Deck 10: Labor Markets and Income Distribution
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/180
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 10: Labor Markets and Income Distribution
1
Assume consumer demand for CD-ROMs increases.The result is a(n):
A) increase in derived demand for workers in the CD-ROM industry.
B) increase in the marginal revenue product of firms in the CD-ROM industry.
C) rightward shift in the market demand for labor curve in the CD-ROM industry.
D) all of the above.
E) none of the above.
A) increase in derived demand for workers in the CD-ROM industry.
B) increase in the marginal revenue product of firms in the CD-ROM industry.
C) rightward shift in the market demand for labor curve in the CD-ROM industry.
D) all of the above.
E) none of the above.
D
2
For a perfectly competitive firm,marginal revenue product is equal to:
A) price minus marginal cost.
B) price times marginal revenue.
C) price times marginal product.
D) none of the above.
A) price minus marginal cost.
B) price times marginal revenue.
C) price times marginal product.
D) none of the above.
C
3
Exhibit 10-1 Labor and output data

In Exhibit 10-1,if product price is fixed at $8,the MRP of the 2nd worker is equal to:
A) $25.
B) $125.
C) $200.
D) $175.
E) $45.

In Exhibit 10-1,if product price is fixed at $8,the MRP of the 2nd worker is equal to:
A) $25.
B) $125.
C) $200.
D) $175.
E) $45.
C
4
Exhibit 10-1 Labor and output data

In Exhibit 10-1,if product price is fixed at $5,the MRP of the 4th worker is equal to:
A) $35.
B) $125.
C) $25.
D) $175.
E) $100.

In Exhibit 10-1,if product price is fixed at $5,the MRP of the 4th worker is equal to:
A) $35.
B) $125.
C) $25.
D) $175.
E) $100.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Troll Corporation sells dolls for $10.00 each in a market that is perfectly competitive.Increasing the number of workers from 100 to 101 would cause output to rise from 500 to 550 dolls per day.The marginal revenue product for the 101st worker is:
A) $10.00.
B) $500.
C) $5,000.
D) $1,010.
A) $10.00.
B) $500.
C) $5,000.
D) $1,010.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A firm's demand curve for labor coincides with the:
A) marginal cost curve.
B) average cost curve.
C) marginal revenue curve.
D) marginal revenue product curve.
A) marginal cost curve.
B) average cost curve.
C) marginal revenue curve.
D) marginal revenue product curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Exhibit 10-1 Labor and output data

In Exhibit 10-1,if product price is fixed at $5,the MRP of the third worker is equal to:
A) $35.
B) $125.
C) $25.
D) $175.
E) $100.

In Exhibit 10-1,if product price is fixed at $5,the MRP of the third worker is equal to:
A) $35.
B) $125.
C) $25.
D) $175.
E) $100.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Tucker Corporation sells its products for $5.00.Tucker's industrial engineers have informed management that hiring one additional worker will increase output by five units per hour.Tucker should hire the additional worker only if the wage rate is:
A) $5.00 or less per hour.
B) $1.00 or more per hour.
C) $25.00 or less per hour.
D) none of the above.
A) $5.00 or less per hour.
B) $1.00 or more per hour.
C) $25.00 or less per hour.
D) none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The increase in a firm's total revenues resulting from hiring an additional unit of labor is known as the marginal:
A) product.
B) revenue product.
C) cost.
D) none of the above.
A) product.
B) revenue product.
C) cost.
D) none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
An apple orchard currently hires 10 workers.The owner estimates that hiring an additional worker would increase apple yields by 20 bushels per day.The price of apples is $15 per bushel.The owner should hire the extra worker if the wage rate is no greater than:
A) $50 per day.
B) $150 per day.
C) $200 per day.
D) $300 per day.
A) $50 per day.
B) $150 per day.
C) $200 per day.
D) $300 per day.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following best describes marginal revenue product (MRP)?
A) MRP is the level of total revenue generated by total employment of labor and capital.
B) MRP is the change in total revenue caused by a one-unit increase in output.
C) MRP is the change in total revenue caused by a one-unit increase in a variable input such as labor.
D) MRP is total revenue divided by the total quantity of a variable input used.
A) MRP is the level of total revenue generated by total employment of labor and capital.
B) MRP is the change in total revenue caused by a one-unit increase in output.
C) MRP is the change in total revenue caused by a one-unit increase in a variable input such as labor.
D) MRP is total revenue divided by the total quantity of a variable input used.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
For a competitive firm,workers' marginal revenue product equals the marginal product of labor times the:
A) wage rate.
B) price of the firm's product.
C) interest rate.
D) firm's total revenue.
A) wage rate.
B) price of the firm's product.
C) interest rate.
D) firm's total revenue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Exhibit 10-1 Labor and output data

In Exhibit 10-1,the marginal product of the 4th unit of labor is equal to:
A) 80.
B) 45.
C) 35.
D) 100.
E) 20.

In Exhibit 10-1,the marginal product of the 4th unit of labor is equal to:
A) 80.
B) 45.
C) 35.
D) 100.
E) 20.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Exhibit 10-1 Labor and output data

In Exhibit 10-1,the marginal product of the 3rd unit of labor is equal to:
A) 80.
B) 45.
C) 35.
D) 100.
E) 25.

In Exhibit 10-1,the marginal product of the 3rd unit of labor is equal to:
A) 80.
B) 45.
C) 35.
D) 100.
E) 25.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A competitive car wash currently hires 4 workers,who together can wash 80 cars per day.The market price of car washes is $5 per wash,and the price of workers is $60 per day.The car wash should hire a fifth worker if it would increase total production to at least:
A) 92 cars per day.
B) 100 cars per day.
C) 104 cars per day.
D) 110 cars per day.
A) 92 cars per day.
B) 100 cars per day.
C) 104 cars per day.
D) 110 cars per day.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Assume Ajax Company employs 100 workers and total revenue is $400 thousand.When Ajax Company employs 101 workers,total revenue is $405 thousand.The marginal revenue product of the 101st workers is:
A) $40 thousand.
B) $5 thousand.
C) $405 thousand.
D) none of the above.
A) $40 thousand.
B) $5 thousand.
C) $405 thousand.
D) none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
When a firm hires an additional unit of labor,the increase in a firm's total revenues is known as the marginal:
A) cost.
B) product.
C) utility product.
D) revenue product.
A) cost.
B) product.
C) utility product.
D) revenue product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following best explains the decline in marginal revenue product (MRP)?
A) As more and more of a variable factor (ex: Labor) is added to a fixed factor (ex: capital), total product become smaller and smaller.
B) As more and more of a variable factor (ex: labor) is added to a fixed factor (ex: capital), marginal product become smaller and smaller as defined by the law of diminishing returns.
C) As more and more of a variable factor (ex: labor) is added to a fixed factor (ex: capital), marginal utility becomes smaller and smaller.
D) As more and more of a variable factor (ex: labor) is added to a fixed factor (ex: capital), marginal revenue product (MRP) become larger and larger.
A) As more and more of a variable factor (ex: Labor) is added to a fixed factor (ex: capital), total product become smaller and smaller.
B) As more and more of a variable factor (ex: labor) is added to a fixed factor (ex: capital), marginal product become smaller and smaller as defined by the law of diminishing returns.
C) As more and more of a variable factor (ex: labor) is added to a fixed factor (ex: capital), marginal utility becomes smaller and smaller.
D) As more and more of a variable factor (ex: labor) is added to a fixed factor (ex: capital), marginal revenue product (MRP) become larger and larger.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Alan Jones owns a company that sells life insurance.When he employs 10 salespersons his firm sells $200,000 worth of contracts per week,and when he employs 11 salespersons,total revenue is $210,000.The marginal revenue product of the 11th salesperson is:
A) $410,000.
B) $10,000.
C) $20,000.
D) $210,000.
A) $410,000.
B) $10,000.
C) $20,000.
D) $210,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Exhibit 10-1 Labor and output data

In Exhibit 10-1,if product price is fixed at $8,the MRP of the 5th worker is equal to:
A) $50.
B) $80.
C) $10.
D) $100
E) $160.

In Exhibit 10-1,if product price is fixed at $8,the MRP of the 5th worker is equal to:
A) $50.
B) $80.
C) $10.
D) $100
E) $160.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
If the wage rate is fixed at a certain level,the:
A) labor supply curve is horizontal.
B) labor supply is a straight upward sloping line.
C) MP must be constant.
D) labor supply will increase at an increasing rate.
E) labor supply will increase at a decreasing rate.
A) labor supply curve is horizontal.
B) labor supply is a straight upward sloping line.
C) MP must be constant.
D) labor supply will increase at an increasing rate.
E) labor supply will increase at a decreasing rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The demand for labor is:
A) derived demand.
B) featherbedding demand.
C) marginal utility demand.
D) all of the above.
A) derived demand.
B) featherbedding demand.
C) marginal utility demand.
D) all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Other things equal,assume consumer demand for children's toys increases.The result is a(n):
A) rightward shift in the market demand for labor curve in the toy industry.
B) increase in the marginal revenue product of firms in the toy industry.
C) increase in derived demand for workers in the toy industry.
D) all of the above.
A) rightward shift in the market demand for labor curve in the toy industry.
B) increase in the marginal revenue product of firms in the toy industry.
C) increase in derived demand for workers in the toy industry.
D) all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Marginal revenue product is measured by:
A) MR x price.
B) MR x MC.
C) TR/MP.
D) MP x price.
E) TC/MP.
A) MR x price.
B) MR x MC.
C) TR/MP.
D) MP x price.
E) TC/MP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
If a union is able to successfully lobby Congress to limit imports of rival products,and thus to raise the demand (and thus price)for goods or services they make,then which of the following best describes the outcome?
A) The supply of labor will increase.
B) The demand for labor will increase.
C) The supply of labor will decrease.
D) The demand for labor will decrease.
A) The supply of labor will increase.
B) The demand for labor will increase.
C) The supply of labor will decrease.
D) The demand for labor will decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The marginal revenue product of labor is:
A) how much labor can be purchased with the revenue from the sale of one more unit of the good.
B) how much does the marginal revenue change when you add more labor.
C) the same as the marginal revenue product of capital in equilibrium.
D) determined by the wage rate.
E) the contribution to total revenue made by the marginal laborer.
A) how much labor can be purchased with the revenue from the sale of one more unit of the good.
B) how much does the marginal revenue change when you add more labor.
C) the same as the marginal revenue product of capital in equilibrium.
D) determined by the wage rate.
E) the contribution to total revenue made by the marginal laborer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Marginal revenue product is defined as the extra:
A) output a firm would receive after hiring one more unit of resource.
B) cost of hiring one more unit of resource
C) revenue earned by selling one more unit of product.
D) revenue earned by hiring one more unit of resource
E) output received by spending one more dollar on resources
A) output a firm would receive after hiring one more unit of resource.
B) cost of hiring one more unit of resource
C) revenue earned by selling one more unit of product.
D) revenue earned by hiring one more unit of resource
E) output received by spending one more dollar on resources

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
A union may attempt to obtain stricter certification requirements or longer apprenticeships.These changes would raise workers' wages because they:
A) create unnecessary unemployment.
B) shift in labor supply curve leftward.
C) decrease the marginal product of labor.
D) reduce management's use of featherbedding.
A) create unnecessary unemployment.
B) shift in labor supply curve leftward.
C) decrease the marginal product of labor.
D) reduce management's use of featherbedding.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
One reason the supply of carpenters is greater than the supply of physicians is because:
A) physicians do not belong to a union.
B) carpenters demand less income.
C) carpenters belong to unions.
D) none of the above.
A) physicians do not belong to a union.
B) carpenters demand less income.
C) carpenters belong to unions.
D) none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following statements concerning the supply of labor is true?
A) The wage rate has no effect on the supply of labor.
B) The labor supply curve is downward sloping.
C) The supply of labor is determined by the prevailing wage rate.
D) The typical labor supply curve is upward sloping.
A) The wage rate has no effect on the supply of labor.
B) The labor supply curve is downward sloping.
C) The supply of labor is determined by the prevailing wage rate.
D) The typical labor supply curve is upward sloping.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The demand for labor curve is identical to the:
A) total wage cost curve.
B) marginal resource curve.
C) total revenue curve.
D) marginal revenue product curve.
E) marginal revenue curve.
A) total wage cost curve.
B) marginal resource curve.
C) total revenue curve.
D) marginal revenue product curve.
E) marginal revenue curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The marginal revenue product can be written as:
A) TR/P.
B) w/Q.
C) MP x P.
D) MRP x P
E) w x L.
A) TR/P.
B) w/Q.
C) MP x P.
D) MRP x P
E) w x L.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Since the demand for labor depends on the demand for the product labor produces,the demand for labor is called:
A) primary demand.
B) secondary demand.
C) dependent demand.
D) derived demand.
A) primary demand.
B) secondary demand.
C) dependent demand.
D) derived demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
A firm's demand for labor depends on,in part,the demand for the firm's product.To summarize this idea,economists say that the demand for labor is:
A) derived demand.
B) marginal demand.
C) secondary demand.
D) monopsonistic demand.
A) derived demand.
B) marginal demand.
C) secondary demand.
D) monopsonistic demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The firm's demand for labor curve is exactly the same as the:
A) wage rate.
B) price of the output.
C) MRP curve.
D) MP curve.
E) labor supply curve.
A) wage rate.
B) price of the output.
C) MRP curve.
D) MP curve.
E) labor supply curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The number of workers hired by a firm at a particular wage rate can be calculated if you know which of the following?
A)c and d.
B)Product supply curve.
C)Marginal product of labor.
D)Marginal factor cost.
E)Marginal revenue product of labor.
A)c and d.
B)Product supply curve.
C)Marginal product of labor.
D)Marginal factor cost.
E)Marginal revenue product of labor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
If unions develop increasingly difficult,expensive,and time-consuming requirements to qualify for membership,which of the following is most likely to occur?
A) Equilibrium market wages will tend to fall.
B) The supply of labor will increase.
C) The supply of labor will remain unchanged.
D) The supply of labor will decrease.
A) Equilibrium market wages will tend to fall.
B) The supply of labor will increase.
C) The supply of labor will remain unchanged.
D) The supply of labor will decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which of the following statements concerning the supply of labor is true?
A) The supply of labor is determined by the prevailing wage rate.
B) The labor supply curve is downward sloping.
C) The wage rate has no effect on the supply of labor.
D) None of the above.
A) The supply of labor is determined by the prevailing wage rate.
B) The labor supply curve is downward sloping.
C) The wage rate has no effect on the supply of labor.
D) None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The marginal revenue product curve is:
A) c and d are correct.
B) c and e are correct.
C) given by the marginal product curve multiplied by the price of the good.
D) the marginal contribution of an additional worker to firm's revenues.
E) the change in total cost that results from employing an additional worker.
A) c and d are correct.
B) c and e are correct.
C) given by the marginal product curve multiplied by the price of the good.
D) the marginal contribution of an additional worker to firm's revenues.
E) the change in total cost that results from employing an additional worker.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Dividing the change in total revenue by the change in labor gives:
A) marginal product of labor.
B) marginal revenue product of labor.
C) the price of the output.
D) demand for the output.
E) economic efficiency.
A) marginal product of labor.
B) marginal revenue product of labor.
C) the price of the output.
D) demand for the output.
E) economic efficiency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The marginal cost of labor for a perfectly competitive firm is given by:
A) the change in total revenue that results from employing an additional worker.
B) the market wage rate.
C) its marginal revenue product curve.
D) the demand curve for labor.
E) the marginal product of labor.
A) the change in total revenue that results from employing an additional worker.
B) the market wage rate.
C) its marginal revenue product curve.
D) the demand curve for labor.
E) the marginal product of labor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
If product price decreases,then:
A) MP will increase.
B) MFC will increase.
C) MRP will increase.
D) MP will decrease.
A) MP will increase.
B) MFC will increase.
C) MRP will increase.
D) MP will decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
If the wage rate is fixed at a certain level,the:
A) total wage cost curve is horizontal.
B) total wage cost curve is a straight upward sloping line.
C) MP must be constant.
D) total wage cost curve will increase at an increasing rate.
E) total wage cost curve will increase at a decreasing rate.
A) total wage cost curve is horizontal.
B) total wage cost curve is a straight upward sloping line.
C) MP must be constant.
D) total wage cost curve will increase at an increasing rate.
E) total wage cost curve will increase at a decreasing rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Exhibit 10-2 Labor supply curve
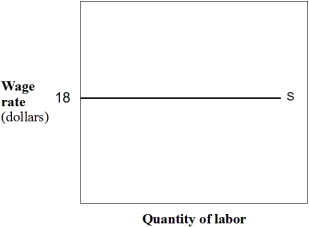
In Exhibit 10-2,the wage for the 6th employee is equal to:
A) $18.
B) $36.
C) $3.
D) $108.
E) unable to determine with this information.

In Exhibit 10-2,the wage for the 6th employee is equal to:
A) $18.
B) $36.
C) $3.
D) $108.
E) unable to determine with this information.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Suppose a change in technology increases the marginal product of labor.The result is a(n):
A) downward movement along the demand for labor curve.
B) rightward shift in the demand for labor curve.
C) leftward shift in the demand for labor curve.
D) upward movement along the demand for labor curve.
A) downward movement along the demand for labor curve.
B) rightward shift in the demand for labor curve.
C) leftward shift in the demand for labor curve.
D) upward movement along the demand for labor curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
If more and better technology is used for producing wheat in the United States than in a lesser-developed country,then the:
A) MRP of the U.S. workers will be higher than the MRP of the workers in the lesser-developed country.
B) MRP of the U.S. workers will be lower than the MRP of the workers in the lesser-developed country.
C) demand for the U.S. workers will be lower than the demand for the workers in the lesser developed country.
D) price of wheat will be higher in the United States than in the lesser-developed country.
E) wages of the U.S. workers will be lower than the wages of the workers in the lesser-developed country.
A) MRP of the U.S. workers will be higher than the MRP of the workers in the lesser-developed country.
B) MRP of the U.S. workers will be lower than the MRP of the workers in the lesser-developed country.
C) demand for the U.S. workers will be lower than the demand for the workers in the lesser developed country.
D) price of wheat will be higher in the United States than in the lesser-developed country.
E) wages of the U.S. workers will be lower than the wages of the workers in the lesser-developed country.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Exhibit 10-2 Labor supply curve

In Exhibit 10-2,the total wage cost of hiring 6 employees is:
A) $18 per hour.
B) $36 per hour.
C) $3 per hour.
D) $108 per hour.
E) $648 per hour.

In Exhibit 10-2,the total wage cost of hiring 6 employees is:
A) $18 per hour.
B) $36 per hour.
C) $3 per hour.
D) $108 per hour.
E) $648 per hour.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Which of the following determines equilibrium wages in perfectly competitive labor markets?
A) The government.
B) Monopoly employers.
C) Where the supply and demand of labor are equal.
D) The requirements of a living wage.
A) The government.
B) Monopoly employers.
C) Where the supply and demand of labor are equal.
D) The requirements of a living wage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
An increase in the demand for a product will shift the demand for labor used to produce the product:
A) downward.
B) leftward.
C) rightward.
D) none of the above, the curve will not shift.
A) downward.
B) leftward.
C) rightward.
D) none of the above, the curve will not shift.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Exhibit 10-3 Supply and demand curves for food servers
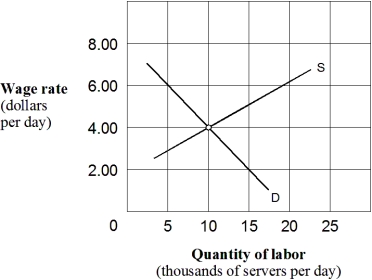
In Exhibit 10-3,the equilibrium wage and the number of food servers employed per day,respectively,are:
A) $2.00 and 5 thousand.
B) $4.00 and 10 thousand.
C) $6.00 and 15 thousand
D) $8.00 and 20 thousand.

In Exhibit 10-3,the equilibrium wage and the number of food servers employed per day,respectively,are:
A) $2.00 and 5 thousand.
B) $4.00 and 10 thousand.
C) $6.00 and 15 thousand
D) $8.00 and 20 thousand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
A decrease in the marginal product of labor would be represented by:
A) increase in labor demand.
B) decrease in labor demand.
C) increase in the quantity demanded of labor.
D) decrease in the quantity demanded of labor.
E) an increase in wages.
A) increase in labor demand.
B) decrease in labor demand.
C) increase in the quantity demanded of labor.
D) decrease in the quantity demanded of labor.
E) an increase in wages.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
One reason the supply of carpenters is greater than the supply of physicians is because:
A) carpenters demand less income.
B) physicians do not belong to a union.
C) of differences in human capital.
D) carpenters belong to unions.
A) carpenters demand less income.
B) physicians do not belong to a union.
C) of differences in human capital.
D) carpenters belong to unions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
An increase in demand for French fries will cause equilibrium wage rates:
A) and quantities of potato workers hired to rise.
B) and quantities of potato workers hired to fall
C) to rise and quantities of potato workers hired to fall.
D) to fall and quantities of potato workers hired to rise
E) and quantities of potato workers hired to stay the same
A) and quantities of potato workers hired to rise.
B) and quantities of potato workers hired to fall
C) to rise and quantities of potato workers hired to fall.
D) to fall and quantities of potato workers hired to rise
E) and quantities of potato workers hired to stay the same

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The labor supply curve facing an individual employer in a perfectly competitive labor market is:
A) upward sloping.
B) downward sloping.
C) horizontal.
D) greater than MFC.
E) the MRP curve.
A) upward sloping.
B) downward sloping.
C) horizontal.
D) greater than MFC.
E) the MRP curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
An individual firm in a competitive labor market faces a(n):
A) horizontal labor supply curve.
B) backward-bending labor supply curve.
C) downward-sloping labor supply curve.
D) upward-sloping labor supply curve.
E) vertical labor supply curve.
A) horizontal labor supply curve.
B) backward-bending labor supply curve.
C) downward-sloping labor supply curve.
D) upward-sloping labor supply curve.
E) vertical labor supply curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Featherbedding allows unions to increase wages by:
A) limiting the supply of labor.
B) increasing firms' demand for labor.
C) forcing firms to accept higher-than-equilibrium wages.
D) reducing labor share of payroll taxes.
A) limiting the supply of labor.
B) increasing firms' demand for labor.
C) forcing firms to accept higher-than-equilibrium wages.
D) reducing labor share of payroll taxes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Which of the following would be a human capital investment?
A) On-the-job training programs.
B) Health care programs.
C) Formal education.
D) All of the above.
A) On-the-job training programs.
B) Health care programs.
C) Formal education.
D) All of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which of the following statements is true?
A) Derived demand for labor depends on the demand for the product labor produces.
B) Unions can either increase demand or decrease the supply of labor.
C) Investment in human capital is expected to increase the demand for those workers.
D) All of the above.
A) Derived demand for labor depends on the demand for the product labor produces.
B) Unions can either increase demand or decrease the supply of labor.
C) Investment in human capital is expected to increase the demand for those workers.
D) All of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
If product price increases,then:
A) MP will increase.
B) MFC will increase.
C) MRP will increase.
D) MP will decrease.
A) MP will increase.
B) MFC will increase.
C) MRP will increase.
D) MP will decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
A worker's accumulated investment in education,training,experience,and health is called:
A) derived labor demand.
B) collective entrepreneurship.
C) seniority.
D) human capital.
A) derived labor demand.
B) collective entrepreneurship.
C) seniority.
D) human capital.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Exhibit 10-3 Supply and demand curves for food servers

In Exhibit 10-3,assume that both input and output markets are perfectly competitive.If one additional server increases the number of meals sold by four per day and each meal sells for $10,each additional food servers will be paid:
A) $16 per day.
B) $32 per day.
C) $36 per day.
D) $40 per day.
E) none of the above.

In Exhibit 10-3,assume that both input and output markets are perfectly competitive.If one additional server increases the number of meals sold by four per day and each meal sells for $10,each additional food servers will be paid:
A) $16 per day.
B) $32 per day.
C) $36 per day.
D) $40 per day.
E) none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Exhibit 10-5 A perfectly competitive labor market

In Exhibit 10-5,when the marginal revenue product is $20.00,the firms should ____ workers.
A) continue hiring
B) stop hiring
C) start firing
D) pay a wage above $15.00 to its workers

In Exhibit 10-5,when the marginal revenue product is $20.00,the firms should ____ workers.
A) continue hiring
B) stop hiring
C) start firing
D) pay a wage above $15.00 to its workers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Exhibit 10-3 Supply and demand curves for food servers

If the equilibrium wage rate in Exhibit 10-3 increased,the cause could be that:
A) the supply of labor increased.
B) the demand for labor decreased.
C) either the demand for labor increased or the supply of labor decreased.
D) none of the above.

If the equilibrium wage rate in Exhibit 10-3 increased,the cause could be that:
A) the supply of labor increased.
B) the demand for labor decreased.
C) either the demand for labor increased or the supply of labor decreased.
D) none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
An advance in technology which increases labor productivity will shift the:
A) labor demand curve to the left.
B) MFC curve to the left.
C) MP curve downward.
D) labor demand curve to the right.
E) product demand to the right.
A) labor demand curve to the left.
B) MFC curve to the left.
C) MP curve downward.
D) labor demand curve to the right.
E) product demand to the right.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Exhibit 10-5 A perfectly competitive labor market

In Exhibit 10-5,at what wage rate will the firms hire these workers?
A) $25.00
B) $20.00
C) $15.00
D) $10.00
E) $0

In Exhibit 10-5,at what wage rate will the firms hire these workers?
A) $25.00
B) $20.00
C) $15.00
D) $10.00
E) $0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
In a competitive labor market,the change in total labor costs divided by the change in labor is always equal to:
A) one.
B) the wage rate.
C) the number of firms in the market.
D) the change in total revenue.
E) the competitive market price of the output.
A) one.
B) the wage rate.
C) the number of firms in the market.
D) the change in total revenue.
E) the competitive market price of the output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Exhibit 10-4 Sally's labor supply data
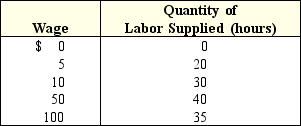
In Exhibit 10-4,if Sally can produce 2 units of output for every hour that she works,then:
A) she will earn a wage of $50.
B) she is not productive enough to be hired at all.
C) her MRP is less than her wage.
D) she will work 30 hours.
E) her wage cannot be determined.

In Exhibit 10-4,if Sally can produce 2 units of output for every hour that she works,then:
A) she will earn a wage of $50.
B) she is not productive enough to be hired at all.
C) her MRP is less than her wage.
D) she will work 30 hours.
E) her wage cannot be determined.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The optimal hiring rule is to employ labor up to the point where:
A) wage = MFC.
B) wage = MP.
C) wage = MR
D) wage = MRP
E) wage = TWC.
A) wage = MFC.
B) wage = MP.
C) wage = MR
D) wage = MRP
E) wage = TWC.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
If the market price of bicycle frames is $500,and frame welders earn a wage of $50,how many welders will be hired?
A) 10.
B) More than 10.
C) Fewer than 10.
D) Hiring will stop when the MP is 10.
E) Hiring will stop when the MP is 0.1.
A) 10.
B) More than 10.
C) Fewer than 10.
D) Hiring will stop when the MP is 10.
E) Hiring will stop when the MP is 0.1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
If the demand for the finished product increases,the:
A) demand for the resources will increase.
B) demand for the resources will decrease.
C) marginal factor cost will increase.
D) marginal factor cost will decrease.
E) MP will increase.
A) demand for the resources will increase.
B) demand for the resources will decrease.
C) marginal factor cost will increase.
D) marginal factor cost will decrease.
E) MP will increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Exhibit 10-4 Sally's labor supply data

In Exhibit 10-4,if the wage rate is $10,how many hours will Sally work?
A) 20.
B) 30.
C) 35.
D) 40.
E) 50.

In Exhibit 10-4,if the wage rate is $10,how many hours will Sally work?
A) 20.
B) 30.
C) 35.
D) 40.
E) 50.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Exhibit 10-5 A perfectly competitive labor market

In Exhibit 10-5,how many thousands of workers are firms willing to hire?
A) 20.
B) 10.
C) 15.
D) All 30 workers.

In Exhibit 10-5,how many thousands of workers are firms willing to hire?
A) 20.
B) 10.
C) 15.
D) All 30 workers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Which of the following can shift the labor demand curve to the right?
A) Decrease in product price.
B) Increase in wages.
C) Decrease in wages.
D) Decrease in the MP.
E) Increase in productivity.
A) Decrease in product price.
B) Increase in wages.
C) Decrease in wages.
D) Decrease in the MP.
E) Increase in productivity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The optimal number of workers to be hired by a firm operating in a competitive labor market is where:
A) P = MRP.
B) MP = MRP.
C) MRP = w.
D) P = w.
E) TWC = w.
A) P = MRP.
B) MP = MRP.
C) MRP = w.
D) P = w.
E) TWC = w.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
A technological advance that increases the productivity of teachers can be expected to have what effects on the equilibrium labor market for teachers?
A) Wages will rise, and quantity of labor will fall.
B) Wages will rise, and quantity of labor will rise.
C) Wages will fall, and quantity of labor will fall.
D) Wages will fall, and quantity of labor will rise.
E) Wages and quantity of labor will remain the same.
A) Wages will rise, and quantity of labor will fall.
B) Wages will rise, and quantity of labor will rise.
C) Wages will fall, and quantity of labor will fall.
D) Wages will fall, and quantity of labor will rise.
E) Wages and quantity of labor will remain the same.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
If the marginal product of labor is always positive,the total revenue will grow with each additional worker.Firms do not continuously hire new workers because:
A) there isn't enough room in the factory.
B) there isn't an infinite number of workers.
C) wages would have to increase.
D) they stop when MRP = wage
E) marginal revenue product will become negative.
A) there isn't enough room in the factory.
B) there isn't an infinite number of workers.
C) wages would have to increase.
D) they stop when MRP = wage
E) marginal revenue product will become negative.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Exhibit 10-3 Supply and demand curves for food servers

In Exhibit 10-3,suppose that in the interest of boosting incomes of the working poor,Congress imposes a minimum wage of $6.00 per hour.This minimum wage rate creates a(n):
A) new labor market equilibrium.
B) excess demand for labor of 10 thousand food servers.
C) excess supply of labor of food servers.
D) situation of full employment for food servers.

In Exhibit 10-3,suppose that in the interest of boosting incomes of the working poor,Congress imposes a minimum wage of $6.00 per hour.This minimum wage rate creates a(n):
A) new labor market equilibrium.
B) excess demand for labor of 10 thousand food servers.
C) excess supply of labor of food servers.
D) situation of full employment for food servers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Exhibit 10-6 Demand for labor curves
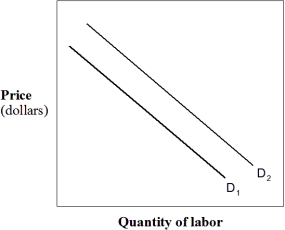
In Exhibit 10-6,which of the following could have caused the shift in labor demand from D₁ to D₂?
A) Increase in wages.
B) Decrease in wages.
C) Decrease in price of product.
D) Decrease in demand for the product.
E) Increase in the demand for the product.

In Exhibit 10-6,which of the following could have caused the shift in labor demand from D₁ to D₂?
A) Increase in wages.
B) Decrease in wages.
C) Decrease in price of product.
D) Decrease in demand for the product.
E) Increase in the demand for the product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Which of the following determines equilibrium wages in perfectly competitive labor markets?
A) The government.
B) Monopoly employers.
C) Where the supply and demand of labor are equal.
D) The requirements of a living wage.
A) The government.
B) Monopoly employers.
C) Where the supply and demand of labor are equal.
D) The requirements of a living wage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Suppose there are 100 identical firms producing package delivery services.One of the firms finds that when it has to pay a wage rate of $7,it hires 20 delivery people.The firm charges an average price of $10 to deliver a package.From this information,we know that the package delivery industry is hiring a total of:
A) 100 workers.
B) 200 workers.
C) 700 workers.
D) 2,000 workers.
E) 10,000 workers.
A) 100 workers.
B) 200 workers.
C) 700 workers.
D) 2,000 workers.
E) 10,000 workers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



