Deck 18: Pulmonary Diagnostic Procedures
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/30
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 18: Pulmonary Diagnostic Procedures
1
A patient presents with absent lung sounds in the left lower lung fields,moderate shortness of breath,and dyspnea.The nurse suspects pneumothorax and notifies the practitioner.Orders for a STAT chest radiography and reading are obtained.Which finding best supports the nurse's suspicions?
A) Blackness in the left lower lung area
B) Whiteness in the left lower lung area
C) Blunted costophrenic angles
D) Elevated left hemidiaphragm
A) Blackness in the left lower lung area
B) Whiteness in the left lower lung area
C) Blunted costophrenic angles
D) Elevated left hemidiaphragm
Blackness in the left lower lung area
2
Determination of oxygenation status by oxygen saturation alone is inadequate.What other value must be known?
A) pH
B) PaCO₂
C)HCO₃¯
D) Hemoglobin (Hgb)
A) pH
B) PaCO₂
C)HCO₃¯
D) Hemoglobin (Hgb)
Hemoglobin (Hgb)
3
The patient's arterial blood gas (ABG)values on room air are PaO₂,40 mm Hg; pH,7.10; PaCO₂,44 mm Hg; andHCO₃¯,16 mEq/L.What is the interpretation of the patient's ABG?
A) Uncompensated respiratory acidosis
B) Uncompensated metabolic acidosis
C) Compensated metabolic acidosis
D) Compensated respiratory acidosis
A) Uncompensated respiratory acidosis
B) Uncompensated metabolic acidosis
C) Compensated metabolic acidosis
D) Compensated respiratory acidosis
Uncompensated metabolic acidosis
4
A patient's pulse oximeter alarm goes off.The monitor reads 82%.What is the first action the nurse should perform?
A) Prepare to intubate.
B) Assess the patient's condition.
C) Turn off the alarm and reapply the oximeter sensor.
D) Increase O₂ level to 4L/NC.
A) Prepare to intubate.
B) Assess the patient's condition.
C) Turn off the alarm and reapply the oximeter sensor.
D) Increase O₂ level to 4L/NC.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The patient's arterial blood gas (ABG)values on room air are PaO₂,70 mm Hg; pH,7.31; PaCO₂,52 mm Hg; and 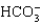 ,24 mEq/L.What is the interpretation of the patient's ABG?
,24 mEq/L.What is the interpretation of the patient's ABG?
A) Uncompensated metabolic alkalosis
B) Uncompensated respiratory acidosis
C) Compensated respiratory acidosis
D) Compensated respiratory alkalosis
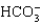 ,24 mEq/L.What is the interpretation of the patient's ABG?
,24 mEq/L.What is the interpretation of the patient's ABG?A) Uncompensated metabolic alkalosis
B) Uncompensated respiratory acidosis
C) Compensated respiratory acidosis
D) Compensated respiratory alkalosis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A patient has the following arterial blood gas (ABG)values: pH,7.20; PaO₂,106 mm Hg; pCO₂,35 mm Hg; andHCO₃¯,11 mEq/L.What symptom would be most consistent with the ABG values?
A) Diarrhea
B) Shortness of breath
C) Central cyanosis
D) Peripheral cyanosis
A) Diarrhea
B) Shortness of breath
C) Central cyanosis
D) Peripheral cyanosis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which arterial blood gas (ABG)values represent uncompensated metabolic acidosis?
A) pH, 7.29; PaCO₂, 57 mm Hg;HCO₃¯ , 22 mEq/L
B) pH, 7.36; PaCO₂, 33 mm Hg;HCO₃¯, 18 mEq/L
C) pH, 7.22; PaCO₂, 42 mm Hg;HCO₃¯, 18 mEq/L
D) pH, 7.52; PaCO₂, 38 mm Hg;HCO₃¯ , 29 mEq/L
A) pH, 7.29; PaCO₂, 57 mm Hg;HCO₃¯ , 22 mEq/L
B) pH, 7.36; PaCO₂, 33 mm Hg;HCO₃¯, 18 mEq/L
C) pH, 7.22; PaCO₂, 42 mm Hg;HCO₃¯, 18 mEq/L
D) pH, 7.52; PaCO₂, 38 mm Hg;HCO₃¯ , 29 mEq/L

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
A patient with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)requires intubation.After the practitioner intubates the patient,the nurse auscultates for breath sounds.Breath sounds are questionable in this patient.Which action would best assist in determining endotracheal tube placement in this patient?
A) Stat chest radiographic examination
B) End-tidal CO₂ monitor
C) Ventilation-perfusion (V/Q) scan
D) Pulmonary artery catheter insertion
A) Stat chest radiographic examination
B) End-tidal CO₂ monitor
C) Ventilation-perfusion (V/Q) scan
D) Pulmonary artery catheter insertion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
A patient presents moderately short of breath and dyspneic.A chest radiographic examination reveals a large right pleural effusion with significant atelectasis.The practitioner would be most likely to prescribe which procedure?
A) Thoracentesis
B) Bronchoscopy
C) Ventilation-perfusion (V/Q) scan
D) Repeat chest radiograph
A) Thoracentesis
B) Bronchoscopy
C) Ventilation-perfusion (V/Q) scan
D) Repeat chest radiograph

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
A bronchoscopy is indicated for a patient with what condition?
A) Pulmonary edema
B) Ineffective clearance of secretions
C) Upper gastrointestinal bleed
D) Instillation of surfactant
A) Pulmonary edema
B) Ineffective clearance of secretions
C) Upper gastrointestinal bleed
D) Instillation of surfactant

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
On admission,a patient presents with a respiratory rate of 28 breaths/min,heart rate of 108 beats/min in sinus tachycardia,and a blood pressure of 140/72 mm Hg.The patient's arterial blood gas (ABG)values on room air are PaO₂,60 mm Hg; pH,7.32; PaCO₂,45 mm Hg; andHCO₃¯ ,26 mEq/L.What action should the nurse anticipate for this patient?
A) Initiate oxygen therapy.
B) Prepare for emergency intubation.
C) Administer 1 ampule of sodium bicarbonate.
D) Initiate capnography.
A) Initiate oxygen therapy.
B) Prepare for emergency intubation.
C) Administer 1 ampule of sodium bicarbonate.
D) Initiate capnography.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
On admission,a patient presents with a respiratory rate of 24 breaths/min,pursed-lip breathing,heart rate of 96 beats/min in sinus tachycardia,and a blood pressure of 110/68 mm Hg.The patient's arterial blood gas (ABG)values on room air are PaO₂,70 mm Hg; pH,7.38; PaCO₂,52 mm Hg; andHCO₃¯ ,34 mEq/L.What diagnoses would be most consistent with the above arterial blood gas values?
A) Acute pulmonary embolism
B) Acute myocardial infarction
C) Congestive heart failure
D) Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
A) Acute pulmonary embolism
B) Acute myocardial infarction
C) Congestive heart failure
D) Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Ventilation-perfusion (V/Q)scans are ordered to evaluate the possibility of which of the following?
A) Pulmonary emboli
B) Acute myocardial infarction
C) Emphysema
D) Acute respiratory distress syndrome
A) Pulmonary emboli
B) Acute myocardial infarction
C) Emphysema
D) Acute respiratory distress syndrome

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
A 75-kg patient is on a ventilator and may be ready for extubation.A respiratory therapist assesses the patient's rapid shallow breathing index (RSBI).Which result best suggests that the patient is ready for a spontaneous breathing trial?
A) RSBI = 150
B) RSBI = 125
C) RSBI = 110
D) RSBI = 90
A) RSBI = 150
B) RSBI = 125
C) RSBI = 110
D) RSBI = 90

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which ABG values reflect compensation?
A) pH, 7.26; PaCO₂, 55 mm Hg;HCO₃¯ , 24 mEq/L
B) pH, 7.30; PaCO₂, 32 mm Hg;HCO₃¯ , 18 mEq/L
C) pH, 7.48; PaCO₂, 30 mm Hg;HCO₃¯ , 22 mEq/L
D) pH, 7.38; PaCO₂, 58 mm Hg;HCO₃¯ , 30 mEq/L
A) pH, 7.26; PaCO₂, 55 mm Hg;HCO₃¯ , 24 mEq/L
B) pH, 7.30; PaCO₂, 32 mm Hg;HCO₃¯ , 18 mEq/L
C) pH, 7.48; PaCO₂, 30 mm Hg;HCO₃¯ , 22 mEq/L
D) pH, 7.38; PaCO₂, 58 mm Hg;HCO₃¯ , 30 mEq/L

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
In a patient who is hemodynamically stable,which procedure can be used to estimate the PaCO₂ levels?
A) PaO₂/FiO₂ ratio
B) A-a gradient
C) Residual volume (RV)
D) End-tidal CO₂
A) PaO₂/FiO₂ ratio
B) A-a gradient
C) Residual volume (RV)
D) End-tidal CO₂

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which blood gas parameter is the acid-base component that reflects kidney function?
A) pH
B) PaO₂
C) PaCO₂
D) HCO₃¯
A) pH
B) PaO₂
C) PaCO₂
D) HCO₃¯

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A patient presents with the following arterial blood gas (ABG)values: pH,7.20; PaO₂,106 mm Hg; PaCO₂,35 mm Hg; andHCO₃¯ ,11 mEq/L.What is the interpretation of the patient's ABG?
A) Uncompensated respiratory acidosis
B) Uncompensated metabolic acidosis
C) Uncompensated metabolic alkalosis
D) Uncompensated respiratory alkalosis
A) Uncompensated respiratory acidosis
B) Uncompensated metabolic acidosis
C) Uncompensated metabolic alkalosis
D) Uncompensated respiratory alkalosis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
A patient is intubated,and sputum for culture and sensitivity is ordered.Which of the following is important for obtaining the best specimen?
A) After the specimen is in the container, dilute thick secretions with sterile water.
B) Apply suction when the catheter is advanced to obtain secretions from within the endotracheal tube.
C) Do not apply suction while the catheter is being withdrawn because this can contaminate the sample with sputum left in the endotracheal tube.
D) Do not clear the endotracheal tube of all local secretions before obtaining the specimen.
A) After the specimen is in the container, dilute thick secretions with sterile water.
B) Apply suction when the catheter is advanced to obtain secretions from within the endotracheal tube.
C) Do not apply suction while the catheter is being withdrawn because this can contaminate the sample with sputum left in the endotracheal tube.
D) Do not clear the endotracheal tube of all local secretions before obtaining the specimen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which patient would be considered hypoxemic?
A) A 70-year-old man with a PaO₂ of 72
B) A 50-year-old woman with a PaO₂ of 65
C) An 84-year-old man with a PaO₂ of 96
D) A 68-year-old woman with a PaO₂ of 80
A) A 70-year-old man with a PaO₂ of 72
B) A 50-year-old woman with a PaO₂ of 65
C) An 84-year-old man with a PaO₂ of 96
D) A 68-year-old woman with a PaO₂ of 80

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
What chest radiography finding is consistent with a left pneumothorax?
A) Flattening of the diaphragm
B) Shifting of the mediastinum to the right
C) Presence of a gastric air bubble
D) Increased radiolucency of the left lung field
A) Flattening of the diaphragm
B) Shifting of the mediastinum to the right
C) Presence of a gastric air bubble
D) Increased radiolucency of the left lung field

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
A patient is admitted with acute lung failure secondary to pneumonia.Arterial blood gas (ABG)values on the current ventilator settings are pH,7.37; PaCO₂,50 mm Hg; and HCO₃¯,27 mEq/L.What is the correct interpretation of the patient's ABG values?
A) Compensated respiratory acidosis
B) Compensated metabolic alkalosis
C) Uncompensated respiratory alkalosis
D) Uncompensated metabolic acidosis
A) Compensated respiratory acidosis
B) Compensated metabolic alkalosis
C) Uncompensated respiratory alkalosis
D) Uncompensated metabolic acidosis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
What medication may be included in the preprocedural medications for a diagnostic bronchoscopy?
A) Aspirin for anticoagulation
B) Vecuronium to inhibit breathing
C) Codeine to decrease the cough reflex
D) Cimetidine to decrease hydrochloric acid secretion
A) Aspirin for anticoagulation
B) Vecuronium to inhibit breathing
C) Codeine to decrease the cough reflex
D) Cimetidine to decrease hydrochloric acid secretion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
What does an intrapulmonary shunting value of 35% indicate?
A) Normal gas exchange of venous blood
B) An abnormal finding indicative of a shunt-producing disorder
C) A serious and potentially life-threatening condition
D) Metabolic alkalosis
A) Normal gas exchange of venous blood
B) An abnormal finding indicative of a shunt-producing disorder
C) A serious and potentially life-threatening condition
D) Metabolic alkalosis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
A patient is admitted with signs and symptoms of a pulmonary embolus (PE).What diagnostic test most conclusive to determine this diagnosis?
A) ABG
B) Bronchoscopy
C) Pulmonary function test
D) V/Q scan
A) ABG
B) Bronchoscopy
C) Pulmonary function test
D) V/Q scan

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Severe coughing and shortness of breath during a thoracentesis are indicative of what complication?
A) Re-expansion pulmonary edema
B) Pleural infection
C) Pneumothorax
D) Hemothorax
A) Re-expansion pulmonary edema
B) Pleural infection
C) Pneumothorax
D) Hemothorax

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
What risk factors need to be considered when preparing a patient for a thoracentesis?
A) Coagulation defects
B) Unstable hemodynamics
C) Pleural effusion
D) Uncooperative patient
E) Empyema
A) Coagulation defects
B) Unstable hemodynamics
C) Pleural effusion
D) Uncooperative patient
E) Empyema

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Nursing management of a patient undergoing a diagnostic procedure entails what nursing actions?
A) Positioning the patient for the procedure
B) Monitoring the patient's responses to the procedure
C) Monitoring vital signs
D) Teaching the patient about the procedure
E) Medicating the patient before and after procedure
A) Positioning the patient for the procedure
B) Monitoring the patient's responses to the procedure
C) Monitoring vital signs
D) Teaching the patient about the procedure
E) Medicating the patient before and after procedure

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
A static lung compliance of 40 mL/cm H₂O is indicative of which disorder?
A) Pneumonia
B) Bronchospasm
C) Pulmonary emboli
D) Upper airway obstruction
A) Pneumonia
B) Bronchospasm
C) Pulmonary emboli
D) Upper airway obstruction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Place the steps for analyzing arterial blood gases in the proper order.
1)Assess HCO₃¯ level for metabolic abnormalities
2)Assess PaO₂ for hypoxemia
3)Examine PaCO₂ for acidosis or alkalosis
4)Re-examine pH to determine level of compensation
5)Examine pH for acidemia or alkalemia
A) 5, 1, 2, 4, 3
B) 2, 5, 3, 1, 4
C) 1, 2, 4, 3, 5
D) 1, 3, 4, 5, 2
1)Assess HCO₃¯ level for metabolic abnormalities
2)Assess PaO₂ for hypoxemia
3)Examine PaCO₂ for acidosis or alkalosis
4)Re-examine pH to determine level of compensation
5)Examine pH for acidemia or alkalemia
A) 5, 1, 2, 4, 3
B) 2, 5, 3, 1, 4
C) 1, 2, 4, 3, 5
D) 1, 3, 4, 5, 2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



