Deck 23: Nutrition Support in Cancer and Aids
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/30
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 23: Nutrition Support in Cancer and Aids
1
Patients who receive chemotherapeutic drugs often develop
A) tremors.
B) anemia.
C) hypertension.
D) abnormal heart rhythms.
A) tremors.
B) anemia.
C) hypertension.
D) abnormal heart rhythms.
B
Chemotherapeutic drugs affect bone marrow and interfere with the production of red blood cells,causing anemia.
Chemotherapeutic drugs affect bone marrow and interfere with the production of red blood cells,causing anemia.
2
The nutrient primarily responsible for maintaining tissue integrity and immunocompetence is/are
A) carbohydrate.
B) protein.
C) vitamins.
D) minerals.
A) carbohydrate.
B) protein.
C) vitamins.
D) minerals.
B
Antibodies,the core of the immune system,are proteins in structure.A direct and simple example of the important role of nutrition in immunity is the link between protein energy malnutrition and suppressed immune function.
Antibodies,the core of the immune system,are proteins in structure.A direct and simple example of the important role of nutrition in immunity is the link between protein energy malnutrition and suppressed immune function.
3
The primary goal in nutrition care of patients with cancer is to
A) prevent further growth of the tumor.
B) reduce nutrients that the tumor feeds on.
C) prevent malnutrition.
D) promote weight gain.
A) prevent further growth of the tumor.
B) reduce nutrients that the tumor feeds on.
C) prevent malnutrition.
D) promote weight gain.
C
The primary goal of nutrition care in cancer is to prevent malnutrition.Negative nitrogen balance is a major systemic effect of cancer.Adequate calories are necessary to spare protein for tissue building.
The primary goal of nutrition care in cancer is to prevent malnutrition.Negative nitrogen balance is a major systemic effect of cancer.Adequate calories are necessary to spare protein for tissue building.
4
Given a functional gastrointestinal tract,the preferred method of feeding a patient with cancer is
A) normal oral intake.
B) a liquid formula diet.
C) tube feeding.
D) total parenteral feeding.
A) normal oral intake.
B) a liquid formula diet.
C) tube feeding.
D) total parenteral feeding.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Mr.T has been undergoing treatment for cancer and has not felt like eating all day and complains of much discomfort and pain.Of the following,which may be an initial intervention to assist in increasing his appetite?
A) administering medication to increase appetite as soon as possible
B) assessing for weight loss and speaking with the physician regarding tube feeding
C) assessing pain and discomfort and providing pain relief measures
D) changing the diet plan to all liquids to make it easier to ingest food items
A) administering medication to increase appetite as soon as possible
B) assessing for weight loss and speaking with the physician regarding tube feeding
C) assessing pain and discomfort and providing pain relief measures
D) changing the diet plan to all liquids to make it easier to ingest food items

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A major systemic effect of cancer is
A) edema.
B) hypoglycemia.
C) dehydration.
D) negative nitrogen balance.
A) edema.
B) hypoglycemia.
C) dehydration.
D) negative nitrogen balance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The capacity of the immune system is compromised by
A) increased metabolism of water-soluble vitamins.
B) increased metabolism caused by emotional stress.
C) severe malnutrition with atrophy of organs and tissues.
D) increased hormonal levels associated with stress.
A) increased metabolism of water-soluble vitamins.
B) increased metabolism caused by emotional stress.
C) severe malnutrition with atrophy of organs and tissues.
D) increased hormonal levels associated with stress.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Cancer therapy that uses radioactive isotopes is
A) surgery.
B) radiation.
C) chemotherapy.
D) x-rays.
A) surgery.
B) radiation.
C) chemotherapy.
D) x-rays.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Ordinarily the cell operates in an orderly fashion under the influence of the
A) genetic code.
B) outside environment.
C) endoplasmic reticulum.
D) nutrients taken into the cell.
A) genetic code.
B) outside environment.
C) endoplasmic reticulum.
D) nutrients taken into the cell.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following describes a disadvantage of abdominal radiation?
A) The structure and function of the bowel may be adversely affected.
B) The radiation can be dispersed to all the abdominal organs once it passes into the cavity.
C) It is hard to pinpoint the precise area to target the radiation.
D) There are no disadvantages.
A) The structure and function of the bowel may be adversely affected.
B) The radiation can be dispersed to all the abdominal organs once it passes into the cavity.
C) It is hard to pinpoint the precise area to target the radiation.
D) There are no disadvantages.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The point at which a mutagen causes irreversible damage to DNA is referred to as
A) neoplasms.
B) promotion.
C) initiation.
D) Progression.
A) neoplasms.
B) promotion.
C) initiation.
D) Progression.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
If salivary secretions are reduced or absent,it may be most helpful to
A) serve a clear liquid diet.
B) use a tube feeding.
C) serve food in semiliquid form.
D) serve water with the meal.
A) serve a clear liquid diet.
B) use a tube feeding.
C) serve food in semiliquid form.
D) serve water with the meal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The cells responsible for synthesis and secretion of antibodies are the
A) immunoglobulins.
B) T cells.
C)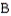 cells.
cells.
D) lymphocytes.
A) immunoglobulins.
B) T cells.
C)
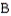 cells.
cells.D) lymphocytes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
For patients with cancer,a good source of dietary protein could be
A) scrambled eggs.
B) applesauce.
C) orange sherbet.
D) green grapes.
A) scrambled eggs.
B) applesauce.
C) orange sherbet.
D) green grapes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The cellular component of the immune system that is derived from the thymus is the
A) T cell.
B)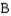 cell.
cell.
C) phagocyte.
D) lymphocyte.
A) T cell.
B)
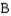 cell.
cell.C) phagocyte.
D) lymphocyte.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
To counteract the hypermetabolic state of cancer,it is important to increase the intake of
A) protein.
B) kilocalories.
C) vitamins.
D) fats.
A) protein.
B) kilocalories.
C) vitamins.
D) fats.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Patients who receive chemotherapy drugs often develop anemia because the drugs
A) damage the bone marrow.
B) prevent iron absorption.
C) interfere with folate metabolism.
D) destroy hemoglobin.
A) damage the bone marrow.
B) prevent iron absorption.
C) interfere with folate metabolism.
D) destroy hemoglobin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Of the following,a side effect of protrease inhibitors is
A) hyperglycemia.
B) hypoglycemia.
C) yachycardia.
D) stroke.
A) hyperglycemia.
B) hypoglycemia.
C) yachycardia.
D) stroke.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
An appropriate intervention for a patient with neutropenia would be to
A) serve only packaged food items.
B) cook food items immediately after thawing.
C) not serve any fresh fruits or vegetables.
D) serve soy-based milk rather than cow's milk.
A) serve only packaged food items.
B) cook food items immediately after thawing.
C) not serve any fresh fruits or vegetables.
D) serve soy-based milk rather than cow's milk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Factors associated with the development of cancer include
A) processed foods.
B) radiation exposure.
C) food-borne disease.
D) diabetes mellitus.
A) processed foods.
B) radiation exposure.
C) food-borne disease.
D) diabetes mellitus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Category 2 CD4 T-Lymphocyte values are defined as
A) less than 200 cells/µL.
B) more than 200 cells/µL.
C) 200 to 499 cells/µL.
D) 800 to 1000 cells/µL.
A) less than 200 cells/µL.
B) more than 200 cells/µL.
C) 200 to 499 cells/µL.
D) 800 to 1000 cells/µL.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Symptoms that may occur during the asymptomatic HIV infection stage include
A) persistent fatigue, night sweats, thrush, and diarrhea.
B) a short bout of flulike syndrome.
C) pneumonia, lymphoma, Kaposi's sarcoma, and tuberculosis.
D) hyperglycemia, heart arrhythmias, and loss of appetite.
A) persistent fatigue, night sweats, thrush, and diarrhea.
B) a short bout of flulike syndrome.
C) pneumonia, lymphoma, Kaposi's sarcoma, and tuberculosis.
D) hyperglycemia, heart arrhythmias, and loss of appetite.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A fundamental effect of HIV infection is
A) nausea.
B) vomiting.
C) major weight loss.
D) cirrhosis.
A) nausea.
B) vomiting.
C) major weight loss.
D) cirrhosis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Nutrition support is a vital care component throughout the progression of HIV infection because of its role in
A) controlling involuntary weight loss and tissue wasting.
B) maintaining cardiac function.
C) preventing the spread of the HIV virus.
D) preventing anemia and constipation.
A) controlling involuntary weight loss and tissue wasting.
B) maintaining cardiac function.
C) preventing the spread of the HIV virus.
D) preventing anemia and constipation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The nutrition care plan for AIDS patients is
A) the same as for all patients.
B) consistent throughout the course of the disease.
C) based only on clinical observations and anthropometry.
D) individualized and continually adjusted throughout the course of the disease.
A) the same as for all patients.
B) consistent throughout the course of the disease.
C) based only on clinical observations and anthropometry.
D) individualized and continually adjusted throughout the course of the disease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Protease inhibitors work by
A) inhibiting the enzyme protease.
B) preventing reverse transcriptase.
C) binding to HIV.
D) enhancing the enzyme lipase.
A) inhibiting the enzyme protease.
B) preventing reverse transcriptase.
C) binding to HIV.
D) enhancing the enzyme lipase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Guidelines for counseling a person with HIV infection include
A) recommending intake of specific combinations of food.
B) expecting significant changes in lifestyle behaviors.
C) promoting optimal nutrition while making the fewest food changes.
D) acting as a catalyst for selecting appropriate lifestyle changes.
A) recommending intake of specific combinations of food.
B) expecting significant changes in lifestyle behaviors.
C) promoting optimal nutrition while making the fewest food changes.
D) acting as a catalyst for selecting appropriate lifestyle changes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The cells that activate the phagocytes are the
A) T cells.
B) B cells.
C) lymphocytes.
D) antigens.
A) T cells.
B) B cells.
C) lymphocytes.
D) antigens.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
An HIV-positive patient should be referred to the clinical dietitian on the AIDS team
A) at the first contact with a health professional.
B) at stage 2 (AIDS-related complex).
C) at stage 3 (final stage of AIDS).
D) when the patient has nutrition-related problems.
A) at the first contact with a health professional.
B) at stage 2 (AIDS-related complex).
C) at stage 3 (final stage of AIDS).
D) when the patient has nutrition-related problems.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Mucositis is an inflammation of the
A) stomach mucosa.
B) intestinal mucosa.
C) oral mucosa.
D) pancreas.
A) stomach mucosa.
B) intestinal mucosa.
C) oral mucosa.
D) pancreas.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



