Deck 8: Domestic Markets for Goods and Services
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/28
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 8: Domestic Markets for Goods and Services
1
When buyers,sellers and intermediaries undertake costly efforts to locate trading partners,reach agreements regarding transaction details and monitor partners' compliance with agreements,and when they suffer losses to partners who fail to fulfill agreements they are paying ____________.We use the term ______________ to encompass all the transport,storage,financing and transaction costs associated with the transfer of goods from their producers to their ultimate users through markets.
A) Transaction costs; transportation prices
B) Transaction costs; transfer costs
C) Transfer costs; transaction costs
D) Intermediary cost; transportation costs
A) Transaction costs; transportation prices
B) Transaction costs; transfer costs
C) Transfer costs; transaction costs
D) Intermediary cost; transportation costs
B
2
Figure 8.1
Market for Traditional Beans in Small Village
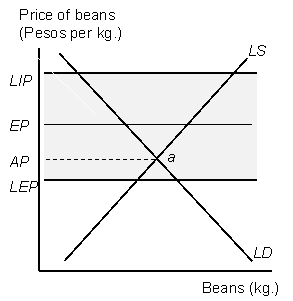
According to Figure 8.1 the local demand schedule (LD)slopes downward because_____________.
A) As the bean price falls,some buyers choose to purchase fewer beans,and some choose to leave the local bean market altogether
B) As the bean price rises,some sellers choose to sell more beans,and some choose to enter the local bean market
C) As the bean price falls,some sellers choose to sell fewer beans,and some choose to leave the local bean market altogether
D) As the bean price rises,some buyers choose to purchase fewer beans,and some choose to leave the local bean market altogether
Market for Traditional Beans in Small Village

According to Figure 8.1 the local demand schedule (LD)slopes downward because_____________.
A) As the bean price falls,some buyers choose to purchase fewer beans,and some choose to leave the local bean market altogether
B) As the bean price rises,some sellers choose to sell more beans,and some choose to enter the local bean market
C) As the bean price falls,some sellers choose to sell fewer beans,and some choose to leave the local bean market altogether
D) As the bean price rises,some buyers choose to purchase fewer beans,and some choose to leave the local bean market altogether
D
3
Figure 8.1
Market for Traditional Beans in Small Village

According to Figure 8.1,if we define LIP as the local import price,EP as the external market price,LEP as the local export price,and AP as the autarky price,and if trade with big city were possible,at what price would the local market eventually settle on?
A) EP
B) AP
C) LIP
D) LEP
Market for Traditional Beans in Small Village

According to Figure 8.1,if we define LIP as the local import price,EP as the external market price,LEP as the local export price,and AP as the autarky price,and if trade with big city were possible,at what price would the local market eventually settle on?
A) EP
B) AP
C) LIP
D) LEP
B
4
The difference between the selling price and the buying price is called the ___________.
A) Profit
B) Consumer surplus
C) Marketing margin
D) Producer surplus
A) Profit
B) Consumer surplus
C) Marketing margin
D) Producer surplus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
If a market is in importing equilibrium,an increase in demand will:
A) Increase consumption but leave the local price unchanged
B) Increase consumption and the local price
C) Decrease consumption and the local price
D) Increase consumption and decrease the local price
A) Increase consumption but leave the local price unchanged
B) Increase consumption and the local price
C) Decrease consumption and the local price
D) Increase consumption and decrease the local price

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Why should governments and NGOs consider switching from food transfers to cash transfers?
A) Corruption
B) Distributing food discourages development by driving down local food prices and discouraging local agricultural production
C) Distributing food discourages development by driving up local food prices and discouraging local agricultural production
D) Governments should never switch from food to cash transfer programs
A) Corruption
B) Distributing food discourages development by driving down local food prices and discouraging local agricultural production
C) Distributing food discourages development by driving up local food prices and discouraging local agricultural production
D) Governments should never switch from food to cash transfer programs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
When middlemen lack competition it is possible that they may command significant ____________,or excess profits derived by exploiting their privileged positions.
A) Marketing rents
B) Consumer surplus
C) Marketing margin
D) Producer surplus
A) Marketing rents
B) Consumer surplus
C) Marketing margin
D) Producer surplus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Figure 8.2
Exporting,Importing and Autarky Equilibrium in the Small Village Bean Market
Panel (a) Panel (b) Panel (c)
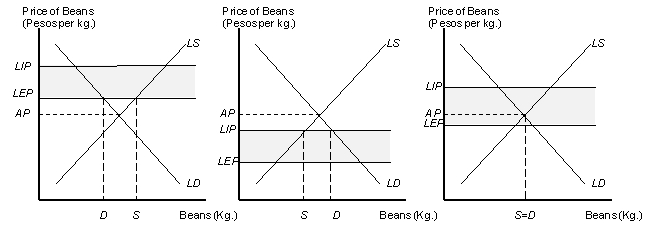
According to Figure 8.2,if we define LIP as the local import price,EP as the external market price,LEP as the local export price,and AP as the autarky price,and if trade with big city were possible,which panel describes a situation where buyers and sellers will chose not trade at all with big city?
A) Panel a
B) Panel b
C) Panel c
D) That situation is not described by any of the panels
Exporting,Importing and Autarky Equilibrium in the Small Village Bean Market
Panel (a) Panel (b) Panel (c)

According to Figure 8.2,if we define LIP as the local import price,EP as the external market price,LEP as the local export price,and AP as the autarky price,and if trade with big city were possible,which panel describes a situation where buyers and sellers will chose not trade at all with big city?
A) Panel a
B) Panel b
C) Panel c
D) That situation is not described by any of the panels

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Firms that specialize in marketing services are called __________ and often benefit from specialization just as producers of tradition goods and services.
A) Wholesalers
B) Transportation specialists
C) Middle-men
D) Market intermediaries
A) Wholesalers
B) Transportation specialists
C) Middle-men
D) Market intermediaries

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
If local food supply is highly _________,cash distributions raise local food prices only a little while encouraging significant _______ in local food production.
A) Elastic; decreases
B) Elastic; increases
C) Inelastic; decreases
D) Inelastic; increases
A) Elastic; decreases
B) Elastic; increases
C) Inelastic; decreases
D) Inelastic; increases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
If a market is in autarky equilibrium,an increase in supply will:
A) Increase local production but leave the local price unchanged
B) Increase local production and the local price
C) Decrease local production and the local price
D) Increase local production and decrease the local price
A) Increase local production but leave the local price unchanged
B) Increase local production and the local price
C) Decrease local production and the local price
D) Increase local production and decrease the local price

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Figure 8.1
Market for Traditional Beans in Small Village

According to Figure 8.1,if we define LIP as the local import price,EP as the external market price,LEP as the local export price,and AP as the autarky price,which distance represents the transfer costs of selling beans to the big city?
A) EP minus LEP
B) EP minus AP
C) LIP minus EP
D) LIP minus LEP
Market for Traditional Beans in Small Village

According to Figure 8.1,if we define LIP as the local import price,EP as the external market price,LEP as the local export price,and AP as the autarky price,which distance represents the transfer costs of selling beans to the big city?
A) EP minus LEP
B) EP minus AP
C) LIP minus EP
D) LIP minus LEP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Figure 8.1
Market for Traditional Beans in Small Village

According to Figure 8.1,if we define LIP as the local import price,EP as the external market price,LEP as the local export price,and AP as the autarky price,which distance represents the transfer costs of purchasing beans from the big city?
A) LIP minus LEP
B) LIP minus AP
C) LIP minus EP
D) LIP minus 0
Market for Traditional Beans in Small Village

According to Figure 8.1,if we define LIP as the local import price,EP as the external market price,LEP as the local export price,and AP as the autarky price,which distance represents the transfer costs of purchasing beans from the big city?
A) LIP minus LEP
B) LIP minus AP
C) LIP minus EP
D) LIP minus 0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
If a market is in exporting equilibrium,an increase in supply will:
A) Increase local production but leave the local price unchanged
B) Increase local production and the local price
C) Decrease local production and the local price
D) Increase local consumption and decrease the local price
A) Increase local production but leave the local price unchanged
B) Increase local production and the local price
C) Decrease local production and the local price
D) Increase local consumption and decrease the local price

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Figure 8.2
Exporting,Importing and Autarky Equilibrium in the Small Village Bean Market
Panel (a) Panel (b) Panel (c)

According to Figure 8.2,if we define LIP as the local import price,EP as the external market price,LEP as the local export price,and AP as the autarky price,and if trade with big city were possible,which panel describes a situation where sellers are exporting beans to big city?
A) Panel a
B) Panel b
C) Panel c
D) That situation is not described by any of the panels
Exporting,Importing and Autarky Equilibrium in the Small Village Bean Market
Panel (a) Panel (b) Panel (c)

According to Figure 8.2,if we define LIP as the local import price,EP as the external market price,LEP as the local export price,and AP as the autarky price,and if trade with big city were possible,which panel describes a situation where sellers are exporting beans to big city?
A) Panel a
B) Panel b
C) Panel c
D) That situation is not described by any of the panels

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following changes would shift the supply schedule to the right?
A) Increase in the price of inputs
B) Increase in the price of the output
C) Decrease in the price of an alternative product produced with similar resources
D) Improvements in technology
A) Increase in the price of inputs
B) Increase in the price of the output
C) Decrease in the price of an alternative product produced with similar resources
D) Improvements in technology

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Figure 8.2
Exporting,Importing and Autarky Equilibrium in the Small Village Bean Market
Panel (a) Panel (b) Panel (c)

According to Figure 8.2,if we define LIP as the local import price,EP as the external market price,LEP as the local export price,and AP as the autarky price,and if trade with big city were possible,which panel describes a situation where buyers are importing beans from big city?
A) Panel a
B) Panel b
C) Panel c
D) That situation is not described by any of the panels
Exporting,Importing and Autarky Equilibrium in the Small Village Bean Market
Panel (a) Panel (b) Panel (c)

According to Figure 8.2,if we define LIP as the local import price,EP as the external market price,LEP as the local export price,and AP as the autarky price,and if trade with big city were possible,which panel describes a situation where buyers are importing beans from big city?
A) Panel a
B) Panel b
C) Panel c
D) That situation is not described by any of the panels

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Private producers will only choose to sell their output when the benefit outweighs the cost.Which of the following could prevent a market from developing?
A) High transportation costs
B) High transfer costs
C) Poor legal system
D) All of the above could prevent a market from developing.
A) High transportation costs
B) High transfer costs
C) Poor legal system
D) All of the above could prevent a market from developing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Figure 8.1
Market for Traditional Beans in Small Village

According to Figure 8.1 the local supply schedule (LD)slopes upward because_____________.
A) As the bean price falls,some buyers choose to purchase fewer beans,and some choose to leave the local bean market altogether
B) As the bean price rises,some sellers choose to sell more beans,and some choose to enter the local bean market
C) As the bean price rises,some sellers choose to sell fewer beans,and some choose to leave the local bean market altogether
D) As the bean price rises,some buyers choose to purchase fewer beans,and some choose to leave the local bean market altogether
Market for Traditional Beans in Small Village

According to Figure 8.1 the local supply schedule (LD)slopes upward because_____________.
A) As the bean price falls,some buyers choose to purchase fewer beans,and some choose to leave the local bean market altogether
B) As the bean price rises,some sellers choose to sell more beans,and some choose to enter the local bean market
C) As the bean price rises,some sellers choose to sell fewer beans,and some choose to leave the local bean market altogether
D) As the bean price rises,some buyers choose to purchase fewer beans,and some choose to leave the local bean market altogether

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The ________ of Jamaica,women who carry agricultural produce to town in baskets on their heads
A) "Higglers"
B) "Wigglers"
C) "Smugglers"
D) "Carriers"
A) "Higglers"
B) "Wigglers"
C) "Smugglers"
D) "Carriers"

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Why might private actors fail to undertake critical transfer cost-reducing investments despite the wide-ranging benefits that might emerge from transfer cost reductions?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which type of industry renders a firm more productive when located near each other than when separated from each other geographically?
A) Economies of scale
B) Economies of scope
C) Comparative advantage
D) Agglomeration economies
A) Economies of scale
B) Economies of scope
C) Comparative advantage
D) Agglomeration economies

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The logic of ____________ indicates that new opportunities for exchange between people with diverse production capabilities increase productivity and expand consumption opportunities by allowing people to specialize in the types of production they do relatively well.
A) Proportionate advantage
B) Relative advantage
C) Comparative advantage
D) Absolute advantage
A) Proportionate advantage
B) Relative advantage
C) Comparative advantage
D) Absolute advantage

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
If local food supply is highly _________,food distributions encourage significant _______ in local food production.
A) Elastic; decreases
B) Elastic; increases
C) Inelastic; decreases
D) Inelastic; increases
A) Elastic; decreases
B) Elastic; increases
C) Inelastic; decreases
D) Inelastic; increases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Governments and humanitarian aid organizations have a long history of distributing free food to needy people.Why are some humanitarian organizations increasingly experimenting,with distributing cash rather than food?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
If production is characterized by __________,then expansion of trade that allows individual producers to serve consumers spread out over larger areas may also increase productivity.
A) Economies of scale
B) Economies of scope
C) Comparative advantage
D) Agglomeration economies
A) Economies of scale
B) Economies of scope
C) Comparative advantage
D) Agglomeration economies

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
A person has a comparative advantage in producing a good if that person:
A) Has higher productivity in producing it than anyone else has
B) Can produce it at a lower opportunity cost than anyone else can
C) Has less desire to consume that good than anyone else has
D) Has more human capital related to that good than anyone else has
A) Has higher productivity in producing it than anyone else has
B) Can produce it at a lower opportunity cost than anyone else can
C) Has less desire to consume that good than anyone else has
D) Has more human capital related to that good than anyone else has

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
It is sometimes thought that the mere existence of marketing margins implies exploitation of small farmers and businessmen,who are cheated out of receiving the full retail price for their produce by middlemen.Can there be a benefit from marketing margins?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



