Deck 1: Environmental Problems, Their Causes, and Sustainability
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/89
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 1: Environmental Problems, Their Causes, and Sustainability
1
An environmentally sustainable society
A)protects natural capital
B)lives off the income natural capital provides
C)does not compromise the ability of future generations to meet their basic needs
D)all of these answers
E)protects natural capital and lives off the income natural capital provides
A)protects natural capital
B)lives off the income natural capital provides
C)does not compromise the ability of future generations to meet their basic needs
D)all of these answers
E)protects natural capital and lives off the income natural capital provides
all of these answers
2
Nutrient recycling is a vital natural service carried out by which natural resource?
A)natural gas
B)clean air
C)topsoil
D)all of these answers
E)two of these answers
A)natural gas
B)clean air
C)topsoil
D)all of these answers
E)two of these answers
topsoil
3
The long-term sustainability of life on planet Earth has depended on
A)solar energy
B)nutrient recycling
C)biodiversity
D)all of these answers
E)nutrient recycling and biodiversity
A)solar energy
B)nutrient recycling
C)biodiversity
D)all of these answers
E)nutrient recycling and biodiversity
all of these answers
4
Select the choice that correctly states the best priority for use of non-renewable resources, such as metals and plastics, from the environmentally sustainable perspective.
A)recycle, reuse, reduce
B)reuse, reduce, recycle
C)reduce, reuse, recycle
D)reduce, recycle, refuse
E)repurpose, recycle, remake
A)recycle, reuse, reduce
B)reuse, reduce, recycle
C)reduce, reuse, recycle
D)reduce, recycle, refuse
E)repurpose, recycle, remake

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following terms encompasses all of the others?
A)natural capital
B)natural resources
C)natural services
D)nutrient cycling
E)photosynthesis
A)natural capital
B)natural resources
C)natural services
D)nutrient cycling
E)photosynthesis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following categories of resources can be degraded if used beyond sustainable yield?
A)renewable resources
B)perpetual resources
C)energy resources
D)mineral resources
E)nonrenewable resources
A)renewable resources
B)perpetual resources
C)energy resources
D)mineral resources
E)nonrenewable resources

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The tragedy of the commons refers to
A)overuse of privately held resources
B)overuse of shared common resources
C)human deaths from polluted shared resources such as air or water
D)government over-regulation of fresh water use
E)all of these answers
A)overuse of privately held resources
B)overuse of shared common resources
C)human deaths from polluted shared resources such as air or water
D)government over-regulation of fresh water use
E)all of these answers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
What is an essential characteristic that indicates whether a resource should be categorized as a renewable resource?
A)It must be an energy resource.
B)It must be a biological resource.
C)It must be recyclable.
D)It must have the capacity to be replenished within days to several hundred years.
E)It must have the capacity to be utilized for immediate economic benefit.
A)It must be an energy resource.
B)It must be a biological resource.
C)It must be recyclable.
D)It must have the capacity to be replenished within days to several hundred years.
E)It must have the capacity to be utilized for immediate economic benefit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
When we speak of protecting the environment, we are referring to
A)all living things on the planet
B)all non-living things such as air, fresh water, and energy
C)all living and non-living things
D)humans and the living and non-living things that affect them only
E)humans and the living things that affect them only
A)all living things on the planet
B)all non-living things such as air, fresh water, and energy
C)all living and non-living things
D)humans and the living and non-living things that affect them only
E)humans and the living things that affect them only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following is a goal of environmental science?
A)Learn how nature works.
B)Understand how we interact with the environment.
C)Live more sustainably.
D)Find ways to deal with environmental problems.
E)All of these answers.
A)Learn how nature works.
B)Understand how we interact with the environment.
C)Live more sustainably.
D)Find ways to deal with environmental problems.
E)All of these answers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following is a social movement dedicated to the protection of the Earth's natural capital?
A)ecology
B)environmental science
C)environmentalism
D)natural science
E)sustainability
A)ecology
B)environmental science
C)environmentalism
D)natural science
E)sustainability

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following areas of study are not important in the study of environmental science?
A)Biology.
B)Chemistry.
C)Geology.
D)Economics.
E)All of these answers.
A)Biology.
B)Chemistry.
C)Geology.
D)Economics.
E)All of these answers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following would best be categorized as a perpetual resource?
A)oil reserves
B)fisheries
C)solar energy
D)forests
E)coal reserves
A)oil reserves
B)fisheries
C)solar energy
D)forests
E)coal reserves

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following is a form of natural capital gained directly or indirectly as a result of solar energy?
A)photosynthesis
B)flowing water
C)wind energy
D)biofuels
E)all of these answers
A)photosynthesis
B)flowing water
C)wind energy
D)biofuels
E)all of these answers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following is best categorized as an example of a natural service?
A)renewable energy
B)nonrenewable energy
C)water purification
D)oil
E)soil
A)renewable energy
B)nonrenewable energy
C)water purification
D)oil
E)soil

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
If a country's ecological footprint is larger than its biological capacity to replenish its renewable resources and absorb the resulting waste and pollution:
A)It is said to have an ecological deficit.
B)It should be supported by other countries with smaller footprints.
C)It is said to be a sustainable society.
D)It is most likely a developing country.
E)More than one of these answers is correct.
A)It is said to have an ecological deficit.
B)It should be supported by other countries with smaller footprints.
C)It is said to be a sustainable society.
D)It is most likely a developing country.
E)More than one of these answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following best depicts what is meant by an ecological footprint?
A)It is the average size of the lot on which a family home is built.
B)It is the number of acres necessary to grow enough food to support a family.
C)It is the geographic area in which a person travels during the course of their average daily activities.
D)It is the amount of biologically-productive land and water needed to supply the people in a particular country or area with necessary resources.
E)It is the amount of tillable agricultural land necessary to supply the food requirements of a nation.
A)It is the average size of the lot on which a family home is built.
B)It is the number of acres necessary to grow enough food to support a family.
C)It is the geographic area in which a person travels during the course of their average daily activities.
D)It is the amount of biologically-productive land and water needed to supply the people in a particular country or area with necessary resources.
E)It is the amount of tillable agricultural land necessary to supply the food requirements of a nation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A set of organisms within a defined area interacting with one another and with their environment of living and non-living matter is called a(n)
A)species
B)ecosystem
C)sustainable society
D)natural resource
E)none of these answers
A)species
B)ecosystem
C)sustainable society
D)natural resource
E)none of these answers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following is an example of recycling?
A)collecting and remelting aluminum beer cans and making them into new cans
B)cleaning and refilling soft-drink bottles
C)selling used clothing at a garage sale
D)saving leftovers in a peanut butter jar
E)using household water to water a garden
A)collecting and remelting aluminum beer cans and making them into new cans
B)cleaning and refilling soft-drink bottles
C)selling used clothing at a garage sale
D)saving leftovers in a peanut butter jar
E)using household water to water a garden

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Evidence that we are living unsustainably includes which of the following?
A)Renewable forests are shrinking.
B)Agricultural lands are deteriorating.
C)The lower atmosphere is warming.
D)Coral reefs are disappearing.
E)All of these answers.
A)Renewable forests are shrinking.
B)Agricultural lands are deteriorating.
C)The lower atmosphere is warming.
D)Coral reefs are disappearing.
E)All of these answers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
About ____ of the world's human population lives in the developing countries.
A)20%
B)40%
C)60%
D)80%
E)90%
A)20%
B)40%
C)60%
D)80%
E)90%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
All of the following are potentially renewable resources except
A)groundwater
B)trees in a forest
C)fertile soil
D)oil
E)animals
A)groundwater
B)trees in a forest
C)fertile soil
D)oil
E)animals

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Effects of pollution might include
A)less diversity of stream life because of road salt runoff
B)acid rain-induced destruction of a statue in your city park
C)increased incidence of respiratory diseases in polluted cities
D)all of these answers
E)both a and b only
A)less diversity of stream life because of road salt runoff
B)acid rain-induced destruction of a statue in your city park
C)increased incidence of respiratory diseases in polluted cities
D)all of these answers
E)both a and b only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
A worldview that holds that we can and should manage the Earth for our own benefit but that we also have an ethical responsibility to be caring stewards is called the
A)planetary management worldview
B)stewardship worldview
C)environmental wisdom worldview
D)none of these answers
E)all of these answers
A)planetary management worldview
B)stewardship worldview
C)environmental wisdom worldview
D)none of these answers
E)all of these answers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which of the following statements about developing countries is true?
A)They are highly industrialized.
B)They have high-average per capita income.
C)They include the United States, Germany, and Japan.
D)They are classified as middle-income or low-income.
E)They have about 85% of the world's wealth and income.
A)They are highly industrialized.
B)They have high-average per capita income.
C)They include the United States, Germany, and Japan.
D)They are classified as middle-income or low-income.
E)They have about 85% of the world's wealth and income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
You generally buy and eat microwave dinners. .After dinner, cardboard tops and plastic trays remain.The least effective way to deal with this type of solid waste problem is to
A)Store leftovers in the plastic trays.
B)Put all of the solid waste in the household trash to be taken to the landfill.
C)Donate the plastic containers to the local nursery schools to use with preschoolers.
D)Recycle the components.
E)All of these answers are effective.
A)Store leftovers in the plastic trays.
B)Put all of the solid waste in the household trash to be taken to the landfill.
C)Donate the plastic containers to the local nursery schools to use with preschoolers.
D)Recycle the components.
E)All of these answers are effective.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which of the following is an environmental benefit of affluence and wealth?
A)Increasing wealth allows for an increased capacity for resource consumption.
B)Increased wealth provides resources to apply toward the creation of environmentally beneficial technologies.
C)Increasing affluence often leads to a desire to travel widely and frequently in order to see the world.
D)The affluence of developed nations is highly desirable and sought after by citizens of developing nations.
E)The typical consumption patterns of affluent nations leads to beneficial environmental conservation practices.
A)Increasing wealth allows for an increased capacity for resource consumption.
B)Increased wealth provides resources to apply toward the creation of environmentally beneficial technologies.
C)Increasing affluence often leads to a desire to travel widely and frequently in order to see the world.
D)The affluence of developed nations is highly desirable and sought after by citizens of developing nations.
E)The typical consumption patterns of affluent nations leads to beneficial environmental conservation practices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Government subsidies to industries can actually contribute to the depletion and degradation of natural capital if the recipient of the subsidy does not
A)contribute to environmental causes
B)include the value of natural capital in the market price of the goods they produce
C)abide by environmental regulations in production practices
D)all of these answers
E)only two of these answers
A)contribute to environmental causes
B)include the value of natural capital in the market price of the goods they produce
C)abide by environmental regulations in production practices
D)all of these answers
E)only two of these answers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The IPAT model states that the key factor in environmental impact in
A)developing countries is resource use
B)developing countries is population size
C)developed countries is resource use
D)developed countries is population size
E)more than one of these answers
A)developing countries is resource use
B)developing countries is population size
C)developed countries is resource use
D)developed countries is population size
E)more than one of these answers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Point sources of pollution
A)enter ecosystems from dispersed and often hard-to-identify sources
B)include runoff of fertilizers and pesticides from farmlands and suburban lawns
C)are cheaper and easier to identify than nonpoint sources
D)are more difficult to control than nonpoint sources
E)are always found in rural areas
A)enter ecosystems from dispersed and often hard-to-identify sources
B)include runoff of fertilizers and pesticides from farmlands and suburban lawns
C)are cheaper and easier to identify than nonpoint sources
D)are more difficult to control than nonpoint sources
E)are always found in rural areas

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which of the following would be categorized as a non-renewable resource?
A)topsoil
B)fisheries
C)solar energy
D)forests
E)coal reserves
A)topsoil
B)fisheries
C)solar energy
D)forests
E)coal reserves

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Nonpoint sources of pollution
A)enter ecosystems from single identifiable sources
B)are more difficult to control than point sources
C)include smokestacks and automobile exhaust pipes
D)are cheaper and easier to identify than point sources
E)are always found in rural areas
A)enter ecosystems from single identifiable sources
B)are more difficult to control than point sources
C)include smokestacks and automobile exhaust pipes
D)are cheaper and easier to identify than point sources
E)are always found in rural areas

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which of the following is a major factor contributing to the degradation of natural capital associated with the pricing of consumable goods?
A)They are priced in such a way that they do not reflect the environmental damage caused by their production.
B)They are priced in such a way as to allow even those in poverty in developing nations to acquire them.
C)They are priced in such a way that only the most affluent purchaser is able to acquire them.
D)Consumers are typically aware of the kinds of environmental damage resulting from the production of the item.
E)None of these answers.
A)They are priced in such a way that they do not reflect the environmental damage caused by their production.
B)They are priced in such a way as to allow even those in poverty in developing nations to acquire them.
C)They are priced in such a way that only the most affluent purchaser is able to acquire them.
D)Consumers are typically aware of the kinds of environmental damage resulting from the production of the item.
E)None of these answers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Root causes of unsustainability include all of the following except
A)wasteful use of resources
B)poverty
C)rapid population growth
D)inclusion of environmental and social costs in market prices
E)All of these answers
A)wasteful use of resources
B)poverty
C)rapid population growth
D)inclusion of environmental and social costs in market prices
E)All of these answers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Nonrenewable resources include
A)oil
B)minerals
C)salt and sand
D)coal
E)all of these answers
A)oil
B)minerals
C)salt and sand
D)coal
E)all of these answers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The resource consumption of the average person in the United States is about _____ times that of the average citizen of India, and about _____ times that of the average person in the world's poorest countries.
A)2, 10
B)5, 10
C)8.6, 15
D)30, 100
E)none of these answers
A)2, 10
B)5, 10
C)8.6, 15
D)30, 100
E)none of these answers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Sustainable yield is the
A)profit yield from a business that operates from the perspective of sustainable living
B)highest rate that a renewable resource can be used indefinitely without reducing its available supply
C)profit from tax breaks tied to sustainable economic practices by businesses
D)all of these answers
E)none of these answers
A)profit yield from a business that operates from the perspective of sustainable living
B)highest rate that a renewable resource can be used indefinitely without reducing its available supply
C)profit from tax breaks tied to sustainable economic practices by businesses
D)all of these answers
E)none of these answers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Pollution cleanup efforts can be ineffective because
A)They often transfer pollutants from one part of the environment to another.
B)Once pollutants are dispersed, it costs too much to reduce them to acceptable levels.
C)They can be overwhelmed by growth in population and consumption.
D)All of these answers.
E)None of these answers.
A)They often transfer pollutants from one part of the environment to another.
B)Once pollutants are dispersed, it costs too much to reduce them to acceptable levels.
C)They can be overwhelmed by growth in population and consumption.
D)All of these answers.
E)None of these answers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Developed countries
A)are high-income
B)are low-income
C)use about 88% of the world's resources
D)make up about 80% of the world's population
E)Are high-income and use about 88% of the worlds resources
A)are high-income
B)are low-income
C)use about 88% of the world's resources
D)make up about 80% of the world's population
E)Are high-income and use about 88% of the worlds resources

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following best describes the concept of environmental degradation?
A)using solar power at a rapid rate
B)growing crops for food
C)cutting trees for wood products faster than the trees can regrow to maturity
D)letting agricultural runoff cause oxygen depletion and fish kills downstream
E)two of these answers
A)using solar power at a rapid rate
B)growing crops for food
C)cutting trees for wood products faster than the trees can regrow to maturity
D)letting agricultural runoff cause oxygen depletion and fish kills downstream
E)two of these answers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Which of the following is not among the three scientific principles of sustainability?
A)economic growth
B)reliance on solar energy
C)biodiversity
D)chemical cycling
E)Population control
A)economic growth
B)reliance on solar energy
C)biodiversity
D)chemical cycling
E)Population control

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Perpetual resources exist in a fixed quantity or stock in the Earth's crust.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
In an environmentally sustainable society, most affluent citizens work to decrease their consumption of products.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Every day, approximately _____ new people are added to the global population.
A)50,000
B)100,000
C)150,000
D)200,000
E)250,000 (a quarter of a million)
A)50,000
B)100,000
C)150,000
D)200,000
E)250,000 (a quarter of a million)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
A resource such as solar energy that is renewed continuously is a called a(n) ____________________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The per capita ecological footprint is the average ecological footprint of an individual in a given country or area.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Polluting chemicals enter the environment only through human activities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
We can say that biodiversity is a factor in maintaining life on this planet.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Recycling nonrenewable metallic resources takes much less energy, water, and other resources and produces less pollution and environmental degradation than exploiting virgin metallic resources.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
An environmentally sustainable society must be based on policies that provide for economic growth and development.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
In 2009, the world population is about
A)6.8 billion people
B)2.9 billion people
C)9.3 billion people
D)6.8 million people
E)7.2 billion people
A)6.8 billion people
B)2.9 billion people
C)9.3 billion people
D)6.8 million people
E)7.2 billion people

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The United States has the world's largest per capita ecological footprint.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The tragedy of the commons is a phenomenon that occurs only when the number of users is small.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
In order for the social changes to occur that will produce sustainable economies, fully 50% of the population of a country must support the change.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Pollution cleanup is considered a short-term solution if population and consumption levels grow without corresponding improvement in pollution control technology.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
If we make a commitment to more sustainable lifestyles and economies now, scientific evidence indicates it will take how long to fully implement the changes?
A)10 years
B)25 years
C)40 years
D)50 years
E)until the year 2100
A)10 years
B)25 years
C)40 years
D)50 years
E)until the year 2100

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
An exponential growth curve is best described as a J-shaped curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Government subsidies can actually encourage companies to conduct business in ways that result in environmental degradation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Rapid population growth and associated poverty are primarily occurring in developing countries and have little impact on environmental degradation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
If industry managers ask the question "How can my company avoid producing polluting air exhaust from my factory?" they are seeking pollution prevent, which is preferable to pollution cleanup.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
It has been estimated that humanity's global ecological footprint exceeds the Earth's biological capacity by about ____________________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
____________________ is the ability of the Earth's various natural systems and human cultural systems and economies to survive and adapt to changing environmental conditions indefinitely.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Pollution ____________________ is cheaper and more effective than pollution ____________________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
____________________ are materials and energy in nature that are essential or useful to humans.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
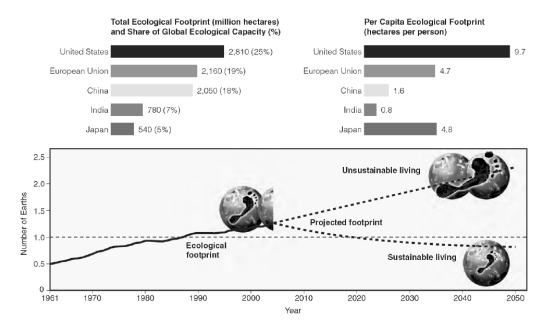
Is India's per capita ecological footprint greater than that of Japan?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Fish, fresh water, wild animals, and fertile soil are examples of ____________________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Developing countries can be classified as moderately developed, middle-income, or as ____________________, least developed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
When we exceed a renewable resource's natural replacement rate, the available supply begins to shrink through a process known as ____________________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
____________________ are functions of nature, such as purification of air and water, that support life and human economies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
A single, identifiable source of pollution is called a(n) ____________________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The three principles of sustainability are chemical cycling, reliance on solar energy, and ____________________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Natural capital is comprised of natural resources and natural ____________________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
An ecological ____________________is an irreversible shift in the behavior of a natural system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
____________________ is the biological science that studies the relationships between living things and their environment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
The highest rate at which a renewable resource can be used indefinitely without reducing its available supply is called its ____________________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Pesticides blown from agricultural lands into the air is an example of ____________________ pollution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
The action of processing plastic or aluminum cans into another usable product is called ____________________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Old drink bottles that are collected, washed, and refilled are an example of ____________________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79

Is India's total ecological footprint greater than that of Japan?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
The IPAT model of environmental impact takes into consideration population size, technology, and ____________________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



