Deck 25: Metabolism and Energetics
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/135
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 25: Metabolism and Energetics
1
The sum of all of the biochemical processes going on within the human body at any given time is called
A)glycolysis.
B)oxidative phosphorylation.
C)catabolism.
D)anabolism.
E)metabolism.
A)glycolysis.
B)oxidative phosphorylation.
C)catabolism.
D)anabolism.
E)metabolism.
E
2
The strategy of eating starchy foods for several days before an athletic event is known as
A)carbohydrate craving.
B)the Atkins diet.
C)carbohydrate loading.
D)glycolysis reaction.
E)overeating.
A)carbohydrate craving.
B)the Atkins diet.
C)carbohydrate loading.
D)glycolysis reaction.
E)overeating.
C
3
During glycolysis
A)a molecule of glucose is converted into two molecules of pyruvic acid.
B)four molecules of ATP are produced.
C)two molecules of ATP are consumed.
D)hydrogen atoms are removed from organic molecules.
E)All of the answers are correct.
A)a molecule of glucose is converted into two molecules of pyruvic acid.
B)four molecules of ATP are produced.
C)two molecules of ATP are consumed.
D)hydrogen atoms are removed from organic molecules.
E)All of the answers are correct.
E
4
The carbon dioxide of respiration is formed during
A)glycolysis.
B)the citric acid cycle.
C)electron transport.
D)the formation of pyruvic acid.
E)the formation of water.
A)glycolysis.
B)the citric acid cycle.
C)electron transport.
D)the formation of pyruvic acid.
E)the formation of water.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The citric acid cycle
A)begins with the formation of a molecule of citric acid.
B)directly produces most of the ATP from the catabolism of glucose.
C)consumes two moles of carbon dioxide.
D)contains enzymes called cytochromes.
E)forms acetyl-CoA from glucose-6-phosphate.
A)begins with the formation of a molecule of citric acid.
B)directly produces most of the ATP from the catabolism of glucose.
C)consumes two moles of carbon dioxide.
D)contains enzymes called cytochromes.
E)forms acetyl-CoA from glucose-6-phosphate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The chemical equation that correctly summarizes the overall reaction in oxidative phosphorylation is
A)H₂ + O₂ → H₂O + O.
B)2 H₂ + O₂ → 2 H₂O.
C)3 H₂ + 2O₂ → 3 H₂O + 2 O.
D)H₂ + O₂ → H₂O.
E)P + 3 O → PO₃.
A)H₂ + O₂ → H₂O + O.
B)2 H₂ + O₂ → 2 H₂O.
C)3 H₂ + 2O₂ → 3 H₂O + 2 O.
D)H₂ + O₂ → H₂O.
E)P + 3 O → PO₃.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
What percent of energy released from catabolism is lost as heat?
A)20
B)30
C)40
D)50
E)60
A)20
B)30
C)40
D)50
E)60

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The ________ of the mitochondrion contains large-diameter pores that are permeable to ions and small organic molecules such as pyruvic acid.
A)inner membrane
B)plasma membrane
C)outer membrane
D)matrix
E)cristae
A)inner membrane
B)plasma membrane
C)outer membrane
D)matrix
E)cristae

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Cells perform catabolism to generate ATP,which can be used for
A)muscle contraction.
B)ion transport.
C)protein synthesis.
D)glycogen synthesis.
E)All of the answers are correct.
A)muscle contraction.
B)ion transport.
C)protein synthesis.
D)glycogen synthesis.
E)All of the answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The major steps in oxidative phosphorylation include all of the following,except
A)removal of hydrogen atoms from a substrate molecule by coenzymes.
B)ionization of hydrogen atoms.
C)increasing the energy level of electrons passing through the electron transport chain.
D)the breaking of carbon-carbon covalent bonds.
E)the acceptance of electrons by oxygen atoms.
A)removal of hydrogen atoms from a substrate molecule by coenzymes.
B)ionization of hydrogen atoms.
C)increasing the energy level of electrons passing through the electron transport chain.
D)the breaking of carbon-carbon covalent bonds.
E)the acceptance of electrons by oxygen atoms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Cells must synthesize new organic compounds
A)to support growth.
B)to perform structural maintenance or repairs.
C)to produce secretions.
D)to store nutrient reserves.
E)All of the answers are correct.
A)to support growth.
B)to perform structural maintenance or repairs.
C)to produce secretions.
D)to store nutrient reserves.
E)All of the answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Cells synthesize new organic components for which of the following reasons?
A)structural maintenance
B)growth and repair
C)produce secretions
D)store nutrients
E)All of the answers are correct.
A)structural maintenance
B)growth and repair
C)produce secretions
D)store nutrients
E)All of the answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Each cytochrome contains
A)a lipoprotein.
B)a metal ion.
C)an ATP synthase.
D)an inorganic salt.
E)All of the answers are correct.
A)a lipoprotein.
B)a metal ion.
C)an ATP synthase.
D)an inorganic salt.
E)All of the answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Reactions within ________ provide most of the energy needed by a typical cell.
A)cytoplasm
B)the plasma membrane
C)the mitochondria
D)the endoplasmic reticulum
E)nucleus
A)cytoplasm
B)the plasma membrane
C)the mitochondria
D)the endoplasmic reticulum
E)nucleus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Although other nutrients can feed into the citric acid cycle,________ yields energy the quickest.
A)glycogen
B)glucose
C)protein
D)fat
E)an amino acid
A)glycogen
B)glucose
C)protein
D)fat
E)an amino acid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
In glycolysis,each molecule of glucose that is catabolized gives a net yield of how many molecules of ATP?
A)2
B)4
C)30
D)36
E)38
A)2
B)4
C)30
D)36
E)38

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
In the ETS,________ accepts electrons from one molecule and transfers them to another.
A)a hydrogen ion
B)a coenzyme
C)the acetyl group
D)ADP
E)NAD
A)a hydrogen ion
B)a coenzyme
C)the acetyl group
D)ADP
E)NAD

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
In the electron transport chain
A)NADH and FADH₂ donate hydrogen atoms.
B)reduced molecules transfer energy to ATP formation.
C)oxidative phosphorylation leads to ATP formation.
D)generates a concentration gradient by pumping hydrogen ions.
E)All of the answers are correct.
A)NADH and FADH₂ donate hydrogen atoms.
B)reduced molecules transfer energy to ATP formation.
C)oxidative phosphorylation leads to ATP formation.
D)generates a concentration gradient by pumping hydrogen ions.
E)All of the answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The function of the citric acid cycle is to
A)remove hydrogen atoms from organic molecules and transfer them to coenzymes.
B)transfer the acetyl group.
C)hydrolyze glucose.
D)produce carbon dioxide.
E)produce water.
A)remove hydrogen atoms from organic molecules and transfer them to coenzymes.
B)transfer the acetyl group.
C)hydrolyze glucose.
D)produce carbon dioxide.
E)produce water.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
In order for glycolysis to proceed,which of the following need not be present?
A)glucose
B)acetyl-CoA
C)ATP
D)NAD
E)ADP
A)glucose
B)acetyl-CoA
C)ATP
D)NAD
E)ADP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
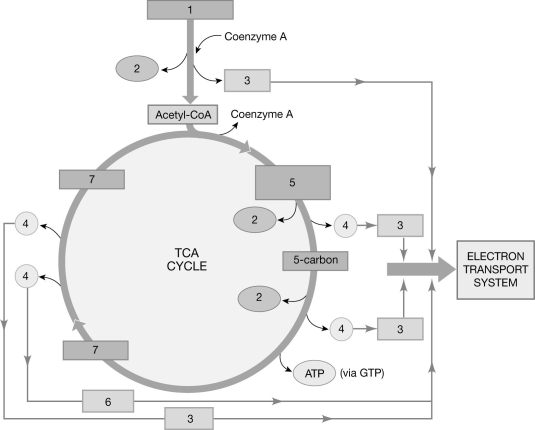
Figure 25-1 The Citric Acid Cycle
Use Figure 25-1 to answer the following questions:
What is the molecule labeled "5"?
A)fumaric acid
B)citric acid
C)4-carbon molecule
D)malic acid
E)oxaloacetic acid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The essential fatty acids are
A)linoleic acid and linolenic acid.
B)leucine and lysine.
C)cholesterol and glycerol.
D)HDLs and LDLs.
E)glycerol and pyruvic acid.
A)linoleic acid and linolenic acid.
B)leucine and lysine.
C)cholesterol and glycerol.
D)HDLs and LDLs.
E)glycerol and pyruvic acid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
If 8 molecules of NADH from the citric acid cycle entered the ETS,how much ATP would be produced?
A)36 ATP
B)32 ATP
C)3 ATP
D)8 ATP
E)24 ATP
A)36 ATP
B)32 ATP
C)3 ATP
D)8 ATP
E)24 ATP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The main purpose of the citric acid cycle is to
A)produce Acetyl CoA.
B)produce proteins for energy storage.
C)phosphorylate glucose molecules.
D)supply hydrogen atoms to the mitochondria.
E)produce citric acid to make vitamin C.
A)produce Acetyl CoA.
B)produce proteins for energy storage.
C)phosphorylate glucose molecules.
D)supply hydrogen atoms to the mitochondria.
E)produce citric acid to make vitamin C.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The citric acid cycle is an aerobic process because
A)ADP is phosphorylated.
B)FADH2 is produced.
C)citric acid molecules have oxygen atoms.
D)oxygen is needed to remove carbon atoms as carbon dioxide.
E)NAH+ is converted into NADH.
A)ADP is phosphorylated.
B)FADH2 is produced.
C)citric acid molecules have oxygen atoms.
D)oxygen is needed to remove carbon atoms as carbon dioxide.
E)NAH+ is converted into NADH.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
In the citric acid cycle,a 2 carbon molecule and a 4 carbon molecule combine to produce
A)fructose-1,6-bisphosphate.
B)carbon dioxide.
C)pyruvic acid.
D)NADH.
E)citric acid.
A)fructose-1,6-bisphosphate.
B)carbon dioxide.
C)pyruvic acid.
D)NADH.
E)citric acid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Oxygen is an important molecule in which of the following:
A)citric acid cycle and ETS
B)glycolysis,citric acid cycle,and ETS
C)citric acid cycle only
D)glycolysis only
E)ETS only
A)citric acid cycle and ETS
B)glycolysis,citric acid cycle,and ETS
C)citric acid cycle only
D)glycolysis only
E)ETS only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28

Figure 25-1 The Citric Acid Cycle
Use Figure 25-1 to answer the following questions:
What is the molecule labeled "2"?
A)hydrogen atoms
B)citric acid
C)NADH
D)carbon dioxide
E)FADH₂

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Hydrogen atoms from one FADH₂ from the citric acid cycle produce how much ATP in the Electron Transport System?
A)32 ATP
B)2 ATP
C)3 ATP
D)4 ATP
E)1 ATP
A)32 ATP
B)2 ATP
C)3 ATP
D)4 ATP
E)1 ATP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The end products of glycolysis are
A)ATP,water,and carbon dioxide.
B)ATP,NADH,and pyruvic acid.
C)ADP and ATP.
D)pyruvic acid and citric acid.
E)NADH and FADH2.
A)ATP,water,and carbon dioxide.
B)ATP,NADH,and pyruvic acid.
C)ADP and ATP.
D)pyruvic acid and citric acid.
E)NADH and FADH2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The citric acid cycle occurs in the
A)cytosol.
B)golgi apparatus.
C)mitochondrial cristae.
D)mitochondrial matrix.
E)ribosome.
A)cytosol.
B)golgi apparatus.
C)mitochondrial cristae.
D)mitochondrial matrix.
E)ribosome.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The end products of aerobic respiration are
A)carbon dioxide,water,and energy (ATP).
B)pyruvic acid and carbon dioxide.
C)carbon dioxide and alcohol.
D)oxygen and water.
E)NADH and FADH2.
A)carbon dioxide,water,and energy (ATP).
B)pyruvic acid and carbon dioxide.
C)carbon dioxide and alcohol.
D)oxygen and water.
E)NADH and FADH2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
What is the role of NADH in metabolism?
A)convert pyruvic acid into acetyl-coA
B)produce bicarbonate ions for a pH buffer
C)transport hydrogen atoms to coenzymes in the mitochondrial cristae
D)produce carbon dioxide
E)phosphorylate ADP into ATP
A)convert pyruvic acid into acetyl-coA
B)produce bicarbonate ions for a pH buffer
C)transport hydrogen atoms to coenzymes in the mitochondrial cristae
D)produce carbon dioxide
E)phosphorylate ADP into ATP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
When NAD+ is ________ it becomes NADH. When NADH is ________ it becomes NAD+.
A)phosphorylated; deaminated
B)reduced; oxidized
C)made; recycled
D)phosphorylated; dephosphorylated
E)oxidized; reduced
A)phosphorylated; deaminated
B)reduced; oxidized
C)made; recycled
D)phosphorylated; dephosphorylated
E)oxidized; reduced

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35

Figure 25-1 The Citric Acid Cycle
Use Figure 25-1 to answer the following questions:
What is the molecule labeled "1"?
A)phosphoglyceric acid
B)citric acid
C)pyruvate acid
D)NADH
E)FADH₂

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
How many net ATP molecules are produced by the complete metabolism (all pathways)of one glucose molecule?
A)2 ATP
B)63 ATP
C)500 ATP
D)36 ATP
E)32 ATP
A)2 ATP
B)63 ATP
C)500 ATP
D)36 ATP
E)32 ATP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Most of the ATP from metabolism is produced in the
A)citric acid cycle.
B)Electron Transport System.
C)cytosol.
D)mitochondrial matrix.
E)glycolysis.
A)citric acid cycle.
B)Electron Transport System.
C)cytosol.
D)mitochondrial matrix.
E)glycolysis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
In oxidative phosphorylation,energy for the synthesis of ATP is directly obtained from
A)the splitting of oxygen molecules.
B)the breaking of the covalent bonds in glucose.
C)the movement of hydrogen ions through channels in the inner mitochondrial membrane.
D)the combination of two atoms of hydrogen and one atom of oxygen to form water.
E)the oxidation of acetyl-CoA.
A)the splitting of oxygen molecules.
B)the breaking of the covalent bonds in glucose.
C)the movement of hydrogen ions through channels in the inner mitochondrial membrane.
D)the combination of two atoms of hydrogen and one atom of oxygen to form water.
E)the oxidation of acetyl-CoA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39

Figure 25-1 The Citric Acid Cycle
Use Figure 25-1 to answer the following questions:
What is the substance labeled "4"?
A)hydrogen atoms
B)citric acid
C)4 carbon molecule
D)NADH
E)FADH₂

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40

Figure 25-1 The Citric Acid Cycle
Use Figure 25-1 to answer the following questions:
What is the molecule labeled "7" ?
A)hydrogen atoms
B)citric acid
C)4 carbon molecule
D)NADH
E)FADH₂

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Metabolism of amino acids in the citric acid cycle yields
A)more energy than lipid metabolism.
B)more energy than carbohydrate metabolism.
C)approximately the same energy as lipid metabolism.
D)approximately the same energy as carbohydrate metabolism.
E)more energy than lipid and carbohydrate metabolism combined.
A)more energy than lipid metabolism.
B)more energy than carbohydrate metabolism.
C)approximately the same energy as lipid metabolism.
D)approximately the same energy as carbohydrate metabolism.
E)more energy than lipid and carbohydrate metabolism combined.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Removal of the amino group from amino acids in the first step of their catabolism requires a coenzyme derived from vitamin ________.
A)A
B)C
C)B₁₂
D)B₆
E)B₉
A)A
B)C
C)B₁₂
D)B₆
E)B₉

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
In the human body,cholesterol is important because it
A)helps waterproof the epidermis.
B)is a lipid component of all cell membranes.
C)is a key constituent of bile.
D)is the precursor of several steroid hormones and vitamin D₃.
E)All of the answers are correct.
A)helps waterproof the epidermis.
B)is a lipid component of all cell membranes.
C)is a key constituent of bile.
D)is the precursor of several steroid hormones and vitamin D₃.
E)All of the answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Sometimes called "good cholesterol," ________ carry excess cholesterol from peripheral tissues to the liver.
A)very-low-density lipoproteins (VLDLs)
B)low-density lipoproteins (LDLs)
C)intermediate-density lipoproteins (IDLs)
D)high-density lipoproteins (HDLs)
E)very-high-density lipoproteins (VHDLs)
A)very-low-density lipoproteins (VLDLs)
B)low-density lipoproteins (LDLs)
C)intermediate-density lipoproteins (IDLs)
D)high-density lipoproteins (HDLs)
E)very-high-density lipoproteins (VHDLs)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
All of the following are true of beta-oxidation,except that
A)it occurs in the mitochondria.
B)fatty acids break down into two-carbon fragments that enter the TCA cycle.
C)lipids are converted into glycogen molecules.
D)it requires coenzyme A,NAD,and FAD.
E)it yields large amounts of ATP.
A)it occurs in the mitochondria.
B)fatty acids break down into two-carbon fragments that enter the TCA cycle.
C)lipids are converted into glycogen molecules.
D)it requires coenzyme A,NAD,and FAD.
E)it yields large amounts of ATP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Urea is formed in the
A)liver.
B)stomach.
C)kidneys.
D)small intestine.
E)large intestine.
A)liver.
B)stomach.
C)kidneys.
D)small intestine.
E)large intestine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Lipids
A)deliver somewhat less energy than an equivalent mass of glucose.
B)are difficult to store since they are not water soluble.
C)yield quick bursts of energy.
D)provide energy for cells with modest energy demands.
E)are the primary nutrient metabolized in cells.
A)deliver somewhat less energy than an equivalent mass of glucose.
B)are difficult to store since they are not water soluble.
C)yield quick bursts of energy.
D)provide energy for cells with modest energy demands.
E)are the primary nutrient metabolized in cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
During the absorptive state,
A)the liver forms glycogen.
B)adipocytes release fatty acids to the circulation.
C)skeletal muscle breaks down glycogen.
D)insulin levels are low.
E)skeletal muscle fibers release glucose.
A)the liver forms glycogen.
B)adipocytes release fatty acids to the circulation.
C)skeletal muscle breaks down glycogen.
D)insulin levels are low.
E)skeletal muscle fibers release glucose.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
During lipolysis
A)triglycerides are converted into molecules of acetyl-CoA.
B)triglycerides are broken down into glycerol and fatty acids.
C)lipids are converted into glucose molecules.
D)lipids are formed from excess carbohydrates.
E)lipids are metabolized to yield ATP.
A)triglycerides are converted into molecules of acetyl-CoA.
B)triglycerides are broken down into glycerol and fatty acids.
C)lipids are converted into glucose molecules.
D)lipids are formed from excess carbohydrates.
E)lipids are metabolized to yield ATP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
A high uric acid level (above 7.4 mg/dl)can lead to the painful condition known as
A)gout.
B)rheumatoid arthritis.
C)anorexia nervosa.
D)lupus.
E)ketosis.
A)gout.
B)rheumatoid arthritis.
C)anorexia nervosa.
D)lupus.
E)ketosis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Lipogenesis generally begins with
A)glucose.
B)amino acids.
C)fatty acids.
D)acetyl-CoA.
E)succinyl-CoA.
A)glucose.
B)amino acids.
C)fatty acids.
D)acetyl-CoA.
E)succinyl-CoA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Catabolism of protein is not a practical source of quick energy because of all of the following,except that
A)proteins are more difficult to break apart than lipids or carbohydrates.
B)the energy yield from protein is less than the yield from lipids.
C)one of the by-products of protein catabolism is ammonia.
D)most individuals have little protein to spare before harming vital organs.
E)extensive catabolism of protein threatens homeostasis.
A)proteins are more difficult to break apart than lipids or carbohydrates.
B)the energy yield from protein is less than the yield from lipids.
C)one of the by-products of protein catabolism is ammonia.
D)most individuals have little protein to spare before harming vital organs.
E)extensive catabolism of protein threatens homeostasis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The largest lipoproteins,ranging in diameter up to 0.5 µm,________ are produced by intestinal epithelial cells from the fats in food.
A)very-low-density lipoproteins (VLDLs)
B)low-density lipoproteins (LDLs)
C)intermediate-density lipoproteins (IDLs)
D)high-density lipoproteins (HDLs)
E)chylomicrons
A)very-low-density lipoproteins (VLDLs)
B)low-density lipoproteins (LDLs)
C)intermediate-density lipoproteins (IDLs)
D)high-density lipoproteins (HDLs)
E)chylomicrons

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
For adults there are ________ essential amino acids.
A)2
B)6
C)8
D)10
E)20
A)2
B)6
C)8
D)10
E)20

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Linoleic acid and linolenic acid are examples of
A)transport proteins.
B)lipoproteins.
C)essential fatty acids.
D)essential amino acids.
E)vitamins.
A)transport proteins.
B)lipoproteins.
C)essential fatty acids.
D)essential amino acids.
E)vitamins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Someone with a total cholesterol level between 200 and 239 mg/dl should
A)modify their diet.
B)lose weight if overweight.
C)have annual checkups.
D)reduce the amount of saturated fat in the diet.
E)All of the answers are correct.
A)modify their diet.
B)lose weight if overweight.
C)have annual checkups.
D)reduce the amount of saturated fat in the diet.
E)All of the answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
In transamination,the amino group of an amino acid is
A)converted to ammonia.
B)converted to urea.
C)transferred to a keto acid.
D)absorbed by water.
E)transferred to acetyl-CoA.
A)converted to ammonia.
B)converted to urea.
C)transferred to a keto acid.
D)absorbed by water.
E)transferred to acetyl-CoA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The conversion of ammonia into a less toxic substance produces
A)ketone bodies.
B)urea.
C)nitrate.
D)acetyl-CoA.
E)water.
A)ketone bodies.
B)urea.
C)nitrate.
D)acetyl-CoA.
E)water.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The lipoproteins that carry absorbed lipids from the intestinal tract to the bloodstream are
A)HDLs.
B)VLDLs.
C)LDLs.
D)chylomicrons.
E)coenzymes.
A)HDLs.
B)VLDLs.
C)LDLs.
D)chylomicrons.
E)coenzymes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
In order to determine the LDL level in a patient's blood it is necessary to measure
A)total cholesterol level.
B)HDL level.
C)triglyceride level.
D)triglyceride and monoglyceride levels.
E)total cholesterol level,HDL level,and triglyceride level.
A)total cholesterol level.
B)HDL level.
C)triglyceride level.
D)triglyceride and monoglyceride levels.
E)total cholesterol level,HDL level,and triglyceride level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The major anion in body fluids is
A)chloride.
B)bicarbonate.
C)sulfate.
D)iodide.
A)chloride.
B)bicarbonate.
C)sulfate.
D)iodide.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
A cation that is essential for muscle contraction,nerve function,and blood clotting is
A)sodium.
B)potassium.
C)calcium.
D)magnesium.
E)selenium.
A)sodium.
B)potassium.
C)calcium.
D)magnesium.
E)selenium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The major cation in cytoplasm is
A)sodium.
B)potassium.
C)calcium.
D)magnesium.
E)iron.
A)sodium.
B)potassium.
C)calcium.
D)magnesium.
E)iron.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
During starvation
A)carbohydrate utilization increases.
B)gluconeogenesis ceases.
C)there is a decline in circulating ketone bodies.
D)muscle proteins are used as an energy source.
E)carbohydrate reserves maintained by metabolizing inorganic compounds.
A)carbohydrate utilization increases.
B)gluconeogenesis ceases.
C)there is a decline in circulating ketone bodies.
D)muscle proteins are used as an energy source.
E)carbohydrate reserves maintained by metabolizing inorganic compounds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
On a tour of African countries,Mark contracts a bad case of traveler's diarrhea.Because he can't eat very much,his body starts to use energy sources other than carbohydrates.This would result in
A)increased levels of urea in the blood.
B)ketosis and a decreased blood pH.
C)increased gluconeogenesis in the liver.
D)lipid metabolism.
E)All of the answers are correct.
A)increased levels of urea in the blood.
B)ketosis and a decreased blood pH.
C)increased gluconeogenesis in the liver.
D)lipid metabolism.
E)All of the answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The major cation in extracellular fluid is
A)sodium.
B)potassium.
C)calcium.
D)magnesium.
E)iron.
A)sodium.
B)potassium.
C)calcium.
D)magnesium.
E)iron.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Glucocorticoids have which of the following effects on general peripheral tissues?
A)They decrease the use of glucose.
B)They increase gluconeogenesis.
C)They increase glycogenolysis.
D)They promote glucose synthesis.
E)All of the answers are correct.
A)They decrease the use of glucose.
B)They increase gluconeogenesis.
C)They increase glycogenolysis.
D)They promote glucose synthesis.
E)All of the answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The element that is necessary for the proper function of the enzyme carbonic anhydrase is
A)iron.
B)cobalt.
C)zinc.
D)selenium.
E)iodine.
A)iron.
B)cobalt.
C)zinc.
D)selenium.
E)iodine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
A balanced diet should
A)include adequate substrates for the production of energy.
B)provide essential amino acids and fatty acids.
C)contain adequate amounts of vitamins and minerals.
D)contain adequate amounts of water.
E)All of the answers are correct.
A)include adequate substrates for the production of energy.
B)provide essential amino acids and fatty acids.
C)contain adequate amounts of vitamins and minerals.
D)contain adequate amounts of water.
E)All of the answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Compounds that cells can use to make glucose include all of the following,except
A)acetyl-CoA
B)glycerol
C)amino acids
D)lactic acid
E)pyruvic acid
A)acetyl-CoA
B)glycerol
C)amino acids
D)lactic acid
E)pyruvic acid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
All of the following occur during the postabsorptive state,except that
A)glycogenolysis occurs in the liver.
B)levels of blood glucose are elevated.
C)ketone bodies may be formed.
D)fat mobilization occurs.
E)gluconeogenesis occurs in the liver.
A)glycogenolysis occurs in the liver.
B)levels of blood glucose are elevated.
C)ketone bodies may be formed.
D)fat mobilization occurs.
E)gluconeogenesis occurs in the liver.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
The presence of ketone bodies in the urine is known as
A)polyuria.
B)hematuria.
C)ketonuria.
D)uremia.
E)ketosis.
A)polyuria.
B)hematuria.
C)ketonuria.
D)uremia.
E)ketosis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
An element that is a component of hemoglobin,myoglobin,and cytochromes is
A)calcium.
B)magnesium.
C)iron.
D)zinc.
E)cobalt.
A)calcium.
B)magnesium.
C)iron.
D)zinc.
E)cobalt.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
When the body is relying on internal energy reserves to continue meeting its energy demands,it is in the
A)postabsorptive state.
B)absorptive state.
C)starvation state.
D)deprivation state.
E)preabsorptive state.
A)postabsorptive state.
B)absorptive state.
C)starvation state.
D)deprivation state.
E)preabsorptive state.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Wally decides to go on a hunger strike to further one of his favorite causes.After many days with nothing but water you would expect to observe
A)elevated levels of glucocorticoids.
B)ketone bodies in his urine.
C)decreased blood pH.
D)decreased blood glucose level.
E)All of the answers are correct.
A)elevated levels of glucocorticoids.
B)ketone bodies in his urine.
C)decreased blood pH.
D)decreased blood glucose level.
E)All of the answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Which of the following complements the actions of glucocorticoids?
A)insulin
B)growth hormone
C)glucagon
D)epinephrine
E)androgens
A)insulin
B)growth hormone
C)glucagon
D)epinephrine
E)androgens

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
A cation that often acts as a cofactor for enzymes is
A)sodium.
B)potassium.
C)calcium.
D)magnesium.
E)zinc.
A)sodium.
B)potassium.
C)calcium.
D)magnesium.
E)zinc.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Nitrogen compounds of the body include all of the following,except
A)amino acids.
B)oxaloacetic acid.
C)creatine.
D)porphyrin.
E)purines.
A)amino acids.
B)oxaloacetic acid.
C)creatine.
D)porphyrin.
E)purines.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
An ion that is a necessary component of high-energy compounds and nucleic acids and a structural component of bone is the ________ ion.
A)chloride
B)sulfate
C)phosphate
D)bicarbonate
E)iodide
A)chloride
B)sulfate
C)phosphate
D)bicarbonate
E)iodide

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
The trace element needed for hemoglobin synthesis is
A)zinc.
B)copper.
C)cobalt.
D)iodine.
E)silicon.
A)zinc.
B)copper.
C)cobalt.
D)iodine.
E)silicon.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



