Deck 26: Input Markets and the Origins of Class Conflict
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/40
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 26: Input Markets and the Origins of Class Conflict
1
Monopsonistic exploitation occurs in any situation in which a factor of production is paid the same as the value of its MRP.
False
2
A market with only one seller and one buyer is a bilateral monopoly.
True
3
A typical labor supply curve shows that, as the wage rate ____________, a worker will choose to devote _______ hours to labor.
A) increases, less
B) increases, more
C) decreases, more
A) increases, less
B) increases, more
C) decreases, more
increases, more
4
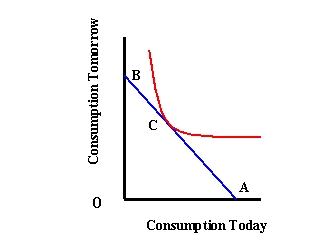
Refer to Exhibit 26-1. Which point represents no consumption in the present, saving everything for the future?
A) A
B) B
C) C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The MPP curve tells us how much extra output, in physical units, will be produced as the firm adds more and more units of labor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A firm with 3 workers produces 8 units of output. When the firm hires 1 additional worker, output increases to 12 units of output. MPP is equal to
A) 4 units
B) 12 units
C) 1 unit
A) 4 units
B) 12 units
C) 1 unit

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A firm's marginal physical product the new workers will produce times the marginal revenue the additional units of output will earn is known as marginal revenue product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Compared to the interest that an entrepreneur must pay on a loan or the opportunity cost of using her or his own funds, the entrepreneur's return on capital must be
A) less
B) greater than or equal to
C) greater
A) less
B) greater than or equal to
C) greater

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The return on a factor above the amount necessary to entice that factor into the production process is called rent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Demand for labor comes from individual
A) workers
B) firms
C) consumers
A) workers
B) firms
C) consumers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Total expenditure is the change in a firm's total wage bill that results from its hiring of one additional unit of labor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The skills of labor are called human capital.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
For most firms, the revenues the firms earn are _______________ the total wages the firms pay their workers.
A) greater than
B) less than
C) equal to
A) greater than
B) less than
C) equal to

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The optimal quantity of labor rule indicates that a profit-maximizing firm will hire labor up to the point at which the MRP it receives from the last unit of labor hired is _______________ the MC of labor.
A) equal to
B) greater than
C) less than
A) equal to
B) greater than
C) less than

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The optimal quantity of labor rule indicates that a profit-maximizing firm will hire labor up to the point at which the marginal revenue product it receives from the last unit of labor hired is equal to one half the marginal cost of labor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The sum of the individual supply curves for all the people who have savings available for investment is the
A) market supply curve for loanable funds
B) market supply curve for labor
C) MRS between consumption today and tomorrow
A) market supply curve for loanable funds
B) market supply curve for labor
C) MRS between consumption today and tomorrow

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The demand curve for labor at a single firm is the same as the firm's marginal
A) physical product curve
B) cost curve
C) revenue product curve
A) physical product curve
B) cost curve
C) revenue product curve

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Demand for labor that is derived from the process of profit maximization is called derived demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
An alternating offer sequential bargaining institution is a structured method of bargaining where each bargainer takes turns making offers. If an offer is accepted, the bargaining stops. If the offer is not accepted, the bargaining proceeds to the next round but, due to the delay, the value of what is being bargained over shrinks.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
If entrepreneur Anita Matsumi invests her own money to build capital equipment for her jam-making business, that investment incurs
A) an opportunity cost
B) no cost
C) only a small filing fee
A) an opportunity cost
B) no cost
C) only a small filing fee

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Demand for loanable funds arises from
A) current or potential producers who need the funds to purchase capital goods
B) individual consumers who save a portion of their income and deposit that portion in a bank
C) Both answers are correct
A) current or potential producers who need the funds to purchase capital goods
B) individual consumers who save a portion of their income and deposit that portion in a bank
C) Both answers are correct

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The change in a firm's total wage bill that results from its hiring of one additional unit of labor is called
A) marginal expenditure
B) total expenditure
C) average expenditure
A) marginal expenditure
B) total expenditure
C) average expenditure

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Describe the two ways that an entrepreneur can obtain funds to build capital equipment and how the entrepreneur decides whether or not to invest.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Why might workers and owners disagree about the fraction of revenues that should be paid to workers as wages?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
How is the equilibrium labor market wage determined?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Why is the price of land entirely determined by the demand curve?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
When a bilateral monopoly exists, the actual market wage will depend on the
A) intersection of supply and demand
B) marginal expenditure and marginal revenue
C) intangible bargaining power of the two parties
A) intersection of supply and demand
B) marginal expenditure and marginal revenue
C) intangible bargaining power of the two parties

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
A monopsony is a market with a single
A) seller
B) buyer
C) firm
A) seller
B) buyer
C) firm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Let C = the cost of capital investment today and R₁ = the return in one year. The rate of return on the investment equals
A) (R1 /C) - 1
B) R1
C) R1 /(1 + π)
A) (R1 /C) - 1
B) R1
C) R1 /(1 + π)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Marginal productivity theory states how free-market economies determine the returns on the factors of production, whereby each factor is paid its marginal
A) revenue product
B) revenue
C) physical product
A) revenue product
B) revenue
C) physical product

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The distribution across the factors of production is called the
A) Pareto-optimal distribution of income
B) functional distribution of income
C) marginal distribution of income
A) Pareto-optimal distribution of income
B) functional distribution of income
C) marginal distribution of income

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
At the equilibrium of the market for loanable funds, the marginal rate of return is just equal to the
A) rate of return on the last profitable project undertaken by society
B) market rate of interest
C) Both answers are correct
A) rate of return on the last profitable project undertaken by society
B) market rate of interest
C) Both answers are correct

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Evaluate the alternating offer sequential bargaining institution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
In the real world, all markets __________ perfectly competitive.
A) are
B) are not
C) must be
A) are
B) are not
C) must be

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The total wage a monopsonist pays for labor is known as
A) marginal expenditure
B) total expenditure
C) average expenditure
A) marginal expenditure
B) total expenditure
C) average expenditure

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
A firm not paying the same wage rate on all units of labor it employs is known as
A) smart business operations
B) wage discrimination
C) illegal behavior
A) smart business operations
B) wage discrimination
C) illegal behavior

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
One interpretation of the Neelin, Sonnenschein, Spiegel experiment is that the subjects were able to perform backward induction when the horizon of a game was only
A) five periods
B) two periods
C) three periods
A) five periods
B) two periods
C) three periods

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
When the total number of periods in the alternating offer sequential bargaining game is finite, there is a unique subgame perfect equilibrium in which the first offer made is accepted. The equilibrium offer is equal to the sum of the decrements in the pie when the first player makes her or his offer. This description is the
A) pie exhaustion theorem
B) alternating offer sequential bargaining equilibrium theorem
C) marginal productivity theorem
A) pie exhaustion theorem
B) alternating offer sequential bargaining equilibrium theorem
C) marginal productivity theorem

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
According to the product exhaustion theorem, when all the factors of production are paid the value of what they produce, then at the long-run equilibrium of a perfectly competitive economy, the sum of their shares of the value of the socially produced pie must equal
A) 100
B) 1/3
C) 1
A) 100
B) 1/3
C) 1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Monopsonistic exploitation occurs in any situation in which a factor of production is paid ______________ the value of its MRP.
A) the same as
B) less than
C) more than
A) the same as
B) less than
C) more than

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



