Deck 5: Humerus and Shoulder Girdle
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/80
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 5: Humerus and Shoulder Girdle
1
What is the name of the insertion point for the deltoid muscle located on the anterolateral surface of the humerus?
A)Surgical neck
B)Deltoid protuberance
C)Deltoid tuberosity
D)Intertubercular sulcus
A)Surgical neck
B)Deltoid protuberance
C)Deltoid tuberosity
D)Intertubercular sulcus
Deltoid tuberosity
2
Part 5 refers to: 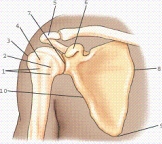
A)the coracoid process.
B)the superior border of scapula.
C)the lateral angle of scapula.
D)none of the above.

A)the coracoid process.
B)the superior border of scapula.
C)the lateral angle of scapula.
D)none of the above.
none of the above.
3
What additional maneuver must be added to the inferosuperior axial shoulder (Lawrence method) projection to best demonstrate a possible Hill-Sachs defect?
A)Increase medial CR angulation.
B)Angle the CR 10° to 15° downward or posteriorly in addition to the medial angle.
C)Perform exaggerated external rotation of the affected upper limb.
D)Increase abduction of the affected upper limb.
A)Increase medial CR angulation.
B)Angle the CR 10° to 15° downward or posteriorly in addition to the medial angle.
C)Perform exaggerated external rotation of the affected upper limb.
D)Increase abduction of the affected upper limb.
Perform exaggerated external rotation of the affected upper limb.
4
Which view and projection of the proximal humerus is represented in the figure? 
A)External rotation, anteroposterior (AP) projection
B)Neutral rotation, AP projection
C)Internal rotation, AP projection
D)External rotation, lateral projection

A)External rotation, anteroposterior (AP) projection
B)Neutral rotation, AP projection
C)Internal rotation, AP projection
D)External rotation, lateral projection

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following structures is not part of the proximal humerus?
A)Lesser tubercle
B)Glenoid process
C)Intertubercular sulcus
D)Anatomic neck
A)Lesser tubercle
B)Glenoid process
C)Intertubercular sulcus
D)Anatomic neck

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following projections can be performed using an orthostatic (breathing) technique?
A)Scapular Y lateral projection
B)Inferosuperior axiolateral projection
C)AP clavicle
D)AP scapula
A)Scapular Y lateral projection
B)Inferosuperior axiolateral projection
C)AP clavicle
D)AP scapula

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Where is the CR centered for a transthoracic lateral projection for proximal humerus?
A)1 inch (2.5 cm) inferior to the acromion
B)Level of the greater tubercle
C)Level of surgical neck
D)Midaxilla
A)1 inch (2.5 cm) inferior to the acromion
B)Level of the greater tubercle
C)Level of surgical neck
D)Midaxilla

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which rotation of the humerus will result in a lateral position of the proximal humerus?
A)Internal rotation (epicondyles perpendicular to image receptor)
B)Neutral rotation (epicondyles 45° to the image receptor)
C)External rotation (epicondyles parallel to the image receptor)
D)None of the above
A)Internal rotation (epicondyles perpendicular to image receptor)
B)Neutral rotation (epicondyles 45° to the image receptor)
C)External rotation (epicondyles parallel to the image receptor)
D)None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Part 3 refers to: 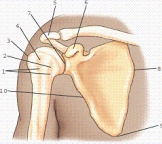
A)the scapulohumeral joint.
B)the glenohumeral joint.
C)the glenoid cavity or fossa.
D)all of the above.

A)the scapulohumeral joint.
B)the glenohumeral joint.
C)the glenoid cavity or fossa.
D)all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which AP projection of the shoulder and proximal humerus is created by placing the affected palm of the hand facing inward toward the thigh?
A)Internal rotation
B)Neutral rotation
C)External rotation
D)AP axial
A)Internal rotation
B)Neutral rotation
C)External rotation
D)AP axial

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
What medial central ray (CR) angle is required for the inferosuperior axial shoulder (Lawrence method)?
A)5° to 10°
B)40° to 45°
C)25° to 30°
D)10° to 15°
A)5° to 10°
B)40° to 45°
C)25° to 30°
D)10° to 15°

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
How much CR angulation should be used for a PA oblique (scapular Y) projection?
A)No CR angle is required.
B)10° to 15°
C)20° to 30°
D)35° to 45°
A)No CR angle is required.
B)10° to 15°
C)20° to 30°
D)35° to 45°

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following shoulder projections best demonstrates the glenoid cavity in profile?
A)Grashey method
B)Clements modification
C)Garth method
D)AP shoulder, neutral rotation
A)Grashey method
B)Clements modification
C)Garth method
D)AP shoulder, neutral rotation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The anterior surface of the scapula is referred to as the:
A)scapular surface.
B)dorsal surface.
C)supraspinous and infraspinous fossa.
D)costal surface.
A)scapular surface.
B)dorsal surface.
C)supraspinous and infraspinous fossa.
D)costal surface.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following shoulder positions is considered a trauma projection (can be performed safely for a possible fracture or dislocation of the proximal humerus)?
A)AP apical oblique axial (Garth method) projection
B)Inferosuperior axial (Clements modification) projection
C)AP projection-internal rotation
D)None of the above
A)AP apical oblique axial (Garth method) projection
B)Inferosuperior axial (Clements modification) projection
C)AP projection-internal rotation
D)None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which term describes the medial end of the clavicle?
A)Acromial extremity
B)Acromion
C)Sternal extremity
D)Acromial tuberosity
A)Acromial extremity
B)Acromion
C)Sternal extremity
D)Acromial tuberosity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
What is the name of the large fossa found within the anterior surface of the scapula?
A)Supraspinous fossa
B)Infraspinous fossa
C)Subscapular fossa
D)Glenoid fossa
A)Supraspinous fossa
B)Infraspinous fossa
C)Subscapular fossa
D)Glenoid fossa

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
How much posterior CR angulation is required for the supine version of the tangential projection (Fisk modification) for the intertubercular (bicipital) sulcus?
A)20° to 30°
B)30° to 40°
C)10° to 15°
D)No angle is used for this projection.
A)20° to 30°
B)30° to 40°
C)10° to 15°
D)No angle is used for this projection.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which ionization chamber(s) for the AEC should be activated for a tangential projection (Fisk modification) for an intertubercular sulcus?
A)Center chamber
B)Both outside chambers
C)Left chamber
D)Cannot use AEC with this projection.
A)Center chamber
B)Both outside chambers
C)Left chamber
D)Cannot use AEC with this projection.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following joints is considered to have a ball and socket (spheroidal) type of movement?
A)Acromioclavicular joints
B)Sternoclavicular joints
C)Bicipital joint
D)Scapulohumeral joint
A)Acromioclavicular joints
B)Sternoclavicular joints
C)Bicipital joint
D)Scapulohumeral joint

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
An AP apical oblique (Garth method) projection for an anteriorly dislocated scapulohumeral joint will project the humerus _____ to the glenoid cavity.
A)superior
B)inferior
C)lateral
D)medial
A)superior
B)inferior
C)lateral
D)medial

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
A radiograph of a PA oblique (scapular Y) lateral position reveals that the scapula is slightly rotated (the vertebral and axillary borders are not superimposed).The axillary border of the scapula is determined to be more lateral compared with the vertebral border.Which of the following modifications should be made for the repeat exposure?
A)Decrease rotation of thorax.
B)Decrease CR angle.
C)Increase rotation of thorax.
D)Abduct the arm more and flex it at the elbow.
A)Decrease rotation of thorax.
B)Decrease CR angle.
C)Increase rotation of thorax.
D)Abduct the arm more and flex it at the elbow.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A radiograph of a transthoracic lateral projection reveals that it is difficult to visualize the proximal humerus due to the ribs and lung markings.The following analog exposure factors were used: 75 kV, 30 mAs, 40-inch (102 cm) SID, grid, and suspended respiration.Which of the following changes will improve the visibility of the proximal humerus?
A)Make the exposure on second inspiration.
B)Use a compression band to prevent patient movement.
C)Use a 72-inch (183-cm) SID.
D)Use an orthostatic (breathing) technique.
A)Make the exposure on second inspiration.
B)Use a compression band to prevent patient movement.
C)Use a 72-inch (183-cm) SID.
D)Use an orthostatic (breathing) technique.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
A radiograph of an AP oblique (Grashey method) projection for the glenoid cavity reveals that the anterior and posterior rims of the glenoid process are not superimposed.Which of the following modifications should produce a more acceptable image?
A)Angle CR 5° to 10° caudad.
B)Angle CR 5° to 10° cephalad.
C)Increase rotation of the body toward the IR.
D)Abduct the arm slightly.
A)Angle CR 5° to 10° caudad.
B)Angle CR 5° to 10° cephalad.
C)Increase rotation of the body toward the IR.
D)Abduct the arm slightly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which of the following modalities best demonstrates shoulder joint pathology such as rotator cuff tears using dynamic evaluation techniques during joint movements?
A)Ultrasound
B)Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
C)Computed tomography (CT)
D)Arthrography
A)Ultrasound
B)Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
C)Computed tomography (CT)
D)Arthrography

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
What type of CR angle is required for the apical AP axial projection?
A)30° caudad
B)15 to 20° cephalad
C)45° caudad
D)10 to 15° caudad
A)30° caudad
B)15 to 20° cephalad
C)45° caudad
D)10 to 15° caudad

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Where is the CR centered for the bilateral acromioclavicular (AC) joint projection on a single 35- × 43-cm (14- × 17-inch) image receptor?
A)At the affected AC joint
B)1 inch (2.5 cm) above the jugular notch
C)At the level of the thyroid cartilage
D)At the sternal angle
A)At the affected AC joint
B)1 inch (2.5 cm) above the jugular notch
C)At the level of the thyroid cartilage
D)At the sternal angle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
A radiograph of an AP clavicle reveals that the sternal extremity is partially collimated off.What should the technologist do?
A)Repeat the AP projection and correct collimation.
B)Make sure the sternal extremity is included on the AP axial projection.
C)Only repeat it if the patient's pain/symptoms involve the sternal extremity.
D)Ask the radiologist whether he or she wants the projection repeated.
A)Repeat the AP projection and correct collimation.
B)Make sure the sternal extremity is included on the AP axial projection.
C)Only repeat it if the patient's pain/symptoms involve the sternal extremity.
D)Ask the radiologist whether he or she wants the projection repeated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which of the following projections will best demonstrate the acromiohumeral space to detect possible spurring?
A)AP oblique projection-Grashey method
B)Inferosuperior axial projection-Clements method
C)PA transaxillary projection-Hobbs modification
D)Apical AP axial projection
A)AP oblique projection-Grashey method
B)Inferosuperior axial projection-Clements method
C)PA transaxillary projection-Hobbs modification
D)Apical AP axial projection

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The inferosuperior axial projection (Clements modification) requires a CR angle of ____ toward axilla if a patient cannot fully abduct extremity 90°.
A)35°
B)none
C)40° to 45°
D)5° to 15°
A)35°
B)none
C)40° to 45°
D)5° to 15°

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which of the following best demonstrates the coracoacromial arch?
A)Neer method
B)West Point method
C)Fisk method
D)Garth method
A)Neer method
B)West Point method
C)Fisk method
D)Garth method

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
A patient comes to the emergency department (ED) with a possible right AC joint separation.Right clavicle and AC joint examinations are ordered.The clavicle is taken first, and a small linear fracture of the midshaft of the clavicle is discovered.What should the technologist do in this situation?
A)Perform the weight-bearing phase as ordered.
B)Reduce the amount of weight that would normally be given to the patient and perform the weight-bearing study.
C)Consult with the ED physician before continuing with the AC joint study.
D)Slowly give the patient more weight to hold until he begins to complain and then complete the AC joint study.
A)Perform the weight-bearing phase as ordered.
B)Reduce the amount of weight that would normally be given to the patient and perform the weight-bearing study.
C)Consult with the ED physician before continuing with the AC joint study.
D)Slowly give the patient more weight to hold until he begins to complain and then complete the AC joint study.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which projection of the shoulder requires that the patient be rotated 45° to 60° toward the IR from a PA position?
A)Inferosuperior axiolateral projection
B)AP oblique projection
C)Lateral scapula projection
D)None of the above
A)Inferosuperior axiolateral projection
B)AP oblique projection
C)Lateral scapula projection
D)None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
A radiograph for an AP projection with external rotation of the proximal humerus reveals that the greater tubercle is profiled laterally.What should be changed to improve this image for a repeat exposure?
A)Rotate epicondyles so they are perpendicular to the image receptor.
B)Move the patient obliquely 10° to 15° toward the affected side.
C)Rotate the arm to place palm of the patient's hand against the thigh.
D)Positioning is acceptable; do not repeat it.
A)Rotate epicondyles so they are perpendicular to the image receptor.
B)Move the patient obliquely 10° to 15° toward the affected side.
C)Rotate the arm to place palm of the patient's hand against the thigh.
D)Positioning is acceptable; do not repeat it.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
How much CR angulation is required for an asthenic patient for an AP axial projection of the clavicle?
A)15°
B)30°
C)45°
D)No CR angulation should be used for this projection.
A)15°
B)30°
C)45°
D)No CR angulation should be used for this projection.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
A patient enters the ED with a midshaft humeral fracture.The AP projection taken on the cart demonstrates another fracture near the surgical neck of the humerus.The patient is unable to stand or rotate the humerus because of the extent of the trauma.What other projection should be taken for this patient?
A)Scapular Y lateral-AP oblique projection
B)Apical oblique projection
C)Horizontal beam transthoracic lateral projection for humerus
D)Rotational lateral projection for humerus
A)Scapular Y lateral-AP oblique projection
B)Apical oblique projection
C)Horizontal beam transthoracic lateral projection for humerus
D)Rotational lateral projection for humerus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
What type of compensating filter is recommended for an AP shoulder projection?
A)Wedge
B)Boomerang
C)Trough
D)Gradient
A)Wedge
B)Boomerang
C)Trough
D)Gradient

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
A referring physician suspects that a subacromial spur may be the cause for a patient's shoulder impingement.She asks the technologist for a projection that would best demonstrate any possible spurs in the suprasinatus outlet.Which of the following projections would accomplish this objective?
A)Tangential projection with 10° to 15° caudad angle
B)Tangential projection with 10° to 15° cephalad angle
C)AP oblique shoulder with 45° caudad angle
D)AP shoulder with 10° to 15° caudad angle
A)Tangential projection with 10° to 15° caudad angle
B)Tangential projection with 10° to 15° cephalad angle
C)AP oblique shoulder with 45° caudad angle
D)AP shoulder with 10° to 15° caudad angle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
A patient comes to radiology for treatment of an arthritic condition of the right shoulder.The radiologist orders AP internal/external rotation projections and an inferosuperior axial projection of the scapulohumeral joint.However, the patient cannot abduct the arm for this projection.Which other projection will best demonstrate the scapulohumeral joint space?
A)AP oblique (Grashey method)
B)Scapular Y lateral
C)Transthoracic lateral
D)AP projection-neutral rotation
A)AP oblique (Grashey method)
B)Scapular Y lateral
C)Transthoracic lateral
D)AP projection-neutral rotation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which alternative landmark can be palpated if unable to locate the coracoid process for the shoulder projection for the obese shoulder?
A)Inferior angle of scapula
B)Greater tubercle of humerus
C)AC joint
D)Lesser tubercle of humerus
A)Inferior angle of scapula
B)Greater tubercle of humerus
C)AC joint
D)Lesser tubercle of humerus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
A patient enters the ED with multiple injuries.The physician is concerned about a dislocation of the left proximal humerus.The patient is unable to stand.Which of the following routines is advisable to best demonstrate this condition?
A)AP shoulder and inferosuperior axial projection
B)AP shoulder and 35° to 45° AP oblique (Grashey method)
C)AP shoulder and Neer projection
D)AP shoulder and recumbent AP oblique (scapular Y) projection
A)AP shoulder and inferosuperior axial projection
B)AP shoulder and 35° to 45° AP oblique (Grashey method)
C)AP shoulder and Neer projection
D)AP shoulder and recumbent AP oblique (scapular Y) projection

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Where is the CR centered for the AP oblique (Grashey method) position for the glenoid cavity?
A)Acromion
B)2 inches (5 cm) medial and inferior to the superolateral border of shoulder
C)Coracoid process
D)1 inch (2.5 cm) superior to the coracoid process
A)Acromion
B)2 inches (5 cm) medial and inferior to the superolateral border of shoulder
C)Coracoid process
D)1 inch (2.5 cm) superior to the coracoid process

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Which one of the following projections/positions should NOT be performed for a possible shoulder dislocation?
A)AP axial oblique (Garth method)
B)Transthoracic lateral (Lawrence method)
C)Inferosuperior axial (Clements modification)
D)Scapular Y
A)AP axial oblique (Garth method)
B)Transthoracic lateral (Lawrence method)
C)Inferosuperior axial (Clements modification)
D)Scapular Y

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
What is a possible radiographic sign for impingement syndrome of the shoulder?
A)Calcified tendons
B)Fluid-filled joint space
C)Fracture of the glenoid rim
D)Bone spurring in acromiohumeral space
A)Calcified tendons
B)Fluid-filled joint space
C)Fracture of the glenoid rim
D)Bone spurring in acromiohumeral space

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Which of the following AP shoulder projections demonstrates the lesser tubercle in profile medially?
A)External rotation
B)Internal rotation
C)Neutral rotation
D)None of the above
A)External rotation
B)Internal rotation
C)Neutral rotation
D)None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
A patient enters the ED with a possible bony defect of the midwing area of the scapula.The patient is able to stand and move the upper limb freely.In addition to the routine AP scapula projection with the arm abducted, which of the following would best demonstrate the involved area?
A)Take an AP apical oblique projection of the shoulder.
B)Take a transthoracic lateral projection of the shoulder region.
C)Have the patient reach across the chest and grasp the opposite shoulder for a lateral scapula projection.
D)Have the patient drop the affected arm behind him or her and take a lateral scapula projection.
A)Take an AP apical oblique projection of the shoulder.
B)Take a transthoracic lateral projection of the shoulder region.
C)Have the patient reach across the chest and grasp the opposite shoulder for a lateral scapula projection.
D)Have the patient drop the affected arm behind him or her and take a lateral scapula projection.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Select the correct method name to match each shoulder projection.(Use each choice only once.)
Tangential, intertubercular sulcus projection
A)Clements modification
B)Neer method
C)Fisk modification
D)Hobbs modification
E)Garth method
F)Grashey method
Tangential, intertubercular sulcus projection
A)Clements modification
B)Neer method
C)Fisk modification
D)Hobbs modification
E)Garth method
F)Grashey method

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Another term for osteoarthritis is:
A)rheumatoid arthritis.
B)bursitis.
C)degenerative joint disease.
D)osteoporosis.
A)rheumatoid arthritis.
B)bursitis.
C)degenerative joint disease.
D)osteoporosis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
A patient is scheduled for an arthrogram.During the course of the study, the radiologist requests a projection to demonstrate the intertubercular sulcus.Which one of the following projections would best demonstrate this structure?
A)Fisk modification
B)Garth method
C)Grashey method
D)Pearson method
A)Fisk modification
B)Garth method
C)Grashey method
D)Pearson method

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
A patient enters the ED with a possible AC joint separation.The patient is paraplegic; therefore, the study cannot be done erect.Which of the following routines would be performed to diagnose this condition?
A)Non-weight-bearing and weight-bearing types of projections performed with the patient recumbent by pulling down on the shoulders
B)Recumbent AP and AP axial projection of the clavicles to include AC joints
C)AP projections of shoulders with external and internal rotation performed recumbent
D)AP and AP apical oblique projection of the shoulder performed recumbent
A)Non-weight-bearing and weight-bearing types of projections performed with the patient recumbent by pulling down on the shoulders
B)Recumbent AP and AP axial projection of the clavicles to include AC joints
C)AP projections of shoulders with external and internal rotation performed recumbent
D)AP and AP apical oblique projection of the shoulder performed recumbent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
What type of CR angle is required for the PA transaxillary projection (Hobbs modification)?
A)CR is perpendicular to IR.
B)5° to 15° toward axilla
C)25° away from axilla
D)10° toward shoulder
A)CR is perpendicular to IR.
B)5° to 15° toward axilla
C)25° away from axilla
D)10° toward shoulder

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
A patient enters the ED with multiple injuries including a possible fracture of the left proximal humerus.Which positioning rotation should be performed to determine the extent of the humerus injury?
A)AP neutral shoulder rotation and carefully rotated internally proximal humerus
B)AP shoulder as is; show radiograph to the ED physician before attempting a rotational lateral projection
C)AP and horizontal beam transthoracic lateral shoulder projection
D)AP and apical oblique shoulder without any arm rotation
A)AP neutral shoulder rotation and carefully rotated internally proximal humerus
B)AP shoulder as is; show radiograph to the ED physician before attempting a rotational lateral projection
C)AP and horizontal beam transthoracic lateral shoulder projection
D)AP and apical oblique shoulder without any arm rotation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
A radiograph of an AP axial projection of the clavicle demonstrates that the clavicle is within the midaspect of the lung apices.What should the technologist do to correct this error?
A)Do nothing; this is an acceptable AP axial clavicle projection.
B)Increase the caudad CR angle during repeat exposure.
C)Increase the cephalic CR angle during repeat exposure.
D)Make the exposure upon complete inspiration.
A)Do nothing; this is an acceptable AP axial clavicle projection.
B)Increase the caudad CR angle during repeat exposure.
C)Increase the cephalic CR angle during repeat exposure.
D)Make the exposure upon complete inspiration.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
A patient enters the ED with a dislocated shoulder.The technologist attempts to position the patient into the transthoracic lateral projection, but the patient is unable to raise the unaffected arm over his head completely.What can the technologist do to compensate for the patient's inability to raise his arm completely?
A)Perform the Grashey method instead.
B)Use a breathing technique.
C)Increase kV to penetrate through both shoulders.
D)Angle the CR 10° to 15° cephalad.
A)Perform the Grashey method instead.
B)Use a breathing technique.
C)Increase kV to penetrate through both shoulders.
D)Angle the CR 10° to 15° cephalad.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Select the correct method name to match each shoulder projection.(Use each choice only once.)
Tangential, supraspinatus outlet projection
A)Clements modification
B)Neer method
C)Fisk modification
D)Hobbs modification
E)Garth method
F)Grashey method
Tangential, supraspinatus outlet projection
A)Clements modification
B)Neer method
C)Fisk modification
D)Hobbs modification
E)Garth method
F)Grashey method

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Which of the following AP shoulder projections demonstrates the greater tubercle in profile medially?
A)External rotation
B)Internal rotation
C)Neutral rotation
D)None of the above
A)External rotation
B)Internal rotation
C)Neutral rotation
D)None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The AP humerus requires that the humeral epicondyles are _____ to the IR.
A)set at a 45° angle
B)parallel
C)perpendicular
D)slightly oblique
A)set at a 45° angle
B)parallel
C)perpendicular
D)slightly oblique

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Select the correct method name to match each shoulder projection.(Use each choice only once.)
AP apical oblique axial projection
A)Clements modification
B)Neer method
C)Fisk modification
D)Hobbs modification
E)Garth method
F)Grashey method
AP apical oblique axial projection
A)Clements modification
B)Neer method
C)Fisk modification
D)Hobbs modification
E)Garth method
F)Grashey method

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
An inferosuperior axial projection (Clements modification) is performed on a patient with a nontraumatic shoulder injury.The patient cannot fully abduct the upper limb 90°.Which of the following modifications of the position should be performed for this patient?
A)Angle CR 30° toward the axilla.
B)Angle CR 5 to 15° toward the axilla.
C)Angle CR 45° toward the elbow AC joint separation.
D)Rotate shoulder slightly anterior to open joint space.
A)Angle CR 30° toward the axilla.
B)Angle CR 5 to 15° toward the axilla.
C)Angle CR 45° toward the elbow AC joint separation.
D)Rotate shoulder slightly anterior to open joint space.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
What is the common term for idiopathic chronic adhesive capsulitis?
A)Bankart lesion
B)Tendinitis
C)Bursitis
D)Frozen shoulder
A)Bankart lesion
B)Tendinitis
C)Bursitis
D)Frozen shoulder

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Select the correct method name to match each shoulder projection.(Use each choice only once.)
AP oblique, glenoid cavity projection
A)Clements modification
B)Neer method
C)Fisk modification
D)Hobbs modification
E)Garth method
F)Grashey method
AP oblique, glenoid cavity projection
A)Clements modification
B)Neer method
C)Fisk modification
D)Hobbs modification
E)Garth method
F)Grashey method

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
An orthostatic (breathing) technique can be performed for the AP projection of the scapula.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The recommended SID for AP AC joint study is 72 inches (~183cm).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
The Hill-Sachs defect is a fracture of the articular surface of the glenoid cavity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
All of the joints of the shoulder girdle are diarthrodial.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
For AC joint weight-bearing studies, patients should not be asked to hold on to the weights with their hands; rather, the weights should be attached to the wrists.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
A radiograph of the inferosuperior axial projection (Lawrence method) demonstrates the acromion process of the shoulder to be located most superiorly (anteriorly).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
A posterior dislocation of the shoulder occurs more frequently than an anterior dislocation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The AP axial (Alexander method) for AC joints requires a 15° cephalic CR angle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Sonography is effective in the dynamic evaluation of the shoulder joint.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Part 3 refers to the greater tubercle. 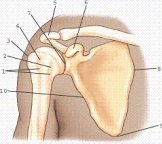


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
The use of a grid during shoulder radiography will result in higher patient dose over nongrid procedures.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Select the correct method name to match each shoulder projection.(Use each choice only once.)
PA transaxillary projection
A)Clements modification
B)Neer method
C)Fisk modification
D)Hobbs modification
E)Garth method
F)Grashey method
PA transaxillary projection
A)Clements modification
B)Neer method
C)Fisk modification
D)Hobbs modification
E)Garth method
F)Grashey method

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Part 10 refers to the vertebral border of the scapula. 


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
For an AP oblique (Grashey method) projection of the shoulder, the CR is centered to the acromion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
PA transaxillary (Hobbs modification) requires a 5° to 15° CR cephalic angle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
The affected arm should not be abducted for an AP scapula projection.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
The PA transaxillary projection (Hobbs modification) is performed to rule out possible shoulder dislocation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
The female clavicle is usually shorter and less curved than that of the male.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Select the correct method name to match each shoulder projection.(Use each choice only once.)
Inferosuperior axial projection
A)Clements modification
B)Neer method
C)Fisk modification
D)Hobbs modification
E)Garth method
F)Grashey method
Inferosuperior axial projection
A)Clements modification
B)Neer method
C)Fisk modification
D)Hobbs modification
E)Garth method
F)Grashey method

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



