Deck 12: Institutions and Cooperation
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/28
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 12: Institutions and Cooperation
1
In Nash equilibrium:
A) Only one player can change his payoffs by changing strategies
B) Both players can change strategies but neither can improve their payout
C) Neither player can change their strategy
D) Both player can change their strategy but only player can improve their payout
A) Only one player can change his payoffs by changing strategies
B) Both players can change strategies but neither can improve their payout
C) Neither player can change their strategy
D) Both player can change their strategy but only player can improve their payout
B
2
A situation in which each player has chosen a strategy that is the best possible response to the strategies chosen by other players is called:
A) strategic equilibrium
B) steady state equilibrium
C) competitive equilibrium
D) Nash equilibrium
A) strategic equilibrium
B) steady state equilibrium
C) competitive equilibrium
D) Nash equilibrium
D
3
Table 12.2
Payoffs to Fisher 1 and Fisher 2 in a
Common Property Resource Prisoners' Dilemma
($ of profit)
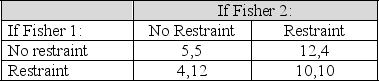
Refer to table 12.2,suppose that two people,Fisher 1 and Fisher 2,have access to a fishing ground,and that each may choose to harvest fish in either a restrained or unrestrained fashion.What is the Nash equilibrium?
A) Fisher 1 and Fisher 2 both choose: no restraint
B) Fisher 1 and Fisher 2 both choose: restraint
C) Fisher 1 chooses restraint and Fisher 2 chooses no restraint
D) Fisher 1 chooses no restraint and Fisher 2 chooses restraint
Payoffs to Fisher 1 and Fisher 2 in a
Common Property Resource Prisoners' Dilemma
($ of profit)

Refer to table 12.2,suppose that two people,Fisher 1 and Fisher 2,have access to a fishing ground,and that each may choose to harvest fish in either a restrained or unrestrained fashion.What is the Nash equilibrium?
A) Fisher 1 and Fisher 2 both choose: no restraint
B) Fisher 1 and Fisher 2 both choose: restraint
C) Fisher 1 chooses restraint and Fisher 2 chooses no restraint
D) Fisher 1 chooses no restraint and Fisher 2 chooses restraint
A
4
In a common prisoners dilemma type game where participants decide whether to cooperate or shirk their responsibility there is often an incentive to ________,or enjoy the benefits of the ________ without contributing to its creation.
A) cooperate; private good
B) free ride; private good
C) cooperate; common resource
D) free-ride; public good
A) cooperate; private good
B) free ride; private good
C) cooperate; common resource
D) free-ride; public good

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
When people harvest fish,wood or water from sources held in common,they enjoy the full benefit of what they harvest ________,much of which falls on others as harvesting becomes more difficult or conflict breaks out.
A) and bear the full cost
B) and bear most of the cost
C) and bear only a fraction of the cost
D) and bear none of the cost
A) and bear the full cost
B) and bear most of the cost
C) and bear only a fraction of the cost
D) and bear none of the cost

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Table 12.1
Utility Payoffs to Thief 1 and Thief 2 in a Classic Prisoners' Dilemma Game
Payoffs are given as utility where U = 10-years in Jail
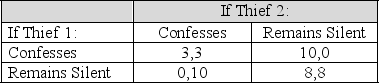
According to ,if the two players can cooperate with each other,how many years in jail will each thief serve?
A) Thief 1 - 2 years; Thief 2 - 2 years
B) Thief 1 - 7 years; Thief 2 - 7 years
C) Thief 1 - 0 years; Thief 2 - 10 years
D) Thief 1 - 10 years; Thief 2 - 0 years
Utility Payoffs to Thief 1 and Thief 2 in a Classic Prisoners' Dilemma Game
Payoffs are given as utility where U = 10-years in Jail

According to ,if the two players can cooperate with each other,how many years in jail will each thief serve?
A) Thief 1 - 2 years; Thief 2 - 2 years
B) Thief 1 - 7 years; Thief 2 - 7 years
C) Thief 1 - 0 years; Thief 2 - 10 years
D) Thief 1 - 10 years; Thief 2 - 0 years

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
People exhibit ________ when they choose actions that are more beneficial to other people (and more costly to themselves)after they witness the others acting in a manner they perceive as fair or generous.They exhibit ________ when they choose actions that are more costly to other people (even if extracting these penalties is costly to themselves)after they witness the others acting in a manner they perceive as unfair or selfish.
A) positive consumption; negative consumption
B) positive externalities; negative externalities
C) positive reciprocity; negative reciprocity
D) good choices; bad choices
A) positive consumption; negative consumption
B) positive externalities; negative externalities
C) positive reciprocity; negative reciprocity
D) good choices; bad choices

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
In standard games theory each player is assumed to derive utility only from current or future consumption with no concern for the impacts of their choice on others.This is called ________ preferences.
A) classical
B) neoclassical
C) behavioral
D) Lexicographic
A) classical
B) neoclassical
C) behavioral
D) Lexicographic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Table 12.1
Utility Payoffs to Thief 1 and Thief 2 in a Classic Prisoners' Dilemma Game
Payoffs are given as utility where U = 10-years in Jail

According to,if Thief 1 confesses and Thief 2 remains silent to the crime,how many years in jail will each thief serve?
A) Thief 1 - 2 years; Thief 2 - 2 years
B) Thief 1 - 7 years; Thief 2 - 7 years
C) Thief 1 - 0 years; Thief 2 - 10 years
D) Thief 1 - 10 years; Thief 2 - 0 years
Utility Payoffs to Thief 1 and Thief 2 in a Classic Prisoners' Dilemma Game
Payoffs are given as utility where U = 10-years in Jail

According to,if Thief 1 confesses and Thief 2 remains silent to the crime,how many years in jail will each thief serve?
A) Thief 1 - 2 years; Thief 2 - 2 years
B) Thief 1 - 7 years; Thief 2 - 7 years
C) Thief 1 - 0 years; Thief 2 - 10 years
D) Thief 1 - 10 years; Thief 2 - 0 years

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
In a two player non-cooperative game where both players have a dominant strategy,
A) there is never a Nash equilibrium.
B) there can be multiple Nash equilibria.
C) there is only one Nash equilibrium.
D) the actual outcome is unpredictable.
A) there is never a Nash equilibrium.
B) there can be multiple Nash equilibria.
C) there is only one Nash equilibrium.
D) the actual outcome is unpredictable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Players with ________ preferences experience a utility ________ when they punish players who have defected.If this change in utility is big enough to outweigh the direct cost to a punisher of inflicting a punishment,then threats of decentralized punishment become credible.
A) neoclassical; boost
B) Lexicographic; drain
C) negative reciprocal; boost
D) positive reciprocal; drain
A) neoclassical; boost
B) Lexicographic; drain
C) negative reciprocal; boost
D) positive reciprocal; drain

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Decisions are ________ when the objective benefits that any one person enjoys after making specified choices depend on the choices made by other people.
A) incremental
B) costly
C) strategic
D) formal
A) incremental
B) costly
C) strategic
D) formal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A player is said to have a _________,or a plan of action that yields the highest payoff no matter what he expects the other player to do.
A) dominant strategy
B) semi-dominant strategy
C) dominated strategy
D) Nash equilibrium
A) dominant strategy
B) semi-dominant strategy
C) dominated strategy
D) Nash equilibrium

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Table 12.1
Utility Payoffs to Thief 1 and Thief 2 in a Classic Prisoners' Dilemma Game
Payoffs are given as utility where U = 10-years in Jail

According to,which statement is true?
A) Thief 1 has a dominant strategy.
B) Thief 1 has a dominant strategy.
C) This game can be referred as Prisoners' Dilemma game.
D) All of the above
Utility Payoffs to Thief 1 and Thief 2 in a Classic Prisoners' Dilemma Game
Payoffs are given as utility where U = 10-years in Jail

According to,which statement is true?
A) Thief 1 has a dominant strategy.
B) Thief 1 has a dominant strategy.
C) This game can be referred as Prisoners' Dilemma game.
D) All of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
In a two player non-cooperative game where neither player has a dominant strategy,
A) there is never a Nash equilibrium.
B) there can be multiple Nash equilibria.
C) there is only one Nash equilibrium.
D) the actual outcome is unpredictable.
A) there is never a Nash equilibrium.
B) there can be multiple Nash equilibria.
C) there is only one Nash equilibrium.
D) the actual outcome is unpredictable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
________ is/are any set of formal rules,informal norms and related enforcement mechanisms that constrain people's choices.
A) Institutions
B) Economics
C) The rule of law
D) Politics
A) Institutions
B) Economics
C) The rule of law
D) Politics

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Table 12.1
Utility Payoffs to Thief 1 and Thief 2 in a Classic Prisoners' Dilemma Game
Payoffs are given as utility where U = 10-years in Jail

According to,what is the Nash equilibrium of this game?
A) Both players remain silent
B) Both players confess
C) There is no equilibrium in this game
D) There isn't enough information to solve this game
Utility Payoffs to Thief 1 and Thief 2 in a Classic Prisoners' Dilemma Game
Payoffs are given as utility where U = 10-years in Jail

According to,what is the Nash equilibrium of this game?
A) Both players remain silent
B) Both players confess
C) There is no equilibrium in this game
D) There isn't enough information to solve this game

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Table 12.1
Utility Payoffs to Thief 1 and Thief 2 in a Classic Prisoners' Dilemma Game
Payoffs are given as utility where U = 10-years in Jail

According to,if Thief 1 and Thief 2 both confess to the crime,how many years in jail will each thief serve?
A) Thief 1 - 2 years; Thief 2 - 2 years
B) Thief 1 - 7 years; Thief 2 - 7 years
C) Thief 1 - 3 years; Thief 2 - 3 years
D) Thief 1 - 10 years; Thief 2 - 0 years
Utility Payoffs to Thief 1 and Thief 2 in a Classic Prisoners' Dilemma Game
Payoffs are given as utility where U = 10-years in Jail

According to,if Thief 1 and Thief 2 both confess to the crime,how many years in jail will each thief serve?
A) Thief 1 - 2 years; Thief 2 - 2 years
B) Thief 1 - 7 years; Thief 2 - 7 years
C) Thief 1 - 3 years; Thief 2 - 3 years
D) Thief 1 - 10 years; Thief 2 - 0 years

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
People's interactions with each other in market and non-market setting are governed by ________.
A) laws
B) economics
C) institutions
D) history
A) laws
B) economics
C) institutions
D) history

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The field of ________,in which researchers construct and test specific hypotheses regarding departures from neoclassical rationality.
A) behavioral economics
B) game theory
C) classical economics
D) neo-classical economics
A) behavioral economics
B) game theory
C) classical economics
D) neo-classical economics

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Why do community-level institutions in developing countries merit close study? Provide three reasons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Norms dictating that any community member earning unusually high income give transfers to members with lower incomes ________ individuals' incentives to invest and innovate,because individuals must bear ________ of innovation while expecting to enjoy ________ the returns.
A) reduce; a fraction of the cost; all of
B) increase; a fraction of the cost; only a fraction
C) reduce; the full cost; only a fraction of
D) increase; the full cost; all of
A) reduce; a fraction of the cost; all of
B) increase; a fraction of the cost; only a fraction
C) reduce; the full cost; only a fraction of
D) increase; the full cost; all of

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Table 12.2
Payoffs to Fisher 1 and Fisher 2 in a
Common Property Resource Prisoners' Dilemma
($ of profit)

Table 12.2 shows an example of:
A) the free rider problem
B) the public good problem
C) tragedy of the Commons
D) efficiency problem
Payoffs to Fisher 1 and Fisher 2 in a
Common Property Resource Prisoners' Dilemma
($ of profit)

Table 12.2 shows an example of:
A) the free rider problem
B) the public good problem
C) tragedy of the Commons
D) efficiency problem

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
What is the important lesson that the prisoners' dilemma game show us?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Table 12.3
Payoffs to Villager 1 and Villager 2 in a Road Maintenance Game
(R is the benefits of a maintained road and the project requires a total of L hours of labor,therefore R-L/2>0 is the net utility payoff)

According to table 12.3,what is the Nash equilibrium if this game is non-cooperative?
A) Villager 1 chooses shirking,Villager 2 chooses shirking.
B) Villager 1 chooses shirking,Villager 2 chooses participating.
C) Villager 1 chooses participating,Villager 2 chooses shirking.
D) Villager 1 chooses participating,Villager 2 chooses participating.
Payoffs to Villager 1 and Villager 2 in a Road Maintenance Game
(R is the benefits of a maintained road and the project requires a total of L hours of labor,therefore R-L/2>0 is the net utility payoff)

According to table 12.3,what is the Nash equilibrium if this game is non-cooperative?
A) Villager 1 chooses shirking,Villager 2 chooses shirking.
B) Villager 1 chooses shirking,Villager 2 chooses participating.
C) Villager 1 chooses participating,Villager 2 chooses shirking.
D) Villager 1 chooses participating,Villager 2 chooses participating.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Canal-based irrigation systems are
A) non-excludable and rival.
B) excludable and rival.
C) excludable and non-rival.
D) non-excludable and non-rival.
A) non-excludable and rival.
B) excludable and rival.
C) excludable and non-rival.
D) non-excludable and non-rival.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Table 12.3
Payoffs to Villager 1 and Villager 2 in a Road Maintenance Game
(R is the benefits of a maintained road and the project requires a total of L hours of labor,therefore R-L/2>0 is the net utility payoff)

According to table 12.3,if it is an assurance game,which of the following statement is true?
A) The Nash equilibrium outcome is Villager 1 chooses shirking,Villager 2 chooses shirking.
B) Villager 1 will choose to participate if she expected Villager 2 to participate and Villager 2 will choose to participate if she expected Villager 1 to participate.
C) When both villagers cooperate in maintaining the road by participating,they both are better off.
D) All of the above.
Payoffs to Villager 1 and Villager 2 in a Road Maintenance Game
(R is the benefits of a maintained road and the project requires a total of L hours of labor,therefore R-L/2>0 is the net utility payoff)

According to table 12.3,if it is an assurance game,which of the following statement is true?
A) The Nash equilibrium outcome is Villager 1 chooses shirking,Villager 2 chooses shirking.
B) Villager 1 will choose to participate if she expected Villager 2 to participate and Villager 2 will choose to participate if she expected Villager 1 to participate.
C) When both villagers cooperate in maintaining the road by participating,they both are better off.
D) All of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Consider an ultimatum bargaining game,in which two players are asked to divide a fixed sum of money.The first person is given the role of Proposer.She must make a proposal to a second player,called the Responder,regarding how to split the sum between them.If the Responder accepts,the players receive the agreed amounts,but if the Responder rejects the proposal,neither player gets anything.
What would the results look like if both players had strictly neoclassical preferences? When this experiment is conducted in practice to do people exhibit neoclassical preferences? Explain.
What would the results look like if both players had strictly neoclassical preferences? When this experiment is conducted in practice to do people exhibit neoclassical preferences? Explain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



