Deck 14: Weather Patterns and Severe Weather
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/65
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 14: Weather Patterns and Severe Weather
1
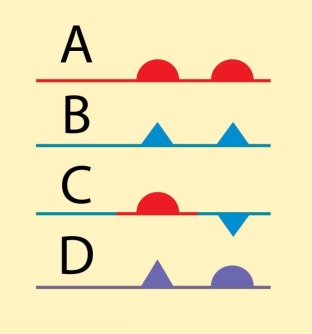
Examine the figure. Which of the symbols shown is used to illustrate a stationary front?
A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
C
2
Which part of a hurricane has the most intense winds?
A)divergence aloft
B)counterclockwise rain bands (clockwise in the southern hemisphere)
C)eye wall
D)eye
A)divergence aloft
B)counterclockwise rain bands (clockwise in the southern hemisphere)
C)eye wall
D)eye
C
3
At any given time, an estimated ________ thunderstorms are in progress on Earth, most of them in the tropics. This results in around ________ thunderstorms on Earth every day.
A)20; 450
B)200; 4,500
C)2,000; 45,000
D)20,000; 450,000
A)20; 450
B)200; 4,500
C)2,000; 45,000
D)20,000; 450,000
C
4
Once warm, moist air, is lifted, the buoyancy necessary to maintain its upward flight is provided by ________.
A)release of latent heat
B)frontal wedging
C)adiabatic cooling
D)lightning and accompanying thunder
A)release of latent heat
B)frontal wedging
C)adiabatic cooling
D)lightning and accompanying thunder

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Several consecutive days of rather constant weather in an area probably indicates ________.
A)warm-front weather
B)cold-front weather
C)air-mass weather
D)occluded front weather
A)warm-front weather
B)cold-front weather
C)air-mass weather
D)occluded front weather

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Should people be more concerned about tornado warnings or tornado watches?
A)tornado warnings
B)tornado watches
C)both mean the same thing
A)tornado warnings
B)tornado watches
C)both mean the same thing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A cyclone is ________.
A)another name for a tornado
B)another name for a hurricane
C)another name for the low-pressure systems that take several days to travel across North America from west to east
D)the term for circulation around any low-pressure center, no matter how large or intense it is
A)another name for a tornado
B)another name for a hurricane
C)another name for the low-pressure systems that take several days to travel across North America from west to east
D)the term for circulation around any low-pressure center, no matter how large or intense it is

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
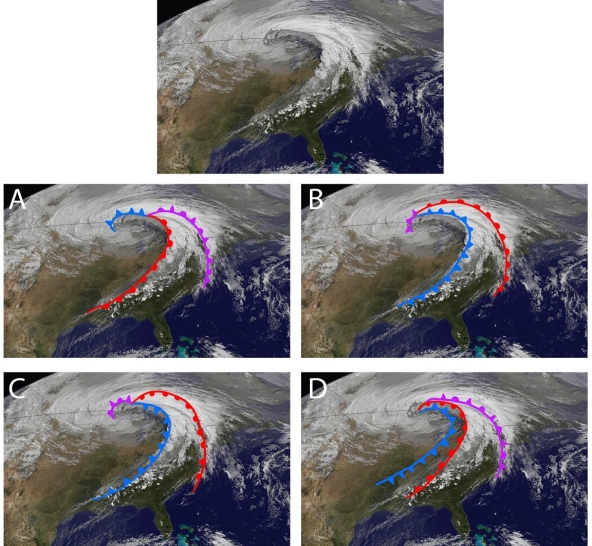
Examine the figure. Based on our best understand of mid-latitude cyclones, which of the four lettered interpretations best matches the weather patterns observed in the "raw" satellite image at top?
A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Cold fronts advance at a rate of about ________.
A)5 to 15 kilometers (3 to 10 miles)per hour
B)25 to 35 kilometers (15 to 20 miles)per hour
C)35 to 50 kilometers (20 to 35 miles)per hour
D)55 to 75 kilometers (34 to 46 miles)per hour
A)5 to 15 kilometers (3 to 10 miles)per hour
B)25 to 35 kilometers (15 to 20 miles)per hour
C)35 to 50 kilometers (20 to 35 miles)per hour
D)55 to 75 kilometers (34 to 46 miles)per hour

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
A cT air mass is ________.
A)cold and dry
B)cold and humid
C)warm and dry
D)warm and humid
A)cold and dry
B)cold and humid
C)warm and dry
D)warm and humid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Where warm, moist, unstable mT air seldom penetrates, such as along the west coast of the United States, ________.
A)there are many thunderstorms
B)there are very few thunderstorms
C)there is no humidity in the air
D)there is an excess of humidity in the air
A)there are many thunderstorms
B)there are very few thunderstorms
C)there is no humidity in the air
D)there is an excess of humidity in the air

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Hurricanes are characterized by ________.
A)intense convective (thunderstorm)activity and strong cyclonic circulation
B)intense convective (thunderstorm)activity and strong anticyclonic circulation
C)mild convective (thunderstorm)activity and strong cyclonic circulation
D)mild convective (thunderstorm)activity and strong anticyclonic circulation
A)intense convective (thunderstorm)activity and strong cyclonic circulation
B)intense convective (thunderstorm)activity and strong anticyclonic circulation
C)mild convective (thunderstorm)activity and strong cyclonic circulation
D)mild convective (thunderstorm)activity and strong anticyclonic circulation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
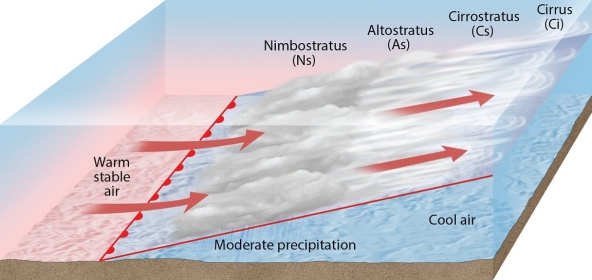
Examine the figure. What weather phenomenon is illustrated here?
A)a warm front
B)a cold front
C)an occluded front
D)a stationary front

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Stationary fronts are distinctive because ________.
A)they occur where a warm front merges with a cold front
B)they stay in one spot on Earth's surface
C)there is no difference in the temperature of the air masses on either side of the front
D)there is no difference in the humidity of the air masses on either side of the front
A)they occur where a warm front merges with a cold front
B)they stay in one spot on Earth's surface
C)there is no difference in the temperature of the air masses on either side of the front
D)there is no difference in the humidity of the air masses on either side of the front

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Occluded fronts form because ________.
A)of the Coriolis effect
B)cold fronts travel at a faster rate than do warm fronts
C)warm fronts travel at a faster rate than do cold fronts
D)air movement is parallel to the front
A)of the Coriolis effect
B)cold fronts travel at a faster rate than do warm fronts
C)warm fronts travel at a faster rate than do cold fronts
D)air movement is parallel to the front

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A mature mid-latitude cyclone with a center of low pressure is about 200 to 300 kilometers (125 to 200 miles)north of your location. If it takes 3 days to pass your location, on which day would temperatures likely be warmest? On which day would they likely be coldest?
A)Day 1 would be warmest; Day 2 would be coldest.
B)Day 2 would be warmest; Day 3 would be coldest.
C)Day 3 would be warmest; Day 2 would be coldest.
D)Day 2 would be warmest; Day 1 would be coldest.
A)Day 1 would be warmest; Day 2 would be coldest.
B)Day 2 would be warmest; Day 3 would be coldest.
C)Day 3 would be warmest; Day 2 would be coldest.
D)Day 2 would be warmest; Day 1 would be coldest.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
An mP air mass is ________.
A)cold and dry
B)cold and humid
C)warm and dry
D)warm and humid
A)cold and dry
B)cold and humid
C)warm and dry
D)warm and humid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
On a weather map, ________ are shown by a line with triangular points on one side.
A)warm fronts
B)cold fronts
C)occluded fronts
D)dragon mouths
A)warm fronts
B)cold fronts
C)occluded fronts
D)dragon mouths

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
An air mass originating in the Gulf of Mexico should be labeled ________.
A)cP
B)mP
C)cT
D)mT
A)cP
B)mP
C)cT
D)mT

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
You are driving west in your car on a clear, warm day. Up ahead, you see a dark band of ominous clouds. Soon, you drive beneath the towering bank of clouds, and things get very dark. For twenty minutes, you are pelted with rain and even some hail. You keep driving west, even though it seems a little sketchy at times. On the radio, you hear that the next county to the north is under a tornado warning. Then the sky lightens, and there is only a little rain. You notice that the temperature outside has dropped by 15°F (8°C). What have you just driven across?
A)a warm front
B)a cold front
C)a mid-latitude cyclone
D)the jet stream
A)a warm front
B)a cold front
C)a mid-latitude cyclone
D)the jet stream

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Hurricanes most often develop in late winter.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
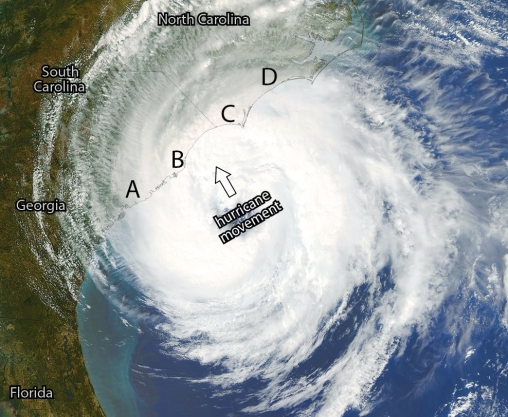

Examine the figure. Of the four lettered locations on the coast of North and South Carolina, which one will likely experience the worst storm surge?
A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Doppler radar is a useful tool for detecting tornadoes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Generally, hurricanes are ________.
A)larger than tornadoes
B)smaller than mid-latitude cyclones
C)areas of heavy rainfall and strong winds
D)all of the above
A)larger than tornadoes
B)smaller than mid-latitude cyclones
C)areas of heavy rainfall and strong winds
D)all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
On average, cold fronts are about twice as steep as warm fronts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Sometimes lightning is produced without any associated thunder.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
In some parts of the world hurricanes are called typhoons or cyclones.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
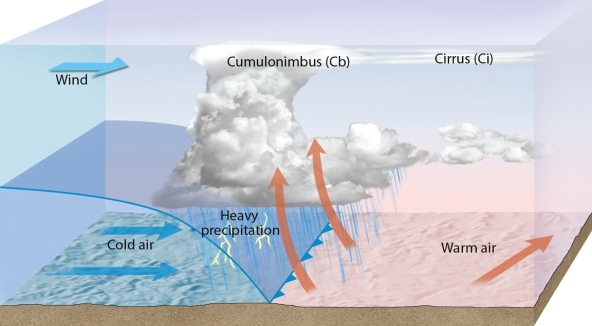
Examine the figure, and then evaluate the truthfulness of this statement: "The figure shows a cold front."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Divergence aloft helps maintain surface lows.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
A tropical storm has stronger winds than a tropical depression.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
When a hurricane enters the coastal zone, the most devastating damage usually results from ________.
A)storm surge
B)flooding
C)wind damage
D)tornadoes
A)storm surge
B)flooding
C)wind damage
D)tornadoes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Continental polar air masses seldom influence the weather south of the Great Lakes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
When a hurricane moves onto land, it rapidly loses its punch; that is, the storm declines in intensity. Which of the factors listed below contribute to this loss of storm energy?
A)friction
B)lack of warm, moist air
C)heating from below by the land surface
D)both A and B
A)friction
B)lack of warm, moist air
C)heating from below by the land surface
D)both A and B

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
A warm front is predicted to come through your area tomorrow. You should prepare for thunderstorms, hail, and tornadoes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The eye of a hurricane is ________.
A)the portion with the highest wind speeds
B)warmer than the rest of the storm
C)along the leading edge of the storm
D)the area of most intense rainfall
A)the portion with the highest wind speeds
B)warmer than the rest of the storm
C)along the leading edge of the storm
D)the area of most intense rainfall

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
When it comes to mid-latitude cyclones and anti-cyclones, airflow aloft has very little relationship (if any)with airflow at Earth's surface.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
A cT air mass is more likely to be found in Arizona than in Louisiana.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Because instability and buoyancy are enhanced by high surface temperatures, thunderstorms are most common in the afternoon and early evening.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Thunderstorms are associated with cumulonimbus clouds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
A tornado watch is issued by the National Weather Service after a tornado has been sighted in an area.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
At the center of a hurricane is a relatively calm region called the ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
When continental polar air moves over a relatively warm lake, such as the Great Lakes, the air mass acquires both heat and moisture, resulting in ________ on the land leeward of the lake.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Maritime tropical air is the source of much, if not most, of the ________ received in the eastern two-thirds of the United States.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Generally, three stages are involved in the development of thunderstorms: the cumulus stage, mature stage, and ________ stage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Compare the characteristics (general weather, movement, etc.)of a cold front to a warm front. Also, briefly explain why they exhibit different characteristics.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Hail, thunder, and tornadoes are all characteristic features of a(n)________ front.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The boundary between air masses having different temperatures (and hence, different densities)is called a(n)________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Match the items in the first column with the correct descriptions in the second column.
A)a scale for ranking how powerful a tornado is
B)an alert that a tornado has been spotted in an area
C)violent windstorms that take the form of a rotating column of air called a vortex that extends downward from a cumulonimbus cloud. Maximum winds can approach 480 kilometers (300 miles)per hour.
D)an alert that conditions in an area may be favorable to the development of tornados
E)a situation where dense cold air actively advances into a region occupied by warmer air
F)tropical cyclones with wind speeds in excess of 119 kilometers (74 miles)per hour. They are fueled by the latent heat that is liberated when huge quantities of water vapor condense.
G)a situation where warmer air actively advances into a region occupied by dense cold air
H)a scale for ranking how powerful a hurricane is
1)cold front
2)warm front
3)Enhanced Fujita intensity scale
4)Saffir-Simpson scale
5)tornado watch
6)tornado warning
7)tornado
8)hurricane
A)a scale for ranking how powerful a tornado is
B)an alert that a tornado has been spotted in an area
C)violent windstorms that take the form of a rotating column of air called a vortex that extends downward from a cumulonimbus cloud. Maximum winds can approach 480 kilometers (300 miles)per hour.
D)an alert that conditions in an area may be favorable to the development of tornados
E)a situation where dense cold air actively advances into a region occupied by warmer air
F)tropical cyclones with wind speeds in excess of 119 kilometers (74 miles)per hour. They are fueled by the latent heat that is liberated when huge quantities of water vapor condense.
G)a situation where warmer air actively advances into a region occupied by dense cold air
H)a scale for ranking how powerful a hurricane is
1)cold front
2)warm front
3)Enhanced Fujita intensity scale
4)Saffir-Simpson scale
5)tornado watch
6)tornado warning
7)tornado
8)hurricane

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
When an active cold front overtakes a warm front a(n)________ forms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
A large body of air that is characterized by a homogeneity of temperature and moisture at any given level is a(n)________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Precipitation along a cold front is generally ________ intense and of ________ duration than precipitation associated with a warm front.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Depending on the context, the word ________ may refer to a tornado, a hurricane, or a large-scale atmospheric system in the mid-latitudes. Though on different scales, all have in common a rotational pattern of winds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Cold fronts are about twice as ________ as warm fronts and move more rapidly, too. These two factors mean warm air is forced aloft more rapidly, and more dramatic weather is produced.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The new generation of weather radar that is capable of detecting precipitation motion directly is called ________ radar.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
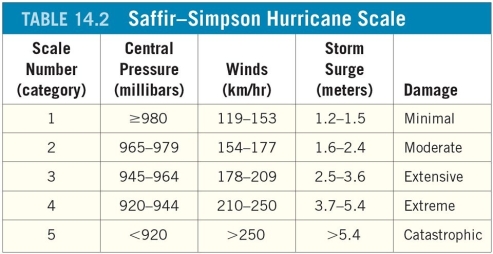
A hurricane that ranks as a Category 4 storm on the Saffir-Simpson scale is moving north towards an east-west-trending section of the Mississippi coast at 40 kilometers per hour. The net winds on the right side of the storm will be ________ kilometers per hour

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
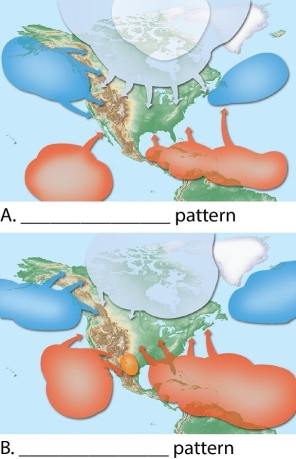
Identify and label each of the color-coded air masses in these two figures. Label figure A and B to state which season they depict.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Summarize the factors that lead to the development, growth, and decay of hurricanes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Describe "Lake effect" snows in the Great Lakes region and how they form.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Tornadoes are violent windstorms that take the form of a rotating column of air called a(n)________ that extends downward from a cumulonimbus cloud.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
________ refers to the situation where a warm air glides up along the edge of a cold air mass.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
A hurricane has slower wind speeds than a tornado does, but it inflicts more damage. Why?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
What does hailstone size indicate about the strength of processes inside a thunderstorm?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
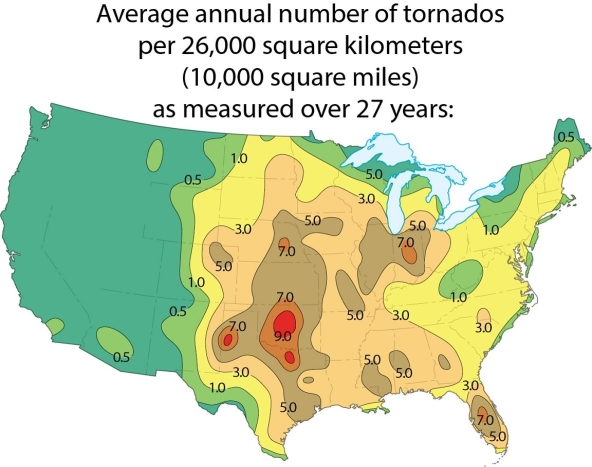
Examine the map showing tornado incidence in the 48 contiguous United States. Why are there so many tornados in the central mid-west?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
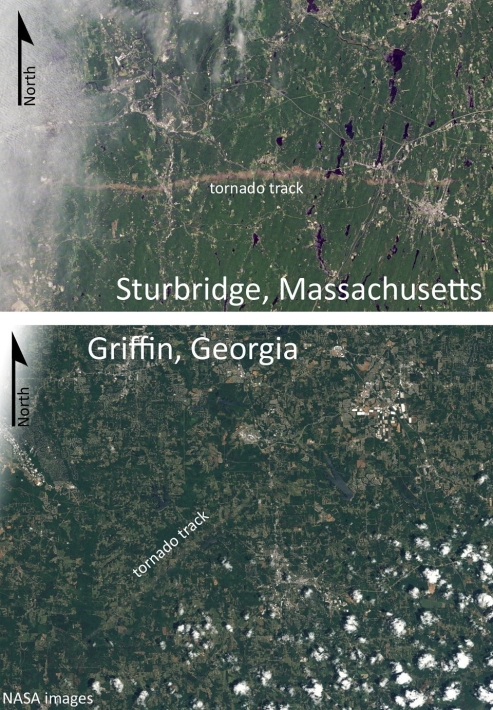
Which of the two tornado tracks shown in these satellite images is typical of the path taken by most tornados in the United States? Explain the "normal" pattern, and suggest a reason for the deviation seen in the other image.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



