Deck 12: Evolution of Low-Mass Stars
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/64
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 12: Evolution of Low-Mass Stars
1
The figure below plots the chemical composition of the Sun as a function of radius for three different times.Which graph represents the correct chemical composition just prior to the Sun becoming a red giant? 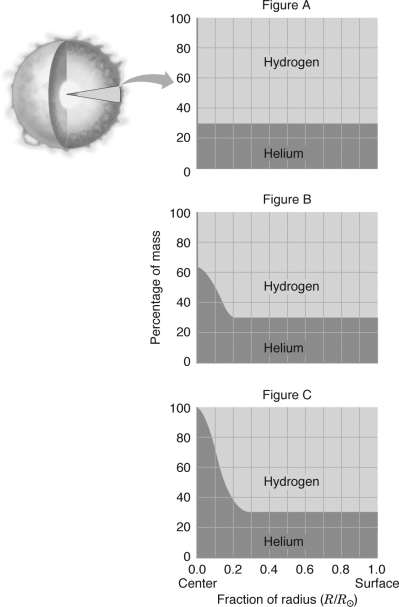
A) Figure A
B) Figure B
C) Figure C
D) No figure is correct.

A) Figure A
B) Figure B
C) Figure C
D) No figure is correct.
Figure C
2
When a G2 star leaves the main sequence,its luminosity:
A) and surface temperature both stay the same.
B) and surface temperature both decrease.
C) increases and its surface temperature decreases.
D) and surface temperature both increase.
A) and surface temperature both stay the same.
B) and surface temperature both decrease.
C) increases and its surface temperature decreases.
D) and surface temperature both increase.
increases and its surface temperature decreases.
3
When a star depletes its core supply of hydrogen,________ dominates in the core and ________ dominates in the atmosphere.
A) pressure; pressure
B) pressure; gravity
C) gravity; gravity
D) gravity; pressure
A) pressure; pressure
B) pressure; gravity
C) gravity; gravity
D) gravity; pressure
gravity; pressure
4
A low-mass main-sequence star's climb up the red giant branch is halted by:
A) the end of hydrogen shell burning.
B) the beginning of helium fusion in the core.
C) electron-degeneracy pressure in the core.
D) instabilities in the star's expanding outer layers.
A) the end of hydrogen shell burning.
B) the beginning of helium fusion in the core.
C) electron-degeneracy pressure in the core.
D) instabilities in the star's expanding outer layers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
In a white dwarf,what is the source of pressure that halts its contraction as it cools?
A) thermal pressure of the extremely hot gas
B) electrons packed so closely that they become incompressible
C) neutrons that resist being pressed further together
D) carbon nuclei that repulse each other strongly because they each contain six protons
A) thermal pressure of the extremely hot gas
B) electrons packed so closely that they become incompressible
C) neutrons that resist being pressed further together
D) carbon nuclei that repulse each other strongly because they each contain six protons

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
As a main-sequence star burns its core supply of hydrogen,what happens?
A) Helium begins to fuse throughout the core.
B) Helium fuses in a shell surrounding the core.
C) Helium fusion takes place only at the very center of the core, where temperature and pressure are highest.
D) Helium builds up as ash in the core.
A) Helium begins to fuse throughout the core.
B) Helium fuses in a shell surrounding the core.
C) Helium fusion takes place only at the very center of the core, where temperature and pressure are highest.
D) Helium builds up as ash in the core.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A main-sequence star is unique because:
A) hydrostatic equilibrium exists at all radii.
B) energy transport occurs via convection throughout much of its interior.
C) hydrogen burning occurs in its core.
D) it emits strong surface winds.
A) hydrostatic equilibrium exists at all radii.
B) energy transport occurs via convection throughout much of its interior.
C) hydrogen burning occurs in its core.
D) it emits strong surface winds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which star spends the least time as a main-sequence star?
A) 0.5 M¤
B) 1 M¤
C) 3 M¤
D) 10 M¤
A) 0.5 M¤
B) 1 M¤
C) 3 M¤
D) 10 M¤

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Degenerate refers to a state of matter at:
A) high temperature.
B) high density.
C) high luminosity.
D) high mass.
A) high temperature.
B) high density.
C) high luminosity.
D) high mass.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The Sun will likely stop being a main-sequence star in:
A) 5,000 years.
B) 5 million years.
C) 500 million years.
D) 5 billion years.
A) 5,000 years.
B) 5 million years.
C) 500 million years.
D) 5 billion years.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
What is the current composition of the Sun's core?
A) 100 percent hydrogen
B) 65 percent hydrogen; 35 percent helium
C) 50 percent hydrogen; 50 percent helium
D) 35 percent hydrogen; 65 percent helium
A) 100 percent hydrogen
B) 65 percent hydrogen; 35 percent helium
C) 50 percent hydrogen; 50 percent helium
D) 35 percent hydrogen; 65 percent helium

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
As a red giant star evolves,hydrogen shell burning proceeds increasingly faster due to:
A) rotational energy from the star's rapid rotation.
B) heat released from the core's contraction.
C) pressure from the contracting envelope.
D) this is a trick question; hydrogen actually burns increasingly slower with time.
A) rotational energy from the star's rapid rotation.
B) heat released from the core's contraction.
C) pressure from the contracting envelope.
D) this is a trick question; hydrogen actually burns increasingly slower with time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which point on the figure below represents the location on the H-R diagram where the star is on the horizontal branch? 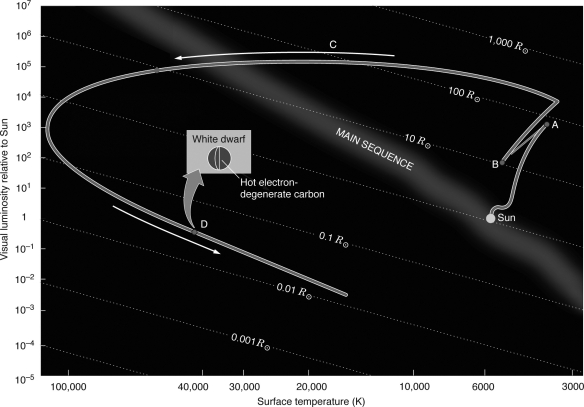
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D

A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
About how long will a 2-M¤ star live as a main-sequence star?
A) 10 million years
B) 1 billion years
C) 10 billion years
D) 100 million years
A) 10 million years
B) 1 billion years
C) 10 billion years
D) 100 million years

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A low-mass red giant star's energy comes from:
A) hydrogen burning to helium in its core.
B) helium burning to carbon in its core.
C) hydrogen burning to helium in a shell surrounding its core.
D) helium burning to carbon in a shell surrounding its core.
A) hydrogen burning to helium in its core.
B) helium burning to carbon in its core.
C) hydrogen burning to helium in a shell surrounding its core.
D) helium burning to carbon in a shell surrounding its core.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The evolutionary cutoff between low- and high-mass stars occurs at approximately:
A) 0.5 M¤.
B) 1 M¤.
C) 4 M¤.
D) 8 M¤.
A) 0.5 M¤.
B) 1 M¤.
C) 4 M¤.
D) 8 M¤.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Helium burns in the core of a horizontal branch star via ________ and produces ________.
A) the triple-alpha reaction; carbon
B) the proton-proton chain; lithium
C) the triple-alpha reaction; oxygen
D) the proton-proton chain; iron
A) the triple-alpha reaction; carbon
B) the proton-proton chain; lithium
C) the triple-alpha reaction; oxygen
D) the proton-proton chain; iron

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
In stellar fusion,the term "ash" refers to:
A) a dusty product of fire from oxidation occurring within the core of the star.
B) the result of nuclear fusion that collects in the core.
C) the result of nuclear fusion that collects in the outer layers of a star.
D) a dusty product of fire from oxidation occurring in the outer layers of the star.
A) a dusty product of fire from oxidation occurring within the core of the star.
B) the result of nuclear fusion that collects in the core.
C) the result of nuclear fusion that collects in the outer layers of a star.
D) a dusty product of fire from oxidation occurring in the outer layers of the star.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The luminosity of a star depends on:
A) its mass, its age, and its distance.
B) its mass.
C) its age.
D) its mass and its age.
A) its mass, its age, and its distance.
B) its mass.
C) its age.
D) its mass and its age.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
What factor is most important in determining a star's position on the main sequence and subsequent evolution?
A) temperature
B) pressure
C) mass
D) radius
A) temperature
B) pressure
C) mass
D) radius

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
You observed three different star clusters and found that the main-sequence turnoff stars in cluster 1 had spectral type A,the main-sequence turnoff stars in cluster 2 had spectral type B,and the main-sequence turnoff stars in cluster 3 had spectral type G.Which star cluster is the oldest?
A) cluster 1
B) cluster 2
C) cluster 3
D) It is impossible to determine their ages given only the spectral types.
A) cluster 1
B) cluster 2
C) cluster 3
D) It is impossible to determine their ages given only the spectral types.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
A star like the Sun will lose about ________ of its mass before it evolves to become a white dwarf.
A) 3 percent
B) 10 percent
C) 40 percent
D) 70 percent
A) 3 percent
B) 10 percent
C) 40 percent
D) 70 percent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
When a low-mass star becomes an AGB star and has a temperature of 3300 K,in which wavelength range will it shine the brightest?
A) visible
B) infrared
C) X-ray
D) radio
A) visible
B) infrared
C) X-ray
D) radio

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
A Type Ia supernova occurs when a white dwarf exceeds a mass of:
A) 0.8 M¤.
B) 1.4 M¤.
C) 2.3 M¤.
D) 5.5 M¤.
A) 0.8 M¤.
B) 1.4 M¤.
C) 2.3 M¤.
D) 5.5 M¤.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The gas in a planetary nebula is composed of:
A) primarily hydrogen from the surrounding interstellar medium.
B) primarily hydrogen from the post-asymptotic giant branch star.
C) hydrogen and elements processed in the core of the post-asymptotic giant branch star.
D) primarily helium from the post-asymptotic giant branch star.
A) primarily hydrogen from the surrounding interstellar medium.
B) primarily hydrogen from the post-asymptotic giant branch star.
C) hydrogen and elements processed in the core of the post-asymptotic giant branch star.
D) primarily helium from the post-asymptotic giant branch star.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Asymptotic giant branch (AGB)stars have high mass-loss rates because they:
A) are rotating quickly.
B) have weak magnetic fields.
C) have strong winds.
D) have low surface gravity.
A) are rotating quickly.
B) have weak magnetic fields.
C) have strong winds.
D) have low surface gravity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Suppose you measured H-R diagrams for the two star clusters pictured below. 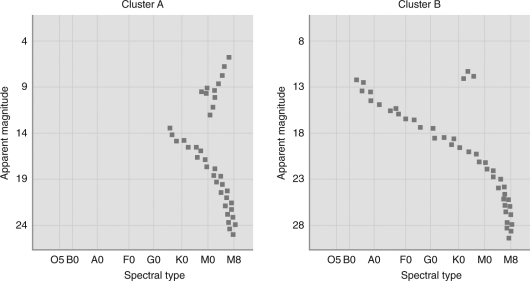
Which of the following statements is TRUE?
A) Cluster A is younger than Cluster B.
B) Cluster A is closer to us than Cluster B.
C) Both a and b are TRUE.
D) Both a and b are FALSE.

Which of the following statements is TRUE?
A) Cluster A is younger than Cluster B.
B) Cluster A is closer to us than Cluster B.
C) Both a and b are TRUE.
D) Both a and b are FALSE.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
During which phase of the evolution of a low-mass star does it have two separate regions of nuclear burning occurring in its interior?
A) main sequence
B) red giant
C) horizontal branch
D) white dwarf
A) main sequence
B) red giant
C) horizontal branch
D) white dwarf

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
What is a planetary nebula?
A) a planet surrounded by a glowing shell of gas
B) the disk of gas and dust surrounding a young star that will soon form a star system
C) the ejected envelope of a giant star surrounding the remains of a star
D) a type of young, medium-mass star
A) a planet surrounded by a glowing shell of gas
B) the disk of gas and dust surrounding a young star that will soon form a star system
C) the ejected envelope of a giant star surrounding the remains of a star
D) a type of young, medium-mass star

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
A single 1-M¤ star will eventually eject significant amounts of which of the following chemical elements into the interstellar medium?
A) hydrogen
B) nickel
C) iron
D) all of the above
A) hydrogen
B) nickel
C) iron
D) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which figure below represents the youngest star cluster? 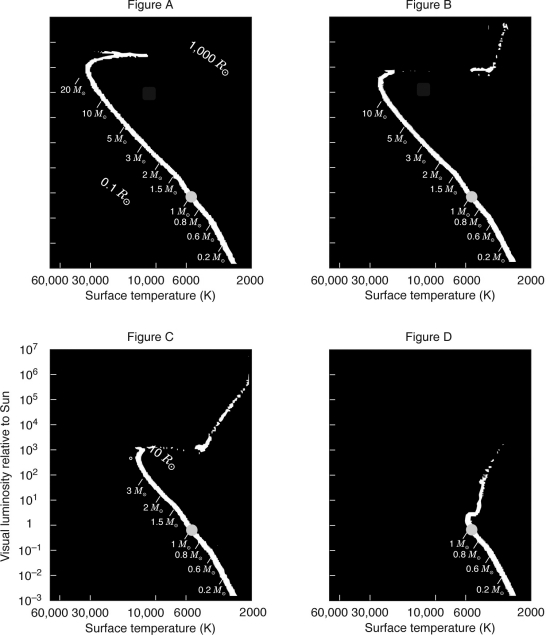
A) Figure A
B) Figure B
C) Figure C
D) Figure D

A) Figure A
B) Figure B
C) Figure C
D) Figure D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The correct order of evolutionary stages for a solar mass star is:
A) main sequence, asymptotic branch, horizontal branch, white dwarf.
B) asymptotic branch, main sequence, horizontal branch, white dwarf.
C) horizontal branch, main sequence, asymptotic branch, horizontal branch, white dwarf.
D) main sequence, horizontal branch, asymptotic branch, white dwarf.
A) main sequence, asymptotic branch, horizontal branch, white dwarf.
B) asymptotic branch, main sequence, horizontal branch, white dwarf.
C) horizontal branch, main sequence, asymptotic branch, horizontal branch, white dwarf.
D) main sequence, horizontal branch, asymptotic branch, white dwarf.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which point on the figure below represents the location on the H-R diagram where the star is expelling mass creating a planetary nebula? 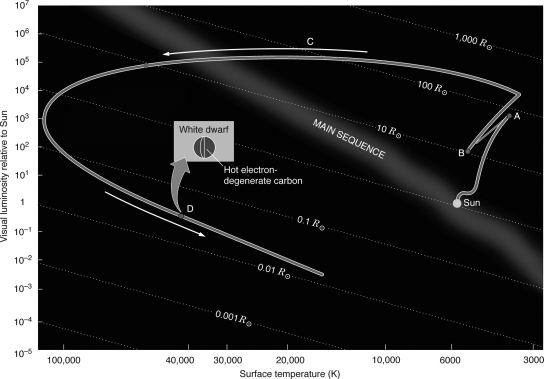
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D

A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
As a solar-type star evolves off the main sequence,its:
A) core and envelope expand.
B) core and envelope shrink.
C) core shrinks and envelope expands.
D) core expands and envelope shrinks.
A) core and envelope expand.
B) core and envelope shrink.
C) core shrinks and envelope expands.
D) core expands and envelope shrinks.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
When helium fusion begins in the core of a red giant star,the situation quickly gets out of control because electron-degeneracy pressure does not respond to changes in:
A) luminosity.
B) density.
C) gravity.
D) temperature.
A) luminosity.
B) density.
C) gravity.
D) temperature.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which figure below represents the oldest star cluster? 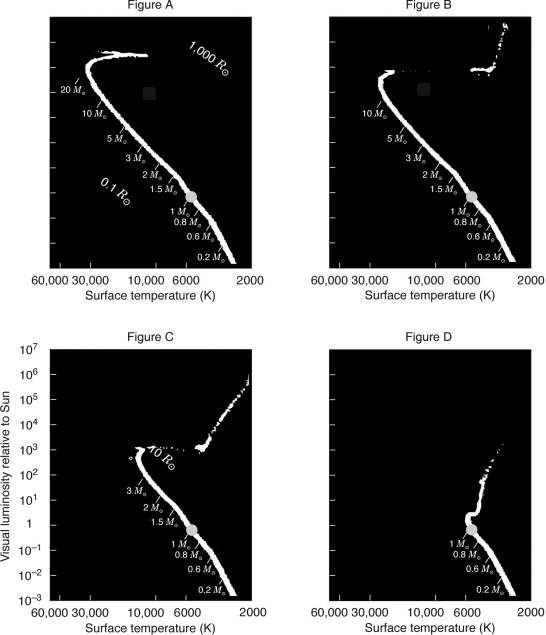
A) Figure A
B) Figure B
C) Figure C
D) Figure D

A) Figure A
B) Figure B
C) Figure C
D) Figure D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
What ionizes the gas in a planetary nebula (see the image below)and makes it visible? 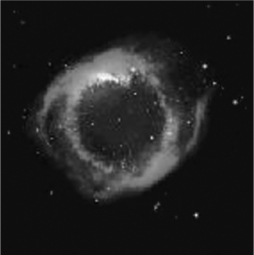
A) X-ray photons emitted by a pulsar
B) ultraviolet photons emitted by a white dwarf
C) the shock wave from a supernova
D) hydrogen burning in the nebular gas

A) X-ray photons emitted by a pulsar
B) ultraviolet photons emitted by a white dwarf
C) the shock wave from a supernova
D) hydrogen burning in the nebular gas

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
What would you need to measure for a planetary nebula (see the image below)to determine how long ago its parent star died? 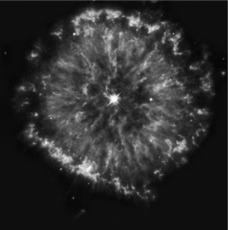
A) the mass of the white dwarf
B) the mass and radius of the white dwarf
C) the nebula's temperature and radius
D) the nebula's radius and expansion velocity

A) the mass of the white dwarf
B) the mass and radius of the white dwarf
C) the nebula's temperature and radius
D) the nebula's radius and expansion velocity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The Ring Nebula (image below)is a planetary nebula that currently has a radius of 0.4 pc and an expansion velocity of 250 km/s.Approximately how long ago did its parent star die and eject its outer layers? 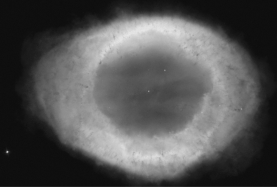
A) 1,600 years ago
B) 3,200 years ago
C) 5,400 years ago
D) 28,000 years ago

A) 1,600 years ago
B) 3,200 years ago
C) 5,400 years ago
D) 28,000 years ago

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
A star's surface temperature during the horizontal branch phase is determined primarily by its:
A) luminosity.
B) chemical composition.
C) magnetic field strength.
D) rotation rate.
A) luminosity.
B) chemical composition.
C) magnetic field strength.
D) rotation rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Calculate the main-sequence lifetimes of the following stars of different spectral types:
B0 (18 M¤),B5 (6 M¤),A5 (2 M¤),F5 (1.3 M¤),and M0 (0.5 M¤).What trend do you notice in your results?
B0 (18 M¤),B5 (6 M¤),A5 (2 M¤),F5 (1.3 M¤),and M0 (0.5 M¤).What trend do you notice in your results?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Describe the triple-alpha process of nuclear fusion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
A Type Ia supernova has a luminosity of approximately:
A) 10,000 L¤.
B) 10 million L¤.
C) 10 billion L¤.
D) 10 trillion L¤.
A) 10,000 L¤.
B) 10 million L¤.
C) 10 billion L¤.
D) 10 trillion L¤.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Label the various regions of an asymptotic giant branch star in the figure below.
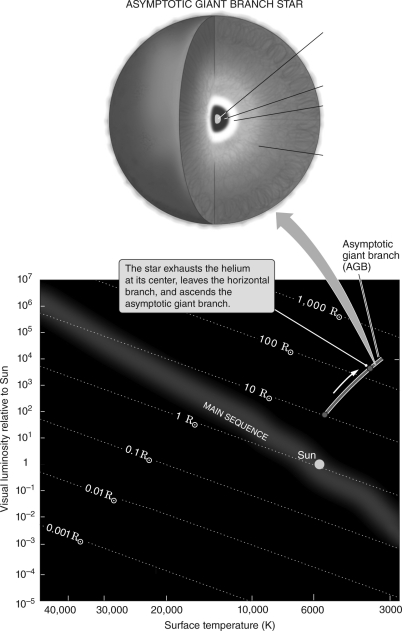


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Label the various regions of a horizontal branch star in the figure below.
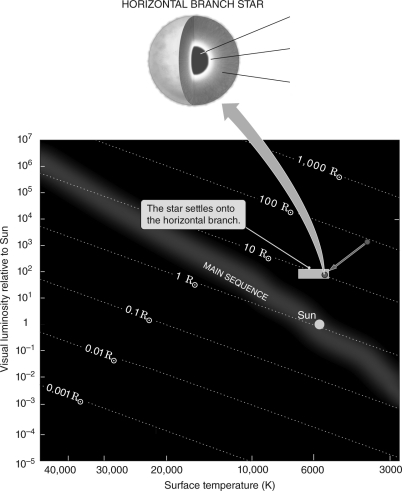


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
How many times longer does a 1.0-M¤ main-sequence star live compared to a 2.1-M¤ main-sequence star?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
How can the core of a star be degenerate with respect to the electrons but nondegenerate with respect to the nuclei?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
What particles are degenerate in a white dwarf?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
What occurs if a white dwarf exceeds the Chandrasekhar limit?
A) Nothing, the white dwarf just gets bigger.
B) The white dwarf contracts to a smaller, hotter object.
C) a nova explosion
D) a type Ia supernova explosion
A) Nothing, the white dwarf just gets bigger.
B) The white dwarf contracts to a smaller, hotter object.
C) a nova explosion
D) a type Ia supernova explosion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Why does helium burning in the core of a giant star not cause the star to become more luminous?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
A nova is the result of which explosive situation?
A) mass transfer onto a white dwarf
B) helium burning in a degenerate stellar core
C) a white dwarf that exceeds the Chandrasekhar limit
D) the collision of members of a binary system
A) mass transfer onto a white dwarf
B) helium burning in a degenerate stellar core
C) a white dwarf that exceeds the Chandrasekhar limit
D) the collision of members of a binary system

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
In what two ways does temperature affect the rate of nuclear reactions?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
One star in a binary will almost always become a red giant before the other because:
A) one star is always larger than the other.
B) binaries always have one star twice as massive as the other.
C) small differences in main-sequence masses yield large differences in main-sequence lifetimes.
D) the more massive binary star always gets more mass from the less massive binary star when both are main-sequence stars.
A) one star is always larger than the other.
B) binaries always have one star twice as massive as the other.
C) small differences in main-sequence masses yield large differences in main-sequence lifetimes.
D) the more massive binary star always gets more mass from the less massive binary star when both are main-sequence stars.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
When the Sun becomes an AGB star,its radius will be approximately 100 R¤.If its mass at this point will be approximately the same as it is now,how will its surface gravity as an AGB star compare to its current surface gravity as a main-sequence star? Note that g = GM/R².

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Why does the core of a main-sequence star have to be hotter to burn helium into carbon than hydrogen into helium?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
A 1-M¤ star in a binary system could create the following chemical element and eject it into the interstellar medium:
A) carbon.
B) helium.
C) iron.
D) all of the above
A) carbon.
B) helium.
C) iron.
D) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
What types of chemical elements can low-mass stars contribute to the enrichment of the interstellar medium,and how are they produced?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Using the figure below,describe how the composition of the Sun varies by radius over time.
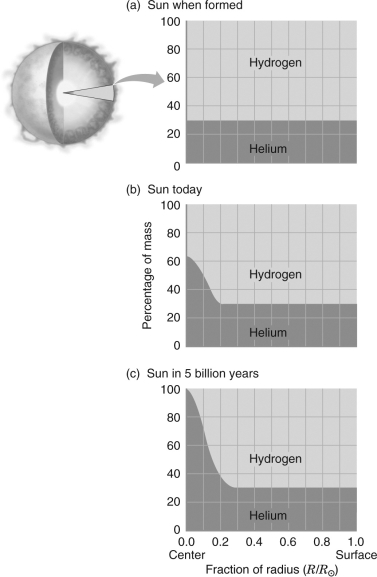


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Explain the two different forms of pressure that support the core of a low-mass main-sequence star and the core of a low-mass red giant star?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
What is the shortest phase of evolution for a 1 solar mass star that we can visibly see?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Explain the significance of Roche lobes in a binary system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The figure below shows the H-R diagram of stars from the cluster 47 Tucanae.Explain what the main-sequence turnoff is and how it can be used to determine the age of the cluster.
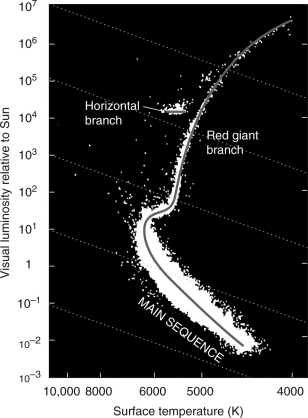


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Suppose you observe three star clusters.Cluster 1 has a main-sequence turnoff point at spectral type G,cluster 2 has a turnoff point at spectral type A,and cluster 3 has a turnoff point at spectral type B.Which cluster is youngest and which is oldest? Explain why.What is the approximate age of the oldest cluster?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Why are novae thought to be recurrent?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



