Deck 2: Patterns in the Skymotions of Earth and the Moon
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/65
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 2: Patterns in the Skymotions of Earth and the Moon
1
All stars denoted on the celestial sphere are:
A) equidistant from Earth.
B) actually planetary bodies of the solar system.
C) at varying distances from Earth.
D) not in the milky Way galaxy.
A) equidistant from Earth.
B) actually planetary bodies of the solar system.
C) at varying distances from Earth.
D) not in the milky Way galaxy.
at varying distances from Earth.
2
At a latitude of +50°,how far above the horizon is the north celestial pole?
A) 0°
B) 40°
C) 50°
D) 90°
A) 0°
B) 40°
C) 50°
D) 90°
50°
3
The shortest day of the year for a person living in the Northern Hemisphere is the:
A) summer solstice.
B) vernal equinox.
C) winter solstice.
D) autumnal equinox.
A) summer solstice.
B) vernal equinox.
C) winter solstice.
D) autumnal equinox.
winter solstice.
4
The meridian is defined as a great circle on the sky on which lie the:
A) celestial equator and vernal equinox.
B) north and south celestial poles.
C) zenith and the north and south celestial poles.
D) zenith and east and west directions.
A) celestial equator and vernal equinox.
B) north and south celestial poles.
C) zenith and the north and south celestial poles.
D) zenith and east and west directions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The direction directly overhead of an observer defines his or her:
A) meridian.
B) celestial pole.
C) circumpolar plane.
D) zenith.
A) meridian.
B) celestial pole.
C) circumpolar plane.
D) zenith.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Assume you are observing the night sky from a typical city in the United States at a latitude of +40°.Use the figure below to determine which constellation of the zodiac would be nearest the meridian at midnight in March. 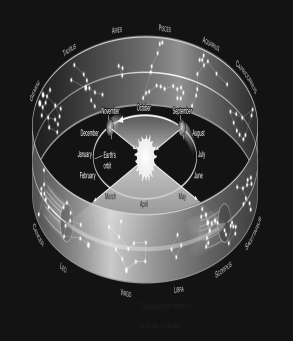
A) Scorpius
B) Gemini
C) Aquarius
D) Leo

A) Scorpius
B) Gemini
C) Aquarius
D) Leo

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
We experience seasons because:
A) Earth's equator is tilted relative to the plane of the Earth's orbit around the Sun.
B) Earth is closer to the Sun in summer and farther from the Sun in the winter.
C) the length of the day is longer in the summer and shorter in the winter.
D) Earth moves with a slower speed in its orbit during summer and a faster speed during winter.
A) Earth's equator is tilted relative to the plane of the Earth's orbit around the Sun.
B) Earth is closer to the Sun in summer and farther from the Sun in the winter.
C) the length of the day is longer in the summer and shorter in the winter.
D) Earth moves with a slower speed in its orbit during summer and a faster speed during winter.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
If the north celestial pole is located on your horizon,what is your latitude?
A) 0°
B) +30°
C) +60°
D) +90°
E) This can never happen.
A) 0°
B) +30°
C) +60°
D) +90°
E) This can never happen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
On which day of the year does the Sun reach its northern-most point in the sky?
A) vernal equinox
B) summer solstice
C) autumnal equinox
D) winter solstice
A) vernal equinox
B) summer solstice
C) autumnal equinox
D) winter solstice

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
If the north celestial pole is located at your zenith,what is your latitude?
A) 0°
B) +30°
C) +60°
D) +90°
E) This occurs at every latitude.
A) 0°
B) +30°
C) +60°
D) +90°
E) This occurs at every latitude.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The ecliptic plane is defined by the motion of ________ in the sky.
A) the Moon
B) the Sun
C) Polaris
D) the stars
A) the Moon
B) the Sun
C) Polaris
D) the stars

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
If the star Polaris has an altitude of 35°,then we know that:
A) our longitude is +55°.
B) our latitude is +55°.
C) our longitude is +35°.
D) our latitude is +35°.
A) our longitude is +55°.
B) our latitude is +55°.
C) our longitude is +35°.
D) our latitude is +35°.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
If you travel 20 miles from home to school in 30 minutes,what is your average velocity?
A) 20 mph
B) 40 mph
C) 0.7 mph
D) 5 mph
A) 20 mph
B) 40 mph
C) 0.7 mph
D) 5 mph

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The apparent path of the Sun across the celestial sphere during a year is called the:
A) prime meridian.
B) ecliptic plane.
C) circumpolar plane.
D) celestial equator.
A) prime meridian.
B) ecliptic plane.
C) circumpolar plane.
D) celestial equator.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The Earth's axial tilt is 23.5 degrees.If the Earth's axial tilt was 15 degrees,which would be TRUE?
A) The seasons would remain the same.
B) Summers would be warmer.
C) Winters would last longer.
D) Winters would be warmer.
A) The seasons would remain the same.
B) Summers would be warmer.
C) Winters would last longer.
D) Winters would be warmer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Leap years occur because:
A) Earth's orbital period around the Sun is decreasing.
B) Earth's orbital period is 365.24 days.
C) the Gregorian calendar contains only 11 months.
D) Earth speeds up in its orbit when it comes closest to the Sun.
A) Earth's orbital period around the Sun is decreasing.
B) Earth's orbital period is 365.24 days.
C) the Gregorian calendar contains only 11 months.
D) Earth speeds up in its orbit when it comes closest to the Sun.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
No matter where you are on Earth,stars appear to rotate about a point called the:
A) zenith.
B) celestial pole.
C) meridian.
D) equinox.
A) zenith.
B) celestial pole.
C) meridian.
D) equinox.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
If you go out at exactly 9 P.M.each evening over the course of 1 month,the position of a given star will move westward by tens of degrees.What causes this motion?
A) Earth's rotation on its axis
B) the revolution of Earth around the Sun
C) the revolution of the Moon around Earth
D) the revolution of the Sun around Earth
A) Earth's rotation on its axis
B) the revolution of Earth around the Sun
C) the revolution of the Moon around Earth
D) the revolution of the Sun around Earth

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Earth's rotational axis precesses in space and completes one revolution every:
A) 200 years.
B) 1,800 years.
C) 26,000 years.
D) 51,000 years.
A) 200 years.
B) 1,800 years.
C) 26,000 years.
D) 51,000 years.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
When the Northern Hemisphere experiences summer,the Southern Hemisphere experiences:
A) spring.
B) summer.
C) fall.
D) winter.
A) spring.
B) summer.
C) fall.
D) winter.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The amount of the Earth's surface receiving sunlight during the day is
A) the same in the northern and southern hemispheres during June.
B) less in the southern hemisphere than in the northern hemisphere during December.
C) more in the northern hemisphere than in the southern hemisphere during December.
D) less in the northern hemisphere than in the southern hemisphere during December.
A) the same in the northern and southern hemispheres during June.
B) less in the southern hemisphere than in the northern hemisphere during December.
C) more in the northern hemisphere than in the southern hemisphere during December.
D) less in the northern hemisphere than in the southern hemisphere during December.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The gibbous is in the "waning" state between the:
A) third quarter and new Moon phases.
B) new Moon and first quarter phases.
C) first and second quarter phases.
D) full Moon and third quarter phases.
A) third quarter and new Moon phases.
B) new Moon and first quarter phases.
C) first and second quarter phases.
D) full Moon and third quarter phases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
For a person who lives at a latitude of +40°,when is the Sun directly overhead at noon?
A) only on the summer solstice
B) only on the vernal and autumnal equinoxes
C) Never
D) Always
A) only on the summer solstice
B) only on the vernal and autumnal equinoxes
C) Never
D) Always

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
If a person on Earth currently views the Moon in a waxing crescent phase,in what phase would the Earth appear to a person on the Moon?
A) waxing crescent
B) waxing gibbous
C) waning gibbous
D) waning crescent
A) waxing crescent
B) waxing gibbous
C) waning gibbous
D) waning crescent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
At what time does a third quarter Moon rise? (Hint: A third quarter Moon occurs approximately 3 weeks after a new Moon.)
A) 12 midnight
B) 12 noon
C) 6 A.M.
D) 6 P.M.
A) 12 midnight
B) 12 noon
C) 6 A.M.
D) 6 P.M.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
At what time does the waxing gibbous phase rise?
A) 3 P.M.
B) 9 A.M.
C) 3 A.M.
D) 9 P.M.
A) 3 P.M.
B) 9 A.M.
C) 3 A.M.
D) 9 P.M.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
A partial lunar eclipse occurs when:
A) the Sun appears to go behind the Moon.
B) the Moon passes through part of Earth's shadow.
C) the Moon shadows part of the Sun.
D) Earth passes through part of the Moon's shadow.
A) the Sun appears to go behind the Moon.
B) the Moon passes through part of Earth's shadow.
C) the Moon shadows part of the Sun.
D) Earth passes through part of the Moon's shadow.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
In regard to the phase of the Moon,the term waxing means:
A) less than half-illuminated.
B) more than half-illuminated.
C) becoming smaller.
D) increasing in brightness.
A) less than half-illuminated.
B) more than half-illuminated.
C) becoming smaller.
D) increasing in brightness.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Assume you are observing the night sky from a typical city in the United States at a latitude of +40°.Use the figure below to determine which constellation of the zodiac would be nearest the meridian at 6 P.M.in September. 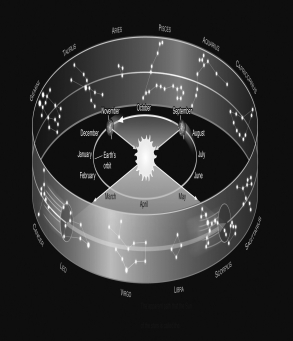
A) Scorpius
B) Gemini
C) Aquarius
D) Leo

A) Scorpius
B) Gemini
C) Aquarius
D) Leo

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
If tonight the Moon is in the waxing gibbous phase,in 3 days the Moon will most likely be in the:
A) new phase.
B) full phase.
C) third quarter phase.
D) first quarter phase.
A) new phase.
B) full phase.
C) third quarter phase.
D) first quarter phase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The Moon undergoes synchronous rotation,and as a consequence the:
A) rotational period of the Moon equals the orbital period of the Moon around Earth.
B) rotational period of the Moon equals the rotational period of Earth.
C) rotational period of the Moon equals the orbital period of Earth around the Sun.
D) Moon does not rotate as it orbits Earth.
A) rotational period of the Moon equals the orbital period of the Moon around Earth.
B) rotational period of the Moon equals the rotational period of Earth.
C) rotational period of the Moon equals the orbital period of Earth around the Sun.
D) Moon does not rotate as it orbits Earth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Assume you are observing the night sky from a typical city in the United States at a latitude of +40°.Use the figure below to determine which constellation of the zodiac would be rising at 10 P.M.in May. 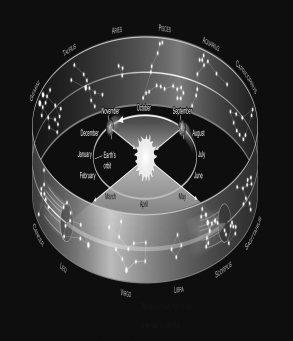
A) Pisces
B) Virgo
C) Gemini
D) Capricornus

A) Pisces
B) Virgo
C) Gemini
D) Capricornus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
If you went out tonight and looked at the sky at midnight,at what time would you have to observe 6 months from now in order to find the stars in exactly the same position in the sky? Assume that you could see the stars at any time,day or night.
A) 6 A.M.
B) noon
C) 6 P.M.
D) midnight
A) 6 A.M.
B) noon
C) 6 P.M.
D) midnight

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
We observe different phases of the Moon because:
A) the Moon passes through different portions of the Earth's shadow during its orbit.
B) some parts of the Moon reflect and other parts absorb sunlight.
C) the orbital position of the Moon determines which portion and how much of the lunar surface is illuminated by sunlight.
D) the Moon emits light in some places and only reflects light in other places.
A) the Moon passes through different portions of the Earth's shadow during its orbit.
B) some parts of the Moon reflect and other parts absorb sunlight.
C) the orbital position of the Moon determines which portion and how much of the lunar surface is illuminated by sunlight.
D) the Moon emits light in some places and only reflects light in other places.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The shortest day of the year for a person living in the Southern Hemisphere is the:
A) summer solstice (June 21).
B) vernal equinox (March 20).
C) winter solstice (December 21).
D) autumnal equinox (September 22).
A) summer solstice (June 21).
B) vernal equinox (March 20).
C) winter solstice (December 21).
D) autumnal equinox (September 22).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
During which lunar phase do solar eclipses occur?
A) new
B) first quarter
C) full
D) third quarter
A) new
B) first quarter
C) full
D) third quarter

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
If there is a full Moon out tonight,approximately how long from now will it be in the third quarter phase?
A) 3 to 4 days
B) 1 week
C) 2 weeks
D) 1 month
A) 3 to 4 days
B) 1 week
C) 2 weeks
D) 1 month

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which of the following is FALSE?
A) Everyone on Earth observes the same phase of the Moon on a given night.
B) The phases of the Moon cycle with a period of approximately 1 month.
C) In some phases, the Moon can be observed during the day.
D) The observed phase of the Moon changes obviously over the course of one night.
A) Everyone on Earth observes the same phase of the Moon on a given night.
B) The phases of the Moon cycle with a period of approximately 1 month.
C) In some phases, the Moon can be observed during the day.
D) The observed phase of the Moon changes obviously over the course of one night.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
In consecutive non-leap years,the exact time at which the Autumnal or Vernal Equinoxes occurs is:
A) later than the times they occurred in the previous year.
B) earlier than the times it occurred in the previous year.
C) exactly the same times they occurred in the previous year.
D) randomly earlier or later than the times they occurred in the previous year.
A) later than the times they occurred in the previous year.
B) earlier than the times it occurred in the previous year.
C) exactly the same times they occurred in the previous year.
D) randomly earlier or later than the times they occurred in the previous year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Assume you are observing the night sky from a typical city in the United States at a latitude of +40°.Use the figure below to determine which month it is if the zodiac constellation Taurus is on your meridian at midnight. 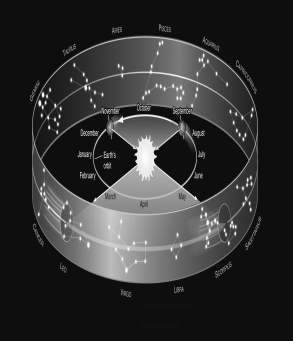
A) July
B) November
C) January
D) May

A) July
B) November
C) January
D) May

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
How does "gibbous" differ from "crescent"?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
On which great celestial circle(s)on the celestial sphere would you find the position of the autumnal equinox?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Approximately how often do lunar eclipses occur?
A) twice every year
B) once per month
C) twice every 11 months
D) once every 11 years
A) twice every year
B) once per month
C) twice every 11 months
D) once every 11 years

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The figure below shows the different phases of the Moon.Label each phase of the Moon.What time would the full Moon be on your meridian? The new Moon?



Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The figure below shows four locations of the Sun on the ecliptic.Label each appropriately with the labels: autumnal equinox,vernal equinox,summer solstice,and winter solstice.
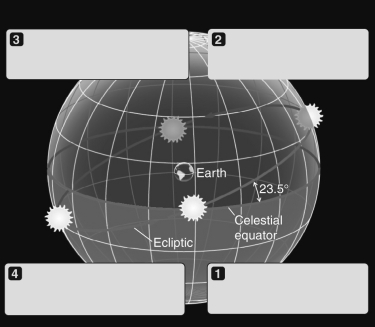


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Earth experiences seasons because of the tilt of its axis.What are the two consequences of this tilt that contribute to the seasons?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Explain why we always see the same side of the Moon from Earth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The center of the Milky Way lies approximately 30° south of the celestial equator.From what latitudes on Earth is it impossible to view the center of our galaxy?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
What would be the effect on the seasons if the tilt of Earth's axis were 10° rather than 23.5°?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
On what place(s)on Earth can you stand and have the great circle of the celestial equator be at the same height relative to your horizon for all 360° of its circumference?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
For an observer in Seattle,Washington,which is located at latitude = +47°,what is the minimum height above the southern horizon that the Sun will have throughout the year,and approximately when will this occur?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
What is the length of day during the equinoxes and solstices? Does it matter if you are in the Northern or Southern Hemisphere?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The figure below is a time exposure of the sky,showing the motion of the stars through the night.What is the name for the stars that never rise or set below the horizon?



Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Explain how you could use the stars to navigate a ship from northeast to southwest in the Northern Hemisphere.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
How is the observed height of Polaris above the horizon related to an observer's latitude? (Hint: Consider three cases of observers located at the equator,the North Pole,and latitude = +45°.)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
For the following figure,label the north and south celestial poles,the celestial equator,and the ecliptic.
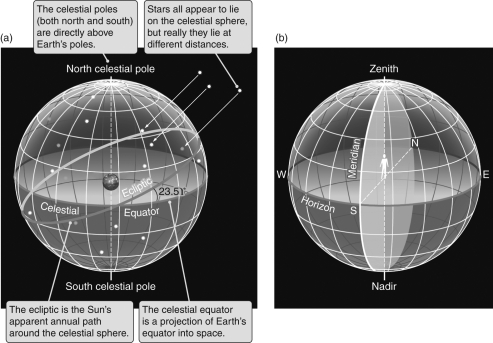


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The figure below shows the different phases of the Moon.Label each phase of the Moon.Approximately what time would the full Moon rise above your horizon? The third quarter Moon? The new Moon? The first quarter Moon?
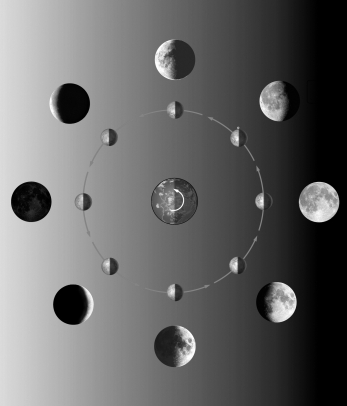


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The figure below shows the different phases of the Moon.Label each phase of the Moon shown.
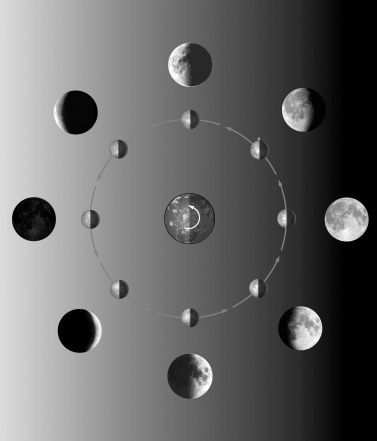


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Solar and lunar eclipses are rare because the Moon's orbital plane is tipped by:
A) 5.2° relative to the plane defined by Earth's equator.
B) 5.2° relative to Earth's orbital plane.
C) 23.5° relative to the plane defined by Earth's equator.
D) 23.5° relative to Earth's orbital plane.
A) 5.2° relative to the plane defined by Earth's equator.
B) 5.2° relative to Earth's orbital plane.
C) 23.5° relative to the plane defined by Earth's equator.
D) 23.5° relative to Earth's orbital plane.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Earth has an average radius of approximately 6.4 × 10³ km.What is the average speed of the ground due to the rotation of Earth at its equator in kilometers per second (km/s)if there are 8.64 × 10⁴ seconds per day?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
How might you use a lunar eclipse to estimate the relative sizes of the Earth and Moon?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
If the Moon was full 3 days ago,what phase will it be tonight and when will it rise and set?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The figure below shows a solar eclipse.What type of solar eclipse is it?



Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Why can a solar eclipse only occur during a new Moon?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
How does the appearance of the first and third quarter Moon phases differ? Why?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



