Deck 4: Energy and Life
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/64
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 4: Energy and Life
1
Which processes can be carried out by producers?
A) Only photosynthesis
B) Only cellular respiration
C) Both photosynthesis and cellular respiration
D) Neither photosynthesis nor cellular respiration
A) Only photosynthesis
B) Only cellular respiration
C) Both photosynthesis and cellular respiration
D) Neither photosynthesis nor cellular respiration
C
2
Which of the following is a waste product of photosynthesis?
A) CO₂
B) H₂O
C) O₂
D) All of the above
A) CO₂
B) H₂O
C) O₂
D) All of the above
C
3
Which of the following is a common energy currency in living cells that powers most living organisms?
A) Sunlight
B) Heat
C) ATP
D) Phosphate
A) Sunlight
B) Heat
C) ATP
D) Phosphate
C
4
We use energy in many ways.What is one thing we cannot do to energy?
A) Destroy it.
B) Waste it.
C) Convert it.
D) Store it.
A) Destroy it.
B) Waste it.
C) Convert it.
D) Store it.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
What is the role of chloroplasts in animals?
A) Produce ATP
B) Carry out photosynthesis
C) Produce sugars
D) None, as animals do not have chloroplasts
A) Produce ATP
B) Carry out photosynthesis
C) Produce sugars
D) None, as animals do not have chloroplasts

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Identify the principal role of photosynthesis.
A) To convert solar energy into the chemical energy of sugars
B) To convert kinetic energy into the chemical energy of sugars
C) To convert the chemical energy of sugars into the chemical energy that fuels life's processes
D) To convert the chemical energy of sugars into heat to maintain an elevated body temperature
A) To convert solar energy into the chemical energy of sugars
B) To convert kinetic energy into the chemical energy of sugars
C) To convert the chemical energy of sugars into the chemical energy that fuels life's processes
D) To convert the chemical energy of sugars into heat to maintain an elevated body temperature

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Choose the pencil that has the lowest potential energy.
A) A pencil on your desk
B) A pencil falling from your desk
C) A pencil hitting the ground after falling from your desk
D) A pencil laying on the ground
A) A pencil on your desk
B) A pencil falling from your desk
C) A pencil hitting the ground after falling from your desk
D) A pencil laying on the ground

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Identify the principal role of cellular respiration.
A) To convert solar energy into the chemical energy of sugars
B) To convert kinetic energy into the chemical energy of sugars
C) To convert the chemical energy of sugars into the chemical energy that fuels life's processes
D) To convert the chemical energy of sugars into heat to maintain an elevated body temperature
A) To convert solar energy into the chemical energy of sugars
B) To convert kinetic energy into the chemical energy of sugars
C) To convert the chemical energy of sugars into the chemical energy that fuels life's processes
D) To convert the chemical energy of sugars into heat to maintain an elevated body temperature

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
What is the role of mitochondria in plants?
A) Produce ATP
B) Carry out photosynthesis
C) Produce sugars
D) None, as plants do not have mitochondria
A) Produce ATP
B) Carry out photosynthesis
C) Produce sugars
D) None, as plants do not have mitochondria

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following statements about heat is false?
A) It can be a measurement of the inefficiency of an energy conversion.
B) It is a form of kinetic energy.
C) It is a highly organized form of energy.
D) It increases the amount of entropy of the system.
A) It can be a measurement of the inefficiency of an energy conversion.
B) It is a form of kinetic energy.
C) It is a highly organized form of energy.
D) It increases the amount of entropy of the system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
How does ATP release energy that can be used by living cells?
A) By being exposed to body heat
B) By breaking a bond within an ATP molecule
C) By being exposed to sunlight
D) By adding more phosphate groups to itself
A) By being exposed to body heat
B) By breaking a bond within an ATP molecule
C) By being exposed to sunlight
D) By adding more phosphate groups to itself

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
What is the definition of energy?
A) The capacity to do work
B) The movement of an object
C) Particles moving in waves through a system
D) The amount of order in a system
A) The capacity to do work
B) The movement of an object
C) Particles moving in waves through a system
D) The amount of order in a system

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Select the ultimate source of energy for nearly every organism on this planet.
A) Plants
B) Heat
C) The sun
D) Sugars
A) Plants
B) Heat
C) The sun
D) Sugars

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which arrow would be most closely related to kinetic energy? 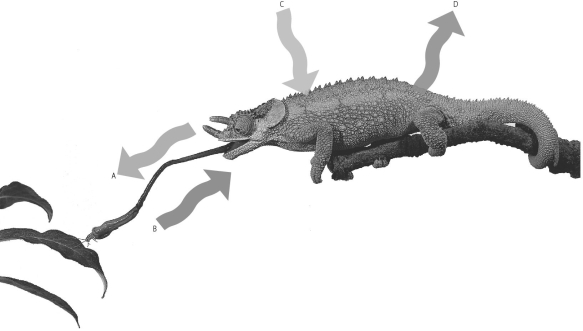
A) Arrow A, the tongue extending
B) Arrow B, the insect being eaten
C) Arrow C, sunlight striking the chameleon
D) Arrow D, heat radiating from the chameleon

A) Arrow A, the tongue extending
B) Arrow B, the insect being eaten
C) Arrow C, sunlight striking the chameleon
D) Arrow D, heat radiating from the chameleon

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Predict what would happen as the entropy of a system approaches 100%.
A) All motion would stop.
B) Randomness would become maximized.
C) Order would become maximized.
D) Heat would decrease.
A) All motion would stop.
B) Randomness would become maximized.
C) Order would become maximized.
D) Heat would decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following can carry out photosynthesis?
A) Seaweeds
B) Bacteria
C) Plants
D) All of the above can carry out photosynthesis
A) Seaweeds
B) Bacteria
C) Plants
D) All of the above can carry out photosynthesis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Since energy cannot be created,which arrow represents the energy that will be converted to chemical energy the chameleon can later use? 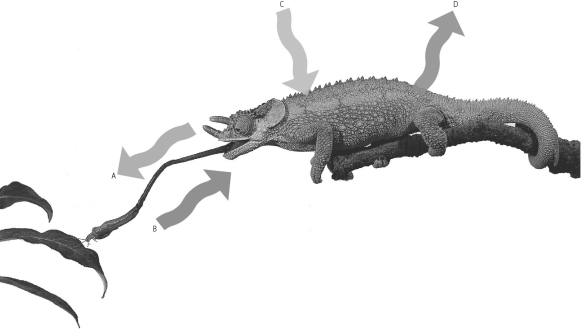
A) Arrow A, the tongue extending
B) Arrow B, the insect being eaten
C) Arrow C, sunlight striking the chameleon
D) Arrow D, heat radiating from the chameleon

A) Arrow A, the tongue extending
B) Arrow B, the insect being eaten
C) Arrow C, sunlight striking the chameleon
D) Arrow D, heat radiating from the chameleon

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The chemical reactions of photosynthesis occur in which cellular organelle?
A) Chloroplasts
B) Nucleus
C) Mitochondria
D) Ribosomes
A) Chloroplasts
B) Nucleus
C) Mitochondria
D) Ribosomes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Water behind a dam has a certain amount of stored energy that can be released as the water falls over the top of the dam.It may be enough energy to turn a mill wheel or an electricity-generating turbine.Choose the term that best describes the type of energy stored in the water at the top of the dam.
A) Chemical
B) Potential
C) Radiant
D) Kinetic
A) Chemical
B) Potential
C) Radiant
D) Kinetic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which processes can be carried out by consumers?
A) Only photosynthesis
B) Only cellular respiration
C) Both photosynthesis and cellular respiration
D) Neither photosynthesis nor cellular respiration
A) Only photosynthesis
B) Only cellular respiration
C) Both photosynthesis and cellular respiration
D) Neither photosynthesis nor cellular respiration

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Identify the role of oxygen in photosynthesis.
A) It is split to form sugar.
B) It is the final electron acceptor.
C) It is a waste product in the light reactions.
D) It is the initial electron releaser.
A) It is split to form sugar.
B) It is the final electron acceptor.
C) It is a waste product in the light reactions.
D) It is the initial electron releaser.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
What is the role of light in photosynthesis?
A) It is the source for electrons.
B) It fixes carbon.
C) It energizes electrons.
D) It splits ATP molecules, which generates energy.
A) It is the source for electrons.
B) It fixes carbon.
C) It energizes electrons.
D) It splits ATP molecules, which generates energy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Organize the following steps of the light reaction in order.
A) Absorb sunlight, capture energy in ATP and NADPH, produce oxygen as a by-product, split water to release electron
B) Absorb sunlight, capture energy in ATP and NADPH, split water to release electron, produce oxygen as a by-product
C) Absorb sunlight, split water to release electron, produce oxygen as a by-product, capture energy in ATP and NADPH
D) Absorb sunlight, produce oxygen as a by-product, split water to release electron, capture energy in ATP and NADPH
A) Absorb sunlight, capture energy in ATP and NADPH, produce oxygen as a by-product, split water to release electron
B) Absorb sunlight, capture energy in ATP and NADPH, split water to release electron, produce oxygen as a by-product
C) Absorb sunlight, split water to release electron, produce oxygen as a by-product, capture energy in ATP and NADPH
D) Absorb sunlight, produce oxygen as a by-product, split water to release electron, capture energy in ATP and NADPH

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
What is a photosystem?
A) Stacks of thylakoids
B) A double-membrane organelle containing thylakoids
C) Clusters of pigments and proteins that capture light energy
D) A leaf or any green part of the plant
A) Stacks of thylakoids
B) A double-membrane organelle containing thylakoids
C) Clusters of pigments and proteins that capture light energy
D) A leaf or any green part of the plant

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The following question(s) relate to the data table below, showing typical fluctuating pH and dissolved oxygen levels in a fish pond with a heavy concentration of algae over a 24-hour period.
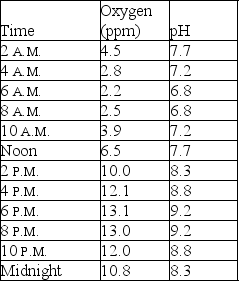
Upon closer examination,the fish appeared to have died from a lack of oxygen.What time of day did the fish most likely die?
A) Late at night
B) Just before dawn
C) In the middle of the afternoon
D) At sundown

Upon closer examination,the fish appeared to have died from a lack of oxygen.What time of day did the fish most likely die?
A) Late at night
B) Just before dawn
C) In the middle of the afternoon
D) At sundown

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Where do the electrons that are excited by the energy in sunlight first come from?
A) NADPH
B) ATP
C) Sugar
D) Water
A) NADPH
B) ATP
C) Sugar
D) Water

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which of the following best describes the chemical equation for photosynthesis?
A) Carbon dioxide + Sugar + Energy = Oxygen + Water
B) Oxygen + Water + Carbon dioxide = Sugar + Energy
C) Water + Carbon dioxide + Energy = Sugar + Oxygen
D) Oxygen + Sugar = Water + Carbon dioxide + Energy
A) Carbon dioxide + Sugar + Energy = Oxygen + Water
B) Oxygen + Water + Carbon dioxide = Sugar + Energy
C) Water + Carbon dioxide + Energy = Sugar + Oxygen
D) Oxygen + Sugar = Water + Carbon dioxide + Energy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Why do some leaves change color (red,yellow,orange,etc.)in the fall?
A) The chlorophyll molecule is modified to absorb different wavelengths of light.
B) The chlorophyll molecule breaks down and other pigments now become visible.
C) When leaves die, the chlorophyll molecules are no longer visible.
D) Cold weather denatures the chlorophyll molecule, and it begins to reflect different colors.
A) The chlorophyll molecule is modified to absorb different wavelengths of light.
B) The chlorophyll molecule breaks down and other pigments now become visible.
C) When leaves die, the chlorophyll molecules are no longer visible.
D) Cold weather denatures the chlorophyll molecule, and it begins to reflect different colors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Identify the role of water in photosynthesis.
A) It is split to form sugar.
B) It is the final electron acceptor.
C) It is a waste product in the light reactions.
D) It is the initial electron releaser when split.
A) It is split to form sugar.
B) It is the final electron acceptor.
C) It is a waste product in the light reactions.
D) It is the initial electron releaser when split.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
How do we know green light is not absorbed by chlorophyll?
A) Green light is the wavelength of light that is reflected instead of absorbed by the chloroplasts.
B) Not enough of the green light penetrates the ozone layer and makes it to the plant.
C) Green light has such a small wavelength that most of it goes straight through the leaves without interacting with the chlorophyll.
D) Green light does not have enough energy to excite an electron in the photosystem.
A) Green light is the wavelength of light that is reflected instead of absorbed by the chloroplasts.
B) Not enough of the green light penetrates the ozone layer and makes it to the plant.
C) Green light has such a small wavelength that most of it goes straight through the leaves without interacting with the chlorophyll.
D) Green light does not have enough energy to excite an electron in the photosystem.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which stage of photosynthesis,if any,can function in the dark?
A) Stage 1 (the light reactions)
B) Stage 2 (the Calvin cycle)
C) Both Stage 1 and Stage 2
D) Neither Stage 1 nor Stage 2
A) Stage 1 (the light reactions)
B) Stage 2 (the Calvin cycle)
C) Both Stage 1 and Stage 2
D) Neither Stage 1 nor Stage 2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Name the fluid-filled interior of the chloroplast.
A) Thylakoids
B) Stroma
C) Grana
D) None of these
A) Thylakoids
B) Stroma
C) Grana
D) None of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The purpose of the Calvin cycle is to produce ________.
A) O₂
B) ATP
C) CO₂
D) Sugar
A) O₂
B) ATP
C) CO₂
D) Sugar

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The following question(s) relate to the data table below, showing typical fluctuating pH and dissolved oxygen levels in a fish pond with a heavy concentration of algae over a 24-hour period.

What is a possible reason for oxygen to be so low by the end of the night?
A) Algae produce oxygen as a by-product of photosynthesis mostly during the day, and not at night.
B) Fish consume oxygen during the night, and oxygen starts to run out by dawn.
C) Both of these explain the low level of oxygen
D) Neither of these explains the low level of oxygen

What is a possible reason for oxygen to be so low by the end of the night?
A) Algae produce oxygen as a by-product of photosynthesis mostly during the day, and not at night.
B) Fish consume oxygen during the night, and oxygen starts to run out by dawn.
C) Both of these explain the low level of oxygen
D) Neither of these explains the low level of oxygen

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Choose the best explanation as to why both consumers and producers perform cellular respiration.
A) Although they may obtain their sugars in different ways, both consumers and producers rely on cellular respiration to make ATP.
B) Both consumers and producers perform cellular respiration to produce the sugars that will be "burned" to fuel the energy of life.
C) Both consumers and producers perform cellular respiration to produce the oxygen necessary to sustain life.
D) Both consumers and producers perform cellular respiration to produce the heat necessary to sustain life.
A) Although they may obtain their sugars in different ways, both consumers and producers rely on cellular respiration to make ATP.
B) Both consumers and producers perform cellular respiration to produce the sugars that will be "burned" to fuel the energy of life.
C) Both consumers and producers perform cellular respiration to produce the oxygen necessary to sustain life.
D) Both consumers and producers perform cellular respiration to produce the heat necessary to sustain life.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which process produces glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (3GP)?
A) Citric acid cycle
B) Fermentation
C) Calvin cycle
D) Glycolysis
A) Citric acid cycle
B) Fermentation
C) Calvin cycle
D) Glycolysis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
What molecule(s)link the light reactions (stage 1 of photosynthesis)to the Calvin cycle (stage 2 of photosynthesis)?
A) The oxygen and carbon dioxide molecules
B) The electron shuttles (ATP and NADPH)
C) The sugars
D) The water
A) The oxygen and carbon dioxide molecules
B) The electron shuttles (ATP and NADPH)
C) The sugars
D) The water

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
How does CO₂ enter a plant?
A) Through the roots
B) Through the stomata
C) Through the stroma
D) Through the grana
A) Through the roots
B) Through the stomata
C) Through the stroma
D) Through the grana

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Plastids are storage organelles.A chloroplast is a type of plastid.What does a chloroplast store?
A) Energy
B) Chlorophyll
C) Carbon
D) Electrons
A) Energy
B) Chlorophyll
C) Carbon
D) Electrons

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The following question(s) relate to the data table below, showing typical fluctuating pH and dissolved oxygen levels in a fish pond with a heavy concentration of algae over a 24-hour period.

You are investigating a massive fish kill in one of the shallow lakes in the area.Lab reports show no toxins in the water,but a monitoring station reported these oxygen and pH values.Based on the table above,what,if any,is the relationship between oxygen and pH?
A) Inverse relationship: when one increases, the other decreases
B) Direct relationship: when one increases, the other also increases
C) Exponential relationship: when one increases, the other increases 10 to 100 times
D) No relationship: there is no pattern between oxygen and pH

You are investigating a massive fish kill in one of the shallow lakes in the area.Lab reports show no toxins in the water,but a monitoring station reported these oxygen and pH values.Based on the table above,what,if any,is the relationship between oxygen and pH?
A) Inverse relationship: when one increases, the other decreases
B) Direct relationship: when one increases, the other also increases
C) Exponential relationship: when one increases, the other increases 10 to 100 times
D) No relationship: there is no pattern between oxygen and pH

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
What is the main purpose of cellular respiration?
A) To produce carbon dioxide
B) To produce sugars
C) To produce ATP
D) To produce oxygen
A) To produce carbon dioxide
B) To produce sugars
C) To produce ATP
D) To produce oxygen

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
During which stage of cellular respiration is the majority of the ATP produced?
A) Glycolysis
B) Citric acid cycle
C) Fermentation
D) Electron transport chain
A) Glycolysis
B) Citric acid cycle
C) Fermentation
D) Electron transport chain

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Explain how molecules other than glucose can be used as energy sources.
A) They can't; cellular respiration is limited to glucose.
B) They have their own unique metabolic pathways.
C) They are modified first and then enter the same metabolic pathway as glucose.
D) Fats, proteins, and other carbohydrates are similar enough to glucose that they utilize the same metabolic pathway without any modifications.
A) They can't; cellular respiration is limited to glucose.
B) They have their own unique metabolic pathways.
C) They are modified first and then enter the same metabolic pathway as glucose.
D) Fats, proteins, and other carbohydrates are similar enough to glucose that they utilize the same metabolic pathway without any modifications.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Can energy be harvested by the cells from glucose without oxygen?
A) Yes, about as much as with oxygen.
B) Yes, but not quite as much as with oxygen.
C) Yes, but much less than with oxygen.
D) No, oxygen is required to harvest any energy from glucose.
A) Yes, about as much as with oxygen.
B) Yes, but not quite as much as with oxygen.
C) Yes, but much less than with oxygen.
D) No, oxygen is required to harvest any energy from glucose.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Why does yogurt taste sharp?
A) It has not been aged long enough to mellow.
B) The taste is from the small amount of alcohol it contains, and alcohol tastes sharp.
C) The taste is from the large amount of carbon dioxide it contains, and carbon dioxide tastes sharp.
D) The taste is from the lactic acid it contains, and acids taste sharp.
A) It has not been aged long enough to mellow.
B) The taste is from the small amount of alcohol it contains, and alcohol tastes sharp.
C) The taste is from the large amount of carbon dioxide it contains, and carbon dioxide tastes sharp.
D) The taste is from the lactic acid it contains, and acids taste sharp.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Alcohol is a waste product produced by yeast in the presence of sugar and the absence of ________.
A) CO₂
B) H₂O
C) O₂
D) ATP
A) CO₂
B) H₂O
C) O₂
D) ATP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Predict how many molecules of carbon dioxide are produced from the mitochondrial "burning" of one molecule of glucose?
A) 1
B) 6
C) 12
D) Not enough information provided
A) 1
B) 6
C) 12
D) Not enough information provided

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
For what purpose does a plant use the sugars produced during photosynthesis?
A) For cellular respiration to produce ATP
B) For storage
C) For making cellulose, which makes the bulk of a plant
D) All of the above
A) For cellular respiration to produce ATP
B) For storage
C) For making cellulose, which makes the bulk of a plant
D) All of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The bulk of a plant is made from ________.
A) minerals from the soil obtained by the roots of a plant
B) sugars from the soil obtained by the roots of a plant
C) the sugars made in photosynthesis, which were made from carbon dioxide
D) oxygen absorbed by the pores in leaves
A) minerals from the soil obtained by the roots of a plant
B) sugars from the soil obtained by the roots of a plant
C) the sugars made in photosynthesis, which were made from carbon dioxide
D) oxygen absorbed by the pores in leaves

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Where do the molecules used as the inputs of the Calvin cycles (ATP and NADPH)come from?
A) They come from the sun.
B) They come from the light reactions.
C) They come from the air.
D) They come from previous Calvin cycles.
A) They come from the sun.
B) They come from the light reactions.
C) They come from the air.
D) They come from previous Calvin cycles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Respiration is called aerobic because ________.
A) it happens in the absence of oxygen
B) it requires oxygen
C) it requires carbon dioxide
D) it happens in mitochondria
A) it happens in the absence of oxygen
B) it requires oxygen
C) it requires carbon dioxide
D) it happens in mitochondria

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Identify the stage (or stages)of cellular respiration that occurs entirely outside of the mitochondria.
A) Citric acid cycle
B) Electron transport chain
C) Glycolysis
D) All of the above
A) Citric acid cycle
B) Electron transport chain
C) Glycolysis
D) All of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Identify the stage of cellular respiration when glucose is split into two molecules of pyruvic acid.
A) Citric acid cycle
B) Calvin cycle
C) Electron transport chain
D) Glycolysis
A) Citric acid cycle
B) Calvin cycle
C) Electron transport chain
D) Glycolysis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
What is the main by-product of cellular respiration?
A) ATP
B) Sugars
C) Oxygen
D) Water
A) ATP
B) Sugars
C) Oxygen
D) Water

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Yeast is used to produce beer and wine but can also make bread rise.All of these processes involve the production of alcohol.Explain why you can eat bread and not get drunk.
A) The heat of cooking bakes out the alcohol.
B) The amount of alcohol produced is too small to be noticeable.
C) The bread-making process produces ethyl alcohol, not isopropyl alcohol.
D) The bread-making process produces isopropyl alcohol, not ethyl alcohol.
A) The heat of cooking bakes out the alcohol.
B) The amount of alcohol produced is too small to be noticeable.
C) The bread-making process produces ethyl alcohol, not isopropyl alcohol.
D) The bread-making process produces isopropyl alcohol, not ethyl alcohol.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
What is the chemical equation for glucose?
A) C₂H₄O₂
B) C₄ H₈O₄
C) C₆H₁₂O₆
D) C₈H₁₆O₈
A) C₂H₄O₂
B) C₄ H₈O₄
C) C₆H₁₂O₆
D) C₈H₁₆O₈

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Where does cellular respiration occur?
A) In the chloroplasts
B) In the mitochondria
C) In the nucleus
D) In the airways of the respiratory system
A) In the chloroplasts
B) In the mitochondria
C) In the nucleus
D) In the airways of the respiratory system

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Identify the role of carbon dioxide in photosynthesis.
A) It is split to become incorporated into sugars.
B) It is split to release electrons.
C) It is a by-product.
D) It is the final electron acceptor.
A) It is split to become incorporated into sugars.
B) It is split to release electrons.
C) It is a by-product.
D) It is the final electron acceptor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
What happens to the ATP molecule after it has been used to do work?
A) It breaks down into carbon dioxide and water.
B) It is split into two molecules of pyruvic acid.
C) It loses a phosphate group and is converted to ADP.
D) It is completely destroyed.
A) It breaks down into carbon dioxide and water.
B) It is split into two molecules of pyruvic acid.
C) It loses a phosphate group and is converted to ADP.
D) It is completely destroyed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Which stage of cellular respiration requires oxygen that you breathe?
A) Glycolysis
B) Citric acid cycle
C) Electron transport chain
D) All of the above
A) Glycolysis
B) Citric acid cycle
C) Electron transport chain
D) All of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Why can't an aerobic bacterium produce as much energy as an animal cell can produce from a gram of sugar?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Explain why mitochondria are often called "the powerhouse of the cell."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
What color of light is not used for photosynthesis? How could you know this just by looking at a leaf?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
What does it mean to "fix" carbon,and during which stage of photosynthesis is carbon fixed?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



