Deck 5: Costs and Production: How Do Businesses Work?
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/117
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 5: Costs and Production: How Do Businesses Work?
1
Which of the following conditions will result in the firm making an economic profit?
A) P > AC
B) P < AC
C) P = AC
D) P = MC
E) AC > P > MC
A) P > AC
B) P < AC
C) P = AC
D) P = MC
E) AC > P > MC
P > AC
2
Implicit costs are:
A) the opportunity cost of the means of production.
B) always paid out of pocket.
C) never greater than explicit costs.
D) always greater than explicit costs.
E) not measured in terms of dollars.
A) the opportunity cost of the means of production.
B) always paid out of pocket.
C) never greater than explicit costs.
D) always greater than explicit costs.
E) not measured in terms of dollars.
the opportunity cost of the means of production.
3
Chuck Diesel Burger is a food truck in Houston,Texas.Imagine that Chuck Diesel Burger's minimum average of all costs (AC)is $3.75 and that its minimum average cost of variable inputs is $2.50.Chuck Diesel Burger will make a positive economic profit if the price is equal to:
A) $4.00.
B) $3.75.
C) $3.00.
D) $2.50.
E) $2.00.
A) $4.00.
B) $3.75.
C) $3.00.
D) $2.50.
E) $2.00.
$4.00.
4
Explicit costs are:
A) the opportunity cost of the means of production.
B) always paid out of pocket.
C) always greater than implicit costs.
D) never greater than implicit costs.
E) what a business sacrifices in order to produce a good.
A) the opportunity cost of the means of production.
B) always paid out of pocket.
C) always greater than implicit costs.
D) never greater than implicit costs.
E) what a business sacrifices in order to produce a good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The out-of-pocket expenses incurred in producing a good are also known as:
A) implicit costs.
B) fiduciary costs.
C) explicit costs.
D) capital costs.
E) wages and prices.
A) implicit costs.
B) fiduciary costs.
C) explicit costs.
D) capital costs.
E) wages and prices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following conditions will result in the firm making zero economic profit?
A) P > AC
B) P < AC
C) P = AC
D) P = MC
E) AC > P > MC
A) P > AC
B) P < AC
C) P = AC
D) P = MC
E) AC > P > MC

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Refer to the accompanying figure.If the price is $8,the firm is making:
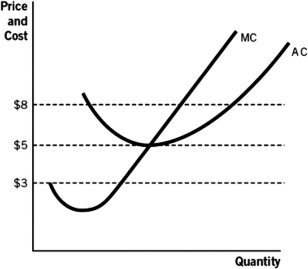
A) a loss on any quantity greater than at the intersection of MC and AC.
B) a profit on any quantity greater than at the intersection of MC and AC
C) a loss on any quantity less than at the intersection of MC and AC.
D) a profit on any quantity less than at P = $8.
E) zero profit.

A) a loss on any quantity greater than at the intersection of MC and AC.
B) a profit on any quantity greater than at the intersection of MC and AC
C) a loss on any quantity less than at the intersection of MC and AC.
D) a profit on any quantity less than at P = $8.
E) zero profit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Every year the U.S.sugar industry,which is dominated by only a few firms,spends millions of dollars lobbying members of Congress and contributing to their re-election campaigns.It does so for both Democrats and Republicans.One goal of these contributions is the preservation of the U.S.sugar quota,which limits the importation of less expensive sugar from other countries.Ultimately,all of these activities are motivated by a desire among U.S.sugar producers to:
A) keep their prices as low as possible.
B) make the market for sugar as competitive as possible.
C) support one political party but not another.
D) keep their profits as high as possible.
E) hire as many employees as they can.
A) keep their prices as low as possible.
B) make the market for sugar as competitive as possible.
C) support one political party but not another.
D) keep their profits as high as possible.
E) hire as many employees as they can.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Refer to the accompanying figure.A firm would be making positive profits if the price is:
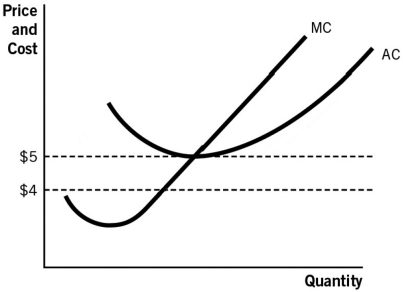
A) anywhere below $5.
B) below $5 but above $4.
C) anywhere above $4.
D) below $4.
E) above $5.

A) anywhere below $5.
B) below $5 but above $4.
C) anywhere above $4.
D) below $4.
E) above $5.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
A firm's decisions are ultimately oriented toward:
A) minimizing the number of employees it hires.
B) maximizing profit.
C) maximizing production.
D) increasing total revenue.
E) negotiating better deals with suppliers.
A) minimizing the number of employees it hires.
B) maximizing profit.
C) maximizing production.
D) increasing total revenue.
E) negotiating better deals with suppliers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Total revenue minus total cost is equal to:
A) producer surplus.
B) dividends.
C) consumer surplus.
D) profit.
E) retained earnings.
A) producer surplus.
B) dividends.
C) consumer surplus.
D) profit.
E) retained earnings.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
When revenue is insufficient to cover cost,the firm:
A) will produce more.
B) will produce less, but more than nothing.
C) gains a profit.
D) breaks even.
E) suffers a loss.
A) will produce more.
B) will produce less, but more than nothing.
C) gains a profit.
D) breaks even.
E) suffers a loss.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
If a firm generates $240,000 in revenue,earns $120,000 in economic profit,and its explicit costs are $80,000,how much are its implicit costs?
A) $160,000
B) $80,000
C) $40,000
D) $60,000
E) $120,000
A) $160,000
B) $80,000
C) $40,000
D) $60,000
E) $120,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
An example of an implicit cost is:
A) a payment on the loan for a piece of equipment not in use.
B) a payment on an electricity bill.
C) wages paid to employees.
D) gasoline costs.
E) forgone wages.
A) a payment on the loan for a piece of equipment not in use.
B) a payment on an electricity bill.
C) wages paid to employees.
D) gasoline costs.
E) forgone wages.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
If a firm wants to cut its costs through more efficient production,we should assume that the firm is trying to:
A) fire its employees.
B) increase its profits.
C) eliminate its competition.
D) buy back its stock.
E) gain control over its market.
A) fire its employees.
B) increase its profits.
C) eliminate its competition.
D) buy back its stock.
E) gain control over its market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Firms will break even if the price they charge is:
A) less than their minimum average of all costs (AC).
B) less than their minimum average cost of fixed inputs.
C) greater than their minimum average cost of variable inputs.
D) greater than their minimum average of all costs (AC).
E) equal to their minimum average of all costs (AC).
A) less than their minimum average of all costs (AC).
B) less than their minimum average cost of fixed inputs.
C) greater than their minimum average cost of variable inputs.
D) greater than their minimum average of all costs (AC).
E) equal to their minimum average of all costs (AC).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Firms will always make a positive economic profit if the price they charge is:
A) less than their minimum average of all costs (AC).
B) less than their minimum average cost of fixed inputs.
C) greater than their minimum average cost of variable inputs.
D) greater than their minimum average of all costs (AC).
E) equal to their minimum average of all costs (AC).
A) less than their minimum average of all costs (AC).
B) less than their minimum average cost of fixed inputs.
C) greater than their minimum average cost of variable inputs.
D) greater than their minimum average of all costs (AC).
E) equal to their minimum average of all costs (AC).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Chief executive officers (CEOs)of major corporations are often paid mostly with stock options (which allow the holder to buy stock at a given price),as opposed to salaries and cash payments.These stock options often cannot be converted into stock and sold until years after they were issued.All this is ultimately intended to create incentives for the CEO to:
A) leave the company after a year or so.
B) lay off as many employees as possible.
C) increase the value of the stock by maximizing company profit.
D) outsource all production to other countries.
E) lobby Congress for subsidies and tax breaks.
A) leave the company after a year or so.
B) lay off as many employees as possible.
C) increase the value of the stock by maximizing company profit.
D) outsource all production to other countries.
E) lobby Congress for subsidies and tax breaks.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
In economics,we assume that firms make decisions in order to:
A) maximize profit.
B) minimize revenues.
C) evade taxes.
D) lobby officials.
E) protect the environment.
A) maximize profit.
B) minimize revenues.
C) evade taxes.
D) lobby officials.
E) protect the environment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
If a firm has total costs of $535,000 and its implicit costs are $165,000,how much are its explicit costs?
A) $3,242
B) $120,000
C) $370,000
D) $700,000
E) $308
A) $3,242
B) $120,000
C) $370,000
D) $700,000
E) $308

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Lauren is the owner of a bakery.Last year,her total revenue was $145,000,her rent was $12,000,her labor costs were $65,000,and her overhead expenses were $15,000.If she could earn $53,000 working for another bakery nearby,we know that her economic profit was:
A) $145,000.
B) $53,000.
C) $12,000.
D) $0.00.
E) $15,000.
A) $145,000.
B) $53,000.
C) $12,000.
D) $0.00.
E) $15,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
An example of an explicit cost is:
A) a payment on a loan for a computer.
B) the savings interest lost by investing $10,000 in capital instead of saving the money.
C) forgone wages.
D) the opportunity cost of a $50,000 investment into a building.
E) the amount of money one could receive for renting a company truck to another business.
A) a payment on a loan for a computer.
B) the savings interest lost by investing $10,000 in capital instead of saving the money.
C) forgone wages.
D) the opportunity cost of a $50,000 investment into a building.
E) the amount of money one could receive for renting a company truck to another business.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Economic profit is equal to:
A) total revenue minus explicit costs.
B) total revenue minus implicit costs.
C) explicit costs plus implicit costs.
D) total revenue minus implicit costs and explicit costs.
E) explicit costs minus implicit costs.
A) total revenue minus explicit costs.
B) total revenue minus implicit costs.
C) explicit costs plus implicit costs.
D) total revenue minus implicit costs and explicit costs.
E) explicit costs minus implicit costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Ralph owns a small pizza restaurant,where he works full-time in the kitchen.His total revenue last year was $100,000,and his rent was $3,000 per month.He pays his one employee $2,000 per month,and the cost of ingredients and overhead averages $500 per month.Ralph could earn $35,000 per year as the manager of a competing pizza restaurant nearby.His total economic profit for the year was:
A) $34,000.
B) -$1,000.
C) $20,000.
D) $65,000.
E) -$35,000.
A) $34,000.
B) -$1,000.
C) $20,000.
D) $65,000.
E) -$35,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Implicit costs can be difficult to measure because:
A) business owners cannot always observe them directly.
B) they are not measured in dollars.
C) they are always very expensive.
D) they are always greater than explicit costs.
E) they include expenses like taxes.
A) business owners cannot always observe them directly.
B) they are not measured in dollars.
C) they are always very expensive.
D) they are always greater than explicit costs.
E) they include expenses like taxes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which of the following is true about explicit costs?
A) They are the opportunity costs of production.
B) They are out-of-pocket expenses.
C) They are not measured in terms of dollars.
D) They are not included when measuring economic profit.
E) They are not included when measuring accounting profit.
A) They are the opportunity costs of production.
B) They are out-of-pocket expenses.
C) They are not measured in terms of dollars.
D) They are not included when measuring economic profit.
E) They are not included when measuring accounting profit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Ralph owns a small pizza restaurant,where he works full-time in the kitchen.His total revenue last year was $100,000,and his rent was $3,000 per month.He pays his one employee $2,000 per month,and the cost of ingredients and overhead averages $500 per month.Ralph could earn $35,000 per year as the manager of a competing pizza restaurant nearby.His total implicit costs for the year were:
A) $100,000.
B) $35,000.
C) $60,000.
D) $66,000.
E) $72,000.
A) $100,000.
B) $35,000.
C) $60,000.
D) $66,000.
E) $72,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Consider the following scenario when answering the following two questions.
Charlie's Churros is a perfectly competitive firm that sells desserts in Houston, Texas. Charlie's Churros currently is taking in $40,000 in revenues and has $15,000 in explicit costs and $25,000 in implicit costs.
Charlie's Churros' economic profits are:
A) $40,000.
B) $15,000.
C) $25,000.
D) $0.
E) $80,000.
Charlie's Churros is a perfectly competitive firm that sells desserts in Houston, Texas. Charlie's Churros currently is taking in $40,000 in revenues and has $15,000 in explicit costs and $25,000 in implicit costs.
Charlie's Churros' economic profits are:
A) $40,000.
B) $15,000.
C) $25,000.
D) $0.
E) $80,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Darrell is the owner of a furniture store.Last year,his total revenue was $525,000 and his total labor costs were $200,000.His overhead expenses,including insurance and legal fees,were $175,000.The rent on his building was $45,000.Darrell could earn $105,000 per year working at a nearby furniture distributor.If his total revenue increases to $600,000 this year and all of his other expenses are held constant,we know that his economic profit is now:
A) $75,000.
B) $600,000.
C) $0.00.
D) $105,000.
E) $200,000.
A) $75,000.
B) $600,000.
C) $0.00.
D) $105,000.
E) $200,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Ralph owns a small pizza restaurant,where he works full-time in the kitchen.His total revenue last year was $100,000,and his rent was $3,000 per month.He pays his one employee $2,000 per month,and the cost of ingredients and overhead averages $500 per month.Ralph could earn $35,000 per year as the manager of a competing pizza restaurant nearby.His accountant,who does not consider implicit costs,would tell him that profit for the year was:
A) -$1,000.
B) $100,000.
C) $72,000.
D) $34,000.
E) $35,000.
A) -$1,000.
B) $100,000.
C) $72,000.
D) $34,000.
E) $35,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Lauren is the owner of a bakery that earns 0 (zero)economic profit.Last year,her total revenue was $145,000,her rent was $12,000,her labor costs were $65,000,and her overhead expenses were $15,000.From this information,we know that her total implicit costs were:
A) $145,000.
B) $53,000.
C) $92,000.
D) $65.000.
E) $15,000.
A) $145,000.
B) $53,000.
C) $92,000.
D) $65.000.
E) $15,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Darrell is the owner of a furniture store.Last year,his total revenue was $525,000 and his total labor costs were $200,000.His overhead expenses,including insurance and legal fees,were $175,000.The rent on his building was $45,000.Darrell could earn $105,000 per year working at a nearby furniture distributor.From this information,we know that his accountant,who does not consider implicit costs,would tell him that profit was:
A) $525,000.
B) $375,000.
C) $150,000.
D) $175,000.
E) $105,000.
A) $525,000.
B) $375,000.
C) $150,000.
D) $175,000.
E) $105,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Ralph owns a small pizza restaurant,where he works full-time in the kitchen.His total revenue last year was $100,000,and his rent was $3,000 per month.He pays his one employee $2,000 per month,and the cost of ingredients and overhead averages $500 per month.Ralph could earn $35,000 per year as the manager of a competing pizza restaurant nearby.His total explicit costs for the year were:
A) $24,000.
B) $6,000.
C) $60,000.
D) $66,000.
E) $72,000.
A) $24,000.
B) $6,000.
C) $60,000.
D) $66,000.
E) $72,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
An explicit cost for a business that manufactures bicycles would be the:
A) value of the products that the firm's employees could produce at another company.
B) salary that the owner of the business could earn elsewhere.
C) goods and services provided by the government with the taxes the firm pays.
D) wages paid to employees.
E) various products that could be made with the steel used to make bicycles.
A) value of the products that the firm's employees could produce at another company.
B) salary that the owner of the business could earn elsewhere.
C) goods and services provided by the government with the taxes the firm pays.
D) wages paid to employees.
E) various products that could be made with the steel used to make bicycles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Economists consider both explicit and implicit costs when measuring economic profit.The reason they consider implicit costs is that:
A) they are more conservative than accountants, who consider only costs that are out-of-pocket.
B) most businesses forget to pay their implicit costs.
C) a business must cover its opportunity costs as well as its out-of-pocket expenses to be truly profitable.
D) implicit costs are typically far larger than explicit costs.
E) implicit costs include expenses like taxes and fees to the government.
A) they are more conservative than accountants, who consider only costs that are out-of-pocket.
B) most businesses forget to pay their implicit costs.
C) a business must cover its opportunity costs as well as its out-of-pocket expenses to be truly profitable.
D) implicit costs are typically far larger than explicit costs.
E) implicit costs include expenses like taxes and fees to the government.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
One difference between implicit costs and explicit costs is that:
A) implicit costs are included in the method accountants use to compute profits, whereas explicit costs are not.
B) implicit costs are included in economic profits, whereas explicit costs are not.
C) explicit costs are included in the method accountants use to compute profits, whereas implicit costs are not.
D) explicit costs are included in economic profits, whereas implicit costs are not.
E) explicit costs involve opportunity costs, whereas implicit costs involve a monetary transaction.
A) implicit costs are included in the method accountants use to compute profits, whereas explicit costs are not.
B) implicit costs are included in economic profits, whereas explicit costs are not.
C) explicit costs are included in the method accountants use to compute profits, whereas implicit costs are not.
D) explicit costs are included in economic profits, whereas implicit costs are not.
E) explicit costs involve opportunity costs, whereas implicit costs involve a monetary transaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Accountants consider only explicit costs when measuring profit,whereas economics consider both implicit and explicit costs.The reason that they ignore implicit costs is that:
A) implicit costs are typically very small.
B) explicit costs are always greater than implicit costs.
C) implicit costs are not out-of-pocket expenses.
D) implicit costs are tax deductible.
E) implicit costs cannot be measured in terms of dollars.
A) implicit costs are typically very small.
B) explicit costs are always greater than implicit costs.
C) implicit costs are not out-of-pocket expenses.
D) implicit costs are tax deductible.
E) implicit costs cannot be measured in terms of dollars.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Lauren is the owner of a bakery.Last year,her total revenue was $145,000,her rent was $12,000,her labor costs were $65,000,and her overhead expenses were $15,000.From this information,we know that her accountant,who does not consider implicit costs,would tell her that profit was:
A) $145,000.
B) $53,000.
C) $65,000.
D) $15,000.
E) $27,000.
A) $145,000.
B) $53,000.
C) $65,000.
D) $15,000.
E) $27,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Consider the following scenario when answering the following two questions.
Charlie's Churros is a perfectly competitive firm that sells desserts in Houston, Texas. Charlie's Churros currently is taking in $40,000 in revenues and has $15,000 in explicit costs and $25,000 in implicit costs.
If Charlie's Churros' profits are computed by the method that accountants use,then they are:
A) $40,000.
B) $15,000.
C) $25,000.
D) $0.
E) $80,000.
Charlie's Churros is a perfectly competitive firm that sells desserts in Houston, Texas. Charlie's Churros currently is taking in $40,000 in revenues and has $15,000 in explicit costs and $25,000 in implicit costs.
If Charlie's Churros' profits are computed by the method that accountants use,then they are:
A) $40,000.
B) $15,000.
C) $25,000.
D) $0.
E) $80,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Lauren is the owner of a bakery that earns 0 (zero)economic profit.Last year,her total revenue was $145,000,her rent was $12,000,her labor costs were $65,000,and her overhead expenses were $15,000.From this information,we know that her total explicit costs were:
A) $80,000.
B) $92,000.
C) $15,000.
D) $77,000.
E) $53,000.
A) $80,000.
B) $92,000.
C) $15,000.
D) $77,000.
E) $53,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Refer to the following graph to answer the questions that follow.
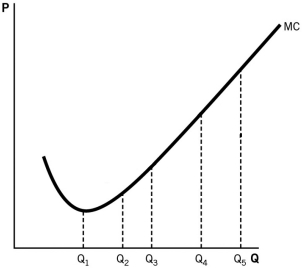
The firm is experiencing diminishing marginal product beyond what level of output along the marginal cost curve?
A) Q5
B) Q1
C) Q2
D) Q3
E) Q4

The firm is experiencing diminishing marginal product beyond what level of output along the marginal cost curve?
A) Q5
B) Q1
C) Q2
D) Q3
E) Q4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Lauren owns a bakery that produces,among other things,wedding cakes.She currently has 7 employees; with 7 employees,her bakery can produce 12 wedding cakes per day.If she hired an eighth employee,her bakery would be able to produce 16 wedding cakes per day.Therefore,the marginal product of the eighth employee is ________ wedding cake(s).
A) 2
B) 1
C) 8
D) 16
E) 4
A) 2
B) 1
C) 8
D) 16
E) 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The production function for automobiles includes:
A) farmland, seeds, rain, and tractors.
B) an aircraft carrier, planes, helicopters, sailors, and pilots.
C) a mall, racks and shelves, mannequins, and sales clerks.
D) lumber, shingles, windows, doors, and carpenters.
E) a factory, an assembly line, workers, and robots.
A) farmland, seeds, rain, and tractors.
B) an aircraft carrier, planes, helicopters, sailors, and pilots.
C) a mall, racks and shelves, mannequins, and sales clerks.
D) lumber, shingles, windows, doors, and carpenters.
E) a factory, an assembly line, workers, and robots.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
If all workers are able to specialize and become more productive as more labor is hired,the amount of total output produced ________ at a(n)________ rate.
A) increases; decreasing
B) increases; constant
C) increases; increasing
D) decreases; increasing
E) decreases; constant
A) increases; decreasing
B) increases; constant
C) increases; increasing
D) decreases; increasing
E) decreases; constant

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The three primary tangible factors of production are:
A) revenue, profits, and costs.
B) price, quantity, and profits.
C) capital, interest, and savings.
D) labor, wages, and training.
E) land, labor, and capital.
A) revenue, profits, and costs.
B) price, quantity, and profits.
C) capital, interest, and savings.
D) labor, wages, and training.
E) land, labor, and capital.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The three primary tangible inputs are:
A) revenue, profits, and costs.
B) price, quantity, and profits.
C) land, labor, and capital.
D) labor, wages, and training.
E) capital, interest, and savings.
A) revenue, profits, and costs.
B) price, quantity, and profits.
C) land, labor, and capital.
D) labor, wages, and training.
E) capital, interest, and savings.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
As a firm hires more labor and each worker is able to specialize,what happens to each additional worker's marginal productivity?
A) It increases at first, then decreases.
B) It increases continuously.
C) It decreases continuously.
D) It decreases at first, then increases.
E) It remains constant, no matter how much labor is hired.
A) It increases at first, then decreases.
B) It increases continuously.
C) It decreases continuously.
D) It decreases at first, then increases.
E) It remains constant, no matter how much labor is hired.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
A firm's production function is similar to a recipe used to make a cake in the sense that the production function shows us the combination of ________ used to produce ________.
A) inputs; output
B) outputs; input
C) costs; profit
D) expenses; revenue
E) taxes; deductions
A) inputs; output
B) outputs; input
C) costs; profit
D) expenses; revenue
E) taxes; deductions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The production function for bookshelves includes:
A) yeast, flour, pans, ovens, and bakers.
B) electric guitars, drums, microphones, musicians, and a stage.
C) foam cushions, fabric, wood, nails, and furniture makers.
D) wood, nails, carpenters, saws, and hammers.
E) wool fabric, buttons, a zipper, a sewing machine, and a tailor.
A) yeast, flour, pans, ovens, and bakers.
B) electric guitars, drums, microphones, musicians, and a stage.
C) foam cushions, fabric, wood, nails, and furniture makers.
D) wood, nails, carpenters, saws, and hammers.
E) wool fabric, buttons, a zipper, a sewing machine, and a tailor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Refer to the following graph to answer the questions that follow.

Based on the graph,at output Q₅ is this firm earning positive,negative,or zero economic profits?
A) We cannot determine the firm's level of profit because we do not know about its revenues.
B) It is earning positive economic profit.
C) Because this is the short run, all firms earn positive economic profit.
D) It is earning zero economic profit.
E) It is earning negative economic profit.

Based on the graph,at output Q₅ is this firm earning positive,negative,or zero economic profits?
A) We cannot determine the firm's level of profit because we do not know about its revenues.
B) It is earning positive economic profit.
C) Because this is the short run, all firms earn positive economic profit.
D) It is earning zero economic profit.
E) It is earning negative economic profit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
A firm has a certain amount of capital and land.As it hires more labor,each worker is able to:
A) earn a higher wage.
B) specialize.
C) work more overtime.
D) purchase more capital.
E) purchase more land.
A) earn a higher wage.
B) specialize.
C) work more overtime.
D) purchase more capital.
E) purchase more land.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Lauren owns a bakery that produces,among other things,wedding cakes.She currently has 5 employees; with 5 employees,her bakery can produce 7 wedding cakes per day.If she hired a sixth employee,her bakery would be able to produce 9 wedding cakes per day.Therefore,the marginal product of the sixth employee is ________ wedding cakes.
A) 5
B) 7
C) 9
D) 2
E) 1.5
A) 5
B) 7
C) 9
D) 2
E) 1.5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Lauren owns a bakery that produces,among other things,wedding cakes.She currently has 6 employees; with 6 employees,her bakery can produce 9 wedding cakes per day.If she hired a seventh employee,her bakery would be able to produce 12 wedding cakes per day.Therefore,the marginal product of the seventh employee is ________ wedding cakes.
A) 9
B) 7
C) 1.71
D) 3
E) 5
A) 9
B) 7
C) 1.71
D) 3
E) 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Another term for factors of production is:
A) outputs.
B) inputs.
C) profits.
D) revenues.
E) costs.
A) outputs.
B) inputs.
C) profits.
D) revenues.
E) costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Marginal product is the change in:
A) total output divided by the change in input.
B) total output plus the change in input.
C) total output minus the change in input.
D) total output times the change in input.
E) input divided by the change in total output.
A) total output divided by the change in input.
B) total output plus the change in input.
C) total output minus the change in input.
D) total output times the change in input.
E) input divided by the change in total output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
If workers are unable to specialize and become more productive as more labor is hired,the amount of total output produced ________ at a(n)________ rate.
A) increases; increasing
B) increases; constant
C) increases; decreasing
D) decreases; increasing
E) decreases; constant
A) increases; increasing
B) increases; constant
C) increases; decreasing
D) decreases; increasing
E) decreases; constant

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The change in total output divided by the change in input is known as:
A) marginal product.
B) marginal cost.
C) specialization.
D) total product.
E) marginal profit.
A) marginal product.
B) marginal cost.
C) specialization.
D) total product.
E) marginal profit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Refer to the following graph to answer the questions that follow.

The firm is experiencing gains from specialization up to what level of output along the marginal cost curve?
A) Q2
B) Q5
C) Q1
D) Q3
E) Q4

The firm is experiencing gains from specialization up to what level of output along the marginal cost curve?
A) Q2
B) Q5
C) Q1
D) Q3
E) Q4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The change in total cost given a change in output is also known as ________ cost.
A) differential
B) marginal
C) average
D) short-run
E) long-run
A) differential
B) marginal
C) average
D) short-run
E) long-run

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
A firm's inputs are also known as its:
A) outputs.
B) profits.
C) factors of production.
D) revenues.
E) costs.
A) outputs.
B) profits.
C) factors of production.
D) revenues.
E) costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Assume that a firm hires an additional employee.If the marginal product for that employee is greater than for the previous employee hired,it must be because:
A) the marginal product of labor is diminishing.
B) all workers are paid the same wage.
C) the workers all perform the exact same set of tasks.
D) there are gains from specialization.
E) all workers are not paid the same wage.
A) the marginal product of labor is diminishing.
B) all workers are paid the same wage.
C) the workers all perform the exact same set of tasks.
D) there are gains from specialization.
E) all workers are not paid the same wage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Steve owns a bike store.His total costs are $1.2 million per year.Last year,Steve sold 1,200 bikes.If Steve sells 1,250 bikes this year (50 more than last year)and his total cost increases to $1.28 million,we know that the:
A) marginal revenue of selling 1,250 bikes is now $1,000.
B) average return of selling bikes has decreased.
C) average cost of selling bikes is unchanged.
D) marginal cost of those 50 bikes is $80,000.
E) marginal cost of those 50 bikes is $1.28 million.
A) marginal revenue of selling 1,250 bikes is now $1,000.
B) average return of selling bikes has decreased.
C) average cost of selling bikes is unchanged.
D) marginal cost of those 50 bikes is $80,000.
E) marginal cost of those 50 bikes is $1.28 million.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
When marginal revenue equals marginal cost:
A) profits are always equal to zero.
B) firms should increase production.
C) firms should decrease production.
D) firms should stop production.
E) firms are maximizing profits, so they should continue at that production level.
A) profits are always equal to zero.
B) firms should increase production.
C) firms should decrease production.
D) firms should stop production.
E) firms are maximizing profits, so they should continue at that production level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
If a firm experiences diminishing marginal product,its marginal cost ________ at a(n)________ rate.
A) increases; increasing
B) decreases; decreasing
C) increases; constant
D) decreases; constant
E) increases; decreasing
A) increases; increasing
B) decreases; decreasing
C) increases; constant
D) decreases; constant
E) increases; decreasing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
In the accompanying table,diminishing marginal product begins after the ________ unit of output.
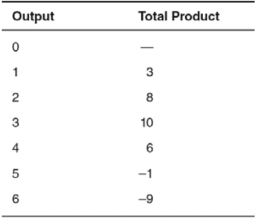
A) second
B) fourth
C) fifth
D) third
E) first

A) second
B) fourth
C) fifth
D) third
E) first

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
In the accompanying table,diminishing marginal product begins after the ________ unit of input.
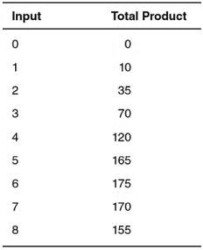
A) first
B) second
C) seventh
D) fourth
E) sixth

A) first
B) second
C) seventh
D) fourth
E) sixth

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Profit maximization occurs when:
A) a firm expands output until marginal revenue is exceeded by marginal cost.
B) a firm expands output until marginal revenue is equal to marginal cost.
C) the price in the market is equal to the firm's marginal revenue.
D) total costs equal total revenue.
E) a firm sets the price at a point above average cost.
A) a firm expands output until marginal revenue is exceeded by marginal cost.
B) a firm expands output until marginal revenue is equal to marginal cost.
C) the price in the market is equal to the firm's marginal revenue.
D) total costs equal total revenue.
E) a firm sets the price at a point above average cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Kimberly owns a cupcake shop in Newport Beach,California.The market for cupcakes is very competitive.At Kimberly's current production level,her marginal cost is $25 and her marginal revenue is $29.To maximize profits,Kimberly should:
A) decrease production.
B) keep production the same.
C) increase the price.
D) decease the price.
E) increase production.
A) decrease production.
B) keep production the same.
C) increase the price.
D) decease the price.
E) increase production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Marginal revenue is the change in total:
A) cost when the firm produces additional units.
B) revenue when the firm spends more money.
C) revenue divided by the change in total cost.
D) revenue when the firm produces additional units.
E) cost divided by the change in total revenue.
A) cost when the firm produces additional units.
B) revenue when the firm spends more money.
C) revenue divided by the change in total cost.
D) revenue when the firm produces additional units.
E) cost divided by the change in total revenue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
If a firm hires another worker and his or her marginal product of labor is 0 (zero),we know that the firm's total output is:
A) 0 (zero).
B) unchanged.
C) increasing.
D) decreasing.
E) equal to the marginal product of that worker.
A) 0 (zero).
B) unchanged.
C) increasing.
D) decreasing.
E) equal to the marginal product of that worker.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
If a firm hires another worker and his or her marginal product of labor is positive,we know that the firm's total output is:
A) decreasing.
B) unchanged.
C) increasing.
D) 0 (zero).
E) equal to the marginal product of that worker.
A) decreasing.
B) unchanged.
C) increasing.
D) 0 (zero).
E) equal to the marginal product of that worker.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
If the marginal product of labor for a firm decreases as more workers are hired,we know that:
A) all workers are paid the same wage.
B) the marginal cost of producing output is decreasing.
C) the gains from specialization are exhausted.
D) the marginal cost of producing output is constant.
E) there are still gains from specialization left to be exploited.
A) all workers are paid the same wage.
B) the marginal cost of producing output is decreasing.
C) the gains from specialization are exhausted.
D) the marginal cost of producing output is constant.
E) there are still gains from specialization left to be exploited.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
When a firm hires another employee and,as a result,total output increases,this change in total output is also known as:
A) total output.
B) marginal employment.
C) marginal product.
D) labor contribution.
E) marginal benefit.
A) total output.
B) marginal employment.
C) marginal product.
D) labor contribution.
E) marginal benefit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
If the marginal product is increasing,the marginal cost of output must be:
A) decreasing.
B) constant.
C) equal to average cost.
D) unchanged.
E) increasing.
A) decreasing.
B) constant.
C) equal to average cost.
D) unchanged.
E) increasing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
If a firm hires another worker and his or her marginal product of labor is negative,we know that the firm's total output is:
A) increasing.
B) decreasing.
C) equal to the marginal product of that worker.
D) unchanged.
E) 0 (zero).
A) increasing.
B) decreasing.
C) equal to the marginal product of that worker.
D) unchanged.
E) 0 (zero).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
If there are gains from specialization in a workplace,hiring another employee means that the marginal product of labor will:
A) decrease.
B) remain the same.
C) increase.
D) be 0 (zero).
E) be negative.
A) decrease.
B) remain the same.
C) increase.
D) be 0 (zero).
E) be negative.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
As a firm hires more workers,its marginal product of labor increases only if:
A) each worker does the same tasks as all others.
B) all workers are paid the same wage.
C) the firm produces commodities.
D) employees are assigned specialized tasks.
E) all workers are paid different wages.
A) each worker does the same tasks as all others.
B) all workers are paid the same wage.
C) the firm produces commodities.
D) employees are assigned specialized tasks.
E) all workers are paid different wages.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
The production function of a restaurant includes items such as labor (i.e.,cooks,waiters,a manager),capital (i.e.,ovens,counters,tables,chairs,and a building),and land.In the short run,the owner of the restaurant will optimize production by employing a variable amount of ________ given a fixed amount of ________.
A) capital; labor and land
B) land; capital and labor
C) labor; capital and land
D) labor; capital and raw materials
E) land; labor and raw materials
A) capital; labor and land
B) land; capital and labor
C) labor; capital and land
D) labor; capital and raw materials
E) land; labor and raw materials

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
If a firm experiences productivity gains from employee specialization,its marginal cost ________ at a(n)________ rate.
A) increases; increasing
B) decreases; increasing
C) decreases; decreasing
D) decreases; constant
E) increases; decreasing
A) increases; increasing
B) decreases; increasing
C) decreases; decreasing
D) decreases; constant
E) increases; decreasing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
In competitive industries such as the lawn-mowing business:
A) firms set the prices for their products with little concern for the consumer.
B) firms are considered to be price makers.
C) market forces prevent firms from charging a higher price.
D) the individual firms are much stronger than the market forces are.
E) the market forces set the quantity in the market but not the prices.
A) firms set the prices for their products with little concern for the consumer.
B) firms are considered to be price makers.
C) market forces prevent firms from charging a higher price.
D) the individual firms are much stronger than the market forces are.
E) the market forces set the quantity in the market but not the prices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



