Deck 4: Moisture and Atmospheric Stability
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/111
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 4: Moisture and Atmospheric Stability
1
Water vapor constitutes about this much of the atmosphere by volume.
A)0-4 percent
B)0-12 percent
C)0-100 percent
D)4-25 percent
E)4-12 percent
A)0-4 percent
B)0-12 percent
C)0-100 percent
D)4-25 percent
E)4-12 percent
A
2
The attractive forces between the hydrogen atoms in one water molecule and the oxygen atoms in another molecule are known as:
A)water bonds
B)liquid bonds
C)hydrogen bonds
D)dark forces
A)water bonds
B)liquid bonds
C)hydrogen bonds
D)dark forces
C
3
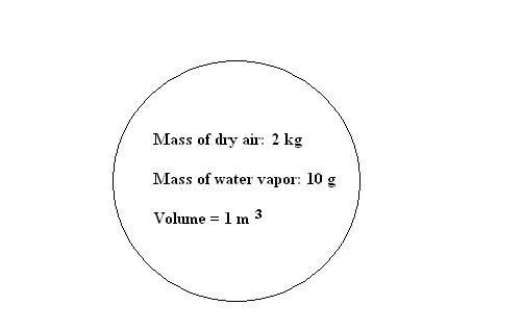
Refer to the diagram of a simple parcel above.What would the absolute humidity be if the volume were to double?
A)5 g/m³
B)20 g/m³
C)2)5 g/m³
D)The absolute humidity would remain unchanged.
A
4
Which of the following requires the GREATEST RELEASE of latent heat energy into the atmosphere?
A)melting of 1 gram of water
B)freezing of 1 gram of water
C)evaporation of 1 gram of water
D)condensation of 1 gram of water
A)melting of 1 gram of water
B)freezing of 1 gram of water
C)evaporation of 1 gram of water
D)condensation of 1 gram of water

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5

Refer to the diagram of a simple parcel above.What is the absolute humidity of this parcel?
A)0)2 g/kg
B)10 g/m³
C)2 g/m³
D)5 g/kg

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Evaporation is a process which tends to keep temperatures cooler where it occurs.This is because the atmosphere:
A)increases the outgoing radiation.
B)reduces the absorption of solar energy.
C)increases the reflection of solar energy.
D)uses energy to change the phase of water instead of increasing air temperature.
E)increases the specific heat.
A)increases the outgoing radiation.
B)reduces the absorption of solar energy.
C)increases the reflection of solar energy.
D)uses energy to change the phase of water instead of increasing air temperature.
E)increases the specific heat.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The heat released when water vapor condenses to form a cloud or when liquid droplets freeze in a cloud:
A)makes the air heavier.
B)adds water to the cloud.
C)cools off the cloud.
D)evaporates more water.
E)helps the cloud to rise higher.
A)makes the air heavier.
B)adds water to the cloud.
C)cools off the cloud.
D)evaporates more water.
E)helps the cloud to rise higher.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
All of the following are properties that make water unique among other substances on Earth EXCEPT:
A)water does not participate easily in hydrogen bonding.
B)water's solid phase is less dense than its liquid phase.
C)water exists naturally in all three phases (solid,liquid,vapor)and changes easily from one to another.
D)water is able to store large quantities of heat.
A)water does not participate easily in hydrogen bonding.
B)water's solid phase is less dense than its liquid phase.
C)water exists naturally in all three phases (solid,liquid,vapor)and changes easily from one to another.
D)water is able to store large quantities of heat.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following processes requires the highest RELEASE of energy from the water molecules?
A)melting
B)freezing
C)condensation
D)deposition
A)melting
B)freezing
C)condensation
D)deposition

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10

Refer to the diagram of a simple parcel above.What additional information would you need in order to be able to calculate the relative humidity of this parcel?
A)air pressure inside the parcel
B)temperature outside of the parcel
C)current temperature/capacity to hold water vapor inside the parcel
D)current vapor pressure inside the parcel

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
As liquid water is evaporated into the atmosphere,heat energy is:
A)absorbed by the remaining liquid.
B)given off by the water vapor.
C)released by the evaporating water.
D)absorbed by the evaporating water.
E)absorbed by the surrounding air.
A)absorbed by the remaining liquid.
B)given off by the water vapor.
C)released by the evaporating water.
D)absorbed by the evaporating water.
E)absorbed by the surrounding air.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12

Refer to the diagram of a simple parcel above.What would the mixing ratio be if the volume were to double?
A)5 g/m³
B)20 g/m³
C)2)5 g/kg
D)The mixing ratio would remain unchanged.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
About what percent of Earth's water can be found in the oceans?
A)97%
B)90%
C)70%
D)53%
A)97%
B)90%
C)70%
D)53%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The amount of water vapor in the air (by volume)usually does not exceed:
A)4 percent.
B)14 percent.
C)100 percent.
D)28 percent.
E)40 percent.
A)4 percent.
B)14 percent.
C)100 percent.
D)28 percent.
E)40 percent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The two changes of state that are the most important part of the water cycle for the atmosphere would be:
A)condensation,freezing.
B)condensation,melting.
C)melting,sublimation.
D)melting,freezing.
E)evaporation,condensation.
A)condensation,freezing.
B)condensation,melting.
C)melting,sublimation.
D)melting,freezing.
E)evaporation,condensation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
? = 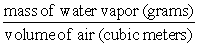 The formula shown above defines the humidity measure known as:
The formula shown above defines the humidity measure known as:
A)the mixing ratio
B)absolute humidity
C)vapor pressure
D)relative humidity
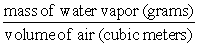 The formula shown above defines the humidity measure known as:
The formula shown above defines the humidity measure known as:A)the mixing ratio
B)absolute humidity
C)vapor pressure
D)relative humidity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Saturation is best defined as:
A)a mixing ratio of at least 100 g/kg.
B)equal numbers of water molecules evaporating from and condensing into a water surface.
C)the point when water molecules completely stop evaporating from a water surface.
D)a vapor pressure greater than 1000 mb.
A)a mixing ratio of at least 100 g/kg.
B)equal numbers of water molecules evaporating from and condensing into a water surface.
C)the point when water molecules completely stop evaporating from a water surface.
D)a vapor pressure greater than 1000 mb.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
? = 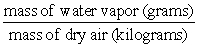 The formula shown above defines the humidity measure known as:
The formula shown above defines the humidity measure known as:
A)the mixing ratio.
B)absolute humidity.
C)vapor pressure.
D)relative humidity.
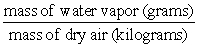 The formula shown above defines the humidity measure known as:
The formula shown above defines the humidity measure known as:A)the mixing ratio.
B)absolute humidity.
C)vapor pressure.
D)relative humidity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19

Refer to the diagram of a simple parcel above.What is the mixing ratio of this parcel?
A)10 g/m³
B)2 g/m³
C)0)2 g/kg
D)5 g/kg

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
In which phase do water molecules have the lowest kinetic energy?
A)vapor
B)liquid
C)ice
D)It has the same kinetic energy in all three phases.
A)vapor
B)liquid
C)ice
D)It has the same kinetic energy in all three phases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
An instrument used to measure relative humidity is called a:
A)hygrometer.
B)hydrometer.
C)humidimeter.
D)aquimeter.
A)hygrometer.
B)hydrometer.
C)humidimeter.
D)aquimeter.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The air in Great Falls,Montana has a temperature of 5°C and a relative humidity of 50%.On the same afternoon,the air in Palm Springs,California has a temperature of 25°C and a relative humidity of 50%.What can be said about the amount of vapor in the air at these two cities?
A)Palm Springs will have a higher vapor content than Great Falls.
B)Great Falls will have a higher vapor content than Palm Springs.
C)Great Falls and Palm Springs will have the same vapor content.
A)Palm Springs will have a higher vapor content than Great Falls.
B)Great Falls will have a higher vapor content than Palm Springs.
C)Great Falls and Palm Springs will have the same vapor content.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The capacity of the air to hold water vapor:
A)increases with a decrease in temperature.
B)decreases with an increase in temperature.
C)increases with an increase in temperature.
D)increases with an increase in pressure.
A)increases with a decrease in temperature.
B)decreases with an increase in temperature.
C)increases with an increase in temperature.
D)increases with an increase in pressure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following is a good explanation for why dew tends to form in the grass at night?
A)Temperatures are coolest in the grass.
B)The atmosphere cannot form clouds at night.
C)Pressure is greatest then.
D)More water vapor is present at night.
A)Temperatures are coolest in the grass.
B)The atmosphere cannot form clouds at night.
C)Pressure is greatest then.
D)More water vapor is present at night.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
An adiabatic process is one in which the:
A)temperature remains constant.
B)altitude of the air parcel remains constant.
C)heat exchanged with the surroundings is zero.
D)pressure on the air parcel remains constant.
E)work done is zero.
A)temperature remains constant.
B)altitude of the air parcel remains constant.
C)heat exchanged with the surroundings is zero.
D)pressure on the air parcel remains constant.
E)work done is zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
During the process of adiabatic cooling,the temperature decreases because the air has:
A)been compressed.
B)lost heat to the colder air at higher altitudes.
C)lost some of its water vapor.
D)expanded to a larger volume.
E)emitted infrared radiation.
A)been compressed.
B)lost heat to the colder air at higher altitudes.
C)lost some of its water vapor.
D)expanded to a larger volume.
E)emitted infrared radiation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
If the air temperature remains constant,evaporating water into the air will ________ the dew point and ________ the relative humidity.
A)increase,decrease
B)not change,increase
C)decrease,increase
D)decrease,decrease
E)increase,increase
A)increase,decrease
B)not change,increase
C)decrease,increase
D)decrease,decrease
E)increase,increase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Assume that the actual vapor content of the air remains constant over the course of a day.How does the relative humidity at 2:00 p.m.probably compare to the relative humidity at 5:00 a.m.?
A)The relative humidity at 2:00 p.m.is higher.
B)The relative humidity at 2:00 p.m.is lower.
C)The relative humidity is the same at 2:00 p.m.as at 5:00 a.m.
A)The relative humidity at 2:00 p.m.is higher.
B)The relative humidity at 2:00 p.m.is lower.
C)The relative humidity is the same at 2:00 p.m.as at 5:00 a.m.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
When the dry and wet bulb temperatures measured by a psychrometer are equal,all but one of the following is true.Which one is false?
A)A rise in temperature would cause condensation.
B)The air is saturated.
C)Water vapor content is at a maximum.
D)Relative humidity is 100 percent.
A)A rise in temperature would cause condensation.
B)The air is saturated.
C)Water vapor content is at a maximum.
D)Relative humidity is 100 percent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The buoyancy of a rising air parcel is greatly affected by:
A)heat released if water vapor condenses.
B)absorption of solar radiation.
C)air pressure.
D)convergence of the parcel.
E)wind speed.
A)heat released if water vapor condenses.
B)absorption of solar radiation.
C)air pressure.
D)convergence of the parcel.
E)wind speed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Relative humidity depends on the water vapor present in the air and the:
A)altitude.
B)dew point.
C)latitude.
D)air temperature.
E)pressure.
A)altitude.
B)dew point.
C)latitude.
D)air temperature.
E)pressure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The most important process of cloud formation in the atmosphere is:
A)cooling by release of latent heat of vaporization.
B)cooling by compression of air.
C)radiation cooling.
D)cooling by expansion of air.
A)cooling by release of latent heat of vaporization.
B)cooling by compression of air.
C)radiation cooling.
D)cooling by expansion of air.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
During a clear,relatively calm day,the relative humidity will tend to ________ from sunrise to early afternoon.
A)decrease
B)remain nearly steady
C)increase
A)decrease
B)remain nearly steady
C)increase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Relative humidity indicates the:
A)probability of precipitation.
B)chance of cloud formation.
C)chance for evaporation of water.
D)nearness to saturation for the air.
E)actual amount of water in the air.
A)probability of precipitation.
B)chance of cloud formation.
C)chance for evaporation of water.
D)nearness to saturation for the air.
E)actual amount of water in the air.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
As the temperature of air is reduced to its dew point,which of these is most likely to occur?
A)freezing
B)condensation
C)melting
D)supercooling
E)evaporation
A)freezing
B)condensation
C)melting
D)supercooling
E)evaporation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
A wet-bulb thermometer and a dry-bulb thermometer are both parts of which meteorological instrument?
A)an anemometer
B)a thermistor
C)a sling psychrometer
D)a barometer
A)an anemometer
B)a thermistor
C)a sling psychrometer
D)a barometer

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The temperature of rising air parcels ________ as they move upward.
A)decreases
B)increases
C)remains constant
D)may either increase or decrease
A)decreases
B)increases
C)remains constant
D)may either increase or decrease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Adiabatic processes are only important for air:
A)masses which remain near the earth's surface.
B)that is saturated.
C)that is polluted.
D)that is stagnant.
E)which is rising or sinking.
A)masses which remain near the earth's surface.
B)that is saturated.
C)that is polluted.
D)that is stagnant.
E)which is rising or sinking.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
In order to have significant snowfall accumulation,dew points must generally be above:
A)0°F.
B)-10°F.
C)10°F.
D)32°F.
A)0°F.
B)-10°F.
C)10°F.
D)32°F.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The property which primarily controls how much water can be present as a gas is:
A)number of particulates present.
B)availability of latent heat.
C)temperature of the air.
D)water's specific heat.
E)amount of dry air gases present.
A)number of particulates present.
B)availability of latent heat.
C)temperature of the air.
D)water's specific heat.
E)amount of dry air gases present.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The atmosphere is most unstable when the temperature of the air ________ with height.
A)is uniform
B)drops rapidly
C)increases slightly
D)decreases slightly
E)increases rapidly
A)is uniform
B)drops rapidly
C)increases slightly
D)decreases slightly
E)increases rapidly

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Which type of lifting mechanism results from warm air lifting over cold air?
A)orographic lifting
B)convective lifting
C)convergence
D)frontal wedging
A)orographic lifting
B)convective lifting
C)convergence
D)frontal wedging

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Why does a rising air parcel cool off?
A)Its relative humidity is less than 100 percent.
B)It loses heat to its surroundings.
C)It loses energy by radiation.
D)It expands.
E)It is unstable.
A)Its relative humidity is less than 100 percent.
B)It loses heat to its surroundings.
C)It loses energy by radiation.
D)It expands.
E)It is unstable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The moist adiabatic rate is different from the dry adiabatic rate because:
A)an unstable air parcel expands more rapidly.
B)latent heat is released inside a parcel of rising saturated air.
C)saturated air is always unstable.
D)a parcel of saturated air weighs less than a parcel of unsaturated air.
E)unsaturated air is always stable.
A)an unstable air parcel expands more rapidly.
B)latent heat is released inside a parcel of rising saturated air.
C)saturated air is always unstable.
D)a parcel of saturated air weighs less than a parcel of unsaturated air.
E)unsaturated air is always stable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
An inversion represents an extremely stable atmosphere because a parcel of air that rises into an inversion will eventually become ________ and ________ dense than the air surrounding it.
A)colder,less
B)colder,more
C)warmer,less
D)warmer,more
A)colder,less
B)colder,more
C)warmer,less
D)warmer,more

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
If your environmental lapse rate is 17 C/km on a partly cloudy afternoon,then the atmosphere is said to be:
A)absolutely unstable.
B)absolutely stable.
C)conditionally stable.
A)absolutely unstable.
B)absolutely stable.
C)conditionally stable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
An increase in the environmental lapse rate of an air layer results in the layer becoming:
A)less stable.
B)an air parcel.
C)cooler.
D)more stable.
E)heavier.
A)less stable.
B)an air parcel.
C)cooler.
D)more stable.
E)heavier.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
These two conditions,working together,will make the atmosphere the most unstable.
A)warm the surface and warm the air aloft
B)warm the surface and cool the air aloft
C)cool the surface and warm the air aloft
D)cool the surface and cool the air aloft
A)warm the surface and warm the air aloft
B)warm the surface and cool the air aloft
C)cool the surface and warm the air aloft
D)cool the surface and cool the air aloft

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
All of the following are lifting mechanisms in the atmosphere EXCEPT:
A)Orographic
B)Divergence
C)Convection
D)Frontal wedging
A)Orographic
B)Divergence
C)Convection
D)Frontal wedging

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Which of these pairs of processes,working together,will make the atmosphere most unstable?
A)cool the surface and cool the air aloft
B)cool the surface and warm the air aloft
C)warm the surface and warm the air aloft
D)warm the surface and cool the air aloft
A)cool the surface and cool the air aloft
B)cool the surface and warm the air aloft
C)warm the surface and warm the air aloft
D)warm the surface and cool the air aloft

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
A large negative temperature lapse rate would occur in a layer with:
A)uniformly cold temperatures throughout.
B)cold air above,warm air below.
C)warm air above,cold air below.
D)uniformly warm temperatures throughout.
A)uniformly cold temperatures throughout.
B)cold air above,warm air below.
C)warm air above,cold air below.
D)uniformly warm temperatures throughout.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The change in the actual air temperature as you go up into the atmosphere is called:
A)environmental lapse rate.
B)convergence.
C)latent heat.
D)conversion.
E)diffusion.
A)environmental lapse rate.
B)convergence.
C)latent heat.
D)conversion.
E)diffusion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
A stable atmosphere is one in which:
A)clouds are forming.
B)upward vertical motions are resisted.
C)rising bubbles of air accelerate upward.
D)temperatures are adiabatic.
A)clouds are forming.
B)upward vertical motions are resisted.
C)rising bubbles of air accelerate upward.
D)temperatures are adiabatic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The vertical motions that occur when the air is unstable are termed:
A)convection.
B)subsidence.
C)cyclonic.
D)geostrophic.
E)convergence.
A)convection.
B)subsidence.
C)cyclonic.
D)geostrophic.
E)convergence.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Natural convection and turbulence are most likely to occur when:
A)temperature decreases rapidly with height.
B)relative humidity is low.
C)temperature increases with height.
D)air pressure is relatively high.
E)wind is nearly calm.
A)temperature decreases rapidly with height.
B)relative humidity is low.
C)temperature increases with height.
D)air pressure is relatively high.
E)wind is nearly calm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The stability of an air layer refers to its:
A)tendency to either sustain or suppress upward vertical motions.
B)albedo.
C)overall density.
D)pressure as measured at its base.
A)tendency to either sustain or suppress upward vertical motions.
B)albedo.
C)overall density.
D)pressure as measured at its base.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
A convergence of winds near the surface is associated with cloud production because it:
A)increases the lapse rate.
B)creates a vortex or spiral pattern.
C)increases the wind speed.
D)increases the dew point.
E)forces the air to rise.
A)increases the lapse rate.
B)creates a vortex or spiral pattern.
C)increases the wind speed.
D)increases the dew point.
E)forces the air to rise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The environmental lapse rate of an air layer next to the ground is strongly influenced by:
A)barometric pressure.
B)relative humidity.
C)heating or cooling of the ground.
D)adiabatic heating.
E)wind speed.
A)barometric pressure.
B)relative humidity.
C)heating or cooling of the ground.
D)adiabatic heating.
E)wind speed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
If your environmental lapse rate is 7 C/km on a partly cloudy afternoon,then the atmosphere is said to be:
A)absolutely stable.
B)absolutely unstable.
C)conditionally stable.
A)absolutely stable.
B)absolutely unstable.
C)conditionally stable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
An air parcel rises over a mountain and cools adiabatically.Which lifting mechanism has acted on this parcel?
A)orographic lifting
B)convective lifting
C)convergence
D)frontal wedging
A)orographic lifting
B)convective lifting
C)convergence
D)frontal wedging

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
If the mixing ratio remains unchanged and the temperature drops,the relative humidity will increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
For the following questions,refer to the diagram shown below.
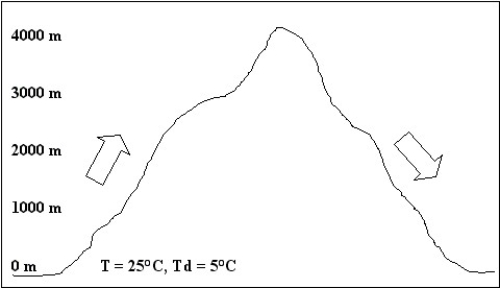
In the diagram shown above,the temperature and dew point at the peak (4000 m)would be: (Assume 100% relative humidity and a wet adiabatic lapse rate of 5°C/km.)
A)both equal to -5°C.
B)both equal to -15°C.
C)equal to -5°C and -10°C,respectively.
D)equal to -15°C and -5°C,respectively.

In the diagram shown above,the temperature and dew point at the peak (4000 m)would be: (Assume 100% relative humidity and a wet adiabatic lapse rate of 5°C/km.)
A)both equal to -5°C.
B)both equal to -15°C.
C)equal to -5°C and -10°C,respectively.
D)equal to -15°C and -5°C,respectively.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
When discussing the water vapor in the air,meteorologists prefer to use absolute humidity rather than mixing ratio.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Which of the following would not be associated with stable atmospheric conditions?
A)buildup of pollutants
B)temperature inversion
C)widespread fog
D)afternoon thunderstorms
A)buildup of pollutants
B)temperature inversion
C)widespread fog
D)afternoon thunderstorms

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
The formation of frost is an example of deposition.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
For the following questions,refer to the diagram shown below.

In the diagram shown above,the parcel would have a temperature of ________ when it reached the base on the leeward side of the mountain.
A)15°C
B)20°C
C)25°C
D)35°C

In the diagram shown above,the parcel would have a temperature of ________ when it reached the base on the leeward side of the mountain.
A)15°C
B)20°C
C)25°C
D)35°C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Sinking or subsiding air cannot form clouds due to the:
A)release of latent heat.
B)loss of particulates.
C)removal of water vapor.
D)formation of unstable layers.
E)warming temperatures.
A)release of latent heat.
B)loss of particulates.
C)removal of water vapor.
D)formation of unstable layers.
E)warming temperatures.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
If the temperature remains unchanged and the mixing ratio drops,the relative humidity will increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
More water is evaporated from the oceans than is returned to the oceans by precipitation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Evaporation is a cooling process.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Plants release water to the atmosphere through the process of sublimation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
A cold air mass that is warmed at its base from contact with the warm ground will have its lapse rate:
A)compressed.
B)decreased.
C)remain constant.
D)increased.
E)changed to an inversion.
A)compressed.
B)decreased.
C)remain constant.
D)increased.
E)changed to an inversion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
For the following questions,refer to the diagram shown below.

Given the conditions shown in the diagram above,the elevation of the cloud base would be:
A)111000 m
B)2000 m
C)2500 m
D)3000 m

Given the conditions shown in the diagram above,the elevation of the cloud base would be:
A)111000 m
B)2000 m
C)2500 m
D)3000 m

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
If air at sea level with a temperature of 27°C is forced up a mountain slope and the air's dew point at the condensation level is 14°C,at what elevation will condensation begin?
A)2700 meters
B)1300 meters
C)1400 meters
D)2600 meters
A)2700 meters
B)1300 meters
C)1400 meters
D)2600 meters

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
The average annual precipitation for the earth is equal to the annual amount of evaporated water.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Which of the following will not cause air to become more unstable?
A)forceful lifting of air
B)subsidence of an air column
C)intense solar heating which warms the air from below
D)upward movement caused by general convergence
A)forceful lifting of air
B)subsidence of an air column
C)intense solar heating which warms the air from below
D)upward movement caused by general convergence

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
It takes 1 calorie to raise 1 gram of water 1°C.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Both absolute humidity and relative humidity change if the temperature of the air changes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
If the environmental lapse rate is less than the wet adiabatic lapse rate,then the atmosphere is:
A)absolutely stable.
B)absolutely unstable
C)conditionally unstable
D)cannot determine from this information.
A)absolutely stable.
B)absolutely unstable
C)conditionally unstable
D)cannot determine from this information.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
The stability of the air layer close to the earth's surface can vary markedly.Much of this variation is caused by:
A)changes in wind speed.
B)changes in pressure.
C)changes in wind direction.
D)changes in heating or cooling of the surface.
A)changes in wind speed.
B)changes in pressure.
C)changes in wind direction.
D)changes in heating or cooling of the surface.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



