Deck 17: The Special Senses
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/166
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 17: The Special Senses
1
Taste receptors are distributed in which of the following places?
A)portions of the larynx
B)anterior tip of the tongue
C)portions of the pharynx
D)surface of the tongue
E)All of the answers are correct.
A)portions of the larynx
B)anterior tip of the tongue
C)portions of the pharynx
D)surface of the tongue
E)All of the answers are correct.
E
2
Which of the following is true of olfactory discrimination?
A)There are 6 primary smells known.
B)The number of olfactory receptors decline as we age.
C)All odorants require the same concentration to activate an olfactory receptor.
D)There are different types of olfactory receptor cells to detect each type of odorant.
E)All of the answers are correct.
A)There are 6 primary smells known.
B)The number of olfactory receptors decline as we age.
C)All odorants require the same concentration to activate an olfactory receptor.
D)There are different types of olfactory receptor cells to detect each type of odorant.
E)All of the answers are correct.
B
3
Which of the following lingual papillae has the largest number of taste buds?
A)pharynx
B)larynx
C)filiform papillae
D)fungiform papillae
E)circumvallate papillae
A)pharynx
B)larynx
C)filiform papillae
D)fungiform papillae
E)circumvallate papillae
E
4
Olfactory information is first received by which part of the brain?
A)frontal lobe
B)cerebellum
C)parietal lobe
D)cerebrum
E)medulla oblongata
A)frontal lobe
B)cerebellum
C)parietal lobe
D)cerebrum
E)medulla oblongata

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Stimulation of nociceptive receptors within the trigeminal nerve might produce a perception of
A)intensely sweet.
B)intensely sour.
C)quite salty.
D)peppery hot.
E)decidedly bitter.
A)intensely sweet.
B)intensely sour.
C)quite salty.
D)peppery hot.
E)decidedly bitter.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Before an olfactory receptor can detect an odorant,it has to
A)contact a specialized olfactory cell.
B)bind to receptors in olfactory cilia.
C)gate open ion channels.
D)respond to applied pressure.
E)be transported to the olfactory bulbs.
A)contact a specialized olfactory cell.
B)bind to receptors in olfactory cilia.
C)gate open ion channels.
D)respond to applied pressure.
E)be transported to the olfactory bulbs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Gustatory receptors are located
A)in the eye.
B)in the ear.
C)on the surface of the tongue.
D)in the nose.
E)on the skin.
A)in the eye.
B)in the ear.
C)on the surface of the tongue.
D)in the nose.
E)on the skin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Taste buds are monitored by which cranial nerve(s)?
A)glossopharyngeal nerve (IX)
B)vagus nerve (X)
C)facial nerve (VII)
D)trigeminal nerve (V)
E)facial nerve (VII),vagus nerve (X),and glossopharyngeal nerve (IX)
A)glossopharyngeal nerve (IX)
B)vagus nerve (X)
C)facial nerve (VII)
D)trigeminal nerve (V)
E)facial nerve (VII),vagus nerve (X),and glossopharyngeal nerve (IX)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
An adult has approximately ________ taste buds.
A)30
B)3,000
C)300,000
D)300
E)30,000
A)30
B)3,000
C)300,000
D)300
E)30,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Olfactory receptors send axons through the cribriform plate.They synapse on neurons in the
A)medulla oblongata.
B)medial geniculate.
C)cerebral cortex.
D)olfactory bulb.
E)olfactory tract.
A)medulla oblongata.
B)medial geniculate.
C)cerebral cortex.
D)olfactory bulb.
E)olfactory tract.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Olfactory glands
A)house the sense of smell.
B)support the olfactory epithelium.
C)react to aromatic molecules.
D)coat the olfactory epithelium with a pigmented mucus.
E)group as olfactory bulbs.
A)house the sense of smell.
B)support the olfactory epithelium.
C)react to aromatic molecules.
D)coat the olfactory epithelium with a pigmented mucus.
E)group as olfactory bulbs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A patient who experienced head trauma has lost the ability to taste spicy food.You should expect damage to cranial nerve ________.
A)VII
B)III
C)IX
D)V
E)XII
A)VII
B)III
C)IX
D)V
E)XII

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Some neural tissues retain stem cells and thus the capacity to divide and replace lost neurons.Which of these special senses can replace its damaged neural receptors?
A)olfaction
B)hearing
C)equilibrium
D)proprioception
E)vision
A)olfaction
B)hearing
C)equilibrium
D)proprioception
E)vision

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Taste buds are monitored by cranial nerves
A)IX,X,XI.
B)VII,VIII,IX.
C)VII,IX,X.
D)V,VII,IX.
E)IX,XI,XII.
A)IX,X,XI.
B)VII,VIII,IX.
C)VII,IX,X.
D)V,VII,IX.
E)IX,XI,XII.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The function of gustatory receptors parallels that of
A)light receptors in the eye.
B)mechanoreceptors in the ear.
C)olfactory receptors.
D)lamellated corpuscles.
E)Meissner corpuscles.
A)light receptors in the eye.
B)mechanoreceptors in the ear.
C)olfactory receptors.
D)lamellated corpuscles.
E)Meissner corpuscles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
How would a molecule that mimics cAMP affect an olfactory receptor?
A)It would increase sodium permeability.
B)It would open chemically-gated sodium channels.
C)It would depolarize the olfactory receptor.
D)It could trigger an afferent action potential.
E)All of the answers are correct.
A)It would increase sodium permeability.
B)It would open chemically-gated sodium channels.
C)It would depolarize the olfactory receptor.
D)It could trigger an afferent action potential.
E)All of the answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
All of the following are true of olfactory pathways,except
A)they project first to the mamillary bodies and then to the thalamus.
B)primary afferents synapse in the olfactory bulb.
C)information flows to the olfactory cortex,hypothalamus,and limbic system.
D)they are the only sensory pathways to reach the forebrain without first synapsing in the thalamus.
E)they exhibit a considerable amount of convergence.
A)they project first to the mamillary bodies and then to the thalamus.
B)primary afferents synapse in the olfactory bulb.
C)information flows to the olfactory cortex,hypothalamus,and limbic system.
D)they are the only sensory pathways to reach the forebrain without first synapsing in the thalamus.
E)they exhibit a considerable amount of convergence.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A normal,relaxed inhalation carries about ________ of the inhaled air to the olfactory organs.
A)50 percent
B)8 percent
C)2 percent
D)35 percent
E)10 percent
A)50 percent
B)8 percent
C)2 percent
D)35 percent
E)10 percent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
All of the following are terms describing the epithelial projections found on the tongue,except
A)fungiform papillae.
B)circumvallate papillae.
C)filiform papillae.
D)gustatory papillae.
E)lingual papillae.
A)fungiform papillae.
B)circumvallate papillae.
C)filiform papillae.
D)gustatory papillae.
E)lingual papillae.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following is not one of the six primary taste sensations?
A)sweet
B)peppery
C)sour
D)salty
E)umami
A)sweet
B)peppery
C)sour
D)salty
E)umami

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
All of the following are true of the fibrous tunic of the eye,except that it
A)consists of the sclera,limbus,and cornea.
B)provides mechanical support and some protection for the eye.
C)produces aqueous humor.
D)contributes substantial focusing power.
E)is where extrinsic eye muscles insert.
A)consists of the sclera,limbus,and cornea.
B)provides mechanical support and some protection for the eye.
C)produces aqueous humor.
D)contributes substantial focusing power.
E)is where extrinsic eye muscles insert.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The vitreous body
A)fills the posterior chamber.
B)helps to stabilize the eye and give physical support to the retina.
C)is replaced at the rate of 20 percent per year until middle age.
D)circulates through the pupil.
E)holds the retina against the lens for proper refraction.
A)fills the posterior chamber.
B)helps to stabilize the eye and give physical support to the retina.
C)is replaced at the rate of 20 percent per year until middle age.
D)circulates through the pupil.
E)holds the retina against the lens for proper refraction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The palpebrae are connected at the
A)eyelids.
B)lateral and medial canthus.
C)lacrimal caruncle.
D)chalazion.
E)conjunctiva.
A)eyelids.
B)lateral and medial canthus.
C)lacrimal caruncle.
D)chalazion.
E)conjunctiva.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
All of the following are true of the lacrimal glands,except that they
A)produce a strongly hypertonic fluid.
B)produce most of the volume of tears.
C)produce lysozyme.
D)produce watery,slightly alkaline secretions.
E)are located in recesses in the frontal bones.
A)produce a strongly hypertonic fluid.
B)produce most of the volume of tears.
C)produce lysozyme.
D)produce watery,slightly alkaline secretions.
E)are located in recesses in the frontal bones.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The ________ covers most of the exposed surface of the eye.
A)conjunctiva
B)cornea
C)iris
D)anterior chamber
E)canthus
A)conjunctiva
B)cornea
C)iris
D)anterior chamber
E)canthus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which of the following produces a lipid-rich secretion that prevents the upper and lower eyelids from sticking together at their edges?
A)palpebra
B)lacrimal caruncle
C)chalazion
D)tarsal gland
E)conjunctiva
A)palpebra
B)lacrimal caruncle
C)chalazion
D)tarsal gland
E)conjunctiva

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
A structure that is located at the medial canthus and contains glands that contribute to a gritty deposit is the
A)palpebra.
B)lacrimal caruncle.
C)chalazion.
D)Meibomian gland.
E)conjunctiva.
A)palpebra.
B)lacrimal caruncle.
C)chalazion.
D)Meibomian gland.
E)conjunctiva.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The shape of the lens is controlled by the
A)pupillary sphincter muscles.
B)pupillary radial muscles.
C)ciliary muscles.
D)iris.
E)cornea.
A)pupillary sphincter muscles.
B)pupillary radial muscles.
C)ciliary muscles.
D)iris.
E)cornea.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The space between the cornea and the iris is the
A)anterior chamber.
B)posterior chamber.
C)canal of Schlemm.
D)aqueous humor.
E)pupil.
A)anterior chamber.
B)posterior chamber.
C)canal of Schlemm.
D)aqueous humor.
E)pupil.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The taste sensation that is triggered by the amino acid glutamate is known as
A)sweet.
B)umami.
C)salty.
D)peppery.
E)sour.
A)sweet.
B)umami.
C)salty.
D)peppery.
E)sour.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The human lens focuses light on the photoreceptor cells by
A)moving up and down.
B)moving in and out.
C)changing shape.
D)opening and closing.
E)dilating and constricting.
A)moving up and down.
B)moving in and out.
C)changing shape.
D)opening and closing.
E)dilating and constricting.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
In the human eye,most refraction occurs when light passes through the
A)iris.
B)cornea.
C)lens.
D)aqueous humor.
E)vitreous humor.
A)iris.
B)cornea.
C)lens.
D)aqueous humor.
E)vitreous humor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The palpebrae
A)are controlled by cranial nerves.
B)contain tarsal glands.
C)cover and protect the eye.
D)are lined with a palpebral conjunctiva.
E)All of the answers are correct.
A)are controlled by cranial nerves.
B)contain tarsal glands.
C)cover and protect the eye.
D)are lined with a palpebral conjunctiva.
E)All of the answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The neural tunic of the eye
A)contains ganglion cells.
B)contains the photoreceptor cells.
C)contains bipolar cells.
D)is the deepest layer of the eyeball.
E)All of the answers are correct.
A)contains ganglion cells.
B)contains the photoreceptor cells.
C)contains bipolar cells.
D)is the deepest layer of the eyeball.
E)All of the answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The transparent portion of the fibrous tunic is the
A)conjunctiva.
B)cornea.
C)iris.
D)pupil.
E)canthus.
A)conjunctiva.
B)cornea.
C)iris.
D)pupil.
E)canthus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The opening in the iris through which light passes is the
A)conjunctiva.
B)cornea.
C)pupil.
D)anterior chamber.
E)posterior chamber.
A)conjunctiva.
B)cornea.
C)pupil.
D)anterior chamber.
E)posterior chamber.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which of the following is true of the vascular tunic of the eye?
A)provides a route for blood vessels and lymphatics that supply tissues of the eye
B)regulates the amount of light entering the eye
C)secretes and reabsorbs the aqueous humor
D)controls the shape of the lens
E)All of the answers are correct.
A)provides a route for blood vessels and lymphatics that supply tissues of the eye
B)regulates the amount of light entering the eye
C)secretes and reabsorbs the aqueous humor
D)controls the shape of the lens
E)All of the answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The part of the eye that determines eye color is the
A)conjunctiva.
B)cornea.
C)iris.
D)pupil.
E)canal of Schlemm.
A)conjunctiva.
B)cornea.
C)iris.
D)pupil.
E)canal of Schlemm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
What structure changes the shape of the lens for far and near vision?
A)aqueous humor
B)ciliary body
C)iris
D)extrinsic eye muscles
E)None,because the lens is rigid.
A)aqueous humor
B)ciliary body
C)iris
D)extrinsic eye muscles
E)None,because the lens is rigid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The space between the iris and ciliary body and the lens is the
A)anterior chamber.
B)posterior chamber.
C)pupil.
D)canal of Schlemm.
E)vitreous body.
A)anterior chamber.
B)posterior chamber.
C)pupil.
D)canal of Schlemm.
E)vitreous body.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
During accommodation,the ciliary muscle ________ and the suspensory ligaments become ________ which,in turn,cause the lens to become ________.
A)contracts; loose; flat
B)relaxes; loose; flat
C)contracts; tight; round
D)contracts; loose; round
E)relaxes; tight; flat
A)contracts; loose; flat
B)relaxes; loose; flat
C)contracts; tight; round
D)contracts; loose; round
E)relaxes; tight; flat

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Why must accommodation occur to view objects closer than 20 feet from the eye?
A)The light rays are convergent and must be bent more.
B)It moves the retina into position to focus on the close object.
C)The light rays are divergent instead of parallel and require more refraction.
D)The iris is too dilated causing the light rays to be out of focus.
E)None of the answers are correct.are true. Accommodation occurs when looking at distant objects 20 feet or farther from the eye.
A)The light rays are convergent and must be bent more.
B)It moves the retina into position to focus on the close object.
C)The light rays are divergent instead of parallel and require more refraction.
D)The iris is too dilated causing the light rays to be out of focus.
E)None of the answers are correct.are true. Accommodation occurs when looking at distant objects 20 feet or farther from the eye.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
A ray of light entering the eye will encounter these structures in which order?
A)conjunctiva → cornea → aqueous humor → lens → vitreous body → retina → choroid
B)vitreous body → retina → choroids → aqueous humor → lens → conjunctiva → cornea
C)cornea → aqueous humor → vitreous body → lens → conjunctiva → choroids → retina
D)conjunctiva → cornea → lens → aqueous humor → vitreous body → retina → choroid
E)cornea → aqueous humor → conjunctiva → lens → vitreous body → retina → choroid
A)conjunctiva → cornea → aqueous humor → lens → vitreous body → retina → choroid
B)vitreous body → retina → choroids → aqueous humor → lens → conjunctiva → cornea
C)cornea → aqueous humor → vitreous body → lens → conjunctiva → choroids → retina
D)conjunctiva → cornea → lens → aqueous humor → vitreous body → retina → choroid
E)cornea → aqueous humor → conjunctiva → lens → vitreous body → retina → choroid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The gelatinous material that gives the eyeball its basic shape is the
A)vitreous humor.
B)aqueous humor.
C)ora serrata.
D)perilymph.
E)posterior cavity.
A)vitreous humor.
B)aqueous humor.
C)ora serrata.
D)perilymph.
E)posterior cavity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
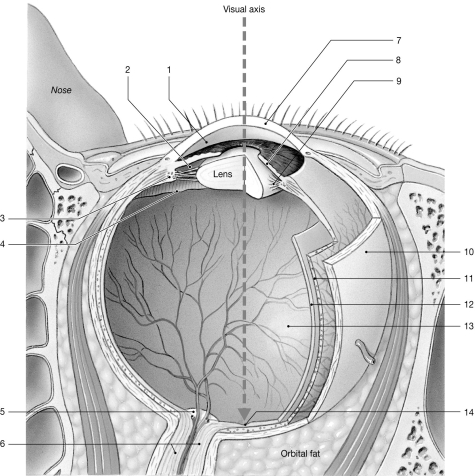
Figure 17-1 The Sectional Anatomy of the Eye
Use Figure 17-1 to answer the following questions:
Identify the structure labeled "7."
A)choroid
B)optic disc
C)sclera
D)retina
E)cornea

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Trace the circulation of aqueous humor from the site of production to the site of where it is reabsorbed: 1. posterior chamber
2) anterior chamber
3) ciliary body
4) canal of Schlemm
5) pupil
A)4,3,1,5,2
B)2,1,5,3,4
C)1,3,4,5,2
D)3,1,5,2,4
E)5,2,4,1,3
2) anterior chamber
3) ciliary body
4) canal of Schlemm
5) pupil
A)4,3,1,5,2
B)2,1,5,3,4
C)1,3,4,5,2
D)3,1,5,2,4
E)5,2,4,1,3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Pupillary muscle groups are controlled by the ANS.Parasympathetic activation causes pupillary ________,and sympathetic activation causes ________.
A)dilation; constriction
B)dilation; dilation
C)constriction; dilation
D)constriction; constriction
E)vasoconstriction; vasoconstriction
A)dilation; constriction
B)dilation; dilation
C)constriction; dilation
D)constriction; constriction
E)vasoconstriction; vasoconstriction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
An area of the retina that contains only cones and is the site of sharpest vision is the
A)outer segment.
B)inner segment.
C)fovea.
D)optic disc.
E)tapetum lucidum.
A)outer segment.
B)inner segment.
C)fovea.
D)optic disc.
E)tapetum lucidum.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
What structure regulates the amount of light that passes to the photoreceptors of the eye?
A)vitreous body
B)cornea
C)ciliary muscle
D)iris
E)lens
A)vitreous body
B)cornea
C)ciliary muscle
D)iris
E)lens

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50

Figure 17-1 The Sectional Anatomy of the Eye
Use Figure 17-1 to answer the following questions:
Identify the space labeled "1."
A)posterior cavity
B)posterior chamber
C)pupil
D)anterior chamber
E)vitreous chamber

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
If your vision is 20/15,this means that you can
A)see 20-point type at 15 feet.
B)see objects at 20 feet that individuals with normal eyesight can see at 15 feet.
C)see objects at 15 feet that individuals with eye problems see at 20 feet.
D)see all 15 eye chart letters from 20 feet.
E)see objects that are 20 feet or less away.
A)see 20-point type at 15 feet.
B)see objects at 20 feet that individuals with normal eyesight can see at 15 feet.
C)see objects at 15 feet that individuals with eye problems see at 20 feet.
D)see all 15 eye chart letters from 20 feet.
E)see objects that are 20 feet or less away.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
A sty ________
A)is often caused by bacteria.
B)is a painful swelling in an eyelash.
C)may involve a sebaceous gland.
D)may involve a tarsal gland.
E)All of the answers are correct.
A)is often caused by bacteria.
B)is a painful swelling in an eyelash.
C)may involve a sebaceous gland.
D)may involve a tarsal gland.
E)All of the answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Which of the following descriptions best matches the term aqueous humor?
A)gelatinous fluid that fills anterior chamber
B)secreted in bright light
C)excessive production may lead to glaucoma
D)converts to vitreous humor with age
E)provides the liquid component of lacrimal secretions
A)gelatinous fluid that fills anterior chamber
B)secreted in bright light
C)excessive production may lead to glaucoma
D)converts to vitreous humor with age
E)provides the liquid component of lacrimal secretions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
During accommodation,the ciliary muscle ________ causing the ciliary body to move ________ and apply ________ tension on the lens.
A)relaxes; forward; more
B)contracts; forward; less
C)contracts; back; more
D)relaxes; inward; less
E)contracts; back; less
A)relaxes; forward; more
B)contracts; forward; less
C)contracts; back; more
D)relaxes; inward; less
E)contracts; back; less

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The optic disc is a blind spot because
A)there are no photoreceptors in that area.
B)the retina lacks nerves in the optic disc .
C)humans are unable to focus light on that area of the retina.
D)the vitreous body is too thick in this area for the passage of light.
E)the fovea prevents light from striking the optic disc.
A)there are no photoreceptors in that area.
B)the retina lacks nerves in the optic disc .
C)humans are unable to focus light on that area of the retina.
D)the vitreous body is too thick in this area for the passage of light.
E)the fovea prevents light from striking the optic disc.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Which of the following is a function of tears?
A)lubricate the eye
B)wash away debris
C)provide oxygen
D)nourish the cornea and conjunctiva
E)All of the answers are correct.
A)lubricate the eye
B)wash away debris
C)provide oxygen
D)nourish the cornea and conjunctiva
E)All of the answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The cornea is part of the
A)iris.
B)fibrous tunic.
C)neural tunic.
D)uvea.
E)choroid.
A)iris.
B)fibrous tunic.
C)neural tunic.
D)uvea.
E)choroid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which of the following description applies to the term myopia?
A)farsightedness
B)nearsightedness
C)normal vision
D)astigmatism
E)age-related decline in accommodation
A)farsightedness
B)nearsightedness
C)normal vision
D)astigmatism
E)age-related decline in accommodation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59

Figure 17-1 The Sectional Anatomy of the Eye
Use Figure 17-1 to answer the following questions:
Identify the structure labeled "9."
A)suspensory ligaments
B)optic disc
C)sclera
D)fovea
E)pupil

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The ciliary muscle contracts to
A)control the amount of light reaching the retina.
B)adjust the shape of the lens for distant vision.
C)adjust the shape of the lens for near vision.
D)control the production of aqueous humor.
E)adjust the shape of the cornea and vitreous.
A)control the amount of light reaching the retina.
B)adjust the shape of the lens for distant vision.
C)adjust the shape of the lens for near vision.
D)control the production of aqueous humor.
E)adjust the shape of the cornea and vitreous.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Which of these anatomical sequences is correct?
A)tympanumincusmalleusstapesoval windowround window
B)tympanumincusmalleusstapesround windowoval window
C)tympanummalleusincusstapesoval windowround window
D)tympanumincusstapesmalleusoval windowround window
E)tympanummalleusincusstapesround windowoval window
A)tympanumincusmalleusstapesoval windowround window
B)tympanumincusmalleusstapesround windowoval window
C)tympanummalleusincusstapesoval windowround window
D)tympanumincusstapesmalleusoval windowround window
E)tympanummalleusincusstapesround windowoval window

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62

Figure 17-1 The Sectional Anatomy of the Eye
Use Figure 17-1 to answer the following questions:
Identify the structure labeled "12."
A)pupil
B)optic disc
C)sclera
D)fovea
E)retina

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
A pigment synthesized from vitamin A is
A)retinal.
B)opsin.
C)rhodopsin.
D)transducin.
E)cGMP.
A)retinal.
B)opsin.
C)rhodopsin.
D)transducin.
E)cGMP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
The first step in the process of photoreception is
A)the bleaching of rods.
B)the bleaching of cones.
C)absorption of a photon by a visual pigment.
D)inhibition of the sodium pumps.
E)release of neurotransmitter.
A)the bleaching of rods.
B)the bleaching of cones.
C)absorption of a photon by a visual pigment.
D)inhibition of the sodium pumps.
E)release of neurotransmitter.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
An elongate outer segment containing membranous discs and a narrow connecting stalk that attaches the outer segment to the inner segment describes
A)a bipolar cell.
B)a photoreceptor.
C)a ganglion cell.
D)an amacrine cell.
E)a horizontal cell.
A)a bipolar cell.
B)a photoreceptor.
C)a ganglion cell.
D)an amacrine cell.
E)a horizontal cell.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The external acoustic meatus ends at
A)the tympanic membrane.
B)the auditory ossicles.
C)the cochlea.
D)the pinna.
E)the vestibule.
A)the tympanic membrane.
B)the auditory ossicles.
C)the cochlea.
D)the pinna.
E)the vestibule.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Where are the visual pigments located in the rods and cones?
A)in the inner segment of photoreceptors
B)in mitochondria located in the outer segment
C)inside membrane discs stacked in the outer segment
D)inside a photosensitive nucleus
E)sandwiched in the cell membrane of the photoreceptors
A)in the inner segment of photoreceptors
B)in mitochondria located in the outer segment
C)inside membrane discs stacked in the outer segment
D)inside a photosensitive nucleus
E)sandwiched in the cell membrane of the photoreceptors

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Under which condition would the release of neurotransmitter by photoreceptors be greatest?
A)under normal room light
B)in a pitch-black room after 30 minutes
C)immediately after going outside in bright sunlight
D)focusing intently on a close object
E)focusing intently on a distant object
A)under normal room light
B)in a pitch-black room after 30 minutes
C)immediately after going outside in bright sunlight
D)focusing intently on a close object
E)focusing intently on a distant object

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Which of the following statements about the retina is true?
A)Ganglion cells send axons to the brain as cranial nerve II.
B)Axons carrying its output synapse in the thalamus.
C)It has photoreceptors that do not respond to dim light.
D)It has photoreceptors that do not respond to red light.
E)All of the answers are correct.
A)Ganglion cells send axons to the brain as cranial nerve II.
B)Axons carrying its output synapse in the thalamus.
C)It has photoreceptors that do not respond to dim light.
D)It has photoreceptors that do not respond to red light.
E)All of the answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70

Figure 17-1 The Sectional Anatomy of the Eye
Use Figure 17-1 to answer the following questions:
Identify the structure labeled "14."
A)pupil
B)optic disc
C)sclera
D)fovea
E)suspensory ligaments

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The following steps occur in rods when they are excited by photons of light. 1.Membrane sodium channels close.
2)Increased phosphodiesterase breaks down cGMP.
3)Retinal changes from the 11-cis form to the 11-trans form.
4)The membrane hyperpolarizes and the rate of neurotransmitter release declines.
5)Opsin activates transducin.
6)Opsin activation occurs.
The proper sequence for these steps is
A)1,6,5,2,4,3.
B)3,6,5,2,1,4.
C)6,3,5,2,1,4.
D)3,6,5,1,2,4.
E)1,3,4,5,6,2.
2)Increased phosphodiesterase breaks down cGMP.
3)Retinal changes from the 11-cis form to the 11-trans form.
4)The membrane hyperpolarizes and the rate of neurotransmitter release declines.
5)Opsin activates transducin.
6)Opsin activation occurs.
The proper sequence for these steps is
A)1,6,5,2,4,3.
B)3,6,5,2,1,4.
C)6,3,5,2,1,4.
D)3,6,5,1,2,4.
E)1,3,4,5,6,2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
The ________ ear collects sounds waves and transmits them to the ________ ear,which contains auditory ossicles
A)inner; middle
B)outer; middle
C)outer; inner
D)middle; inner
E)superficial; deep
A)inner; middle
B)outer; middle
C)outer; inner
D)middle; inner
E)superficial; deep

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
When all three cone populations are stimulated equally,we perceive
A)red.
B)blue.
C)green.
D)white.
E)blackness.
A)red.
B)blue.
C)green.
D)white.
E)blackness.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
In the light-adapted state,
A)photoreceptors are much more sensitive to stimulation.
B)photoreceptors are much less sensitive to stimulation.
C)we can only see color,and not black and white.
D)we would see better in the dark.
E)colors are dull.
A)photoreceptors are much more sensitive to stimulation.
B)photoreceptors are much less sensitive to stimulation.
C)we can only see color,and not black and white.
D)we would see better in the dark.
E)colors are dull.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Having to adjust to a dark room after walking in from bright light is because
A)the breakdown of rhodopsin to opsin occurs slowly.
B)the lens requires time to accommodate dim light.
C)rods exposed to strong light need time to regenerate rhodopsin.
D)rhodopsin does not function in dim light.
E)only cones function in dim light.
A)the breakdown of rhodopsin to opsin occurs slowly.
B)the lens requires time to accommodate dim light.
C)rods exposed to strong light need time to regenerate rhodopsin.
D)rhodopsin does not function in dim light.
E)only cones function in dim light.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
There are three different types of cones,each one sensitive to different light energies.These cones are designated
A)red,yellow,blue.
B)red,green,blue.
C)red,green,yellow.
D)yellow,red,blue.
E)red,white,blue.
A)red,yellow,blue.
B)red,green,blue.
C)red,green,yellow.
D)yellow,red,blue.
E)red,white,blue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Which of the following is true about rhodopsin?
A)called visual purple
B)is bleached during photoreception
C)is the visual pigment in rods
D)consists of opsin + retinal
E)All of the answers are correct.
A)called visual purple
B)is bleached during photoreception
C)is the visual pigment in rods
D)consists of opsin + retinal
E)All of the answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
When a rod is stimulated by light,
A)the plasma membrane becomes hyperpolarized.
B)the retinal changes from the 11-cis to the 11-trans form.
C)less neurotransmitter is released.
D)cGMP decreases and sodium channels close.
E)All of the answers are correct.
A)the plasma membrane becomes hyperpolarized.
B)the retinal changes from the 11-cis to the 11-trans form.
C)less neurotransmitter is released.
D)cGMP decreases and sodium channels close.
E)All of the answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
A sudden increase of light into the eye would cause
A)contraction of the sphincter pupillary muscles.
B)contraction of the radial pupillary muscles.
C)conversion of 11-trans to 11-cis retinal.
D)a decrease in the size of the pupil.
E)parasympathetic stimulation to the pupil.
A)contraction of the sphincter pupillary muscles.
B)contraction of the radial pupillary muscles.
C)conversion of 11-trans to 11-cis retinal.
D)a decrease in the size of the pupil.
E)parasympathetic stimulation to the pupil.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Visual pigments are derivatives of the compound
A)retinal.
B)opsin.
C)rhodopsin.
D)transducin.
E)cGMP.
A)retinal.
B)opsin.
C)rhodopsin.
D)transducin.
E)cGMP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 166 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



