they had expected, will decrease the quantity of output supplied.
A) Firms will find production more profitable than they had expected, and will increase the quantity of output supplied.
B) Firms will find production less profitable than they had expected, and will decrease the quantity of output supplied.
C) Firms, because they are making less profit than they had expected, will increase the quantity of output supplied.
D) Resource owners, because they are making a lower profit than they had expected, will decrease the quantity of output supplied.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48

Refer to the table in the exhibit.Consider the aggregate demand and the aggregate supply schedule #3.What is the equilibrium output level and price level?
A) Output is $6.50, and price level is 120.
B) Output is $6.00, and price level is 130.
C) Output is $5.00, and price level is 150.
D) Output is $5.50, and price level is 140.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
What relationship is illustrated by the aggregate supply curve?
A) the price of a particular good, and the quantity of that good supplied by all firms producing that good
B) the price of a particular good, and the quantity of that good supplied by the aggregate economy
C) the price level, and the quantity of all goods supplied in the economy
D) the price level, and the quantity purchased of all goods in the economy
A) the price of a particular good, and the quantity of that good supplied by all firms producing that good
B) the price of a particular good, and the quantity of that good supplied by the aggregate economy
C) the price level, and the quantity of all goods supplied in the economy
D) the price level, and the quantity purchased of all goods in the economy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Suppose the price level is lower than expected.How will this affect output?
A) Businesses will decrease production.
B) Businesses will increase production.
C) Initially, the short-run aggregate supply curve will shift leftward, but later the movement will be downward along the curve.
D) Initially, the short-run aggregate supply curve will shift leftward, but later the movement will be upward along the curve.
A) Businesses will decrease production.
B) Businesses will increase production.
C) Initially, the short-run aggregate supply curve will shift leftward, but later the movement will be downward along the curve.
D) Initially, the short-run aggregate supply curve will shift leftward, but later the movement will be upward along the curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Which of the following is fixed in the short run but NOT in the long run?
A) output
B) quantity of goods and services demanded
C) all input prices
D) at least one input price
A) output
B) quantity of goods and services demanded
C) all input prices
D) at least one input price

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Suppose the actual price level is below the expected price level.Given implicit or explicit resource price agreements, what effect will this have on the short-run aggregate supply curve?
A) The economy will move rightward along the short-run aggregate supply curve.
B) The economy will move leftward along the short-run aggregate supply curve.
C) The short-run aggregate supply curve will shift to the left.
D) The short-run aggregate supply curve will become flatter.
A) The economy will move rightward along the short-run aggregate supply curve.
B) The economy will move leftward along the short-run aggregate supply curve.
C) The short-run aggregate supply curve will shift to the left.
D) The short-run aggregate supply curve will become flatter.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Which of the following occurs as macroeconomic output expands in the short run?
A) The nominal cost of labour decreases.
B) The demand for nonlabour resources decreases.
C) Equipment wears out faster.
D) The nominal cost per unit of output falls.
A) The nominal cost of labour decreases.
B) The demand for nonlabour resources decreases.
C) Equipment wears out faster.
D) The nominal cost per unit of output falls.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Between 2004 and 2014, Jack's salary increased from $100,000 per year to $200,000 per year.The price index increased from 100 to 300 during the same period.Which statement best describes Jack's situation?
A) Jack's real income increased, and his money income decreased.
B) Jack's real income increased, and his money income increased.
C) Jack's real income decreased, and his money income decreased.
D) Jack's real income decreased, and his money income increased.
A) Jack's real income increased, and his money income decreased.
B) Jack's real income increased, and his money income increased.
C) Jack's real income decreased, and his money income decreased.
D) Jack's real income decreased, and his money income increased.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Why does the short-run aggregate supply curve slope upward?
A) because quantity supplied increases when cost per unit falls
B) because quantity supplied decreases when cost per unit falls
C) because quantity supplied increases when the price level increases
D) because quantity supplied increases when GDP decreases
A) because quantity supplied increases when cost per unit falls
B) because quantity supplied decreases when cost per unit falls
C) because quantity supplied increases when the price level increases
D) because quantity supplied increases when GDP decreases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Suppose nominal wage rates increase by 2 percent per year and the price level increases by 5 percent per year.How will real wages be affected?
A) Real wages will increase by 5 percent per year.
B) Real wages will increase by 3 percent per year.
C) Real wages will decrease by 5 percent per year.
D) Real wages will decrease by 3 percent per year.
A) Real wages will increase by 5 percent per year.
B) Real wages will increase by 3 percent per year.
C) Real wages will decrease by 5 percent per year.
D) Real wages will decrease by 3 percent per year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57

Refer to the table in the exhibit.Consider the aggregate demand and the aggregate supply schedule #2.What is the equilibrium output level and price level?
A) Output is $7.00, and price level is 110.
B) Output is $6.50, and price level is 120.
C) Output is $6.00, and price level is 130.
D) Output is $5.50, and price level is 140.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Suppose a firm is comparing its marginal revenue (MR) and marginal cost (MC).What circumstances would cause the firm to expand its production?
A) if MR is greater than MC
B) if MR is less than MC
C) if MR equals MC
D) if MR equals 0
A) if MR is greater than MC
B) if MR is less than MC
C) if MR equals MC
D) if MR equals 0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which of the following is NOT assumed to be constant along a short-run aggregate supply curve?
A) the actual price level
B) the state of technology
C) the size and quality of the labour force
D) the size and quality of the capital stock
A) the actual price level
B) the state of technology
C) the size and quality of the labour force
D) the size and quality of the capital stock

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Which pair of variables has a positive relationship in the short run?
A) inflation and unemployment
B) inflation and real GDP
C) the actual price level and aggregate quantity supplied
D) the actual price level and unemployment
A) inflation and unemployment
B) inflation and real GDP
C) the actual price level and aggregate quantity supplied
D) the actual price level and unemployment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Suppose the actual and expected price levels are initially equal, and the expected price level falls.Which of the following will occur over the long run?
A) The economy will move rightward along the short-run aggregate supply curve.
B) The economy will move leftward along the short-run aggregate supply curve.
C) The short-run aggregate supply curve will shift to the right.
D) The short-run aggregate supply curve will shift to the left.
A) The economy will move rightward along the short-run aggregate supply curve.
B) The economy will move leftward along the short-run aggregate supply curve.
C) The short-run aggregate supply curve will shift to the right.
D) The short-run aggregate supply curve will shift to the left.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
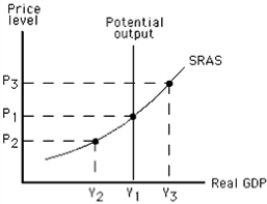
Refer to the graph in the exhibit.Suppose the actual price level exceeds the expected price level.What might the equilibrium output be in the short run?
A) Y₁
B) Y₂
C) Y3
D) 0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Suppose government does NOT intervene in the economy.How would an expansionary gap be closed in the long run?
A) by a rightward shift of the short-run aggregate supply curve
B) by a leftward shift of the short-run aggregate supply curve
C) by a movement to the right along a fixed short-run aggregate supply curve
D) by a movement to the left along a fixed short-run aggregate supply curve
A) by a rightward shift of the short-run aggregate supply curve
B) by a leftward shift of the short-run aggregate supply curve
C) by a movement to the right along a fixed short-run aggregate supply curve
D) by a movement to the left along a fixed short-run aggregate supply curve

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Suppose the economy is experiencing an expansionary gap.Which of the following will occur in the long run?
A) Workers will negotiate nominal wage increases that will shift the SRAS curve to the left.
B) Workers will negotiate nominal wage increases that will shift the SRAS curve to the right.
C) Employers will negotiate lower nominal wages, relative to prices, that will shift the SRAS curve to the right.
D) Employers will negotiate lower nominal wages, relative to prices, that will shift the SRAS curve to the left.
A) Workers will negotiate nominal wage increases that will shift the SRAS curve to the left.
B) Workers will negotiate nominal wage increases that will shift the SRAS curve to the right.
C) Employers will negotiate lower nominal wages, relative to prices, that will shift the SRAS curve to the right.
D) Employers will negotiate lower nominal wages, relative to prices, that will shift the SRAS curve to the left.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Suppose the expected price level falls below the actual price level.In terms of production, how will firms react?
A) They will increase production in the short run.
B) They will decrease production in the short run.
C) They will maintain production in the short run but will increase prices.
D) They will maintain production in the short run but will decrease prices.
A) They will increase production in the short run.
B) They will decrease production in the short run.
C) They will maintain production in the short run but will increase prices.
D) They will maintain production in the short run but will decrease prices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66

Refer to the graph in the exhibit.Which of the following would represent an expansionary gap?
A) Y₂ - Y₁
B) Y3 - Y₁
C) Y₂ - Y3
D) Y₂ + Y₁

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Suppose an expansionary gap is closed in the long run by firms' actions.How will output level and price level be affected?
A) Output will decrease and price level will increase.
B) Output will increase and price level will decrease.
C) Output will increase and price level will increase.
D) Output will decrease and price level will decrease.
A) Output will decrease and price level will increase.
B) Output will increase and price level will decrease.
C) Output will increase and price level will increase.
D) Output will decrease and price level will decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68

Refer to the graph in the exhibit.Suppose P₁ is the prevailing price level.Which of the following best describes the situation?
A) There is an expansionary gap.
B) The price level will decrease.
C) The expected price level is the same as the actual price level.
D) The unemployment rate is below the natural unemployment rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
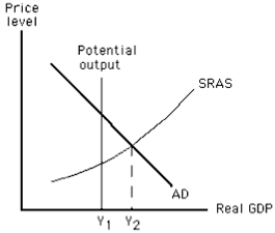
Refer to the graph in the exhibit.What is the term for the distance between Y₁ and Y₂?
A) an expansionary gap
B) a recessionary gap
C) an increase in potential output
D) the natural rate of unemployment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
How are prices and output affected when the long-run aggregate supply curve shifts left?
A) Prices increase and output increases.
B) Prices decrease and output decreases.
C) Prices increase and output decreases.
D) Prices decrease and output increases.
A) Prices increase and output increases.
B) Prices decrease and output decreases.
C) Prices increase and output decreases.
D) Prices decrease and output increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
What is an expansionary gap equal to?
A) real GDP minus nominal GDP
B) nominal GDP minus real GDP
C) actual short-run output minus potential output
D) the current period's nominal GDP minus the preceding period's nominal GDP
A) real GDP minus nominal GDP
B) nominal GDP minus real GDP
C) actual short-run output minus potential output
D) the current period's nominal GDP minus the preceding period's nominal GDP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72

Refer to the graph in the exhibit.Which of the following would represent a recessionary gap?
A) Y₁ - Y₂
B) Y₁ - Y₃
C) Y₂ - Y₃
D) Y₁ + Y₂

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Suppose an expansionary gap is closed in the long run.How will nominal GDP and real GDP be affected?
A) Nominal GDP will decline, and real GDP will decline.
B) Nominal GDP will increase, and real GDP will increase.
C) Nominal GDP will increase, but real GDP will decline.
D) Nominal GDP will decline, but real GDP will increase.
A) Nominal GDP will decline, and real GDP will decline.
B) Nominal GDP will increase, and real GDP will increase.
C) Nominal GDP will increase, but real GDP will decline.
D) Nominal GDP will decline, but real GDP will increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74

Refer to the graph in the exhibit.In this situation, how would long-run equilibrium be established?
A) by a decrease of short-run aggregate supply in order to close the expansionary gap
B) by an increase of short-run aggregate supply in order to close the expansionary gap
C) by a decrease of short-run aggregate supply in order to close the contractionary gap
D) by an increase of short-run aggregate supply in order to close the contractionary gap

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Which of the following shifts the short-run aggregate supply curve to the left?
A) an increase in the price level
B) an increase in the expected price level
C) an increase in the capital stock
D) an increase in interest rates
A) an increase in the price level
B) an increase in the expected price level
C) an increase in the capital stock
D) an increase in interest rates

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Suppose resource suppliers and demanders find out that their price expectations were wrong.What will occur when they take corrective actions?
A) The corrective actions will cause the economy to move away from the potential output level.
B) The corrective actions will raise the unemployment level above the natural rate of unemployment.
C) The corrective actions will shift the aggregate demand curve.
D) The corrective actions will shift the short-run aggregate supply curve.
A) The corrective actions will cause the economy to move away from the potential output level.
B) The corrective actions will raise the unemployment level above the natural rate of unemployment.
C) The corrective actions will shift the aggregate demand curve.
D) The corrective actions will shift the short-run aggregate supply curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Which of the following best describes how an economy overcomes an expansionary gap in the long run if the government does NOT intervene?
A) In the long run, this gap will be closed by an increase in aggregate demand.
B) In the long run, this gap will close when resource suppliers negotiate lower resource payments.
C) In the long run, this gap will close when the short-run aggregate supply curve shifts rightward.
D) In the long run, this gap will close when resource suppliers negotiate higher resource payments.
A) In the long run, this gap will be closed by an increase in aggregate demand.
B) In the long run, this gap will close when resource suppliers negotiate lower resource payments.
C) In the long run, this gap will close when the short-run aggregate supply curve shifts rightward.
D) In the long run, this gap will close when resource suppliers negotiate higher resource payments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78

Refer to the graph in the exhibit.Suppose the actual price level is lower than the expected price level.What might equilibrium output be in the short run?
A) Y₂
B) Y₁
C) Y₃
D) zero

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79

Refer to the graph in the exhibit.Suppose P₃ is the prevailing price level.How will prices be affected in the long run, assuming a hands-off policy by government?
A) The price level will rise.
B) The price level will fall.
C) The price level will remain the same.
D) The price level will first rise, and then fall.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Which of the following adjusts to bring aggregate supply and demand into balance?
A) the price level
B) the real rate of interest
C) the money supply
D) technology
A) the price level
B) the real rate of interest
C) the money supply
D) technology

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



