Deck 9: Cost and Choice
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/39
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 9: Cost and Choice
1
When an entrepreneur is able to vary some inputs, but has at least one input that cannot be varied, the producer will examine a
A) long-run cost function
B) short-run cost function
C) immediate-run cost function
A) long-run cost function
B) short-run cost function
C) immediate-run cost function
short-run cost function
2
Isocost curves are curves in which all combinations of inputs on the curve are equally expensive.
True
3
The assumption is that the goal of an entrepreneur is to
A) drive costs down to zero
B) maximize revenue regardless of cost
C) maximize profit
A) drive costs down to zero
B) maximize revenue regardless of cost
C) maximize profit
maximize profit
4
A homothetic production function has the property that, whenever we multiply inputs by a factor λ, the marginal rate of technical substitution between all inputs doubles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A production function in which inputs (capital and labor) must be used in a certain fixed proportion to produce output is known as the Leontief production function.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Cost functions define a relationship between cost and output that describes the most ____________ way to produce any given output.
A) efficient
B) expensive
C) sophisticated
A) efficient
B) expensive
C) sophisticated

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
When an entrepreneur is able to vary all inputs and can therefore seek the optimal combination of inputs from among all possible combinations, the producer will examine a
A) long-run cost function
B) short-run cost function
C) immediate-run cost function
A) long-run cost function
B) short-run cost function
C) immediate-run cost function

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The output expansion path is the curve containing the tangency points between the isocost curves and the isoquants, presenting the set of input combinations that produces any given output level at the least cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
A cost function demonstrates the relationship between cost and quantity, which will tell how much it will cost to produce each quantity of a product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The mixture of inputs that produces a particular level of output at the lowest cost is called the optimal combination of inputs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Once a producer has chosen a quantity of output to produce, finding the optimal combination of inputs will depend upon the
A) price of the output
B) income of the vendors
C) cost of the inputs
A) price of the output
B) income of the vendors
C) cost of the inputs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The formula for the elasticity of substitution is Ϭ = (Δk / k) / (Δw / w).Δ

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A particular type of production function that has the property that, whenever we multiply its inputs by a factor λ, we simply obtain the same output we started with multiplied by λᴷ where K is the degree of homogeneity is known as a homogeneous production function.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The loci of efficient points for products are
A) cost curves
B) demand curves
C) marginal product curves
A) cost curves
B) demand curves
C) marginal product curves

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Isocost curves farther away from the origin have __________ costs.
A) greater
B) lower
C) equivalent
A) greater
B) lower
C) equivalent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
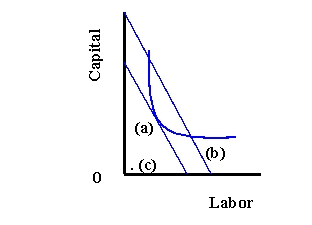
Refer to Exhibit 9-1. Which point represents the least-cost input combination?
A) (a)
B) (b)
C) (c)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The negative of the relative costs of the inputs is represented by the _________ of an isocost curve.
A) slope
B) length
C) thickness
A) slope
B) length
C) thickness

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
In order to produce any given amount of output in the least-cost way, choose the combination of inputs that is located on the lowest ___________ curve ___________ to the ___________ associated with the desired level of output.
A) isocost, tangent, isoquant
B) isocost, perpendicular, isoquant
C) isoquant, tangent, isocost
A) isocost, tangent, isoquant
B) isocost, perpendicular, isoquant
C) isoquant, tangent, isocost

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The effort to produce most cheaply involves finding the ________________ way to combine inputs in order to attain any given level of output.
A) least-cost
B) highest-cost
C) higest-revenue
A) least-cost
B) highest-cost
C) higest-revenue

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
If input prices are fixed, isocost curves are convex curves.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
At the point of the optimal input combination, the marginal rate of technical substitution (MRTS) __________________ the ratio of the pricds of the inputs.
A) is less than
B) is greater than
C) equals
A) is less than
B) is greater than
C) equals

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
With a Cobb-Douglas technology, when α+ β= 1, we have
A) constant returns to scale
B) increasing returns to scale
C) decreasing returns to scale
A) constant returns to scale
B) increasing returns to scale
C) decreasing returns to scale

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The function that associates the cost of the least-cost input combination, when all input levels are variable, with each possible level of output is called the
A) long-run cost function
B) long-run production function
C) increasing returns to scale function
A) long-run cost function
B) long-run production function
C) increasing returns to scale function

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Write as full a description of a cost function as possible.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
(a)
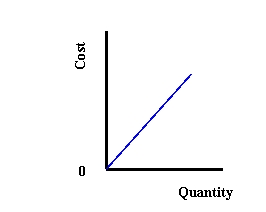
(b)
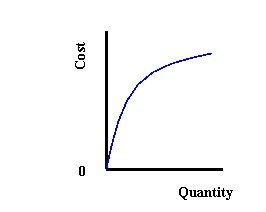
(c)
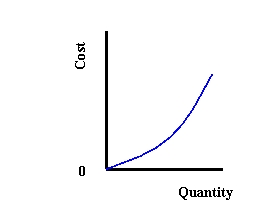
Refer to Exhibit 9-3. Which graphs shows a cost function for a Cobb-Douglas production function with increasing returns to scale?
A) (a)
B) (b)
C) (c)

(b)

(c)

Refer to Exhibit 9-3. Which graphs shows a cost function for a Cobb-Douglas production function with increasing returns to scale?
A) (a)
B) (b)
C) (c)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
A cost function associated with the Leontief technology is a
A) straight line
B) concave curve
C) convex curve
A) straight line
B) concave curve
C) convex curve

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The equation y 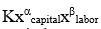 is the algebraic for which production function?
is the algebraic for which production function?
A) Leontief
B) Cobb-Douglas
C) short-run
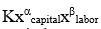 is the algebraic for which production function?
is the algebraic for which production function?A) Leontief
B) Cobb-Douglas
C) short-run

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
(a)

(b)

(c)

Refer to Exhibit 9-3. Which graphs shows a cost function for a Cobb-Douglas production function with decreasing returns to scale?
A) (a)
B) (b)
C) (c)

(b)

(c)

Refer to Exhibit 9-3. Which graphs shows a cost function for a Cobb-Douglas production function with decreasing returns to scale?
A) (a)
B) (b)
C) (c)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
What is the difference between finding the optimal combination of inputs in the short run versus in the long run?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
How does a producer choose the optimal combination of inputs in the short run?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
With a Cobb-Douglas technology, when α+ β> 1, we have
A) constant returns to scale
B) increasing returns to scale
C) decreasing returns to scale
A) constant returns to scale
B) increasing returns to scale
C) decreasing returns to scale

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Describe the reasons for input substitution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
If capital becomes very expensive and labor is cheap, a producer will want to use more units of labor and fewer units of capital if the technology permits this substitution. What measures how freely the producer can vary inputs as their relative prices change, but the amount of output produced remains constant?
A) homothetic production function
B) elasticity of substitution
C) income elasticity of demand
A) homothetic production function
B) elasticity of substitution
C) income elasticity of demand

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
(a)

(b)

(c)

Refer to Exhibit 9-3. Which graphs shows a cost function for a Cobb-Douglas production function with constant returns to scale?
A) (a)
B) (b)
C) (c)

(b)

(c)

Refer to Exhibit 9-3. Which graphs shows a cost function for a Cobb-Douglas production function with constant returns to scale?
A) (a)
B) (b)
C) (c)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
In the equation y 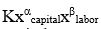 , K represents
, K represents
A) the quantity of capital
B) a constant that shows how productive the technology is
C) the quantity of labor
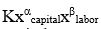 , K represents
, K representsA) the quantity of capital
B) a constant that shows how productive the technology is
C) the quantity of labor

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
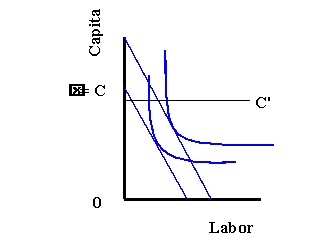
Refer to Exhibit 9-2. If capital is fixed at
 , then this graph the optimal combination of inputs in the
, then this graph the optimal combination of inputs in theA) short run
B) long run
C) immediate run

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
With a Cobb-Douglas technology, when α+ β< 1, we have
A) constant returns to scale
B) increasing returns to scale
C) decreasing returns to scale
A) constant returns to scale
B) increasing returns to scale
C) decreasing returns to scale

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The returns to scale of a Leontief production function are
A) increasing
B) decreasing
C) constant
A) increasing
B) decreasing
C) constant

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
State the geometric and algebraic conditions for optimal input combinations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



