Deck 3: Economic Growth
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/32
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 3: Economic Growth
1
If a Brazilian works in U.S,the value of final goods and services he produced is counted in Brazil's ____ and U.S.'s ____.
A) GDP; GDP
B) GDP; GNP
C) GNP; GDP
D) GNP; GNP
A) GDP; GDP
B) GDP; GNP
C) GNP; GDP
D) GNP; GNP
C
2
Economic growth is defined as:
A) the rate of increase in an economy's nominal GDP.
B) the rate of increase in an economy's real GDP.
C) the rate of increase in an economy's average income.
D) the rate of increase in an economy's price level.
A) the rate of increase in an economy's nominal GDP.
B) the rate of increase in an economy's real GDP.
C) the rate of increase in an economy's average income.
D) the rate of increase in an economy's price level.
C
3
When the World Bank use the "Atlas" conversion factors in comparing GDP per capita across countries,the developing countries tend to look ____ relative to the developed countries than when the comparison employs PPP exchange rates.
A) poorer
B) richer
C) the same
D) these two methods cannot be compared
A) poorer
B) richer
C) the same
D) these two methods cannot be compared
A
4
Constant returns to scale refers to a situation that when capital and labor both double,
A) output more than doubles
B) output less than doubles
C) output just doubles
D) output does not change
A) output more than doubles
B) output less than doubles
C) output just doubles
D) output does not change

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Gross Domestic Product (GDP)is defined as the total value of ____ goods and services produced within a country's borders over a year.
A) intermediate
B) final
C) consumption
D) capital
A) intermediate
B) final
C) consumption
D) capital

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
If we graph the average product of labor as a function of the quantity of capital employed by a firm operating along its production function.When the capital per worker increases,the average product of labor curve is
A) upward sloping
B) shifts upwards
C) downward sloping
D) shifts downwards
A) upward sloping
B) shifts upwards
C) downward sloping
D) shifts downwards

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
For three years,Dreamland has been growing at a steady annually compounded rate of 10 percent,if Dreamland's GDP per capita starts with $20,000,what will be the GDP per capita after three years?
A) $20,000
B) $26,000
C) $26,620
D) $200,000
A) $20,000
B) $26,000
C) $26,620
D) $200,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Diminishing marginal product of labor refers to as the quantity of labor increases,
A) average product of labor reaches a maximum.
B) marginal product of labor decreases.
C) total product of labor reaches a maximum.
D) average product of labor decreases.
A) average product of labor reaches a maximum.
B) marginal product of labor decreases.
C) total product of labor reaches a maximum.
D) average product of labor decreases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Nominal GDP growth is calculated as the growth rate of the value of goods and services using ____ prices while real GDP growth is calculated as the growth rate of the value of goods and services using ____ prices.
A) current; real
B) current; constant
C) constant; current
D) constant; real
A) current; real
B) current; constant
C) constant; current
D) constant; real

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following best describes a production function?
A) The maximum profit generated from given levels of factors of production.
B) The maximum level of output generated from given levels of factors of production.
C) All levels of factors of production that could produce a given level of output.
D) All levels of output that can be generated from given levels of factors of production.
A) The maximum profit generated from given levels of factors of production.
B) The maximum level of output generated from given levels of factors of production.
C) All levels of factors of production that could produce a given level of output.
D) All levels of output that can be generated from given levels of factors of production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A loaf of bread purchased by your professor would be described as
A) an intermediate good.
B) a final good.
C) a financial good.
D) a used good.
A) an intermediate good.
B) a final good.
C) a financial good.
D) a used good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The per capita value of income earned by everyone in an economy is equal to the per capita value of ____.
A) government expenditure
B) expenditure of all businesses in the economy
C) goods produced in the economy
D) goods and services produced in the economy
A) government expenditure
B) expenditure of all businesses in the economy
C) goods produced in the economy
D) goods and services produced in the economy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The following graph shows: No Systematic Tendency for Poorer Countries to "Catch Up"
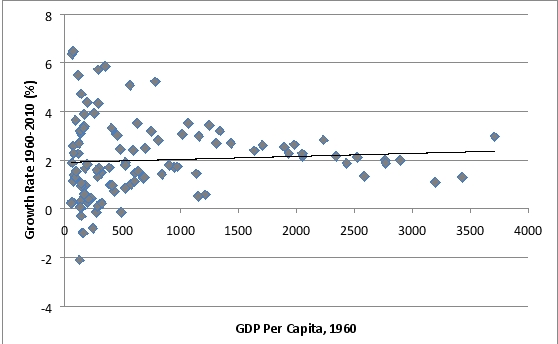 Source: Heston,et al.(2012).
Source: Heston,et al.(2012).
A) lower income countries consistently grew faster than higher income countries.
B) the average income of lower income countries eventually will catch up with developed country levels.
C) no tendency that lower income countries are growing faster than higher income countries.
D) the growth rates of many lower income countries are similar
 Source: Heston,et al.(2012).
Source: Heston,et al.(2012).A) lower income countries consistently grew faster than higher income countries.
B) the average income of lower income countries eventually will catch up with developed country levels.
C) no tendency that lower income countries are growing faster than higher income countries.
D) the growth rates of many lower income countries are similar

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The marginal product of labor ( )is the increase in total output associated with a
A) one unit increase in the quantity of labor,while holding the quantity of capital and technology constant.
B) one unit increase in the quantity of labor,while also increasing the quantity of capital by one unit and technology constant.
C) one unit increase in the quantity of labor,while also increasing the quantity of capital and technology by the same proportion.
D) one dollar increase in the price of labor,while holding the price of capital constant.
A) one unit increase in the quantity of labor,while holding the quantity of capital and technology constant.
B) one unit increase in the quantity of labor,while also increasing the quantity of capital by one unit and technology constant.
C) one unit increase in the quantity of labor,while also increasing the quantity of capital and technology by the same proportion.
D) one dollar increase in the price of labor,while holding the price of capital constant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The value added of a production activity is:
A) the profit this production activity generates.
B) the value of the final goods produced minus the value of intermediate goods used in this activity.
C) the value of intermediate goods used in this activity.
D) the value of the final goods produced minus the costs of this production.
A) the profit this production activity generates.
B) the value of the final goods produced minus the value of intermediate goods used in this activity.
C) the value of intermediate goods used in this activity.
D) the value of the final goods produced minus the costs of this production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
If one country is growing at a growth rate of 2 percent per year,how many years would you expect for it to double income per capita?
A) 36 years
B) 72 years
C) 14 years
D) 100 years
A) 36 years
B) 72 years
C) 14 years
D) 100 years

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The average product of labor ( )is the equal to
A) total quantity of labor employed divided by the total output.
B) total amount of output produced divided by price of the output.
C) the increase in total output.
D) total amount of output produced divided by the quantity of labor employed.
A) total quantity of labor employed divided by the total output.
B) total amount of output produced divided by price of the output.
C) the increase in total output.
D) total amount of output produced divided by the quantity of labor employed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
If Nike,an American corporation,produces shoes in China.This would:
A) count as part of U.S. GDP since it is a American corporation.
B) count for both U.S. GDP and Chinese GDP.
C) count for U.S. GDP but not for Chinese GDP.
D) count for Chinese GDP but not for U.S. GDP.
A) count as part of U.S. GDP since it is a American corporation.
B) count for both U.S. GDP and Chinese GDP.
C) count for U.S. GDP but not for Chinese GDP.
D) count for Chinese GDP but not for U.S. GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Increasing returns to scale refers to a situation that when capital and labor both double,
A) output more than doubles
B) output less than doubles
C) output just doubles
D) output does not change
A) output more than doubles
B) output less than doubles
C) output just doubles
D) output does not change

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Economic growth takes place when total income grows ______ the population.
A) faster than
B) slower than
C) at the same speed as
D) independently of
A) faster than
B) slower than
C) at the same speed as
D) independently of

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Decreasing returns to scale refers to a situation that when capital and labor both double,
A) output more than doubles
B) output less than doubles
C) output just doubles
D) output does not change
A) output more than doubles
B) output less than doubles
C) output just doubles
D) output does not change

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
________ provides a method to examine the differences in GDP per capita across countries at the same time.
A) Growth accounting
B) Development accounting
C) Total factor productivity
D) Growth theory
A) Growth accounting
B) Development accounting
C) Total factor productivity
D) Growth theory

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
________ provides a method to examine the differences determinants in GDP per capita growth over time within individual countries.
A) Growth accounting
B) Development accounting
C) Total factor productivity
D) Growth theory
A) Growth accounting
B) Development accounting
C) Total factor productivity
D) Growth theory

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
An economy is growing at 5%,suppose physical capital per worker grows at 4%,human capital per worker grows at 3% and assume that physical capital share of output is 0.3,how much does total factor productivity grow?
A) 0.7 percentage points
B) 1 percentage points
C) 1.2 percentage points
D) 1.7 percentage points
A) 0.7 percentage points
B) 1 percentage points
C) 1.2 percentage points
D) 1.7 percentage points

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Provide a list of proximate sources of economic growth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The purpose of growth accounting exercises is to identify
A) how fast the capital per worker grows.
B) how much of GDP per capita growth can be attributed to factor accumulation versus TFP growth.
C) how fast technology improves
D) how fast GDP per capita grows
A) how fast the capital per worker grows.
B) how much of GDP per capita growth can be attributed to factor accumulation versus TFP growth.
C) how fast technology improves
D) how fast GDP per capita grows

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
An economy is growing at 5%,suppose physical capital per worker grows at 4%,human capital per worker grows at 3% and assume that physical capital share of output is 0.3,how much growth does it contribute to the growth in physical capital per worker?
A) 0.7 percentage points
B) 1 percentage points
C) 1.2 percentage points
D) 1.7 percentage points
A) 0.7 percentage points
B) 1 percentage points
C) 1.2 percentage points
D) 1.7 percentage points

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
If we graph the average product of labor as a function of the quantity of capital employed by a firm operating along its production function,when the technology improves while holding both labor and capital constant,the average product of labor curve is
A) upward sloping
B) shifts upwards
C) downward sloping
D) shifts downwards
A) upward sloping
B) shifts upwards
C) downward sloping
D) shifts downwards

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which of the following may increase labor productivity for a firm?
A) increasing capital per worker
B) improving technology
C) increasing its technical efficiency
D) all of the above
A) increasing capital per worker
B) improving technology
C) increasing its technical efficiency
D) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following does not contribute in the growth in total factor productivity?
A) increasing capital per worker
B) technology improvement
C) reductions in unemployment
D) reductions in rent-seeking and other wasteful activities
A) increasing capital per worker
B) technology improvement
C) reductions in unemployment
D) reductions in rent-seeking and other wasteful activities

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Why is understanding growth in aggregate labor productivity important for understanding economic growth?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Does success in economic growth guarantee success in development?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



