Deck 9: Labor Markets
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/28
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 9: Labor Markets
1
If employers are perfectly competitive profit maximizers then they hire labor until:
A) The VMPL equals the average total cost
B) The VMPL equals the average variable cost
C) The VMPL equals the wage
D) The VMPL is greater than the average fixed cost
A) The VMPL equals the average total cost
B) The VMPL equals the average variable cost
C) The VMPL equals the wage
D) The VMPL is greater than the average fixed cost
C
2
Empirical studies have revealed a process called ___________,involving the birth of innovative firms and the death of other firms,can be responsible for a large fraction of ______________ in developing and developed countries
A) Technological advancement; wage growth
B) Technological advancement; productivity growth
C) Creative destruction; productivity growth
D) Creative destruction; wage growth
A) Technological advancement; wage growth
B) Technological advancement; productivity growth
C) Creative destruction; productivity growth
D) Creative destruction; wage growth
C
3
Successful economic growth requires structural changes or
A) Changing the natural rate of unemployment
B) Shifts in the nature and location of economic activity
C) Increasing structural unemployment
D) Building new machines or factories
A) Changing the natural rate of unemployment
B) Shifts in the nature and location of economic activity
C) Increasing structural unemployment
D) Building new machines or factories
B
4
In order for economic growth from an investment or innovation to lead to increases in the standards of living for _______,it should cause the _______schedule to rise,causing a ________for labor and an increase in wages.
A) Skilled laborers; demand; increase in demand
B) Unskilled laborers; supply; decrease in supply
C) Unskilled laborers; VMPL; increase in demand
D) Skilled laborers; supply; increase in supply
A) Skilled laborers; demand; increase in demand
B) Unskilled laborers; supply; decrease in supply
C) Unskilled laborers; VMPL; increase in demand
D) Skilled laborers; supply; increase in supply

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
When workers receive a specified pay per acre weeded,or per kilogram harvested they earn:
A) Piece rates
B) Fringe benefits
C) Wage premiums
D) Compensating differentials
A) Piece rates
B) Fringe benefits
C) Wage premiums
D) Compensating differentials

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Agrarian employment arrangements use:
A) Higher paid permanent labor
B) Higher paid temporary workers
C) Lower paid permanent labor
D) Lower paid temporary workers
A) Higher paid permanent labor
B) Higher paid temporary workers
C) Lower paid permanent labor
D) Lower paid temporary workers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Figure 9.1
The Effects of an Employer-Specific Labor Demand Increase when Labor is Perfectly Mobile(a) (b) (c)
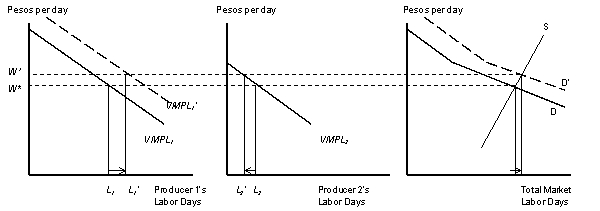
According to Figure 9.1 which of the panels depicts,when producer 1 increases wages to attract workers from producer 2,what happens to total labor in the market?
A) Producer 1 increases labor,producer 2 decreases labor the total labor used stays the same
B) Producer 1 decreases labor,producer 2 decreases labor the total labor used increased
C) Producer 1 decreases labor,producer 2 increases labor the total labor increased
D) Producer 1 increases labor,producer 2 decreases labor the total labor increased
The Effects of an Employer-Specific Labor Demand Increase when Labor is Perfectly Mobile(a) (b) (c)

According to Figure 9.1 which of the panels depicts,when producer 1 increases wages to attract workers from producer 2,what happens to total labor in the market?
A) Producer 1 increases labor,producer 2 decreases labor the total labor used stays the same
B) Producer 1 decreases labor,producer 2 decreases labor the total labor used increased
C) Producer 1 decreases labor,producer 2 increases labor the total labor increased
D) Producer 1 increases labor,producer 2 decreases labor the total labor increased

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Employment in jobs that make poor use of their skills or employ only a fraction of the labor time they are willing to offer is referred to as:
A) Underemployment
B) Unemployment
C) Is not counted as employed or unemployed
D) Is a discouraged worker phenomenon
A) Underemployment
B) Unemployment
C) Is not counted as employed or unemployed
D) Is a discouraged worker phenomenon

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The wage premiums required leaving workers indifferent about working in dangerous conditions instead of a lower paying,but better condition job is referred to as:
A) Compensation packages
B) Fringe benefits
C) Wage premium
D) Compensating differentials
A) Compensation packages
B) Fringe benefits
C) Wage premium
D) Compensating differentials

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Over the course of development,the shares of manufacturing and service sectors in GDP tend to _______,while the agricultural sector _______.
A) Fall; rises
B) Fall; also falls
C) Rise; also rises
D) Rise; declines
A) Fall; rises
B) Fall; also falls
C) Rise; also rises
D) Rise; declines

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Figure 9.1
The Effects of an Employer-Specific Labor Demand Increase when Labor is Perfectly Mobile(a) (b) (c)

According to Figure 9.1 which of the panels depicts a firm who invested in a technological innovation that is labor using,in the sense that it improves the Value of the marginal product of labor?
A) Panel a
B) Panel b
C) Panel c
D) Panel and a and b.
The Effects of an Employer-Specific Labor Demand Increase when Labor is Perfectly Mobile(a) (b) (c)

According to Figure 9.1 which of the panels depicts a firm who invested in a technological innovation that is labor using,in the sense that it improves the Value of the marginal product of labor?
A) Panel a
B) Panel b
C) Panel c
D) Panel and a and b.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
If labor use is ___________ then there is no way to make one person better off,without making any other person worse off,simply by _____________.
A) Equitable; paying everyone a higher wage
B) Inefficient; reallocating resources across different uses
C) Efficient; paying workers a higher wage
D) Efficient; reallocating labor across different uses
A) Equitable; paying everyone a higher wage
B) Inefficient; reallocating resources across different uses
C) Efficient; paying workers a higher wage
D) Efficient; reallocating labor across different uses

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
As long as labor markets are perfectly competitive and workers are mobile,__________ in the demand for low-skill labor in any one sector or location bring _________ for _________workers.
A) Increases; decreases in prices; unskilled
B) Increases; rising wages; all
C) Increases; rising prices; all
D) Decreases; increased income; skilled
A) Increases; decreases in prices; unskilled
B) Increases; rising wages; all
C) Increases; rising prices; all
D) Decreases; increased income; skilled

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following is not an investment in human capital?
A) acquisition of skills through primary and secondary schools
B) Job Training
C) Learning by doing tasks on the job
D) Purchasing a tool to improve labor productivity
A) acquisition of skills through primary and secondary schools
B) Job Training
C) Learning by doing tasks on the job
D) Purchasing a tool to improve labor productivity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
When labor supply is _______,asset growth that increases the demand for low-skill labor _________ and well-being __________ for the low-skill workers already in the market.
A) Elastic; reduces wages; significantly
B) Elastic; raises wages; insignificantly
C) Inelastic; decreases wages; insignificantly
D) Inelastic; raises wages,significantly
A) Elastic; reduces wages; significantly
B) Elastic; raises wages; insignificantly
C) Inelastic; decreases wages; insignificantly
D) Inelastic; raises wages,significantly

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
All of the following are reasons why a labor market may remain segmented rather than eventually settling into a competitive labor market except:
A) A minimum wage above the competitive equilibrium wage
B) A minimum wage below the competitive equilibrium wage
C) Labor unions
D) It may be profitable for firm to maintain higher pay rather than facing a high search cost and high training costs
A) A minimum wage above the competitive equilibrium wage
B) A minimum wage below the competitive equilibrium wage
C) Labor unions
D) It may be profitable for firm to maintain higher pay rather than facing a high search cost and high training costs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
When the supply of labor is highly _______,the increased demand for labor generates _______ benefits for low-skill workers.
A) Elastic; many
B) Elastic; few
C) Inelastic; few
D) Inelastic; many
A) Elastic; many
B) Elastic; few
C) Inelastic; few
D) Inelastic; many

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Figure 9.2
Equilibrium in Markets for Low- and High-Skill Labor(a) (b)
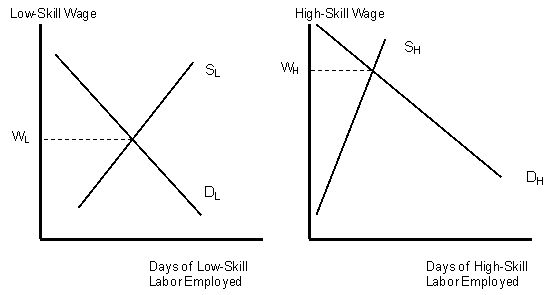
According to figure 9.2 the wage for high skilled labor WH is higher than the wage for unskilled WL workers because:
A) Unskilled workers are less productive and more scarce
B) High skilled workers are less productive and more abundant
C) High skill workers are more productive and more scarce
D) Unskilled workers are more productive and more scarce
Equilibrium in Markets for Low- and High-Skill Labor(a) (b)

According to figure 9.2 the wage for high skilled labor WH is higher than the wage for unskilled WL workers because:
A) Unskilled workers are less productive and more scarce
B) High skilled workers are less productive and more abundant
C) High skill workers are more productive and more scarce
D) Unskilled workers are more productive and more scarce

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Rather than implementing _________ where governments provide cash transfers to workers who have recently become unemployed,many developing country governments attempt instead to reduce workers' vulnerability to unemployment through_______________,which require employers to give workers advance notice of firing,to make large lump sum severance payments to workers they dismiss,or to obtain government approval before laying off workers.
A) Underemployment benefits; private institutions
B) Unemployment insurance; job security regulations
C) Job security regulations; unemployment benefits
D) Unemployment insurance; unemployment benefits
A) Underemployment benefits; private institutions
B) Unemployment insurance; job security regulations
C) Job security regulations; unemployment benefits
D) Unemployment insurance; unemployment benefits

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
When a firm offers a wage higher than the competitive equilibrium due to high search and training costs of replacing employees they are paying___________.
A) Minimum wages
B) Efficiency wages
C) Competitive wages
D) Premium wages
A) Minimum wages
B) Efficiency wages
C) Competitive wages
D) Premium wages

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Workers reap _________ productivity benefit of general training in the form of __________.
A) Most of the; increased wages
B) The full; increased leisure hours
C) The full; increased wages
D) A small fraction of the; increased leisure hours
A) Most of the; increased wages
B) The full; increased leisure hours
C) The full; increased wages
D) A small fraction of the; increased leisure hours

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
What costs are associated with migration of workers?
A) If migration is temporary workers will take with them any training they received
B) It can cause private safety net institutions to break-down
C) Tends to raise transmission of infectious diseases
D) All of the above are costs of migration
A) If migration is temporary workers will take with them any training they received
B) It can cause private safety net institutions to break-down
C) Tends to raise transmission of infectious diseases
D) All of the above are costs of migration

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
If firms have to _______ of the workers they train to keep them from being poached the firm's costs may increase by _________ as the increase in revenue,which gives employers _______ to invest in training of their workers.
A) Raise wages; the same amount; no incentive
B) Raise wages; less than; a strong incentive
C) Lower wages; more than; no incentive
D) Raise prices; more than; a strong incentive
A) Raise wages; the same amount; no incentive
B) Raise wages; less than; a strong incentive
C) Lower wages; more than; no incentive
D) Raise prices; more than; a strong incentive

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
What has empirical research pointed to as the most important determinants of migration decisions? Include four or more conditions that could lead to increased migration.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
How can governments expand private sector training activities
A) They can provide training services
B) They can offer employee loans to us in purchasing job training
C) They can tax private employers
D) All of the above
A) They can provide training services
B) They can offer employee loans to us in purchasing job training
C) They can tax private employers
D) All of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Under which conditions can investments and innovations that lead to the same rate of economic growth make it more likely to channel benefits to low-wage workers than others?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
What is the effect of a technological improvement that only affects some firms in the market?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
When workers acquire skills,they transform themselves from low-skill to high-skill workers.This shifts the supply schedule for low-skill workers to the _______ and shifts the supply schedule for high-skill workers to the ______ ,tending to _______ wages for low-skill workers and ________ wages for high-skill workers.
A) Left; right; raise; reduce
B) Right; right; reduce; raise
C) Left; left ; raise; reduce
D) Right; left; reduce; raise
A) Left; right; raise; reduce
B) Right; right; reduce; raise
C) Left; left ; raise; reduce
D) Right; left; reduce; raise

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



