Deck 15: Trade and Policy Reform in Latin America
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/66
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 15: Trade and Policy Reform in Latin America
1
From 1900 to 1960,Latin America's real GDP grew
A)slower than Europe, Asia, and the U.S.
B)as fast or faster than Europe, Asia, and the U.S.
C)faster than Europe and the U.S. but slower than Asia.
D)faster than Asia, but slower than Europe and the U.S.
A)slower than Europe, Asia, and the U.S.
B)as fast or faster than Europe, Asia, and the U.S.
C)faster than Europe and the U.S. but slower than Asia.
D)faster than Asia, but slower than Europe and the U.S.
B
2
Growth in Latin America in the 1970s was largely fueled by
A)monetary expansion.
B)government spending.
C)export growth.
D)capital inflows.
A)monetary expansion.
B)government spending.
C)export growth.
D)capital inflows.
B
3
The 1980s were a Lost Decade for Latin America.
True
4
Import substitution industrialization in Latin America
A)relied on increased exports.
B)provided subsidies for exports.
C)shifted the bulk of exports away from primary commodities.
D)created disincentives to export.
A)relied on increased exports.
B)provided subsidies for exports.
C)shifted the bulk of exports away from primary commodities.
D)created disincentives to export.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The concept of "economic pessimism" stems from
A)the theory and empirical fact which states that developing nations face declining export prices relative to increasing import prices.
B)the fact that economic growth in an era of globalization is difficult to attain.
C)the fact that smaller countries would not enjoy comparative advantage unless they are allowed to subsidize some of their industries.
D)the fact that it is impossible to achieve desired economic development without adopting full democratic principles.
A)the theory and empirical fact which states that developing nations face declining export prices relative to increasing import prices.
B)the fact that economic growth in an era of globalization is difficult to attain.
C)the fact that smaller countries would not enjoy comparative advantage unless they are allowed to subsidize some of their industries.
D)the fact that it is impossible to achieve desired economic development without adopting full democratic principles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Raul Prebisch was an Argentine economist who argued that
A)the terms of trade would decline for primary commodity exports.
B)the terms of trade would decline for manufactured goods exports.
C)the terms of trade for Latin American economies could not be improved.
D)the terms of trade for high-income countries would inevitably worsen.
A)the terms of trade would decline for primary commodity exports.
B)the terms of trade would decline for manufactured goods exports.
C)the terms of trade for Latin American economies could not be improved.
D)the terms of trade for high-income countries would inevitably worsen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Latin America has more trade agreements than any other region,and it has some of the oldest as well.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
ISI policies were brought to an end primarily by
A)their inability to solve the crises of the 1980s.
B)authoritarian governments interested in total control over the economy.
C)populist politicians.
D)protests by consumers.
A)their inability to solve the crises of the 1980s.
B)authoritarian governments interested in total control over the economy.
C)populist politicians.
D)protests by consumers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Rent seeking
A)is unlikely the more heavily engaged government planners are with the economy.
B)is more likely where institutions are strong.
C)is not likely to lead to waste and efficiency.
D)is more likely when government policy creates something of value that government officials are charged with distributing.
A)is unlikely the more heavily engaged government planners are with the economy.
B)is more likely where institutions are strong.
C)is not likely to lead to waste and efficiency.
D)is more likely when government policy creates something of value that government officials are charged with distributing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The terms of trade are
A)the terms negotiated in a trade agreement.
B)exports plus imports divided by GDP.
C)the value of the real exchange rate.
D)the ratio of export prices to import prices.
A)the terms negotiated in a trade agreement.
B)exports plus imports divided by GDP.
C)the value of the real exchange rate.
D)the ratio of export prices to import prices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The terms of trade (TOT)is defined as
A)(index of export prices)/(index of import prices).
B)(home-country currency)/(foreign-country currency).
C)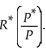
D)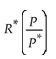
A)(index of export prices)/(index of import prices).
B)(home-country currency)/(foreign-country currency).
C)
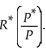
D)
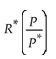

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Indirectly,overvalued exchange rates in Latin America caused
A)a capital shortage in agriculture.
B)a capital shortage in industry.
C)a capital abundance in agriculture.
D)an increase in competitive pressures faced by industry.
A)a capital shortage in agriculture.
B)a capital shortage in industry.
C)a capital abundance in agriculture.
D)an increase in competitive pressures faced by industry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which four nations account for most of the population and economic activity in Latin America?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Latin America
A)is significantly smaller than the NAFTA market in terms of population.
B)has a smaller population, but a larger GDP than the NAFTA market.
C)has a larger population than the NAFTA market.
D)is similar in population to the NAFTA market.
A)is significantly smaller than the NAFTA market in terms of population.
B)has a smaller population, but a larger GDP than the NAFTA market.
C)has a larger population than the NAFTA market.
D)is similar in population to the NAFTA market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Rapid growth of government spending in Latin America in the 1970s led to
A)the Debt Crisis.
B)rapid economic growth.
C)direct foreign investment.
D)capital outflows.
A)the Debt Crisis.
B)rapid economic growth.
C)direct foreign investment.
D)capital outflows.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Overvalued exchange rates were a persistent problem under ISI policies.In part,this was a deliberate policy in order to
A)increase imports.
B)discourage exports.
C)help targeted industries sell their exports.
D)help targeted industries buy imports.
A)increase imports.
B)discourage exports.
C)help targeted industries sell their exports.
D)help targeted industries buy imports.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Over time,the terms of trade of Latin American countries have generally ________,and the terms of trade of developed countries have generally ________.
A)worsened; worsened
B)worsened; improved
C)improved; worsened
D)improved; improved
A)worsened; worsened
B)worsened; improved
C)improved; worsened
D)improved; improved

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Proponents of ISI assumed that governments
A)were capable of identifying and correcting market failures.
B)were capable of identifying and correcting the excesses of economic populists.
C)should enact orthodox stabilization plans.
D)could control the terms of trade.
A)were capable of identifying and correcting market failures.
B)were capable of identifying and correcting the excesses of economic populists.
C)should enact orthodox stabilization plans.
D)could control the terms of trade.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
According to Prebisch and other ISI theoreticians,countries should begin to shift their comparative advantage away from primary commodity production by first producing
A)industrial goods such as pumps and generators.
B)complex consumer goods such as autos and appliances.
C)simple consumer goods such as food products and textiles.
D)minerals and agricultural products.
A)industrial goods such as pumps and generators.
B)complex consumer goods such as autos and appliances.
C)simple consumer goods such as food products and textiles.
D)minerals and agricultural products.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Briefly describe economic growth in Latin America from 1900 to the 1980s.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
What is the primary reason exchange rates were overvalued under ISI?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
An economic populist movement
A)is likely to create long-term economic stability.
B)favors promotion of export-based industries and fiscal austerity.
C)is less likely to use expansionary policy due to inflation risks.
D)uses economic tools to obtain support from labor and domestically oriented businesses.
A)is likely to create long-term economic stability.
B)favors promotion of export-based industries and fiscal austerity.
C)is less likely to use expansionary policy due to inflation risks.
D)uses economic tools to obtain support from labor and domestically oriented businesses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of populist regimes?
A)Nationalistic ideologies
B)Focus on economic growth
C)Focus on income redistribution
D)Focus on controlling inflation
A)Nationalistic ideologies
B)Focus on economic growth
C)Focus on income redistribution
D)Focus on controlling inflation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Populist policies are not successful even in the immediate short run at stimulating the economy and creating jobs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Alan Garcia
A)in his first Presidency in Peru, followed free market economic policies.
B)nationalized the property of the financial services sector during his first Presidency.
C)was never freely elected in Peru and ruled with the support of the military.
D)maintained balanced budgets and helped Peru avoid the economic problems most Latin American nations were experiencing in the 1980s.
A)in his first Presidency in Peru, followed free market economic policies.
B)nationalized the property of the financial services sector during his first Presidency.
C)was never freely elected in Peru and ruled with the support of the military.
D)maintained balanced budgets and helped Peru avoid the economic problems most Latin American nations were experiencing in the 1980s.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
What are the three initial conditions that trigger economic populism?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
One problem of ISI was
A)the failure to consider that government officials may make inefficient decisions.
B)the overemphasis on improvements in the rural rather than the urban sector.
C)the oversupply of complex technical goods.
D)the undervaluation of currencies to promote export growth.
A)the failure to consider that government officials may make inefficient decisions.
B)the overemphasis on improvements in the rural rather than the urban sector.
C)the oversupply of complex technical goods.
D)the undervaluation of currencies to promote export growth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Inflationary tendencies and even hyperinflation in many Latin American countries have been exacerbated by the tendency of governments to
A)tax too heavily.
B)regulate too heavily.
C)print money to finance policies to stimulate the economy.
D)keep out foreign competition.
A)tax too heavily.
B)regulate too heavily.
C)print money to finance policies to stimulate the economy.
D)keep out foreign competition.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Many economist believe that misguided macroeconomic policies did more to create the Debt Crisis of the 1980s than ISI.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
At the end of the populist cycle,workers are better off than they were before the populist cycle began in terms of real wages and job creation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
What benefits did an overvalued currency offer a domestic economy in the ISI period? Which sectors were typically harmed by overvalued currencies?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Describe the policies that would be associated with Import Substitution Industrialization.What are the primary criticisms of these policies?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Overvalued exchange rates benefit consumers in the short run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The first phase of a typical cycle of economic populism is usually
A)hyperinflation.
B)rising growth and rising wages.
C)falling growth and falling wages.
D)rising unemployment.
A)hyperinflation.
B)rising growth and rising wages.
C)falling growth and falling wages.
D)rising unemployment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
ISI policies increased competition and lowered prices in most economies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Today,primary commodities
A)are not a major export for most of Latin America.
B)are highly valued relative to manufactured goods.
C)have benefited from increased demand from growing world economies.
D)are not subject to business cycles.
A)are not a major export for most of Latin America.
B)are highly valued relative to manufactured goods.
C)have benefited from increased demand from growing world economies.
D)are not subject to business cycles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The acceleration of inflation that characterizes many economic populist movements is usually the result of
A)a rapid increase in the demand for exports.
B)the printing of money to finance government budget deficits.
C)current account deficits.
D)import substitution policies.
A)a rapid increase in the demand for exports.
B)the printing of money to finance government budget deficits.
C)current account deficits.
D)import substitution policies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Explain how an economic populist regime usually progresses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Explain the reasons for export pessimism in Latin American countries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Why might export pessimism be wrong?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Initially,the U.S.and the IMF believed that
A)the Debt Crisis would require long-term structural changes.
B)Latin American economies did not need assistance.
C)capital inflows would be unable to solve the debt problems.
D)the Debt Crisis was a temporary liquidity problem.
A)the Debt Crisis would require long-term structural changes.
B)Latin American economies did not need assistance.
C)capital inflows would be unable to solve the debt problems.
D)the Debt Crisis was a temporary liquidity problem.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
In order to accumulate the resources that they needed to make interest payments,Latin American countries were forced to used macroeconomic policies that
A)devalued their currencies and caused deep recessions.
B)revalued their currencies and caused increased inflation.
C)devalued their currencies and caused increased inflation.
D)revalued their currencies and caused deep recessions.
A)devalued their currencies and caused deep recessions.
B)revalued their currencies and caused increased inflation.
C)devalued their currencies and caused increased inflation.
D)revalued their currencies and caused deep recessions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The Baker Plan emphasized renewed commercial bank loans as a way to restart capital flows to Latin America.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Latin American economies have become relatively more closed to international trade since 1985.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
What do structural reform policies emphasize?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
How does the IMF approach the problem of failing economic populist regimes?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The reform movements that began in many Latin American economies in the late 1980s favored
A)competitive devaluations.
B)stronger military budgets.
C)imports substitution policies.
D)a stronger role for markets and more openness.
A)competitive devaluations.
B)stronger military budgets.
C)imports substitution policies.
D)a stronger role for markets and more openness.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Explain the events that triggered the Debt Crisis and the Lost Decade.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Most analysts in the United States and the international financial community initially perceived the debt crisis as a temporary,short-run liquidity problem so they advised increasing capital flows to Latin America.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The Lost Decade began in 1990 when Colombia announced that it lacked the international reserves it needed to pay the interest and principle due on its foreign debt.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The main difference between stabilization policies and structural reform policies is that stabilization policies
A)focus on microeconomic issues and structural reform policies focus on the macroeconomic environment.
B)focus on macroeconomic issues and structural reform policies focus on the microeconomic environment.
C)are rarely used by reform governments; they prefer to use structural reform policies in their place.
D)create less unemployment than structural reform policies.
A)focus on microeconomic issues and structural reform policies focus on the macroeconomic environment.
B)focus on macroeconomic issues and structural reform policies focus on the microeconomic environment.
C)are rarely used by reform governments; they prefer to use structural reform policies in their place.
D)create less unemployment than structural reform policies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The accumulation of international debt increased the debt service requirements of the indebted countries.After the debt crisis began,this caused
A)the adoption of expansionary policies to return to growth.
B)large capital inflows to service the debt.
C)the adoption of strongly contractionary policies to reduce consumption and government deficits.
D)an intensification of industrial policies targeted on import substitutes.
A)the adoption of expansionary policies to return to growth.
B)large capital inflows to service the debt.
C)the adoption of strongly contractionary policies to reduce consumption and government deficits.
D)an intensification of industrial policies targeted on import substitutes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The Lost Decade refers to the years between approximately
A)1980 and 1990.
B)1987 and 1997.
C)1972 and 1980.
D)1960 and 1970.
A)1980 and 1990.
B)1987 and 1997.
C)1972 and 1980.
D)1960 and 1970.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Reform of a country's trading system,including the reduction or elimination of trade barriers,is an example of
A)an orthodox stabilization plan.
B)a heterodox stabilization plan.
C)import substitution industrialization.
D)structural reform.
A)an orthodox stabilization plan.
B)a heterodox stabilization plan.
C)import substitution industrialization.
D)structural reform.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The external shock that hit Mexico and other Latin American countries in the early 1980s that caused the Lost Decade was a collapse in world oil prices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
One year into the crisis,Argentina's interest payments were roughly equal to
A)100 percent of exports.
B)60 percent of exports.
C)45 percent of exports.
D)10 percent of exports.
A)100 percent of exports.
B)60 percent of exports.
C)45 percent of exports.
D)10 percent of exports.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
One of the main causes of economic inequality in Latin America is the
A)failure of governments to support urban consumers.
B)lack of progress in raising agricultural productivity.
C)lack of governmental interest in solving the problem of inequality.
D)focus of governments on agricultural exports to the detriment of food production.
A)failure of governments to support urban consumers.
B)lack of progress in raising agricultural productivity.
C)lack of governmental interest in solving the problem of inequality.
D)focus of governments on agricultural exports to the detriment of food production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Private capital flows in the form of both direct and portfolio investment began to return to Latin America after 1989,effectively marking the end of the Lost Decade.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The Baker Plan for addressing the debt crisis was based on the assumption that
A)most countries would eventually default on their debt.
B)forgiveness of some of the debt was inevitable.
C)hyperinflation would eventually reduce the real value of the debt.
D)renewed lending by U.S. and European banks would restore growth and make the debt manageable.
A)most countries would eventually default on their debt.
B)forgiveness of some of the debt was inevitable.
C)hyperinflation would eventually reduce the real value of the debt.
D)renewed lending by U.S. and European banks would restore growth and make the debt manageable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
While the Brady Plan did not end the debt crisis,it was a significant step toward greater stability in the Latin American region.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Briefly describe orthodox stabilization policies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
An orthodox model calls for cutting government spending,reforming the tax system to increase compliance and revenues,and limiting the creation of new money.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The difference between an orthodox stabilization plan and a heterodox stabilization plan is that the orthodox plan
A)targets the problem of inflation, while the heterodox plan targets unemployment.
B)reduces trade flows less than the heterodox plan.
C)does not include higher taxes and the heterodox plan does.
D)does not include wage and price controls and the heterodox plan does.
A)targets the problem of inflation, while the heterodox plan targets unemployment.
B)reduces trade flows less than the heterodox plan.
C)does not include higher taxes and the heterodox plan does.
D)does not include wage and price controls and the heterodox plan does.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
What is called for with heterodox stabilization policies?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
A heterodox model would not call for freezing wages and prices,but an orthodox one would.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
What economic problems persist in Latin America? How has this shaped recent policy in the region and why are changes particularly challenging?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



