Deck 10: The Restless Ocean
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/64
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 10: The Restless Ocean
1
Fetch is ________.
A)a method of shoreline erosion control
B)the distance between the trough of a wave and the still water level
C)the circular pattern made by water particles when a wave passes
D)the distance over which the wind blows over open water
A)a method of shoreline erosion control
B)the distance between the trough of a wave and the still water level
C)the circular pattern made by water particles when a wave passes
D)the distance over which the wind blows over open water
D
2
________ are huge circular-moving current systems that dominate the surface of the ocean within an ocean basin.
A)Tombolos
B)Gyres
C)Coriolis
D)Upwellings
A)Tombolos
B)Gyres
C)Coriolis
D)Upwellings
B
3
The center of each of Earth's five major gyres is found at about ________ latitude.
A)0° (the equator)
B)30°
C)60°
D)90°
A)0° (the equator)
B)30°
C)60°
D)90°
B
4
Which of the following is an example of "hard stabilization" designed to prevent or retard shoreline erosion?
A)seawall
B)groin
C)breakwater
D)all of the above
A)seawall
B)groin
C)breakwater
D)all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following shoreline features is a result of erosion?
A)spit
B)estuary
C)tombolo
D)sea arch
A)spit
B)estuary
C)tombolo
D)sea arch

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Waves begin to "feel bottom" when the depth of water is ________.
A)equal to one-half the wavelength
B)equal to the wavelength
C)twice as great as the wavelength
D)equal to the fetch
A)equal to one-half the wavelength
B)equal to the wavelength
C)twice as great as the wavelength
D)equal to the fetch

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
One result of wave refraction is that wave energy is concentrated ________.
A)on headlands projecting into the water
B)on tombolos
C)in bays, coves, and other recessed areas between headlands
D)on spits
A)on headlands projecting into the water
B)on tombolos
C)in bays, coves, and other recessed areas between headlands
D)on spits

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Chesapeake Bay and Delaware Bay are ________.
A)associated with a submergent coast
B)former river valleys that were flooded by a rise in sea level
C)excellent examples of large estuaries
D)all of the above
A)associated with a submergent coast
B)former river valleys that were flooded by a rise in sea level
C)excellent examples of large estuaries
D)all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
One disadvantage of beach nourishment as compared to hard stabilization is ________.
A)beach nourishment is permanent
B)hard stabilization may increase erosion
C)beach nourishment is expensive
D)hard stabilization makes the coast more scenic for recreation
A)beach nourishment is permanent
B)hard stabilization may increase erosion
C)beach nourishment is expensive
D)hard stabilization makes the coast more scenic for recreation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following shoreline features is a result of deposition?
A)barrier island
B)sea stack
C)wave-cut platform
D)marine terrace
A)barrier island
B)sea stack
C)wave-cut platform
D)marine terrace

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The height, length, and period of a wave depend upon ________.
A)the length of time the wind has blown
B)the wind speed
C)the fetch
D)all of the above
A)the length of time the wind has blown
B)the wind speed
C)the fetch
D)all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Longshore currents and beach drift ________.
A)move in opposite directions
B)both have net movement that is parallel to the shore
C)are oriented at 90° to each other
D)are found only in deep water, and never close to the shore
A)move in opposite directions
B)both have net movement that is parallel to the shore
C)are oriented at 90° to each other
D)are found only in deep water, and never close to the shore

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
In the Northern Hemisphere, the Coriolis effect causes surface currents in the ocean to be deflected slightly ________ compared to the winds that cause them.
A)to the left
B)to the right
C)to the north
D)to the south
A)to the left
B)to the right
C)to the north
D)to the south

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The daily tidal range is of the least magnitude during ________.
A)the daytime
B)spring tides
C)neap tides
D)slack water
A)the daytime
B)spring tides
C)neap tides
D)slack water

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Waves approaching a beach at an oblique angle ________.
A)cause beach drift
B)cause hard stabilization
C)cause coasts to switch from submergence to emergence
D)make tides rise and fall
A)cause beach drift
B)cause hard stabilization
C)cause coasts to switch from submergence to emergence
D)make tides rise and fall

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
When waves reach shallow water they tend to be ________, which makes them become parallel to the shore.
A)reflected
B)refracted
C)translated
D)eroded
A)reflected
B)refracted
C)translated
D)eroded

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
You visit a coastal area for the first time. You note the presence of marine terraces, sea stacks, and sea arches. Based on these features, the area is likely to be ________.
A)experiencing a spring tide
B)in need of beach nourishment
C)an emergent coast
D)a submergent coast
A)experiencing a spring tide
B)in need of beach nourishment
C)an emergent coast
D)a submergent coast

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following is correct regarding a wave in the open ocean?
A)Water particles move vertically in circular orbital motion.
B)Water particles move in a straight line, in the same direction that the wave is moving.
C)Water particles move in a straight line, in the opposite direction that the wave is moving.
D)Water particles move in an almost circular horizontal path.
A)Water particles move vertically in circular orbital motion.
B)Water particles move in a straight line, in the same direction that the wave is moving.
C)Water particles move in a straight line, in the opposite direction that the wave is moving.
D)Water particles move in an almost circular horizontal path.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The energy that drives surface ocean currents such as the Gulf Stream comes from ________.
A)the Coriolis effect
B)salinity variations
C)temperature differences
D)prevailing wind patterns
A)the Coriolis effect
B)salinity variations
C)temperature differences
D)prevailing wind patterns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
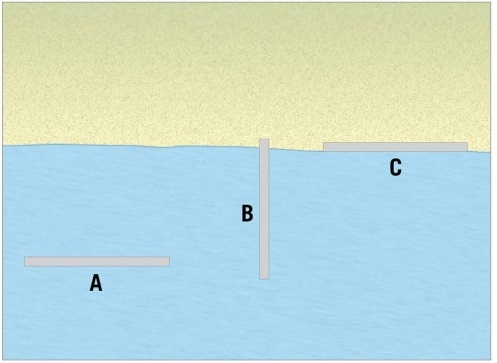
Examine the figure. Of the three forms of hard stabilization illustrated here, which one is the groin?
A)A
B)B
C)C
D)none of these is a groin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Beach drift and longshore currents only develop when waves' direction of approach is perpendicular to the shoreline.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
When viewed from above, the North Atlantic Gyre displays a clockwise sense of motion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A ________ is an isolated remnant of bedrock standing above a wave-cut platform.
A)sea arch
B)sea stack
C)marine terrace
D)wave-cut cliff
A)sea arch
B)sea stack
C)marine terrace
D)wave-cut cliff

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
To measure wave period, the best tool to use would be a ruler.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
As the tide rises, water flows in toward the shore as the ebb tide.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Groins are constructed for the purpose of maintaining or widening beaches that are losing sand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Although the Sun influences the tides, its gravitational effect is considerably less than the effect of the Moon.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Waves begin to "feel bottom" at a depth that is about one-half their wavelength.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Large estuaries are more common on a(n)________ coastline.
A)emergent
B)submergent
C)stable
D)eroding
A)emergent
B)submergent
C)stable
D)eroding

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Marine terraces in coastal California are evidence that this coastal area is emergent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
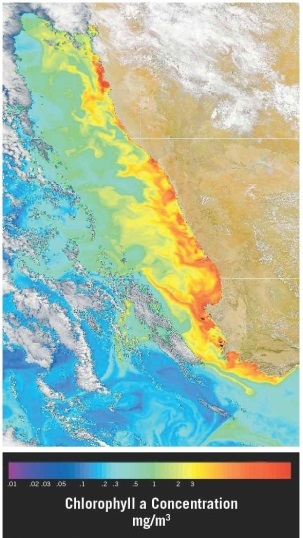
Examine the satellite view of chlorophyll concentrations in the southern Atlantic Ocean along the southwest coast of Africa (the nations of Namibia and South Africa). Which of the following statements offers the best explanation for the observed pattern(s)?
A)This is an area of downwelling, where water is sinking due to the higher density it gains when sea ice forms and salinity increases.
B)This is an area of upwelling, where nutrient-rich water is rising due to winds blowing over the ocean's surface.
C)This is an area of shallow water and waves breaking as they "feel bottom."
D)The coast is a "dead zone," an area of very low biological activity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The largest daily tidal range occurs in association with spring tides.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
A baymouth bar is an example of "hard stabilization," a feature constructed by people to control wave erosion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Cold currents can trigger desertification because they stabilize air that might otherwise rise and generate precipitation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Spring tides occur in conjunction with the full Moon or the new Moon.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Deep ocean currents are driven by thermohaline circulation, rather than prevailing winds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Tidal flats are submerged during ebb tide.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Erosional retreat of a(n)________ leads to enlargement and extension of a wave-cut platform in the inland direction.
A)wave-cut cliff
B)marine terrace
C)sea arch
D)spit
A)wave-cut cliff
B)marine terrace
C)sea arch
D)spit

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Barrier islands are common on the Gulf Coast but rare or absent along the Pacific Coast of the United States.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Upwelling, the rising of water from deeper layers of the ocean, is a wind-induced movement that brings ________ water to the surface.
A)cold, nutrient-rich
B)cold, nutrient-poor
C)warm, nutrient-rich
D)warm, nutrient-poor
A)cold, nutrient-rich
B)cold, nutrient-poor
C)warm, nutrient-rich
D)warm, nutrient-poor

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Match the items in the first column with the correct descriptions in the second column.
A)building structures along the coastline to prevent movement of sand
B)a deposit of sediment resulting from a flood current passing through an inlet
C)like the Atlantic coast of the United States, an area of sea level rise relative to the land
D)the amount of time it takes for two wave crests to pass the same point
E)like the Pacific coast of the United States, an area of land uplift relative to sea level
F)the sawing and grinding action of water armed with rock fragments
G)pumping sand onto the beach from some other area, temporarily replenishing the sediment supply
H)the distance from one wave crest to the next
1)abrasion
2)wave period
3)wavelength
4)hard stabilization
5)beach nourishment
6)submergent
7)emergent
8)tidal delta
A)building structures along the coastline to prevent movement of sand
B)a deposit of sediment resulting from a flood current passing through an inlet
C)like the Atlantic coast of the United States, an area of sea level rise relative to the land
D)the amount of time it takes for two wave crests to pass the same point
E)like the Pacific coast of the United States, an area of land uplift relative to sea level
F)the sawing and grinding action of water armed with rock fragments
G)pumping sand onto the beach from some other area, temporarily replenishing the sediment supply
H)the distance from one wave crest to the next
1)abrasion
2)wave period
3)wavelength
4)hard stabilization
5)beach nourishment
6)submergent
7)emergent
8)tidal delta

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
________ are low-lying zones that are alternately covered by water during flood tide and exposed following ebb tide.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
________ is the rising of cold water from deeper layers to replace warmer surface water.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
A shoreline is a(n)________, a common boundary where different parts of a system interact.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Because deep ocean circulation is driven largely by variations in water temperature and salinity, it is also called ________ circulation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Currents within the surf zone that flow parallel to the shore are known as ________ currents.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
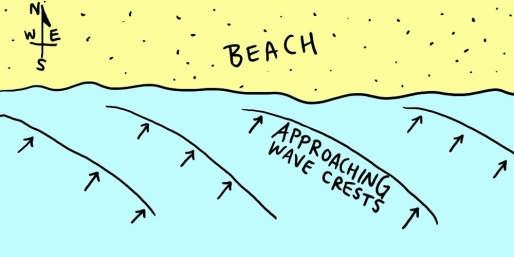
Examine the map shown in the figure. If you were to go swimming in the ocean along this shoreline, which way would the longshore current carry you? ________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
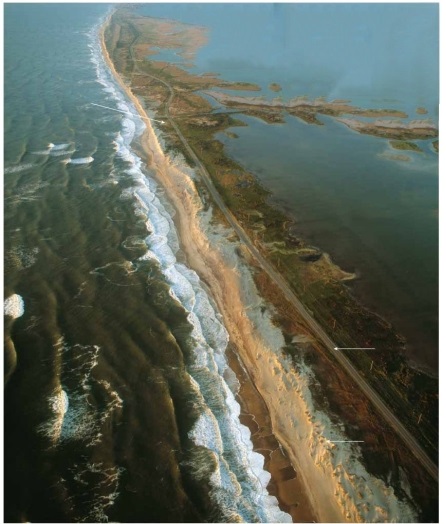

Does this photograph show a tombolo, a barrier island, a sea arch, or a marine terrace? ________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Examine the figure. Identify and label each of the lettered locations with the name of the shoreline feature shown there.
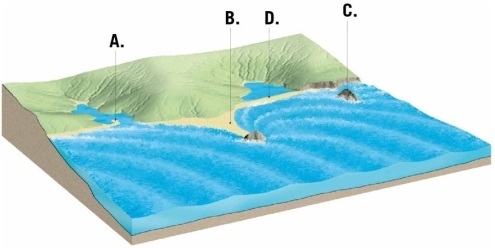


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The ________ is the distance the wind has traveled across open water.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
A(n)________ is a place where fresh and salt water mix, such as a drowned river valley along a submergent coast.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
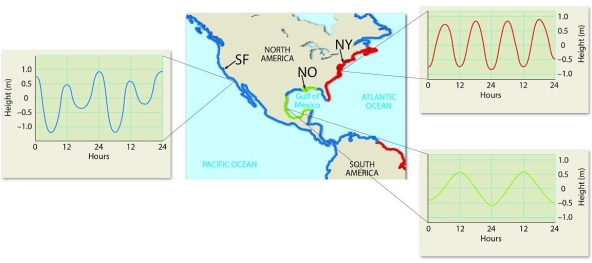
Examine the figure.
Identify the type and describe the tidal patterns observed over the course of a day in three U.S. cities: San Francisco, California (SF), New Orleans, Louisiana (NO), and New York, New York (NY).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
If uplift of the land occurs, a wave-cut platform may become a new ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Breakwaters, sea walls, and groins are all examples of ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
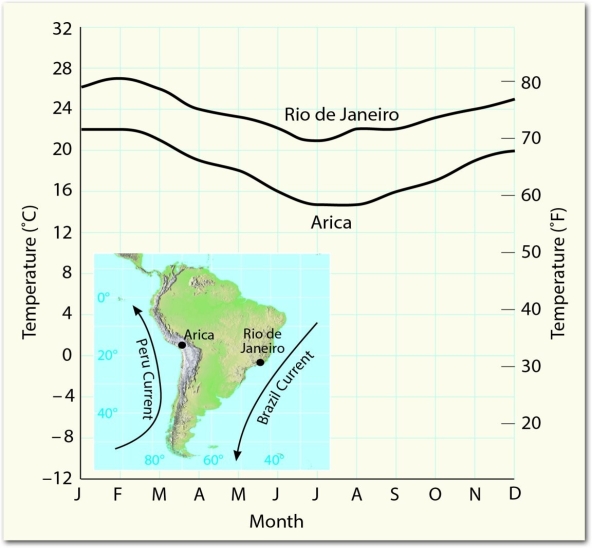
Examine the figure and use the information provided there to explain the different temperature trends seen in Arica and Rio de Janeiro.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Describe some of the options available to people when it comes to coping with erosion along shorelines.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
If a spit grows as it is deposited, and extends completely across the former mouth of an estuary, separating it from the open sea, it has become a(n)________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
As a deep-water wave enters shallow water, the part of the wave in the most shallow water slows down. The deeper-water portion of the wave crest keeps moving at a relatively rapid speed. This wave refraction causes the entire wave crest to progressively rotate toward being ________ with the shoreline.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
________ are large circular-moving currents of water within an ocean basin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Turbulent water created by breaking waves is known as ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
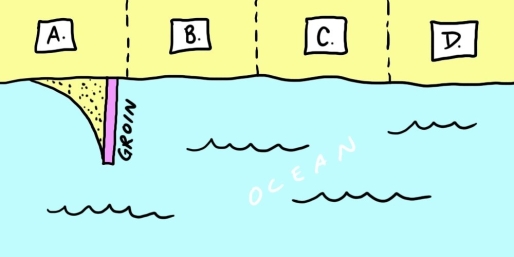
Examine the map shown here. You are considering buying property "C" on this stretch of coastline. Before signing the contract on the property, you hear that the owners of property "B" are considering building a groin like their neighbors recently did on property "A." Should you reconsider your purchase? Explain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
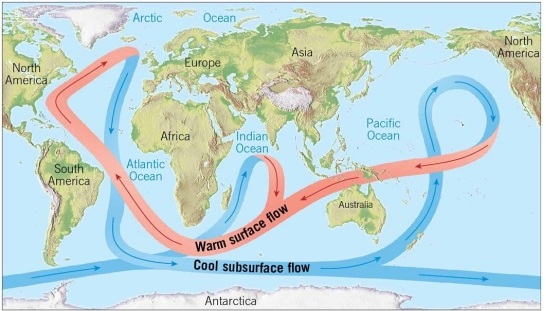
Climate change is particularly acute in the Arctic. Some scientists are concerned about the melting of the Greenland ice sheet because the extra water will cause sea level to rise around the globe. However, another concern is related to the thermohaline "conveyer belt" of ocean circulation. How might the melting of the Greenland ice sheet cause changes to that pattern of currents?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Fossil fuels are a cheap way to make electricity, but burning them generates greenhouse gases. Nuclear power produces a lot of low-carbon energy, but nuclear accidents may release dangerous radioactivity. Windmills generate electricity from the movement of air currents, but the wind doesn't always blow. In light of all these "down sides" to energy production, consider how you might harness longshore currents to produce electricity. Describe your plan in detail, and sketch out how it would work. What might be some of the potential drawbacks to your plan?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



